
INTERACTIVE DEFORMATION AND VISUALIZATION OF LARGE
VOLUME DATASETS
Florian Schulze, Katja B
¨
uhler and Markus Hadwiger
VRVis Research Center for Virtual Reality and Visualization, Donau City Str. 1, Vienna, Austria
Keywords:
Deformation, Resampling, Volume Rendering.
Abstract:
This paper presents an integrated approach for interactive direct volume deformation and simultaneous visual-
ization. The fundamental requirement is that interactive performance without pre-processing must be achieved
for large volume data, where at any time up to one million elements participate in a deformation that is applied
interactively by picking and dragging in the 3D view. Current physically-based approaches are still one or
two orders of magnitude away from this goal. In contrast, our approach extends the non-physical ChainMail
algorithm and combines it with on-the-fly resampling and GPU ray-casting. Special transfer functions assign
material properties depending on volume density. The affected subvolume is deformed and resampled onto a
rectilinear grid on the CPU, and updates the volume on the GPU w here it is rendered using ray-casting. While
the deformation is already being displayed, its quality is simultaneously refined via an iterative relaxation
procedure executed in a parallel thread.
1 INTRODUCTION
This paper follows a vision first published in 1995:
Thought as natural extension to direct volume render-
ing, Sarah F. Gibson formulated the idea for a system
that allows direct deformation, cutting and carving of
volume data (Gibson, 1995). She introduced the so
called ChainMail algorithm allowing in its extension
modeling of deformation of inhomogeneous materi-
als. Similar to direct volume rendering, the deforma-
tion is directly performed at the voxel level of the vol-
ume without any pre-processing.
The ChainMail algorithm provides only a non
physics based deformation scheme, but is able to de-
form large structures in real time: Having in mind
that a small volume dataset of 256
3
consists already
of more than 16 million voxels, existing physically
based approaches are still far away from being able to
deform such structures at interactive frame rates with-
out previous simplification. Due to the limited avail-
able computational power at the time of first publica-
tion of the algorithm and its extensions, simultaneous
volume rendering of the whole dataset during the de-
formation process was not possible, and Sarah Gibson
formulated this task as future work (Gibson, 1999).
This paper presents a framework that integrates
high quality real time visualization with direct defor-
mation of volume data fulfilling the following require-
ments:
• Full information of the original data is available
throughout the whole process: Deformation and
visualization are directly performed at the voxel
level of the volume.
• The deformation is not physically correct, but
plausible depending on the underlying data.
• No time-consuming preprocessing is necessary,
like segmentation, simplifications and adaptive hi-
erarchy generation.
• The system reaches interactive frame rates for si-
multaneous simulation and visualization.
Basis of the proposed deformation system is the
Enhanced ChainMail algorithm (Schill et al., 1998)
that is taken as initialization step for a relaxation
solver that allows also simulation of elastic deforma-
tion. Handling of the high amounts of data has been
addressed by a specialized data structure and memory
management system. A new image order resampling
39
Schulze F., Bühler K. and Hadwiger M. (2007).
INTERACTIVE DEFORMATION AND VISUALIZATION OF LARGE VOLUME DATASETS.
In Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Computer Graphics Theory and Applications - AS/IE, pages 39-46
DOI: 10.5220/0002082200390046
Copyright
c
SciTePress

algorithm has been developed to provide simultane-
ous visualization of the deformed data using the pow-
erful GPU accelerated volume rendering framework
described in (Scharsach et al., 2006).
The paper is organized as follows: Related work
is discussed in the next section. A short summary
of the Chain Mail algorithm and existing extensions
is given in section 3. Section 4 outlines the general
workflow of our system. The two-step deformation
method is explained in section 5 including details on
the basic chain mail implementation, relaxation, and
material definition. Visualization and related issues
are addressed in section 6, interaction methods are
discussed in section 7. The paper closes with results
in section 8, and a summary in section 9.
2 RELATED WORK
Detailed discussion of the extensively available re-
lated work on physically based deformation methods
of (volumetric) objects is beyond the scope of this
paper. The interested reader is referred to two State
of the Art Reports presented at Eurographics 2005
(Nealen et al., 2005; Chen et al., 2005) giving an ex-
cellent general overview.
Considering physically based approaches for di-
rect deformation and visualization of volume data,
modern point based mesh free methods (M
¨
uller et al.,
2004; M
¨
uller et al., 2005) seem to be the most natural
approach to deal directly with medical volume data:
theoretically, no preprocessing is required and defor-
mation could be directly performed on the volume if
each voxel would be modeled as particle or phyxel.
