
ANONYMOUS PREPAID CONTENT VIEWING SYSTEM WITH
MOBILE TERMINAL
Toshiyuki Fujisawa, Kazuto Ogawa, Takeshi Kimura
Science & Technical Research Laboratories, Japan Broadcasting Corporation, 1-10-11 Kinuta, Setagaya-Ku, Tokyo, Japan
Masaki Inamura, Toshiaki Tanaka
KDDI R&D Laboratories Inc., 2-1-15 Ohara, Fujimino-shi, Saitama, Japan
Keywords:
Electronic prepaid ticket, anonymity, offline, blind signature, CAS, Digital Broadcasting.
Abstract:
A number of content viewing systems that use electronic money have been proposed recently. These systems’
access control uses license information stored in the specific hardware such as a set-top box (STB), which
is distributed by broadcasters or communication carriers. However, such an access control decreases the
usability of the system, since users cannot carry around a STB. To solve this problem, other content viewing
systems uses an electronic prepaid ticket and a tamper resistant module (TRM) for digital broadcasting. In
such a system, license information stored in the TRM is transferred to a user’s mobile terminal, such as a
cellular phone. The user, who carries this mobile terminal, can view contents away from home. This kind of
system requires the license information to be managed securely and the electronic prepaid ticket payment to
be performed correctly. In this paper, we propose another system that meets these requirements and enables
anonymous viewing with a low CPU cost.
1 INTRODUCTION
Japanese digital broadcasting currently implements a
digital rights management (DRM) system that uses
conditional access system (CAS) cards (ARIB, 2005).
Each CAS card is a smart card with a tamper-resistant
module (TRM), and it is inserted in a receiver. In
addition, content distribution services implement a
DRM that uses a set-top box (STB) with on-board li-
cense information distributed by the carrier over the
Internet. In these systems, the TRM in the CAS card
and STB decodes the control data, extracts decryption
keys from license information, and manages contract
data. However, if a user wants to view content away
from home, she/he must carry her/his TRM from the
CAS card or STB. Consequently, family members at
home would not be able to view any content until the
TRM is returned.
Besides this problem, users naturally want to pre-
serve their privacy so that third parties, like content
providers or research companies, cannot obtain per-
sonal information, such as content viewed or places
visited by the user. This need for privacy may be true
even for pay-per-view channels. Hence, an anony-
mous content viewing system is required.
There are a number of approaches to solve these
problems with electronic money (Okamoto and Ohta,
1992; Camenisch et al., 2005). In addition, other ap-
proaches with electronic tokens and with blind sig-
natures have been developed, whereby a digital sig-
nature is made without disclosing information to the
signer beforehand (Song and Korba, 2003; Shige-
tomi et al., 2003; Chaum, 1982; Chaum, 1989). This
method can ensure anonymity and allow a user carry-
ing an electronic ticket or a token to view content out-
side the home. However, it incurs a heavy CPU load,
since an exponent calculation is necessary to use a to-
ken. This means the number of processes in a TRM
of the CAS card or STB would be large.
Another method employs a group signature
(Ogawa et al., 2005). When a user makes a contract
with content providers, she/he uses a group signature
to ensure anonymity. However, this method uses a to-
ken, and the CPU cost to deal with the token is heavy.
In addition, since the general manager of the group
signature can identify the signer, the system can not
provide perfect anonymity.
These previous proposals are difficult to process,
281
Fujisawa T., Ogawa K., Kimura T., Inamura M. and Tanaka T. (2007).
ANONYMOUS PREPAID CONTENT VIEWING SYSTEM WITH MOBILE TERMINAL.
In Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Security and Cryptography, pages 281-288
DOI: 10.5220/0002126002810288
Copyright
c
SciTePress

given the limited resources of the TRM in a CAS
card or STB. Consequently, content viewing systems
ought to consider the limited resources of the CAS
card or STB. The methods in (Inamura et al., 2006;
Fujisawa et al., 2006) are developed, considering such
limitations. These proposed systems have characteris-
tics that can transfer license information and perform
anonymous processing that issues and pays prepaid
tickets. In addition, these systems can be used any-
time and anywhere. They use two different primi-
tive cryptographic technologies: asymmetric key en-
cryption or symmetric key encryption. The former
encryption ensures anonymity with a blind signature.
The latter enables anonymity and offline payment for
viewing contents, and it also reduces the cost of man-
agement.
Here, we review the previous methods that can
work with limited resources, and propose a new sys-
tem that exploits their advantages with different prim-
itive cryptographic technologies. In addition, we pro-
pose a new method that prevents illegal use of elec-
tronic prepaid tickets. In section 2, we describe the
service model and requirements for security. We also
describe problems of the previous methods (Inamura
et al., 2006; Fujisawa et al., 2006). In section 3, we
propose the improved system that does not have the
previous methods’ problems. In section 4, we discuss
the requirements for security and the system. Section
5 is the conclusion.
2 SERVICE MODEL AND
SECURITY REQUIREMENTS
2.1 Service Model
The method of payment is determined when the user
makes a contract with the license administrator. The
user can request the license administrator to provide
prepaid tickets through the user interface (UI) of a
mobile terminal or a receiver at home. After the
TRM in a receiver authenticates the mobile terminal,
the license administrator issues the electronic prepaid
ticket, which is then stored on the TRM in the mobile
terminal. When the user uses a prepaid ticket, she/he
selects content by using the receiver-UI (outside) and
pays the fee to a TRM in a receiver (outside) with the
prepaid ticket stored in her/his mobile terminal. The
license administrator collects the used prepaid tickets.
It pays the content providers through a bank. Figure
1 shows the service model.
2.2 Requirements
This service model consists of the following entities:
a TRM in a CAS card or STB at home or outside, a
mobile terminal, a license administrator, banks, and
content providers. The user pays to view content with
prepaid tickets. The following characteristics are re-
quired for security and the system:
(a) Sound charge: In order to view content outside
the home, the TRM in a receiver (outside) gets the
equivalent value of a prepaid ticket with the con-
tent fee. The charge is processed based on license
data in the TRM.
(b) Unforgeability: No one can generate or change
the value of a prepaid ticket.
