
ROLE AND TASK BASED AUTHORIZATION MANAGEMENT
FOR PROCESS-VIEW
Mei-Yu Wu
Department of Information Management, Chung Hua University, No. 707, Sec. 2, WuFu Rd., Hsinchu, Taiwan
Duen-Ren Liu
Institute of Information Management, National Chiao Tung University, Hsinchu, Taiwan
Keywords: Role-based access control, process-view, authorization management, separation of duty.
Abstract: Role-based authorizations for assigning tasks of workflows to roles/users are crucial to security management
in workflow management systems. The authorizations must enforce separation of duty (SoD) constraints to
prevent fraud and errors. This work discusses the authorization management of organizational roles in a
process-view. A process-view, an abstracted process (workflow) derived from a base process, can provide
adaptable task granularity to suit different needs of workflow participants. A novel authorization mechanism
is proposed to derive a role’s permissions on virtual activities based on the role’s permissions on base activi-
ties. The proposed authorization mechanisms consider duty-conflict relationships among base activities to
enforce SoD.
1 INTRODUCTION
A workflow (process) consists of a set of tasks (ac-
tivity), and the ordering of tasks, or control flow
dependencies, that specify the order of execution
among the tasks. (Georgakopoulos et al., 1995)
Workflows commonly process sensitive business
information. Therefore, adequate access control
mechanisms are needed to protect workflow-related
sensitive information from insecure access.
Role-based access control (RBAC), (Ferraiolo et
al., 1995), (Ferraiolo and Kuhn, 1992), (Sandhu et al.,
1996) has become a widely accepted access control
mechanism for security management. Role-based
authorizations for assigning tasks of workflows to
roles/users are crucial to security management in
workflow management systems. The authorizations
must enforce separation of duty (SoD) constraints to
prevent fraud and errors.
A novel virtual workflow process, i.e., a proc-
ess-view, in a WfMS is proposed by Shen and Liu
(Shen and Liu, 2004). A process-view, i.e., an ab-
stracted process derived from an implemented base
process, is employed to provide aggregate abstraction
of a process. They focused on develop view mecha-
nism in workflow management systems. They did not
discuss the aggregation of virtual activity and per-
missions for a role in a process-view.
This work discusses the authorization manage-
ment of organizational roles in a process-view. The
derivation of a virtual process (process-view) in-
volves grouping the base activities in a base process
and aggregation functions into virtual activities. This
work defines several permissions for a role on base
activities. The permissions for a role on a virtual
activity are according to the permissions of aggre-
gated base activities under strict or lenient privilege
principle. An algorithm is proposed to derive per-
missions for a role on the virtual activity in general
cases. The derivation also considers the duty-conflict
relationships among base activities.
2 RELATED WORK
Role-based access control (RBAC), (Ferraiolo et al.,
1995), (Ferraiolo and Kuhn, 1992), (Sandhu et al.,
1996) has become a widely accepted access control
85
Wu M. and Liu D. (2007).
ROLE AND TASK BASED AUTHORIZATION MANAGEMENT FOR PROCESS-VIEW.
In Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Security and Cryptography, pages 85-90
DOI: 10.5220/0002126300850090
Copyright
c
SciTePress

mechanism for security management. In role-based
access control model, a user can play several roles
and a role can be assigned to several users. The per-
mission assignments are not assigned to users but to
roles. Separation of duty (SoD) (Ferraiolo et al.,
1995), (Gligor et al., 1998), (Nash and Poland, 1990)
(Sandhu et al., 1996), (Simon and Zurko, 1997) is an
important feature of role-based access control model.
SoD is a security principle to spread the responsibility
and authority for a complex action or task over dif-
ferent users or roles, to prevent fraud and errors.
Several researchers (Ahn et al., 2002), (Atluri and
Huang, 1996), (Bertino et al., 1999), (Huang and
Atluri, 1999) have addressed role-based access con-
trol and authorization management in workflow sys-
tems. The major issues concern the design of
role-based authorization mechanisms in support of
separation of duty. Workflow management system
allows various participants to collaborate in effec-
tively managing a workflow-controlled business
process. Shen and Liu (Shen and Liu, 2004) propose a
process-view workflow management to provide ap-
propriate process abstraction for various roles within
an enterprise. Virtual activities are derived through
the bottom-up aggregation of base activities to pro-
vide various levels of abstraction of a base process.
They focus the process-view derived from base
process and do not analyze the permissions for a role
on a virtual activity in a process-view.
3 AUTHORIZATION
MANAGEMENT FOR
PROCESS-VIEW
A workflow consists of a set of tasks, and their order
of execution, according to control flow dependencies.
