
A DISTRIBUTED MULTI-ROBOT SENSING SYSTEM USING AN
INFRARED LOCATION SYSTEM
Anssi Kemppainen, Janne Haverinen and Juha R
¨
oning
Department of Electrical and Information Engineering, University of Oulu, Finland
Keywords:
Distributed sensing, relative pose estimation, multi-robot system, formation control.
Abstract:
Distributed sensing refers to measuring systems where, instead of one sensor, multiple sensors are spatially
distributed to improve the robustness of the system, increase the relevancy of the measurements and cut costs,
since smaller and less precise sensors are used. Spatially distributed sensors fuse their measurements into the
same co-ordinates, which requires the relative positions of the sensors. In this paper we present a distributed
multi-robot sensing system in which the relative poses (positions and orientations) of the robots are estimated
using an infrared location system. The relative positions are estimated using intensity and bearing measure-
ments of received infrared signals. The relative orientations are obtained by fusing the position estimates of
the robots. The location system enables a group of robots to perform distributed and co-operative environ-
ment sensing by maintaining a given formation while the group measures distributions of light and a magnetic
field, for example. In the experiments, a group of three robots moved and collected spatial information (i.e.
illuminance and compass headings) from the given environment. The information was stored on grid maps
that present illuminance and compass headings. The experiments demonstrated the feasibility of using the
distributed multi-robot sensing system in mobile sensing applications.
1 INTRODUCTION
Distributed sensing (Brooks and Iyengar, 1998), (Cat-
terall et al., 2003) refers to measuring systems where,
instead of one sensor, multiple sensors are spatially
distributed to improve the robustness of the system,
increase the relevancy of the measurements and cut
costs, since smaller and less precise sensors are used.
In the robotic domain, distributed sensing enables
multi-robot systems (MRS) to perform mapping and
exploration (Sujan et al., 2004), allocate tasks among
robots (Pagello et al., 2006), and plan paths and navi-
gate in an unknown or partially unknown environment
(Cai et al., 1996), for example.
Distributed sensing in an unknown enviroment
benefits from knowing the relative locations of sen-
sors. The relative locations enable the sensors to place
their measurements into the same sensor-centric map.
Autonomous sensing systems are able to use one sen-
sor as an origin of the co-ordinates, while the other
sensors measure the surrounding area. Such systems
do not require an external infrastructure for position-
ing (GPS, WLAN, etc.). However, the measurement
range of the relative location system must be sufficient
to encompass the sensing area.
In this paper we present a distributed multi-robot
sensing system that uses an infrared location system
(Kemppainen et al., 2006). The location system es-
timates the relative poses (positions and orientations)
of the robots. Related systems have been presented
that exploit several techniques, including laser range
finders (Schneider and Wildermuth, 2004), (Mon-
tesano et al., 2004), (Howard et al., 2003),(Moors
et al., 2003), ultrasonic TOF measurement (Shoval
and Borenstein, 2001), (Grabowski et al., 2000) and
vision (Montesano et al., 2005), (Spletzer et al.,
2001), to locate and recognise other robots. A com-
parison of the infrared location system and related
systems was discussed in (Kemppainen et al., 2006).
We selected infrared sensors since they are small and
capable of relative angle measurements between an
emitter and receiver. In addition, infrared radiation
280
Kemppainen A., Haverinen J. and Röning J. (2007).
A DISTRIBUTED MULTI-ROBOT SENSING SYSTEM USING AN INFRARED LOCATION SYSTEM.
In Proceedings of the Fourth International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics, pages 280-283
DOI: 10.5220/0001648502800283
Copyright
c
SciTePress

does not reflect from walls and object surfaces as
much as ultrasound. In relative angle measurements,
the effects of multipath reflection would be crucial be-
cause of ambiguous angle estimates.
To demonstrate the distributed sensing system in
mobile sensing applications, we conducted experi-
ments where a group of three robots measured the dis-
tributions of illuminance and a magnetic field while
maintaining a triangle formation.
2 INFRARED LOCATION
SYSTEM
The infrared location system, originally presented in
(Kemppainen et al., 2006), is a vital part of the multi-
robot system (Haverinen et al., 2005) that enables the
robots to maintain a given formation while sensing the
environment. The key idea of the location system is to
estimate the relative positions without data transmis-
sion between the robots. However, radio transmission
is used to share estimates among the group in order
to enable the robots to estimate their relative orienta-
tions.