The approaches mentioned above and reported in
(Nealen et al., 2005; Chen et al., 2005) provide phys-
ically correct deformation, but due to their compu-
tational complexity, none of them is able to handle
more than 100k elements at interactive frame rates,
even if GPU accelerated integration schemes are used
(Georgii and Westermann, 2006; Mosegaard et al.,
2005). Simultaneous visualization of deformed ob-
jects is another bottleneck, especially if surfaces have
to be reconstructed on the fly, like it is the case in gen-
eral for particle-based (Desbrun and Cani, 1998) and
point-based approaches (Adams et al., 2005). Nealen
et al. (Nealen et al., 2005) stated in the conclusions of
the state of the art report: ”Yet even with the current
methodology, the algorithms and models have seen
somewhat limited application in production environ-
ments and videos games. One reason for this is the
lack of computational power...”.
Existing approaches addressing directly the defor-
mation of volumes, i.e. without previous mesh ex-
traction and/or simplification, are mainly based on
space or ray deformation techniques: either a coarser
structure (e.g. bounding boxes (Singh et al., 2003),
volume or surface geometry (Westermann and Rezk-
Salama, 2001)) is deformed and the deformation of
the volume itself is computed as displacement based
on the deformation of the shape. This can be done ei-
ther directly or indirectly by deformation of the rays
during rendering. But these approaches also do not
perform deformation at the the finest level. To cap-
ture fine structures, extensive preprocessing (segmen-
tation, geometric reconstruction) has to be done.
Spatial transferfunctions (Chen et al., 2003) allow
geometric, procedural and hierarchical definition of
deformations performed on volumes: geometric de-
formation rules can be assigned to each voxel by a
previously defined function. Arbitrary interactive de-
formation is not possible with this technique.
To our knowledge, the ChainMail algorithm (Gib-
son, 1997) is the only existing algorithm able to per-
form interactive deformation of common size volume
datasets directly on voxel level. The ChainMail al-
gorithm itself is not a physically based deformation
method and is only able to simulate plastic defor-
mation, but an additional relaxation step as proposed
in (Gibson, 1999) can be used to get more realistic
and elastic deformations. Furthermore, the connected
data structure allows easy manipulation of the volume
like cutting and carving. A generalization of Chain-
Mail to arbitrary mesh topologies, the Generalized
ChainMail Algorithm, has been proposed by (Li and
Brodlie, 2003). A complete system for planning of
arthroscopic knee surgery (Gibson et al., 1998) and
a biomechanical simulation of the vitreous humor in
the eye (Schill et al., 1998) based on the (enhanced)
chain mail demonstrated the general applicability of
the method.
The next section give an overview of the basic
functionality and limitations of existing ChainMail
implementations.
3 CHAINMAIL REVISITED
Data structures. The classical ChainMail algo-
rithm is designed to operates on data elements ini-
tially arranged in a three dimensional axis aligned
grid defined by x-,y-,z-axes. Each element is con-
nected with its six direct neighbors by ChainMail
constraints that are defined as axis aligned regions
describing the set of valid positions for each neigh-
bor element. Figure 1 shows the definition of a valid
region for a neighbor in x-direction described by its
minimal and maximal distance in x-direction and the
GRAPP 2007 - International Conference on Computer Graphics Theory and Applications
40
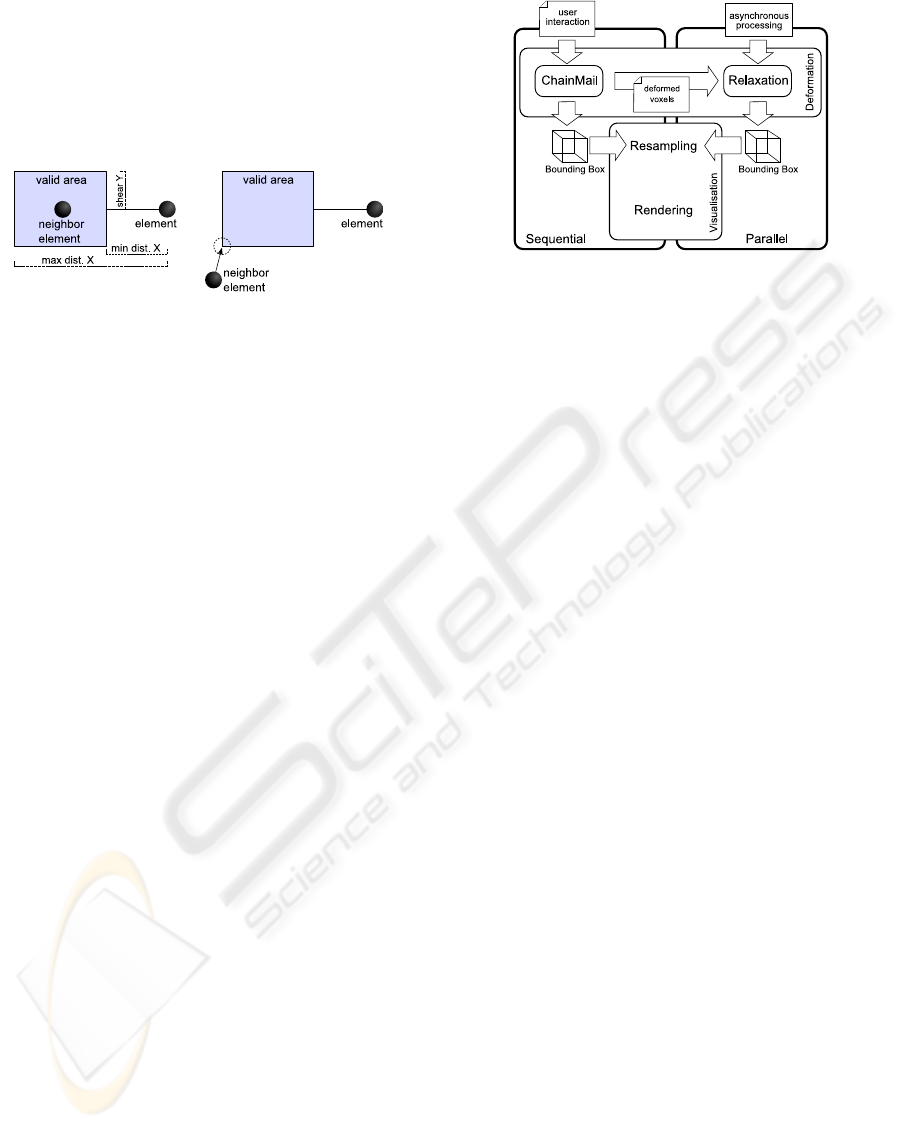
allowed deviations (shear) in y- and, in the 3D case,
also in z-direction. Valid regions for other neighbors
are defined in an analogous way. Material properties
can be directly modeled by modification of the Chain-