(c) Wiretapping Impossibility: Ticket data must not
be revealed even if wiretapping occurs.
(d) Double-spending Impossibility: Double-spending
must be detected even if a user uses duplicated
prepaid tickets.
(e) Anonymity: It should be impossible to identify
users during issuing or paying of prepaid tickets.
(f) Divisibility: Prepaid tickets can be divided into
smaller value tickets.
(g) Offline: Prepaid tickets should be able to be used
without the TRM in a receiver being connected to
the license administrator.
2.3 Problems with Previous Methods
(Inamura et al., 2006; Fujisawa
et al., 2006)
The two previous systems (Inamura et al., 2006; Fu-
jisawa et al., 2006) implementing this service model
used different primitive cryptographic technologies.
One system is based on asymmetric key encryp-
tion and digital signatures (Inamura et al., 2006). In
order to ensure anonymity, this system uses blind sig-
natures when issuing prepaid tickets. This system at-
taches a serial number to a prepaid ticket, and pre-
vents illegal use by having the license administrator
manage the serial number. It cannot reveal the rela-
tionship between the user and serial number since the
issuance protocol uses blind signatures. However, this
system cannot deal with the payment protocol unless
the TRM in a receiver is connected to the license ad-
ministrator, since it is necessary to verify the serial
number at the license administrator when paying for
prepaid tickets. On the other hand, it may be impos-
sible to collect prepaid tickets, since many receivers
may converge on the server connections of the license
administrator.
SECRYPT 2007 - International Conference on Security and Cryptography
282
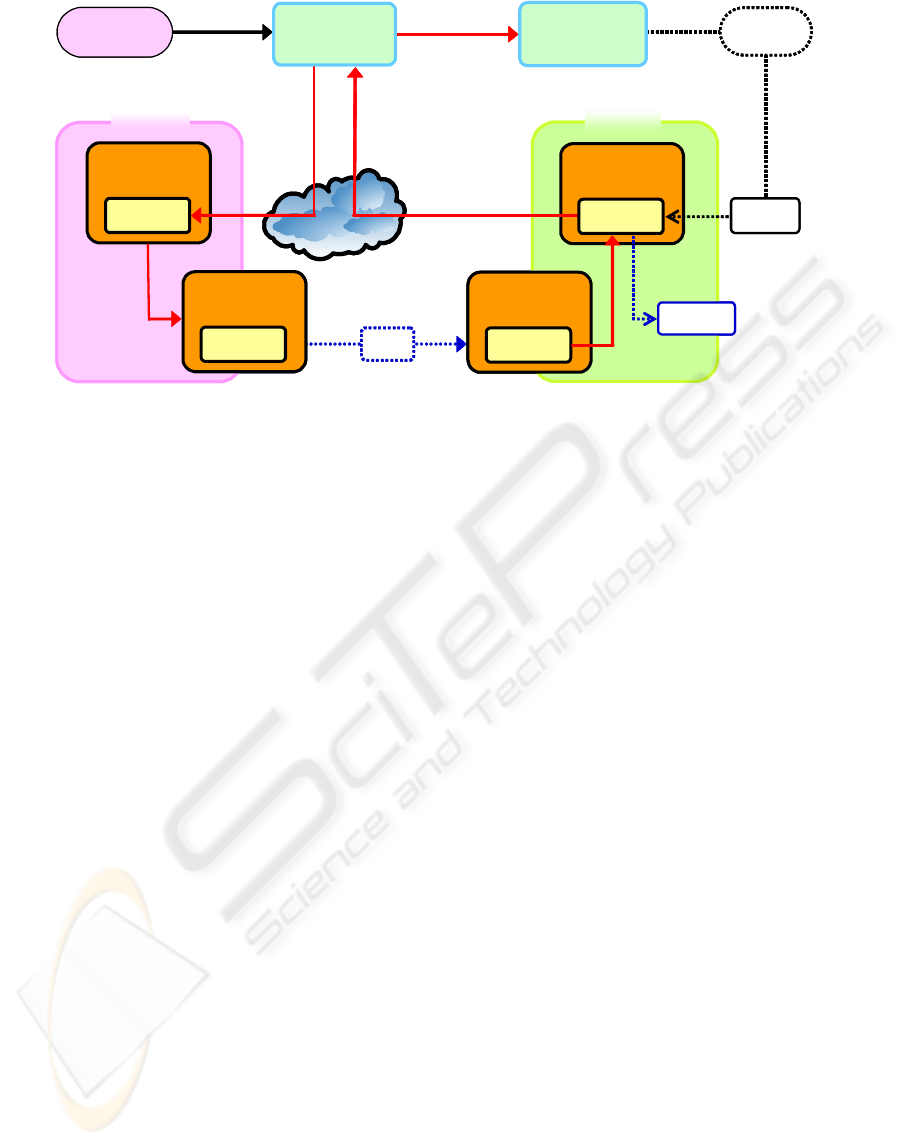
User’s Account
TRM
Home
Outside
Network
2. Transfer
1. Issuance
3. Payment
(Prepaid Ticket)
5. Revenue
Distribution
Payment
(real cash)
4. Forward
Receiver
(home)
Receiver
(outside)
TRM
Mobile
Terminal
TRM
Mobile
Terminal
Viewing
Contents
License
Administrator
Content
Provider
TRM
move
Broadcast
or online
User’s Account
TRM
Home
Outside
Network
2. Transfer
1. Issuance
3. Payment
(Prepaid Ticket)
5. Revenue
Distribution
Payment
(real cash)
4. Forward
Receiver
(home)
Receiver
(outside)
TRM
Mobile
Terminal
TRM
Mobile
Terminal
Viewing
Contents
License
Administrator
Content
Provider
TRM
move
Broadcast
or online
Figure 1: Prepaid Content Viewing Service Model.
The other system is based on symmetric key en-
cryption(Fujisawa et al., 2006). It processes quickly
even with the limited resources of a CAS card or STB.