The location system uses intensity and bearing
measurements of received signals to estimate the lo-
cations of other robots in polar co-ordinates. By shar-
ing these estimates among the group of robots, it is
possible to also estimate their relative orientations. In
addition, each robot is identified through different fre-
quencies in the received signal.
Figure 1 presents the main components of the lo-
cation system. A conical mirror reflects an emitted
signal sideways into a unified zone, whereas beam
collector collects signals from other robots. A servo
system with a DC motor, Hall-effect sensors and dis-
crete PID controller is used to rotate the beam collec-
tor at a constant angular velocity. The measurement
range of the system is approximately five metres, giv-
ing the most accurate estimates for radial co-ordinates
when the distance between two robots is in the range
of [0.5; 2.5 m].
3 EXPERIMENTS
Experiments were conducted to demonstrate the fea-
sibility of using the distributed multi-robot sensing
system in mobile sensing applications. For exam-
ple, co-operative mapping in an unknown environ-
ment requires moving platforms that are capable of
measuring spatial information and estimating the rel-
ative positions of the robots. For our experiments, we
1
2
3
5
6
7
4
2
1
3
5
4
6
7
8
Figure 1: The actual system and the illustration of mechan-
ics: 1) mirror, 2) emitter, 3) receiver, 4) beam collector,
5) aperture, 6) DC motor and Hall-effect-sensors, 7) see-
through body, 8) control electronics.
implemented a distributed sensing system in which a
group of three robots measured spatial information in
a given environment.
3.1 Formation Control
Formation control enables a multi-robot system to
measure spatial distributions while moving across the
measurement area. The measurement range of the
infrared location system is restricted to five metres,
and to be able to fuse spatial measurements onto the
same map, the multi-robot system is required to main-
tain limited relative distances. Formation control is
required not only to limit the distance between the
robots, but also to enable co-ordinated sensing in or-
der to reduce mapping time.
In our experiments one of the robots acted as a
leader and the other two followed the leader. To-
gether they constituted a right-angle triangular forma-
tion where the distance between the leader and the fol-
lowers was 1.5 metres. For each following robot, for-
mation control consisted of two P controllers; one for
translational and the other for rotational speed con-
trol. The infrared location system updated the relative
pose measurements approximately every three sec-
onds, giving the relative poses of the following robots
in the leader’s co-ordinates. Fig. 2 presents how er-
rors in the relative orientation and position were used
in the rotational and translational speed controllers
(respectively).
The control cycle length in each controller was
200 ms, while the location system updated poses only
once every three seconds. In order to update pose er-
rors in each control cycle, each robot estimated their
relative movements using odometer readings. In the
experiments, the odometer readings enabled the for-
mation to be driven at a 10 cm/s translational velocity.
A DISTRIBUTED MULTI-ROBOT SENSING SYSTEM USING AN INFRARED LOCATION SYSTEM
281
The following robot
The leader robot
Objective position
t
e
r
e
Figure 2: The pose of the following robot relative to the
leader is estimated and used to control the robot to the ob-
jective position. P controllers use rotation e
r
and translation
e
t
errors to control rotational and translational speeds of the
robot.
3.2 Spatial Measurements
In the experiments, three robots measured distribu-
tions of light and a magnetic field over a given en-
vironment, producing maps of illuminance and com-
pass headings. Fig. 3 presents the trajectories of the
robots while moving and measuring the environment.
The leader was driven from position (50 cm, -250 cm)
to position (20 cm, 450 cm), while the group main-
tained a triangular formation. Spatial measurements
were stored on grid maps presented in the leader’s co-
ordinates.
−400−300−200−100 0 100 200 300 400 500
−400
−300
−200
−100
0
100
200
300
400
500
X coordinate (cm)
Y coordinate (cm)
Trajectories
Figure 3: Trajectories in global coordinates.