Mail constraints. Extent and form of the valid region
are directly connected to stiffness/softness of the sim-
ulated material.
Figure 1: Left: ChainMail constraints. Right: Constraint
violation.
Algorithm. If translation of an element causes con-
straint violations, i.e. one of the neighbors is moved
outside of its valid region, the ChainMail algorithm
solves the constraints by sequentially moving the el-
ements into the valid regions. Each moved element
can cause new constraint violations, hence the order
of element processing is important. The original al-
gorithm provides uniform propagation of the defor-
mation by processing candidates of the six different
major directions on a rotational basis.
ChainMail has the advantage that its complexity
does not grow with the number of elements of the ob-
ject but only with the number of affected elements.
The performance of the algorithm is based on two fea-
tures of the algorithm:
1. The deformation is calculated depending on sim-
ple constraints.
2. Each element of the dataset is processed at most
once per deformation step.
Existing Extensions. The original ChainMail algo-
rithm solves only geometrical constraints. To achieve
an optimal energy configuration Gibson presented an
additional simple relaxation step in (Gibson, 1997).
The algorithm iterates over each element and moves
it towards an equilibrium position which is placed
in the center of its neighbors. A second drawback
of the original ChainMail algorithm is that it is not
well suited to process inhomogeneous data. To over-
come this limitation the Enhanced ChainMail algo-
rithm (Schill et al., 1998) has been proposed. The
equal deformation propagation into each direction is
replaced by an importance driven approach where ele-
ments with a higher amount of constraint violation are
processed first. This method leads to a shock wave
like deformation propagation that propagates faster
through stiff material. The simple midpoint-based re-
laxation scheme proposed in connection with the orig-
Figure 2: Workflow.
inal ChainMail does not allow the definition of mate-
rial parameters and is therefore not suitable for the en-
hanced ChainMail. Up to now, no relaxation scheme
addressing this problem in connection with the En-
hanced ChainMail algorithm has been proposed.
4 SYSTEM OVERVIEW
An overview of our deformation system is depicted in
figure 2. Initial deformation input is provided by user
interaction through a pick and drag interface (see sec-
tion 7). The user input is processed by an extended
ChainMail solver (see section 5.1) which computes
a preliminary but fast deformation. The result can
be visualized immediately but it is also forwarded to
the relaxation solver which is initialized with the de-
formed voxels. Our relaxation method (section 5.2)
optimizes the deformation for more realistic material
behavior, but since relaxation is a time consuming it-
erative process, this routine is invoked in a second
thread on the CPU and parallel to the rendering step
performed on the GPU. Rendering is done by GPU-
based direct volume raycasting (section 6). To do so,
the deformed volume data needs to be resampled into
a rectilinear grid and has to be transferred into graph-
ics card memory. Since resampling is a time consum-
ing task as well, and the amount of data that has to be
downloaded to graphics memory should be as small as
possible, only the changed area of the volume will be
considered. For this reason both deformation methods
provide bounding boxes which describe the affected
part of the volume.
The deformation and rendering cycle performs as
follows. At the begin of each loop it is checked if
the user is actively manipulating the volume. In this
case ChainMail deformation and visualization is per-
formed sequentially. In the other case the relaxation
solver is invoked in parallel to the rendering routine.