To ensure anonymity when issuing a prepaid ticket, a
pseudo-user identity is attached to a prepaid ticket so
the system does not directly know the relationship be-
tween the user and prepaid tickets. This system also
ensures the anonymity of the relationship between
viewing content and the user when she/he pays for
prepaid tickets since it sums the fees for each content
provider during a certain period. The license admin-
istrator collects the summed fees by polling in order
to distribute the load on its server. However, although
the receiver (outside) does not deal with payment pro-
cessing for prepaid tickets and forwarding process-
ing for contents fees at the same time, this system is
not perfectly anonymous to the license administrator
when the user pays for prepaid tickets, since the re-
ceiver (outside) knows the pseudo-user identity and
what content is being viewed at the same time.
3 OUR PROTOCOLS
3.1 Point of Our Work
The problems of the previous methods (Inamura
et al., 2006; Fujisawa et al., 2006) are heavy load
on servers and lack of perfect anonymity. Hence,
we solve such problems by using a method based on
asymmetric key encryption in issuance protocol and
also a method based on symmetric key encryption in
payment protocol. In order to process quickly, our
system uses a symmetric key encryption to transfer
data between entities. But for key exchange, it uses
asymmetric key encryption between the receiver and
the mobile terminal. In addition, we improve the
construction of the prepaid ticket. Below we describe
these improvements.
Issuance Protocol:
• It uses blind signatures in order to ensure perfect
anonymity.
• It holds the times, which the prepaid ticket has
been used, within the prepaid ticket data.
Payment Protocol:
• The license administrator collects summed fees of
contents during a certain period in the TRM of the
receiver (outside), for offline processing.
• The TRM in the receiver (outside) issues a new
prepaid ticket based on used prepaid tickets.
When it does so, it adds one to the times, which
the prepaid ticket has been used.
• The license administrator verifies the serial num-
ber when it collects the summed fees for each con-
tent provider by polling.
3.2 Protocols
3.2.1 Overview of Our Protocols
Our system is composed of five entities: the license
administrator, a TRM in a receiver home, outside, a
mobile terminal and content providers, and it employs
four protocols: registration for a mobile terminal, is-
suance for a prepaid ticket, payment for content fee,
forwarding for summed fees of contents.
ANONYMOUS PREPAID CONTENT VIEWING SYSTEM WITH MOBILE TERMINAL
283

The identity of the user’s mobile terminal is con-
verted into a pseudo identity (ID
a
) with a one-way
function. The ID
a
is registered in the TRM in the re-
ceiver (home) and is used to verify the user’s mobile
terminal for the issuance of a prepaid ticket.
In the protocols, each communication must be se-
cure. For this purpose, a master key (K
m
) is shared
among the license administrator and all TRMs (home,
outside). Moreover, the protocols use work keys
(K
w
/K
wt
), which are generated at a TRM and ex-
changed by using asymmetric key encryption. The
work key K
w
, which is shared by the TRM (home)
and the mobile terminal, is generated when the mo-
bile terminal is registered through the TRM in the re-
ceiver. K
w
is used when a prepaid ticket is issued to
the mobile terminal. Another work key, K
wt
, which
is shared temporarily between the TRM (outside) and
the mobile terminal, is generated in the TRM and is
transferred to the mobile terminal with an asymmetric
key encryption method.
Prepaid tickets are processed in the TRM in the re-
ceiver or mobile terminal. The payment is calculated,
and the balance is issued as a new prepaid ticket.
To ensure the anonymity of the relationship be-
tween viewing content and the user, the TRM sums
the values of prepaid tickets collected during a cer-
tain period, and the total amount due each content
provider is transmitted to the license administrator.
The protocols described below are based on the
following assumptions.
Assumptions:
(a) A mobile terminal mounts a PKI function and can
deal with it, and it has public keys and secret keys.
(b) The license administrator mounts a PKI function
and can deal with it, and it has public keys and
secret keys.
(c) Although the TRM in a receiver mounts a PKI
function and can deal with it, the TRM does not
have a public key or a secret key itself.
(d) The license administrator and all TRMs in the re-
ceiver share a master key (K
m
). The MAC (mes-
sage authentication code) of the prepaid ticket
data is keyed with K
m
. It also uses K
m
when it
verifies a contracted receiver, which is managed
by the license administrator.
(e) The license administrator and the TRM in a re-
ceiver are trustworthy. They do not perform any
illegal acts on the issuance or the charge of a pre-
paid ticket.
(f) No one can obtain or substitute internal informa-
tion or processing in a TRM.
(g) MAC is used to authenticate the sender.
In the followings, we use these notations.
Notations:
• STB: set-top box, which is a receiver distributed
by the carrier.
• receiver: A receiver with an inserted CAS card or
a STB.
• UI: user interface
• r
n
: random number used in a challenge-response
process
• rc
n
: random number
• K
w
: a work key that is shared by the TRM in a
receiver and a mobile terminal.
• K
wt
: a work key that is shared temporarily be-
tween the TRM in a receiver and a mobile ter-
minal. A new K
wt
is generated whenever prepaid
tickets are used.
• K
m
: the master key shared by all TRMs in a re-
ceiver and the license administrator.
• pk, pk
t
: a mobile terminal has a public key. It in-
volves work key (K
w
/K
wt
) exchange.
• ID
a
: the identity of a mobile terminal, for in-
stance, the phone’s contract number.
• MAC(m, k): message authentication code, which
encrypts a message (m) with a shared key (k).
Message (ALL) denotes all encrypt data.
• pENC(m, k): Encrypted data of message (m) with
a key (k). The encryption method is asymmetric
key encryption.
• sENC(m, k): Encrypted data of message (m) with
a key (k). The encryption method is symmetric
key encryption.
• LID: a license identity, for instance, the identity
of the TRM in a receiver or a STB.
• X
i
: values of prepaid tickets issued
• S
i
, Z, T
i
, rc: serial number of prepaid ticket (S
i
),
balance (Z), times the ticket has been used (T
i
)
and random number for padding (rc)
• BL(m): Blind data of message (m) generated by
the user using a blind signature scheme.
• SIG
LID
(m): Digital signature of message (m) gen-
erated by the license administrator.