The various tasks in a workflow are typically per-
formed by multiple collaborating users/roles in an
organization. A role implicitly defines a job position
and its corresponding authority to perform a set of
tasks. Each task is assigned to one or more roles.
Users are assigned appropriate roles based on their
capabilities. A role can be assigned to one or several
users. Moreover, roles are partially ordered by or-
ganizational position within the organization.
WfMS can help decision makers fully utilize
business processes. However, workers (representing
organizational roles) cannot easily obtain a global
view of a complex and large workflow. A proc-
ess-view, an abstracted process derived from a base
process, is proposed to provide adaptable task
granularity in previous related work (Shen and Liu,
2004). Process-view is a good solution that different
workflow participants can acquire different needs and
types of authority. For example, a general manager
may require aggregated information on a specific
process rather than detailed information. In addition,
an accounting manager may not have the authority or
need to know each specific step of the production
flow.
This work discusses the authorization manage-
ment of organizational roles in a process-view. Sev-
eral base activities are aggregated into a virtual ac-
tivity in a process-view. An organizational role r’s
permissions on a virtual activity va
i
can be derived
from r’s permissions on those base activities belong
to va
i
. Moreover, the derivation needs to consider the
duty-conflict relationships among base activities.
3.1 Grouping and Data Aggregations
The derivation of a virtual process (process-view)
involves grouping the base activities in a base process
into virtual activities. A virtual activity contains a set
of base activities in the base process. Base activities
may manipulate some data objects. Data aggregations
may be specified on a virtual activity to provide ag-
gregate views of data derived from the data objects of
base activities. In general, data aggregations may
apply aggregate functions on collections of data ob-
jects manipulated by base activities of a virtual ac-
tivity. These aggregate functions are used in simple
statistical computations, including SUM, AVERAGE,
MAXIMUM and MINIMUM, that summarize in-
formation from data objects handled by the base
activities. Different roles may have different needs of
data aggregations that are defined by the process
modeler.
Let va
i
represent a virtual activity and a
j
denote a
base activity. D
r
(va
i
) denotes the aggregate data ob-
ject of va
i
for role r; D(a
j
) denotes the data object
handled by a
j
, i.e., data object of a
j
, for brevity;
r
va
i
S
is the set of base activities that are specified in the
data aggregation of va
i
for role r;
r
va
i
DS is the set of
data objects of base activities in
r
va
i
S used to derive
the aggregate data object of va
i
for role r; and F
denotes an aggregate function.
r
va
i
S ={ a
j
| a
j
∈ va
i
: a
j
is specified in the data
aggregation of va
i
for role r }
r
va
i
DS
={ D(a
j
) | a
j
∈
r
va
i
S }
The formal expression of aggregating the data
objects of base activities to derive the data object of
va
i
for role r is illustrated in the following.
SECRYPT 2007 - International Conference on Security and Cryptography
86
D
r
(va
i
)= F ({D(a
j
) | a
j
∈
r
va
i
S }) i.e., D
r
(va
i
) = F (
r
va
i
DS )
Notably,
r
va
i
S
may include all or partial base ac-
tivities in
va
i
, as specified in the data aggregation for
role
r defined by the process modeler. The aggregate
function may apply to some or all data objects of base
activities in
va
i
.