INTERACTIVE DEFORMATION AND VISUALIZATION OF LARGE VOLUME DATASETS
41

5 TWO-STEP DEFORMATION
The proposed deformation system allows processing
of large volume data sets with inhomogeneous mate-
rials. The system has been realized as two-step defor-
mation system providing in the first step a rough and
fast ChainMail based deformation, followed in a sec-
ond step by a successive refinement based on a phys-
ically motivated relaxation scheme.
5.1 Step 1: Enhanced ChainMail
The first step of our deformation system is based on
the Enhanced ChainMail (Schill et al., 1998) algo-
rithm that allows handling of inhomogeneous data,
i.e. the definition of different deformation properties
per material (see section 5.3).
The ChainMail deformation process performs in the
same way as proposed in the original literature,
but extensions have been developed concerning data
structure and data handling.
Data Structure and Memory Management. Basi-
cally we use a similar data structure as presented by
Gibson et al. The original volume data (in most cases
two bytes per voxel) is wrapped with an explicit po-
sition, a unique id, neighborhood information, a time
stamp and flags. In our implementation we came up
with a data structure using 64 bytes for one voxel.
In contrast to the original implementations we
consider much larger datasets (up to 1GB), hence
preparing the whole volume dataset for deformation
can easily reach the limit of available main memory.
Therefore we extended the data structure with a brick-
ing scheme to reduce the allocation in main memory,
similar to the method for GPU based volume render-
ing provided by (Weiler et al., 2000). The volume is
subdivided in small bricks, 32×32×32 in size. These
data blocks are generated only if they are needed for
the deformation process.
The data structure is controlled by a memory man-
agement algorithm. This algorithm keeps track of the
available and already allocated memory. Every time
data for deformation is missing the memory man-
ager is invoked to generate the block which contains
the missing data. If the system runs out of memory
an unused data block is freed before generating the
new one. In this way the available memory does not
limit the possible volume size but the number of data
blocks which can be deformed at one time.
5.2 Step 2: Relaxation
As described in section 3, ChainMail comes with
the advantage of simplicity and speed but generates
Figure 3: Spring placement, axis aligned (structural)
springs left and diagonal springs right.
only a very coarse approximation of soft body de-
formations. The relaxation step described in this
section is suited to handle inhomogeneous data, and
improves the previous deformation result of the En-
hanced ChainMail algorithm by adding additional
physical constraints.
Our goal was to implement a relaxation system
providing physically plausible improvements of the
initial ChainMail deformations while still performing
at interactive frame rates. For this purpose we prpose
a relaxation scheme similar to the approach presented
in (Brown et al., 2002) that is directly derived from
physically-based mass-spring methods. Our system
based on the following basic relaxation step:
F
t+∆t
i
= D(p
t
i
) (1)
p
t+∆t
i
= p
t
i
+ α · F
t+∆t
i
(2)
A displacement function D is evaluated to calculate a
vector F
i
which moves the node into the equilibrium
position. Material properties are modeled with this
displacement function. Then the node position p
i
is
updated with F
i
scaled by a step size α < 1. High
values for α lead to faster convergence but can lead to
instability as well.
Displacement Function D. The behavior of mate-
rial is modeled using linear springs to connect the el-
ements. Linear springs are described by Hooke’s Law
as
f
t+∆t
i,j
= −k
i,j
· (p
t
i
− p
t
j
) (3)
where i denotes the node and j the neighbor. The con-
stant k
i,j
denotes the stiffness of the spring between
node i and j. Since the spring tries to preserve a de-
fined distance between the nodes, the rest length d
ij
is introduced into the equation.
f
t+∆t
i,j
= −k
i,j
· (d
i,j
−
p
t
i
− p
t
j
) · (p
t
i
− p
t
j
) (4)
The force vector of node i is calculated by summing
all springs.
F
t+∆t
i
= D(p
t
i
) =
X
j∈σ(i)
f
t+∆t
i,j
(5)
GRAPP 2007 - International Conference on Computer Graphics Theory and Applications
42

The springs are spanned to the axis aligned neighbors
to preserve the grid structure and to the diagonally
opposite elements (see fig. 3) which introduces shear
resistance and volume preservation behavior.
Node processing. A generic relaxation algorithm
iterates over all elements and solves the local con-
straints. In the special case of a 3D grid deformation
problem we can take advantage of the fact that during
one iteration an element can only influence its direct
neighbors.
The relaxation process performs on a list of ele-
ments which are affected by the deformation. The list
is initialized with all elements the previous ChainMail
step has touched. During relaxation elements can be
deleted from the list if a certain convergence criterion
is fulfilled. In our implementation we use the length
of the movement that has to be below some threshold:
p
t
i
− p
t−∆t
i
< . If convergence for the given el-
ement is not reached, all direct neighbors are added
to the list. To avoid adding nodes more than once,
a special flag in the element data structure shows if
the node is in the list or not. A single linked list
is used because this implementation has the smallest
overhead for inserting and deleting items.