• Y: Fee of content selected by the user
• Pro
j
, Pay
j
(Y): Pro
j
is the identity of the content
provider (1 ≤ j ≤ N
p
) and Pay
j
(Y) is the content
fee paid to the content provider
SECRYPT 2007 - International Conference on Security and Cryptography
284
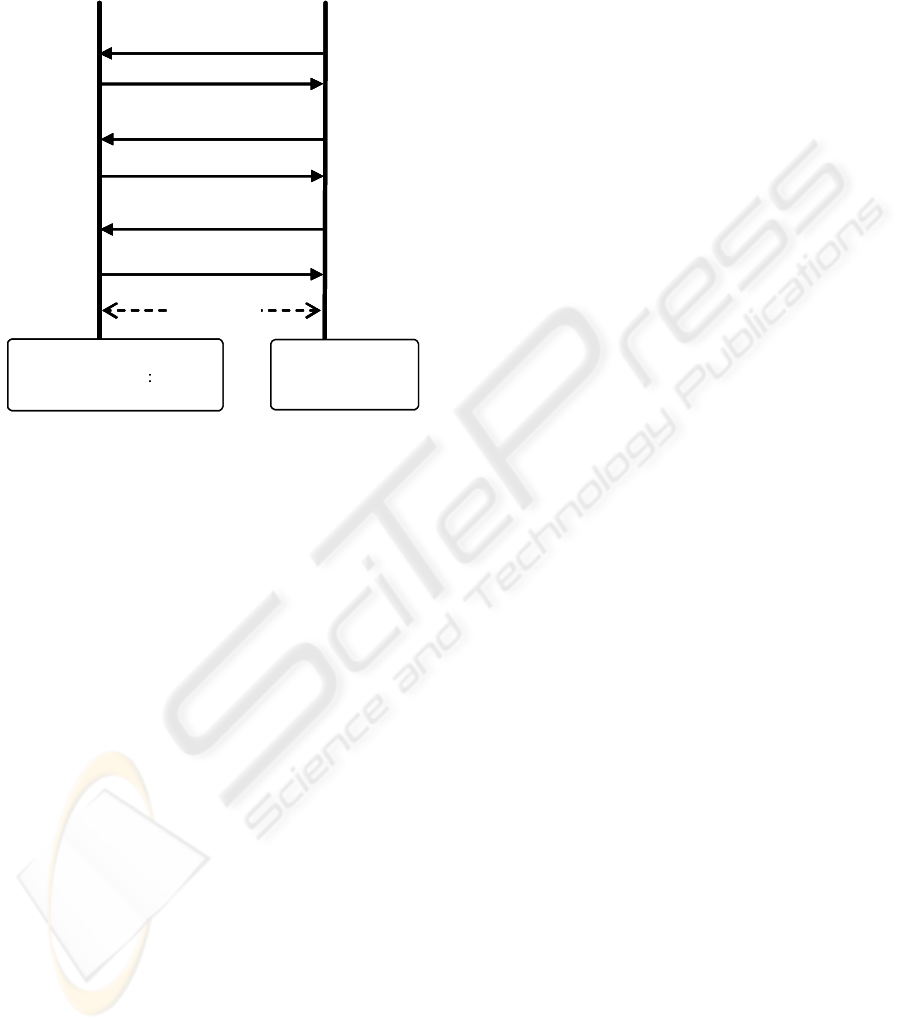
3.2.2 Mobile Terminal Registration
TRM
(Receiver (home))
Mobile
Terminal
Generate r
0
r
0
Certificate
(Including
pk, ID
a
)
Certificate
(Including pk, ID
a
)
pENC(K
w
||r
0
, pk)
Generate K
w
sENC(r
0
, K
w
)
||MAC(ALL, K
w
)
ACK
Store K
w
Registration Request
TRM DB
Mobile Terminal
1
K
w
: ID
a
:
Share K
w
Registrate
K
w
, ID
a
Work Key
Recording Area
K
w
TRM
(Receiver (home))
Mobile
Terminal
Generate r
0
r
0
Certificate
(Including
pk, ID
a
)
Certificate
(Including pk, ID
a
)
pENC(K
w
||r
0
, pk)
Generate K
w
sENC(r
0
, K
w
)
||MAC(ALL, K
w
)
ACK
Store K
w
Registration Request
TRM DB
Mobile Terminal
1
K
w
: ID
a
:
Share K
w
Registrate
K
w
, ID
a
Work Key
Recording Area
K
w
Figure 2: Registration of Mobile Terminal.
Prepaid tickets are stored on the mobile terminal.
The mobile terminal must be registered once with a
TRM in a receiver (home) before a prepaid ticket is
issued. The registration protocol registers the mobile
terminal by using the receiver-UI. Figure 2 shows the
mobile terminal registration protocol.
1. The TRM in the receiver receives a request for
registration, and sends a random number (r
0
) to
the mobile terminal.
2. The mobile terminal sends a public key certificate
including the key (pk) itself.
3. The TRM generates a work key (K
w
) and sends
data encrypted with pk, pENC(K
w
||r
0
, pk), to the
mobile terminal.
4. The mobile terminal sends encrypted data,
sENC(r
0
, K
w
)||MAC(ALL, K
w
), with K
w
to the
TRM in the receiver.
5. The TRM verifies the random number (r
0
). If
the verification succeeds, the TRM sends the ac-
knowledge signal (ACK) to the mobile terminal.
The TRM registers K
w
and ID
a
in database.
6. The mobile terminal records K
w
.
3.2.3 Prepaid Ticket Issuance
The prepaid ticket issuance protocol is performed as
follows. Figure 3 shows this protocol.
1. The TRM in the receiver receives a request for is-
suance, and sends a random number (r
1
) to the
mobile terminal as a challenge.
2. The mobile terminal generates response data,
ID
a
||MAC(ID
a
||r
1
, K
w
), using the recorded K
w
and sends it to the TRM.
3. If the verification of the response succeeds, a user
inputs the money value for the prepaid ticket (X
0
)
by using the receiver-UI.
4. The TRM generates a serial number for the
prepaid ticket (S
i
), and blinds S
i
. Furthermore,
the TRM generates issuance request data,
sENC(X
0
||LID, K
m
)||BL(S
i
)||MAC(ALL, K
m
),
and sends it to the license administrator.