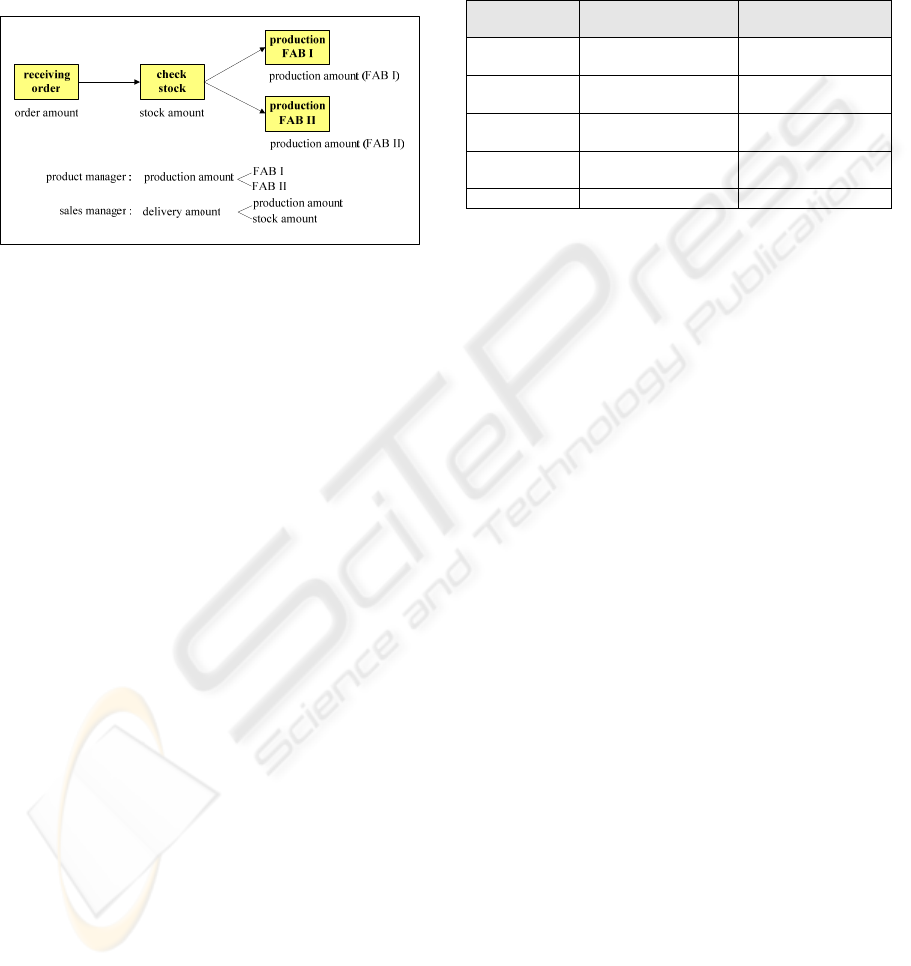
Figure 1: Example of a virtual activity “scheduling pro-
duction”.
Figure 1 illustrates a virtual activity “scheduling
production” which represents an abstraction of four
base activities “receiving order”, “check stock”,
“production FAB I” and “production FAB II”. Only
production data are described for clarity. The data
objects of “receiving order”, “check stock”, “pro-
duction FAB I” and “production FAB II” are order
amount, stock amount, production amount (FAB I),
and production amount (FAB II), respectively. The
sales manager only needs to know the delivery
amount, including production distribution and stock
amount but not the production details.
managersales
va
i
DS = { D(production FAB I),
D(production FAB II), D(stock amount)}
The production manager may want to know the pro-
duction amount but not the stock amount.
managerproduct
va
i
DS = { D(production FAB I),
D(production FAB II)}
3.2 The Permissions on an Activity
A role is a job function defined as a named collection
of responsibilities, which reflect organizational
regulations and business procedures. Several per-
missions on an activity are defined and illustrated in
Table 1. A role is assigned a collection of the per-
missions on base activities. The permissions of role r
on a virtual activity
va
i
can be derived from role r’s
permissions on base activities in
va
i
. Notably, if role r
only has the agg_view permission without the view
permission on
a
j
, then role r can not read the data
object of a
j
. Moreover, the permissions have implied
relationships as shown in Table 1.
Table 1: Permissions on activity.
3.3 Permissions on a Virtual Activity
without Considering Duty-conflict
Relationships among Base Activities
This section presents the derivations of the permis-
sions of a role
r on a virtual activity without consid-
ering duty-conflict relationships among the base
activities. Next section presents the derivations con-
sidering the duty-conflict relationships among the
base activities.
Let P(
r, a
j
) be the set of permissions of role r on
an base activity
a
j
and P(r, va
i
) be the set of permis-
sions of role r on a virtual activity va
i
. For strict
privilege principle, P(
r,va
i
) can be derived by the
intersection of permissions on base activities belong
to
va
i
, as illustrated in the following.
I
ij
vaa
ji
arPvarP
∈∀
= ),(),(
For example, the base activities,
a
1
, a
2
and a
3
in
the base process, are aggregated into the virtual ac-
tivity,
va
1
, in the process-views. If P(r, a
1
), P(r, a
2
),
P(r, a
3
) is {manage}, {execute} and {view}, respec-
tively. According to the strict privilege principle, P(
r,
va
1
) are the intersection of permissions on base ac-
tivities belong to
va
1
, which results in {view}. Nota-
bly, the implied permissions shown in Table 1 should
be considered in deriving the permissions on a virtual
activity.