The advantage of processing the nodes in a wave
propagation order during relaxation is discussed in
(Brown et al., 2002). Our implementation, uses this
advantage without any overhead: The relaxation al-
gorithm is initialized with elements collected from the
ChainMail routine. Since ChainMail also works in a
wave propagation order no additional sorting has to
be done.
5.3 Material Definition
The material specifications with ChainMail and re-
laxer properties are managed in a global list. The as-
signment is done through a lookup table which takes
the voxel value as key. Using a lookup table has the
advantage that material properties can be easily mod-
ified while the system is running.
Applying material specifications via voxel values
has similarities to transfer functions for volume ren-
dering. In this case ranges of key values share one
material. Interpolation of the parameters is not yet
implemented but considered as future work.
The properties of each material have to be defined
for the ChainMail solver and for the relaxation solver.
Both deformation settings should produce as similar
results as possible since the relaxer converges faster
if ChainMail provides a good start configuration. A
simple mapping from ChainMail constraints to spring
properties can be designed by directly relating the size
of a valid region with the stiffness of related springs.
Figure 4: Volume deformation with inhomogeneous mate-
rial. The inner sphere remains undeformed because of the
very soft (invisible) padding to the outer sphere.
6 VISUALIZATION
As a result of deformation the volume data is or-
ganized in an unstructured grid. Different meth-
ods for rendering scattered data have been devel-
oped which can be categorized in direct and indi-
rect methods. Direct rendering of a deformed vol-
ume dataset can be done using the projected tetrahe-
dra algorithm (Shirley and Tuchmany, 1991; Weiler
et al., 2003), the point-based approach called splatting
(Westover, 1990; Neophytou and Mueller, 2005) or
a texture-based approach presented in (Rezk-Salama
et al., 2001; Westermann and Rezk-Salama, 2001).
In contrast, indirect methods require a resampling
step to transform the unstructured data into a recti-
linear volume representation which can be rendered
using any direct volume rendering technique.
In this work we have chosen the indirect method
because GPU-accelerated direct volume rendering is
outclassing other volume rendering methods in qual-
ity and performance.
6.1 Resampling
Weiler et al. presented in (Weiler and Ertl, 2001)
an efficient object-order resampling approach. This
method is based on simple rasterization of a volume
that is defined by tetrahedra. The subdivision of the
deformed grid in tetrahedra would result in five times
more (and smaller) tetrahedrons than voxels. This in-
duces that iterating the destination voxels (in image
order) is more efficient than iterating over tetrahedra.
Therefore we developed a new image-order re-
sampling algorithm. This makes it necessary to solve
the point location problem emphasized in (Weiler and
Ertl, 2001) , i.e. to find the influencing elements in the
deformed dataset corresponding to a discrete position
in destination the domain.
For each voxel in the destination volume two steps
have to be performed. First, find the (deformed) ele-
ment that is placed next to the resampling position
INTERACTIVE DEFORMATION AND VISUALIZATION OF LARGE VOLUME DATASETS
43
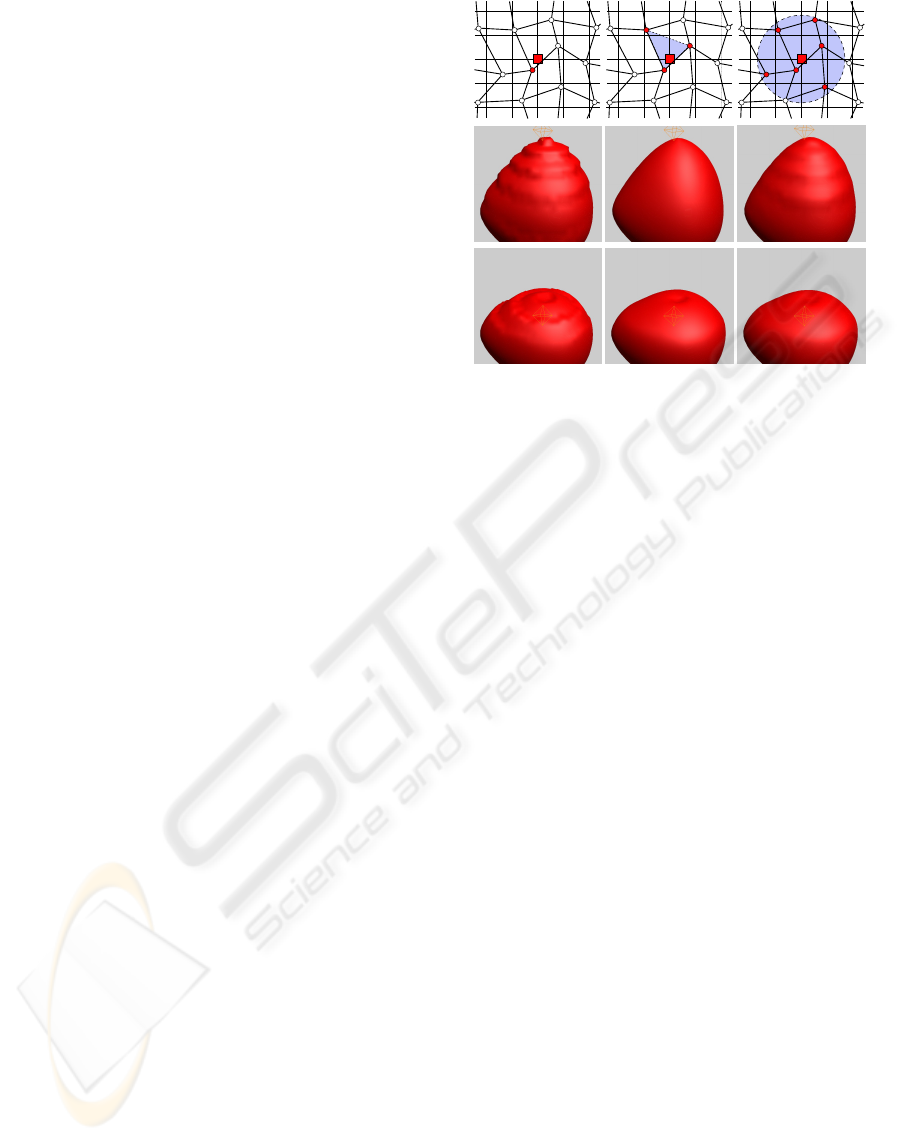
(the nearest neighbor). Second, compute an interpo-
lation for the resampling position.
Nearest Neighbor Search. The first step is solved
by an incremental search algorithm which traverses