5. If the verification of the MAC(ALL, K
m
) sent by
the TRM succeeds, the prepaid ticket fee is paid
by direct debit from the user’s bank account. The
fee depends on a LID being a TRM identity. Fur-
thermore, the license administrator signs the blind
data, generates a part of the prepaid ticket data,
sENC(SIG
LID
(BL(S
i
)), K
m
)||MAC(ALL, Km),
and sends them to the TRM.
6. The TRM unblinds the data sent by the license
administrator and verifies it. If the verification
succeeds, the TRM encrypts the full prepaid ticket
data, sENC(rc||T
i
||Z||S
i
||SIG
LID
(S
i
)||MAC(rc||
T
i
||Z||S
i
||SIG
LID
(S
i
), K
m
), K
w
)||MAC(ALL, K
w
),
and sends it to the mobile terminal.
7. The mobile terminal decrypts the prepaid ticket
data with the K
w
, rc||T
i
||Z||S
i
||SIG
LID
(S
i
)||
MAC(rc||T
i
||Z||S
i
||SIG
LID
(S
i
), K
m
), and stores it.
3.2.4 Prepaid Ticket Payment
The prepaid ticket payment protocol is conducted be-
tween the mobile terminal and the TRM in the re-
ceiver (outside) as follows. Figure 4 shows this pro-
tocol.
1. The TRM in the receiver (outside) receives a pay-
ment request and sends a random number (r
2
) to
the mobile terminal.
2. The mobile terminal sends a public key certificate
including the key (pk
t
) itself.
3. The TRM generates a temporal work key (K
wt
),
which is generated at each payment, and sends
data encrypted with pk
t
, pENC(K
wt
||r
2
, pk
t
), to
the mobile terminal.
4. The mobile terminal sends data encrypted with
K
wt
, sENC(r
2
, K
wt
)||MAC(ALL, K
wt
), to the TRM
in the receiver.
ANONYMOUS PREPAID CONTENT VIEWING SYSTEM WITH MOBILE TERMINAL
285
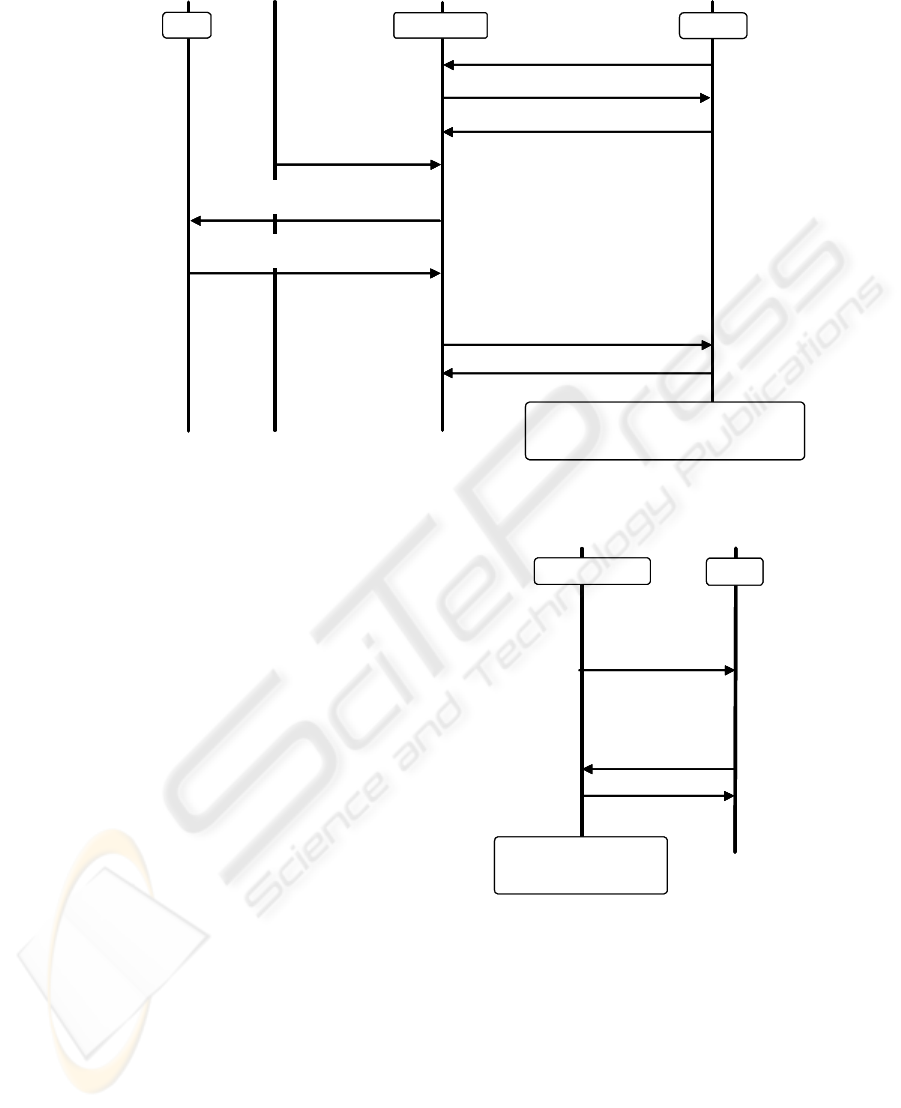
License
Administrator
Mobile
Terminal
Generate Z,rc,MAC
Set T
i
K
w
, ID
a
Receiver-
UI
K
m
Verify ID
a
Input X
0
sENC(X
0
||LID, K
m
)||BL(S
i
)
||MAC(ALL, K
m
)
Generate
S
i
, BL(S
i
), MAC
sENC(SIG
LID
(BL(S
i
)),K
m
)
||MAC(ALL, K
m
)
Verify MAC
Pay by Direct Debit
Digital Signature
Issue Prepaid Ticket
Prepaid Ticket
rc||T
i
||Z||S
i
||SIG
LID
(S
i
)
||MAC(rc||T
i
||Z||S
i
||SIG
LID
(S
i
), K
m
)
Store
Prepaid Ticket
r
1
ID
a
||MAC(ID
a
||r
1
, K
w
)
Generate r
1
ACK
TRM
(Receiver (home))
K
m
, K
w
, ID
a
Verify SIG
LID
(BL(S
i
))
Issuance Request
sENC(rc||T
i
||Z||S
i
||SIG
LID
(S
i
)
||MAC(rc||T
i
||Z||S
i
||SIG
LID
(S
i
), K
m
), K
w
)
||MAC(ALL, K
w
)
License
Administrator
Mobile
Terminal
Generate Z,rc,MAC
Set T
i
K
w
, ID
a
Receiver-
UI
K
m
Verify ID
a
Input X
0
sENC(X
0
||LID, K
m
)||BL(S
i
)
||MAC(ALL, K
m
)
Generate
S
i
, BL(S
i
), MAC
sENC(SIG
LID
(BL(S
i
)),K
m
)
||MAC(ALL, K
m
)
Verify MAC
Pay by Direct Debit
Digital Signature
Issue Prepaid Ticket
Prepaid Ticket
rc||T
i
||Z||S
i
||SIG
LID
(S
i
)
||MAC(rc||T
i
||Z||S
i
||SIG
LID
(S
i
), K
m
)
Store
Prepaid Ticket
r
1
ID
a
||MAC(ID
a
||r
1
, K
w
)
Generate r
1
ACK
TRM