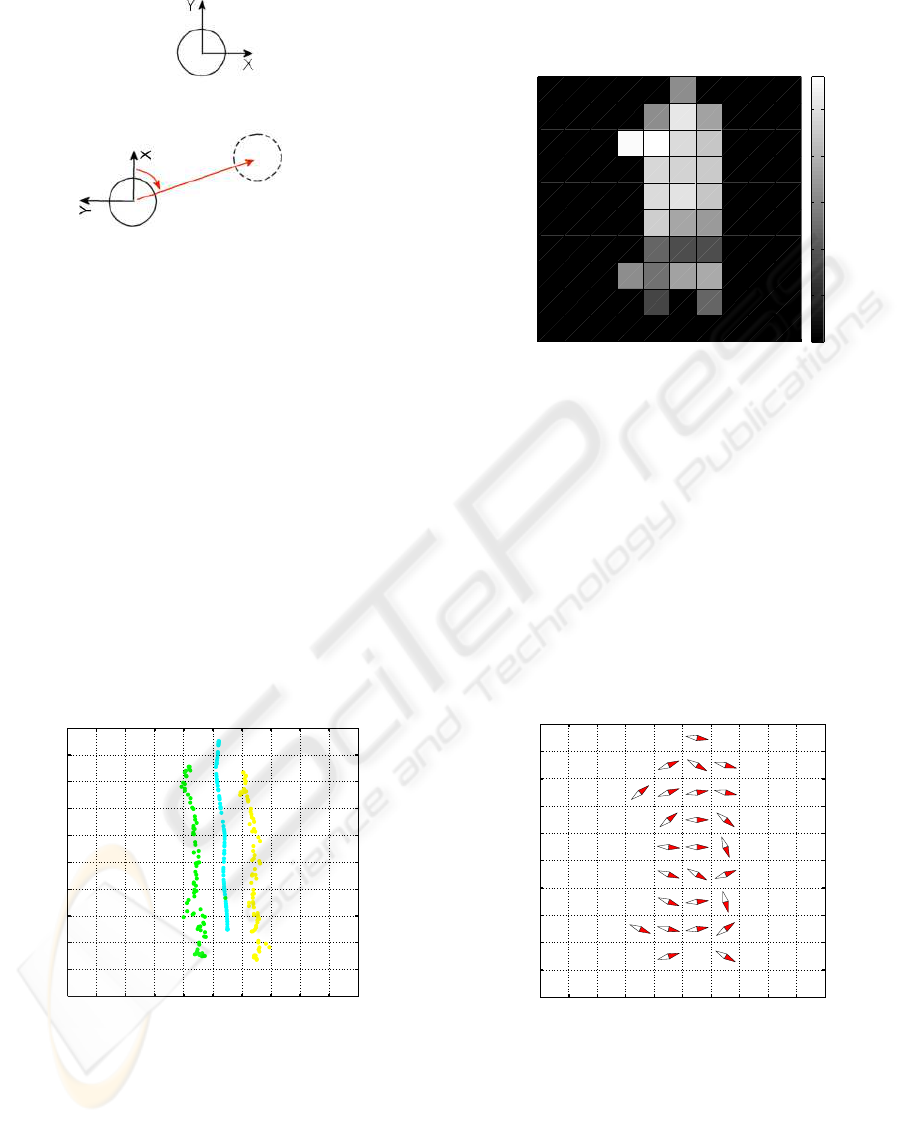
Fig. 4 presents a grid map of illuminance, where
the highest intensity is depicted with white colour and
the lowest intensity, for the cells not visited, with
black colour. This gives spatial information about the
distribution of light in the given environment. The
cells with the highest intensities are close to lights and
the cells with the smallest intensities are shadowed ar-
eas close to chairs, plants and walls.
−500 0 500
−500
−400
−300
−200
−100
0
100
200
300
400
500
Illuminance
X coordinate (cm)
Y coordinate (cm)
0
20
40
60
80
100
Figure 4: Illumincance in global coordinates.
Fig. 5 presents a grid map of compass headings
with a bidirectional arrow, where red points to the
north and white to the south. Since compass head-
ings are disturbed indoors by electric cables and metal
structures, the values of the compass headings give us
spatial information about the magnetic field in the en-
vironment. However, in the experiments, the mag-
netic field of the measured environment was paral-
lel, which gave us small spatial variations in compass
heading.
−400−300−200−100 0 100 200 300 400 500
−400
−300
−200
−100
0
100
200
300
400
500
X coordinate (cm)
Y coordinate (cm)
Compass heading
Figure 5: Compass heading in global coordinates.
The experiments demonstrated distributed sens-
ing in a group of robots to produce distributions of
illuminance and a magnetic field. All the measure-
ments were tied to the co-ordinates of the leading
robot. Since the ground truth positions were miss-
ing, positioning errors in the global co-ordinates of
ICINCO 2007 - International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
282

the sensing robots were affected by the odometer er-
ror of the leading robot and the errors of the infrared
location system. In addition, the grid size in the ex-
periments was 1x1 metres, which gave only a coarse
picture of the true distributions. However, these pre-
liminary experiments demonstrated the feasibility of
using the infrared location system in distributed au-
tonomous sensing systems.