the deformed grid toward the resampling position.
The algorithm starts with an initial element and tries
to find in each iteration step an element in the local
neighborhood that is placed nearer to the goal. For
this algorithm it is important that the grid remains in
a status where this steepest descent-like optimization
method does not get stuck in a local minimum.
Local minima arise if the grid structure is inter-
nally overlapping as a result of deformation. Theo-
retically, both deformation methods keep local neigh-
borhood relationships and prevent the grid from over-
lapping. Especially the ChainMail algorithm defines
very strict constraints which limit the relative posi-
tion of the neighbor elements. Practically, ChainMail
is optimized for speed and not for accuracy and over-
lapping might occur in some cases. Hence the defor-
mation system can easily produce grid configurations
where the naive implementation fails to find better el-
ements in the neighborhood. To escape from this “lo-
cal minima” we introduce two heuristics:
• Start the search algorithm with an estimated jump,
i.e. performing a number of traversing steps over
the most promising neighbor links if the current
node can not be the nearest neighbor because of
its distance to the goal.
• If no better element can be found, check if it is
possible for the element to be the nearest neigh-
bor. If not, perform an estimated jump.
At the beginning of the resampling step an initial
start point for the search is needed. We are using sim-
ply the element which would be the nearest neighbor
in the undeformed grid. The resampling algorithm is
performed line wise, hence local coherence can be ex-
ploited by using the last nearest neighbor as start point
for the next search.
The presented search algorithm finds the nearest
neighbor in more than 99% of all cases. Rarely,
small resampling artifacts can be observed because of
a failed search but in exchange the search algorithm
performs with a almost constant complexity if local
coherence is exploited.
Interpolation. Once the nearest neighbor is found
the value for the resampled voxel is computed. In
addition to a method that directly uses the nearest
neighbor value (nearest neighbor resampling) two in-
terpolation methods have been implemented. Figure 5
shows rendering results after deformation and resam-
pling. In the second row the visible material is ex-
panded which means the space between the nodes is
Figure 5: Comparison: First column nearest neighbor, sec-
ond column barycentric interpolation, third column radial
basis functions with a radius of 1.4 and gaussian weight
distribution. The first row shows a 2D simplification of the
used interpolation method.
bigger as usual. In the third row we see a compressed
volume where the nodes stick more together.
Optimization. To save computation time only de-
formed parts of the volume are resampled: While
deforming the smallest bounding box enclosing all
moved voxels is tracked, and transferred to the GPU
for visualization.
6.2 Rendering
The actual rendering is done through GPU accelerated
direct volume ray casting (refer to (Scharsach et al.,
2006) for further details). The graphics card mem-
ory is initialized with the original volume data. Both
steps of the deformation (ChainMail and relaxation)
send their results to the GPU and successively replace
the original volume by the resampled parts of the de-
formed volume for visualization. The update is done
after each iteration step. In this way only small parts
of the volume have to be replaced and the exchange
of the volume has no influence on the rendering speed
which stays interactive during the whole deformation
process.