(Receiver (home))
K
m
, K
w
, ID
a
Verify SIG
LID
(BL(S
i
))
Issuance Request
sENC(rc||T
i
||Z||S
i
||SIG
LID
(S
i
)
||MAC(rc||T
i
||Z||S
i
||SIG
LID
(S
i
), K
m
), K
w
)
||MAC(ALL, K
w
)
Figure 3: Issuance of Prepaid Ticket.
5. The TRM verifies the random number (r
2
). If the
verification succeeds, the TRM obtains a content
fee (Y), which is a content selected by a user. The
TRM sends the content fee data, Y||MAC(Y, K
wt
),
to the mobile terminal.
6. The mobile terminal sends the prepaid ticket data
that needs a content fee (Y), sENC((rc||T
i
||Z||S
i
||
SIG
LID
(S
i
))||MAC(rc||T
i
||Z||S
i
||SIG
LID
(S
i
), K
m
),
K
wt
)||MAC(ALL, K
wt
), to the TRM.
7. The TRM verifies the digital signature
(SIG
LID
(S
i
)). If the verification succeeds,
the TRM charges the content fee to the prepaid
tickets and calculates the balance of the prepaid
tickets. The TRM changes the incremental value
of times the ticket has been used (T
i
) and issues
a new prepaid ticket based on the balance of
the previous prepaid ticket. The TRM sends
new prepaid ticket data, sENC(rc||T
i
||Z||S
i
||
SIG
LID
(S
i
)||MAC(rc||T
i
||Z||S
i
||SIG
LID
(S
i
), K
m
),
K
wt
)||MAC(ALL, K
wt
), to the mobile terminal.
8. The mobile terminal decrypts prepaid ticket data
with K
wt
, rc||T
i
||Z||S
i
||SIG
LID
(S
i
)||MAC(rc||T
i
||
Z||S
i
||SIG
LID
(S
i
), K
m
) and stores it.
3.2.5 Contents Fee Forwarding
The forwarding for the content fees protocol sends
the used prepaid tickets from the TRM in the receiver
(outside) to the license administrator as follows. Fig-
ure 5 shows this protocol.
License
Administrator
TRM
(Receiver (outside))
K
m
, history sets
sENC((S
i1
||T
i1
)||…
||(S
iN
||T
iN
)
||(Pro
1
||Pay
1
)||…
||(Pro
Np
||Pay
Np
), K
m
)
||MAC(ALL, K
m
)
DB
History Sets{(S
i1
, T
i1
)…}
, {(Pro
1
, Pay
1
)…}
K
m
ACK
Forward Request
Verify MAC
Verify
Set {(S
i
,T
i
)}
i=i1,…,iN
Generate MAC
,Sets {(S
i
, T
i
)}
i=i1,…,iN
,Sets {(Pro
j
, Pay
j
)}
j=1,…,Np
License
Administrator
TRM
(Receiver (outside))
K
m
, history sets
sENC((S
i1
||T
i1
)||…
||(S
iN
||T
iN
)
||(Pro
1
||Pay
1
)||…
||(Pro
Np
||Pay
Np
), K
m
)
||MAC(ALL, K
m
)
DB
History Sets{(S
i1
, T
i1
)…}
, {(Pro
1
, Pay
1
)…}
K
m
ACK
Forward Request
Verify MAC
Verify
Set {(S
i
,T
i
)}
i=i1,…,iN
Generate MAC
,Sets {(S
i
, T
i
)}
i=i1,…,iN
,Sets {(Pro
j
, Pay
j
)}
j=1,…,Np
Figure 5: Content Fee Forwarding.
1. The license administrator sends a forwarding re-
quest, which is scheduled, to the TRM in the re-
ceiver (outside).
2. The TRM generates forwarding data,
sENC({(S
i
||T
i
)}
i
||{(Pro
j
||Pay
j
)}
j=1,··· ,N
p
,
K
m
)||MAC(ALL, K
m
), that comprises the pair
of the serial number of the paid ticket and the
times it has been used, and the pair of the content
provider identity and summed fees for each
content provider, and sends them.