4 CONCLUSION AND FUTURE
WORKS
In this paper we presented a distributed multi-robot
sensing system that uses an infrared location sys-
tem. The infrared location system estimates poses in
a multi-robot system, enabling the robots to maintain
a given formation while sensing the environment. In
addition, knowing their poses enables the robots to
place their measurements on the same map.
We conducted an experiment where a group of
three robots moved and measured spatial informa-
tion in a right-angle triangular formation. Leader-
follower formation control used pose estimates and P
controllers to control the rotational and translational
speeds of the following robots. In the experiments we
measured spatial distributions of illuminance and a
magnetic field, which gave us information about shad-
owing objects, metal structures and electric cables. In
addition, since the information is spatially distributed,
it can be used in mapping and localization applica-
tions.
The main contribution of the research was the con-
struction and validation of a distributed multi-robot
sensing system for mobile sensing applications. Fu-
ture research will focus on developing methods for
multi-robot exploration utilising spatial information.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors gratefully acknowledge the support of the
Academy of Finland.
REFERENCES
Brooks, R. R. and Iyengar, S. S. (1998). Multi-sensor fu-
sion: fundamentals and applications with software.
Prentice-Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA.
Cai, A., Fukuda, T., Arai, F., and Ishihara, H. (1996). Co-
operative path planning and navigation based on dis-
tributed sensing. In IEEE International Conference
on Robotics and Automation (ICRA-96), pages 2079 –
2084, Minneapolis.
Catterall, E., Laerhoven, K. V., and Strohbach, M. (2003).
Self-organization in ad hoc sensor networks: an em-
pirical study. In ICAL 2003: Proceedings of the eighth
international conference on Artificial life, pages 260–
263, Cambridge, MA, USA. MIT Press.
Grabowski, R., Navarro-Serment, L., Paredis, C., and
Khosla, P. (2000). Heterogeneous teams of modu-
lar robots for mapping and exploration. Autonomous
Robots, 8(3):293–308.
Haverinen, J., Parpala, M., and R
¨
oning, J. (2005). A minia-
ture mobile robot with a color stereo camera system
for swarm robotics research. In IEEE International
Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA2005),
pages 2494–2497, Barcelona, Spain.
Howard, A., Mataric, M., and Sukhatme, G. (2003). Putting
the ’i’ in team: an ego-centric approach to cooperative
localization. In International Conference on Robotics
and Automation.
Kemppainen, A., Haverinen, J., and R
¨
oning, J. (2006). An
infrared location system for relative pose estimation
of robots. In 16-th CISM-IFToMM Syposium of Robot
Design, Dynamics, and Control (ROMANSY 2006),
pages 379–386, Warsaw, Poland.
Montesano, L., Gaspar, J., Santos-Victor, J., and Montano,
L. (2005). Fusing vision-based bearing measurements
and motion to localize pairs of robots. In International
Conference on Robotics and Automation.
Montesano, L., Montano, L., and Burgard, W. (2004). Rel-
ative localization for pairs of robots based on uniden-
tifiable moving features. In International Conference
on Intelligent Robots and Systems.
Moors, M., Schneider, F. E., and Wildermuth, D. (2003).
Relative position estimation in a group of robot. In
International Conference on Climbing and Walking
Robots.
Pagello, E., D’Angelo, A., and Menegatti, E. (2006). Co-
operation issues and distributed sensing for multirobot
systems. Proceedings of the IEEE, 94(7):1370–1383.
Schneider, F. and Wildermuth, D. (2004). Using an ex-
tended kalman filter for relative localisation in a mov-
ing robot formation. In International Workshop on
Robot Motion and Control.
Shoval, S. and Borenstein, J. (2001). Measuring the relative
position and orientation between two mobile robots
with binaural sonar. In International Topical Meeting
on Robotics and Remote Systems.
Spletzer, J., Das, A., Fierro, R., Taylor, C., Humar, V., and
Ostrowski, J. (2001). Cooperative localization and
control for multi-robot manipulation. In Conference
on Intelligent Robots and Systems.
Sujan, V. A., Dubowsky, S., Huntsberger, T. L., Aghazar-
ian, H., Cheng, Y., and Schenker, P. S. (2004). An
architecture for distributed environment sensing with
application to robotic cliff exploration. Auton. Robots,
16(3):287–311.
A DISTRIBUTED MULTI-ROBOT SENSING SYSTEM USING AN INFRARED LOCATION SYSTEM
283