7 USER INTERACTION
For user interaction a simple mouse pick and drag in-
terface was implemented. Picking is done through
first hit raycasting. The mouse click position in win-
dow space is transformed into a 3D ray. This ray is
traced through the volume. If a voxel value is found
GRAPP 2007 - International Conference on Computer Graphics Theory and Applications
44

Table 1: Timing tests.
data set dimension size rendering only rendering + ChainMail rendering + relaxation
hydrogen 64×64×64 0.5 MB 31.1 fps 30 fps 15.50 fps
endoscopy 512×512×128 64 MB 11.3 fps 9.5 fps 7.3 fps
head 512×512×333 166.5 MB 15.3 fps 9.1 fps 6.90 fps
beetle 832×832×494 652.1 MB 4.23 fps 3.65 fps 3.45 fps
Figure 6: Deformation of the “head” dataset containing 87.3
million voxels. Local deformations involving 2.5 million
voxels (ear) and 0.7 million voxels (mouth).
bigger than some given iso value, the algorithm stops
and a hit point is found.
It has been shown to be quite difficult to find a
proper iso value for picking if volume rendering with
complex transfer functions is used. Therefore a spe-
cial rendering mode which combines direct volume
rendering with first hit raycasting (Scharsach et al.,
2006) allows visualization and adaptation of a chosen
iso-surface on the fly For picking, the same iso value
is used and the hitpoint corresponds to the visual feed-
back.
8 RESULTS
For timing tests an intel dual core machine with 2.4
GHz, 2 GB of RAM and a Nvidia Quadro FX 3400
graphics adapter with 256 MB RAM was used. Table
1 shows the overall performance of the system stated
in framerates. The listed results prove that the defor-
mation system remains interactive even if very large
datasets are used. The results have been produced in
normal use case situations with up to 1 million voxel
per deformation such as the examples shown in figure
6.
The execution speed has been measured for the
sub-modules of the deformation system as well. The
ChainMail algorithm reaches an average performance
of 2.34· 10
6
elements
second
, the computation cost is growing
linearly with the number of deformed elements.
The performance of the resampling algorithm de-
pends on the used interpolation method. Nearest
neighbor resampling reaches an average performance
of 4.41 · 10
6
v oxel
second
, barycentric coordinates interpo-
lation 2.46 · 10
6
v oxel
second
and interpolation using RBF
1.48 · 10
6
v oxel
second
.
The performance of the relaxation step is difficult
to measure. The algorithm iterates 2.3 · 10
7
elements
second
but each element has to be processed many times un-
til convergence is reached. The number of needed it-
erations depends on the size of the deformation and
on the material parameters. Tests have shown that
a deformation with two million elements involved is
relaxed within 3 seconds, while the system remains
fully interactive.
9 SUMMARY AND DISCUSSION
We have presented a complete system for interactive
deformation of inhomogeneous volume data com-
bined with high quality rendering. Unlike other defor-
mation systems we perform all computations directly
at the voxel level without any simplification or prepro-
cessing. Our system has proven to be able to handle
datasets with more than 650 MB ( 340 million voxels)
while more than 1 million voxels can be interactively
deformed simultaneously.
Due to the high amounts of elements that have to
be deformed, the Enhanced ChainMail plus relaxation
approach for the deformation system turned out as the
only possible solution. However, the choice was a
trade off between accuracy and interactivity and is not
able to reach the physical exactness of finite element
or mass-spring systems. The integration of more ex-
act deformation systems is considered as future work
and will become more and more possible with in-
creasing computational power, like the recently intro-
duced PPUs (Physics Processing Units).
The resampling based visualization system has
proven to be well suited for the given problem. The
main advantage is the possibility to integrate the de-
formation system seamlessly into the high quality di-
rect volume rendering framework. However, the im-
INTERACTIVE DEFORMATION AND VISUALIZATION OF LARGE VOLUME DATASETS
45

plementation of direct approaches able to render un-
structured data directly are also considered as future
work to overcome the resampling overhead.
REFERENCES
Adams, B., Keiser, R., Pauly, M., Guibas, L., Gross, M.,
and Dutr
´
e, P. (2005). Efficient raytracing of deforming
point-sampled surfaces. Computer Graphics Forum,
24(3):677–684.
Brown, J., Sorkin, S., Bruyns, C., Latombe, J.-C., Mont-
gomery, K., and Stephanides, M. (2002). Algorithmic
tools for real-time microsurgery simulation. Medical
Image Analysis, 6(3):289–300.
Chen, M., Correa, C., Islam, S., Jones, M., Shen, P.-Y.,
D.Silver, Walton, S., and Willis, P. (2005). Deform-
ing and animating discretely sampled object represen-
tations. In Eurographics - State of the Art Reports,
pages 113–140.
Chen, M., Silvery, D., Winter, A. S., Singhy, V., and Cornea,
N. (2003). Spatial transfer functions - a unified ap-
proach to specifying deformation in volume modeling
and animation. In Proceedings of Volume Graphics,
pages 35–44.
Desbrun, M. and Cani, M.-P. (1998). Active implicit surface
for animation. In Proceedings of Graphics Interface,
pages 143–150.