3. The license administrator verifies {S
i
, T
i
}
i
. If S
i
SECRYPT 2007 - International Conference on Security and Cryptography
286
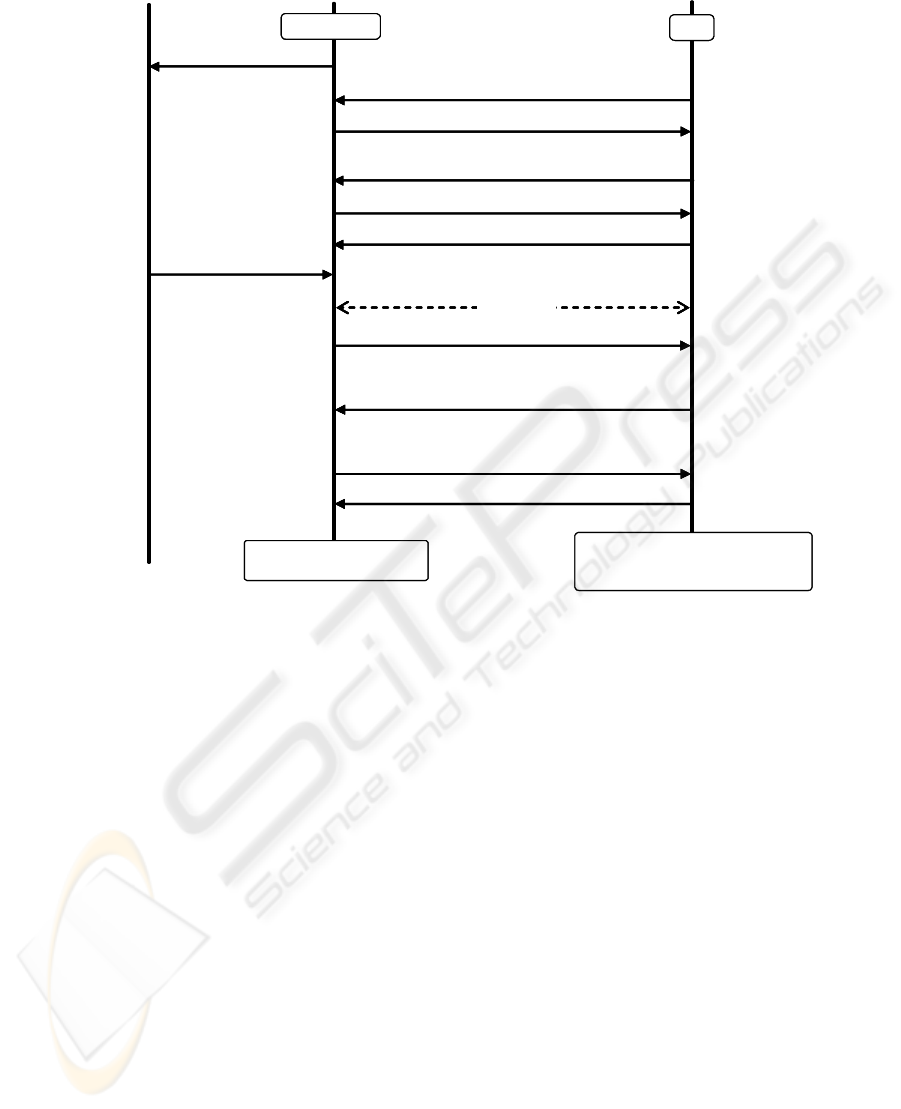
Mobile
Terminal
Generate K
wt
pENC(K
wt
||r
2
, pk
t
)
Verify SIG
LID
(S
i
)
Charge Z=Z-Y
Set Count T
i
Generate rc, MAC
K
w
Receiver-
UI
Request Prepaid Ticket
Value Y
Generate MAC
Store
Prepaid Ticket
sENC((rc||T
i
||Z||S
i
||SIG
LID
(S
i
))
||MAC(rc||T
i
||Z||S
i
||SIG
LID
(S
i
), K
m
), K
wt
)
||MAC(ALL, K
wt
)
Prepaid Ticket
rc||T
i
||Z||S
i
||SIG
LID
(S
i
)
||MAC(rc||T
i
||Z||S
i
||SIG
LID
(S
i
), K
m
)
sENC(rc||T
i
||Z||S
i
||SIG
LID
(S
i
)
||MAC(rc||T
i
||Z||S
i
||SIG
LID
(S
i
), K
m
), K
wt
)
||MAC(ALL, K
wt
)
TRM
(Receiver (outside))
K
m
, K
w
, IDa
Set (Content,Y)
Select Content
Pro
i
, Y
Encryption
ACK
Y||MAC(Y, K
wt
)
DB
(Pro
p
, Pay
p
(Y)), (S
i
, T
i
)
Payment Request
Generate r
2
r
2
sENC(r
2
, K
wt
)||MAC(ALL, K
wt
)
Certificate
(Including pk
t
, ID
a
)
Certificate
(Including pk
t
, ID
a
)
Share K
wt
Mobile
Terminal
Generate K
wt
pENC(K
wt
||r
2
, pk
t
)
Verify SIG
LID
(S
i
)
Charge Z=Z-Y
Set Count T
i
Generate rc, MAC
K
w
Receiver-
UI
Request Prepaid Ticket
Value Y
Generate MAC
Store
Prepaid Ticket
sENC((rc||T
i
||Z||S
i
||SIG
LID
(S
i
))
||MAC(rc||T
i
||Z||S
i
||SIG
LID
(S
i
), K
m
), K
wt
)
||MAC(ALL, K
wt
)
Prepaid Ticket
rc||T
i
||Z||S
i
||SIG
LID
(S
i
)
||MAC(rc||T
i
||Z||S
i
||SIG
LID
(S
i
), K
m
)
sENC(rc||T
i
||Z||S
i
||SIG
LID
(S
i
)
||MAC(rc||T
i
||Z||S
i
||SIG
LID
(S
i
), K
m
), K
wt
)
||MAC(ALL, K
wt
)
TRM
(Receiver (outside))
K
m
, K
w
, IDa
Set (Content,Y)
Select Content
Pro
i
, Y
Encryption
ACK
Y||MAC(Y, K
wt
)
DB
(Pro
p
, Pay
p
(Y)), (S
i
, T
i
)
Payment Request
Generate r
2
r
2
sENC(r
2
, K
wt
)||MAC(ALL, K
wt
)
Certificate
(Including pk
t
, ID
a
)
Certificate
(Including pk
t
, ID
a
)
Share K
wt
Figure 4: Payment of Prepaid Ticket.
is not in the database, the license administrator
records (S
i
, T
i
) in it. If S
i
is in it, the license ad-
ministrator verifies whether T
i
is a duplication or
ordinal number. If the verification succeeds, the
license administrator superposes the value of T
i
on
the record for S
i
in the database.