Georgii, J. and Westermann, R. (2006). A multigrid frame-
work for real-time simulation of deformable bodies.
Computers and Graphics, 30(3):408–415.
Gibson, S., Fyock, C., Grimson, E., Kanade, T., Kikinis,
R., Lauer, H., McKenzie, N., Mor, A., Nakajima, S.,
Ohkami, H., R.Osborne, Samosky, J., and Sawada, A.
(1998). Simulating surgery using volumetric object
representations, real-time volumerendering, and hap-
tic feedback. Medical Image Analysis, 2(2):121–132.
Gibson, S. F. F. (1995). Beyond volume rendering: Visu-
alization, haptic exploration, an physicalmodeling of
voxel-based objects. In Proceedings of Visualization
in Scientific Computing, pages 9–24. Springer-Verlag
Wien.
Gibson, S. F. F. (1997). 3D chainmail: A fast algorithm
for deforming volumetric objects. In Proceedings of
Symposium on Interactive 3D Graphics, pages 149–
154.
Gibson, S. F. F. (1999). Using linked volumes to model ob-
ject collisions, deformation, cutting, carving,and join-
ing. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Com-
puter Graphics, 5(4):333–348.
Li, Y. and Brodlie, K. (2003). Soft object modelling
with generalised chainmail - extending the bound-
aries of web-based graphics. Comput. Graph. Foru m,
22(4):717–728.
Mosegaard, J., Herborg, P., and Sorensen, T. S. (2005). A
gpu accelerated spring mass system for surgical sim-
ulation. In 13th Medicine Meets Virtual Reality Con-
ference, volume 111 of Studies in Health Technology
and Informatics, pages 342–348. IOS Presss.
M
¨
uller, M., Heidelberger, B., Teschner, M., and Gross, M.
(2005). Meshless deformations based on shape match-
ing. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 24(3):471–478.
M
¨
uller, M., Keiser, R., Nealen, A., Paily, M., Gross, M.,
and Alexa, M. (2004). Point based animation of elas-
tic, plastic and melting objects. In Proceedings of Eu-
rographics/ACM Symposium on Computer Animation,
pages 141–151.
Nealen, A., M
¨
uller, M., Keiser, R., Boxerman, E., and Carl-
son, M. (2005). Physically based deformable models
in computer graphics. In Eurographics - State of the
Art Reports, pages 71–94.
Neophytou, N. and Mueller, K. (2005). Gpu accelerated
image aligned splatting. In Fujishiro, I. and Gr
¨
oller,
E., editors, Proceedings of Volume Graphics, pages
197–205.
Rezk-Salama, C., Scheuering, M., Soza, G., and Greiner,
G. (2001). Fast volumetric deformation on gen-
eral purpose hardware. In Proceedings of the ACM
SIGGRAPH/EUROGRAPHICS workshop on Graph-
ics Hardware, pages 17–24.
Scharsach, H., Hadwiger, M., Neubauer, A., Wolfsberger,
S., and B
¨
uhler, K. (2006). Perspective isosurface and
direct volume rendering for virtual endoscopyapplica-
tions. In Proceedings of Eurovis 2006.
Schill, M. A., Gibson, S. F. F., Bender, H.-J., and M
¨
anner,
R. (1998). Biomechanical simulation of the vitreous
humor in the eye using an enhancedChainMail algo-
rithm. In Proceedings of Medical Image Computa-
tion and Computer Integrated Surgery, volume 1496
of Lecture Notes in Computer Science, pages 679–
687.
Shirley, P. and Tuchmany, A. (1991). A polygonal approxi-
mation to direct scalar volume rendering. In Proceed-
ings of Workshop on Volume Visualization, volume 24,
pages 63–70.
Singh, V., Silver, D., and Cornea, N. (2003). Real-time vol-
ume ma nipulation. In Proceedings of the Eurograph-
ics/IEEE TVCG Workshop on Volume Graphics, vol-
ume 45 of ACM International Conference Proceeding
Series, pages 45–51.
Weiler, M. and Ertl, T. (2001). Hardware-software-balanced
resampling for the interactive visualization of unstruc-
tured grids. In Proceedings of IEEE Visualization,
pages 199–206.
Weiler, M., Kraus, M., Merz, M., and Ertl, T. (2003).
Hardware-based view-independent cell projection.
volume 9, pages 163 – 175.
Weiler, M., Westermann, R., Hansen, C. D., Zimmerman,
K., and Ertl, T. (2000). Level-of-detail volume render-
ing via 3D textures. In IEEE Symposium on Volume
Visualization and Graphics, pages 7–13.
Westermann, R. and Rezk-Salama, C. (2001). Real-time
volume deformations. Computer Graphics Forum,
20(3):443–451.
Westover, L. (1990). Footprint evaluation for volume ren-
dering. In Proceedings of ACM SIGGRAPH, pages
367–376.
GRAPP 2007 - International Conference on Computer Graphics Theory and Applications
46