4. The license administrator sends ACK to the TRM
and distributes the content fees to each content
provider.
4 DISCUSSION
We discuss the security requirements outlined in sec-
tion 2.2.
(a) Sound charge: The sound charge consists of the
correctness of a prepaid ticket value during issu-
ing and the correctness of a new issued prepaid
ticket based on a calculated value when paying
for the prepaid tickets in the TRM of a receiver
(outside). The prepaid ticket data related to the is-
suance, which is encrypted with K
m
, is issued by
the license administrator. Under the assumption
that the license administrator and the TRM in a
receiver (home) are trustworthy, the data is cor-
rect. Hence, the processes in Sec.3.2 guarantee a
sound charge.
(b) Unforgeability: Since prepaid tickets are de-
crypted in the TRM of a receiver and a mobile
terminal, and are calculated in a TRM of the re-
ceiver, they are unforgeable. Moreover, the MAC
of the prepaid ticket data is keyed with K
m
and
is attached to every transaction in order to detect
illegal prepaid tickets. It is hard to generate cor-
rect prepaid tickets and to change a value of a pre-
paid ticket without K
m
. Unforgeability is achieved
through the use of a TRM and a MAC. In addi-
tion, balance data of a prepaid ticket is stored as
a plain text in a mobile terminal, for calculating
needed number of prepaid tickets on a mobile ter-
minal. But a prepaid ticket ensures security by
MAC, which is encrypted with K
m
in a TRM.
(c) Wiretapping Impossibility: To use prepaid tickets,
it is necessary to know the serial number. Even
if an attacker obtains prepaid ticket data during
a communication between entities, he would be
hard for him to use it since it is data encrypted or
blinded.
ANONYMOUS PREPAID CONTENT VIEWING SYSTEM WITH MOBILE TERMINAL
287

(d) Double-spending Impossibility: The license ad-
ministrator can detect illegal prepaid tickets by
verifying the serial number of a prepaid ticket and
the times it has been used. Hence it is possible
to prevent double-spending even if a user uses a
duplicated prepaid ticket.
(e) Anonymity: The license administrator cannot as-
certain the relationship between the user and the
serial number of a prepaid ticket when issuing a
prepaid ticket. The TRM in a receiver (outside)
cannot identify the user since the prepaid ticket
data is encrypted with K
wt
when paying for pre-
paid tickets. In addition, prepaid tickets are peri-
odically summed. This process deletes history of
each user’s viewing content. It is impossible to
extract the user’s individual viewing content from
the summed prepaid ticket value. Hence, it en-
sures anonymity to the license administrator and
the TRM in a receiver (outside). The user can thus
view content anonymously.
(f) Divisibility: The TRM in a receiver can calculate
arbitrary values and issue a new prepaid ticket.
It can detect illegal prepaid tickets, and Double-
spending is impossible, even if a user uses dupli-
cated prepaid tickets before calculation.
(g) Offline: The TRM in a receiver (outside) calcu-
lates the sum total of contents fees for each con-
tent provider. It does not converge on forward-
ing processes since the license administrator col-
lects content fees summed by polling, which de-
termines the schedule itself. Hence, it operates
offline since it is not necessary for the license ad-
ministrator to be connected with the TRM in a re-
ceiver (outside) when the user views content.
5 CONCLUSION
We considered the problems of previously proposed
systems, including lack of perfect anonymity and load
distribution. Our protocol ensures anonymity by us-
ing blind signatures when issuing a prepaid ticket and
it cannot directly identify the relationship between the
user and the serial number when paying for prepaid
tickets. In addition, by attaching a serial number and
the times the ticket has been used to the prepaid ticket
data, it becomes possible to detect illegal acts such as
double-spending. We will develop a software simula-
tor and investigate the management method, including
how to deal with cumulative serial numbers and how
to detect illegal operations when paying for prepaid
tickets.
REFERENCES
ARIB (2005). ARIB STD-B25 Conditional Access System
Specifications for Digital Broadcasting. Association
of Radio Industries and Bussinesses, Tokyo, 4th edi-
tion.
Camenisch, J., Hohenberger, S., and Lysyanskaya, A.
(2005). Compact e-cash. In EUROCRYPT’05, 24th
Annual International Conference on the Theory and
Applications of Cryptographic Techniques. Springer-
Verlag.
Chaum, D. (1982). Blind signatures for untraceable pay-
ments. In CRYPTO’82, 2nd Annual International
Cryptology Conference. Springer-Verlag.
Chaum, D. (1989). Online cash checks. In EURO-
CRYPT’89, Workshop on the Theory and Applications
of Cryptographic Techniques. Springer-Verlag.
Fujisawa, T., Inamura, M., Ogawa, K., Kimura, T., and
Tanaka, T. (2006). Prepaid viewing system for mo-
bile terminal. In WPMC’06, International Sympo-
sium on Wireless Personal Multimedia Communica-
tions. WPMC.
Inamura, M., Tanaka, T., Fujisawa, T., Ogawa, K., and
Kimura, T. (2006). Flexible license transfer system
using mobile terminal. In SECRYPT’06, 1st Interna-
tional Conference on Security and Cryptography. IN-
STICC.
Ogawa, K., Hanaoka, G., and Imai, H. (2005). Extension
of broadcasting service by using electric tokens. In
SCIS’05, Symposium on Cryptography and Informa-
tion Security 2005. SCIS.
Okamoto, T. and Ohta, K. (1992). Universal electronic cash.
In CRYPTO’92, 12th Annual International Cryptol-
ogy Conference. Springer-Verlag.
Shigetomi, R., Otsuka, A., Ogawa, T., and Imai, H. (2003).
Refreshable tokens and its application to anonymous
loan. In SCIS’03, Symposium on Cryptography and
Information Security 2003. SCIS.
Song, R. and Korba, L. (2003). Pay-tv system with strong
privacy and non-repudiation protection. In IEEE
Trans. on Consumer Electronics. IEEE.
SECRYPT 2007 - International Conference on Security and Cryptography
288