Above derivation may be too strict for data aggrega-
tion, since the derivation shows that if a role
r does
not have
agg_view permission on all base activities in
va
i
, then the permissions of role r on virtual activity
va
i
will not contain agg_view permission. However,
data aggregation may be specified on part of base
activities in
va
i
. A role r should be able to read D
r
(va
i
),
the aggregate data object of a virtual activity
va
i
, if
Permissions
on activity a
j
Descriptions
Implied Permis-
sions on activity a
j
manage Manage; Read the
data object of a
j
view, agg_view,
awareness
execute Execute; Read/Write
the data object of a
j
view, agg_view,
awareness
view Read the data object
of a
j
agg_view,
awareness
agg_view Read aggregate data
object
awareness
awareness Be aware of a
j
null
ROLE AND TASK BASED AUTHORIZATION MANAGEMENT FOR PROCESS-VIEW
87

role r has the
agg_view permission on all base activity a
j
∈
r
va
i
S ,
as described in the following equation.
agg_view ∈ P(r, va
i
), if P(r, a
j
) contains agg_view
permission for all
a
j
∈
r
va
i
S
If a role
r has the agg_view permission but not the
view permission on a base activity a
j
in a virtual ac-
tivity
va
i
; the agg_view permission on va
i
is derived
for role
r. Role r may deduce the data object of a
j
that
r does not have the permission to view. For example,
a virtual activity,
va
1
, is aggregated from two base
activities,
a
1
and a
2
. A personal computer manufac-
turer contains two factories. Each factory reports the
amount of product to head office, where
a
1
reports the
amount of product in factory one, two thousands PCs,
and
a
2
reports the amount of product in factory two,
three thousands PCs. The
va
1
reports the total amount
of product in both factories, i.e. five thousands PCs.
However, the permission of a role
r can only know
the amount of product in factory one, and not factory
two. Role
r should not have the permission to know
the total amount of product in both factories, since the
amount of product in factory two may be deduced.
Accordingly, the derivation of the
agg_view permis-
sion on a virtual activity is modified as the following,
by considering the data deduction rule.
Equation (1):
I
ij
vaa
ji
arPvarP
∈∀
= ),(),(
agg_view ∈ P(r, va
i
), if P(r, a
j
) contains agg_view
permission for all a
j
∈
r
va
i
S ; and the data deduction rule
is satisfied.
Data deduction rule:
There is no data deduction on the data object of a
j
for
a
j
∈
r
va
i
S and view ∉ P(r, a
j
).
Some enterprises adopt lenient privilege principle
to increase the convenient and flexibility in process
management. Least privilege principle is to make sure
that only those permissions required for the activities
conducted by members of the role are assigned to the
role. For least privilege principle, the permissions of
role
r on a virtual activity are the necessary access
rights defined by the process modeler.
3.4 Permissions on a Virtual Activity
Considering Duty-conflict
Relationships among Base Activities
A base process contains a set of tasks, and some
duty-conflict relationships may exist among tasks.
The derivation of a role
r’s permissions on a virtual
activity needs to consider duty-conflict relationships
among base activities.
For strict privilege principle (SPP), if the base
activities
a
x
and a
y
are duty-conflict tasks, a
x
⊕ a
y
;
virtual activity
va
i
only contains
two base activities a
x
and
a
y
, the permission of a role r on virtual activity va
i
is illustrated in Table 2 (under SPP).
Two base activities
a
x
and a
y
are duty-conflict
activities that are aggregated as a virtual activity
va
i
.
According to the authorization rules for SoD, two
duty-conflict tasks cannot be assigned to the same
role. If role
r has the execute permission on both base
activities
a
x
and a
y
, then only the minimum and basic
permission “
awareness” on va
i
can be authorized to
role
r. Moreover, under the strict privilege principle,
if role
r has the view permission on both base activi-
ties
a
x
and a
y
, then only the “awareness” permission
on
va
i
can be authorized to role r. Notably, the implied
permissions should be considered.
For the case that role
r has the view permission on
a
x
and the agg_view permission on a
y
, the agg_view
permission on va
i
can be authorized to role r, if the
data deduction rule is satisfied; otherwise, only the
“
awareness” permission on va
i
can be authorized to
role
r. The data deduction rule states that there is no
data deduction on the data object of
a
j
for
a
j
∈
r
va
i
S
and
view ∉ P(r, a
j
). A role should not deduce some
unauthorized permissions on the data objects. For
example, three base activities are aggregated into a
virtual activity
va
i
. If role r has the view permission
on one base activity
a
x
and the agg_view permission
on the other two base activities
a
y
and
a
z
, the agg_view
(e.g. SUM aggregation) permission on
va
i
can be
authorized to role
r, since role r can not deduce the
data information of
a
y
and
a
z
. Nevertheless, if a role
has the
view permission on a
x
and
a
y
; and the
agg_view permission (no view permission) on a
z
, the
agg_view (e.g. SUM aggregation) permission on va
i
can not be authorized to role
r, since role r can deduce
the data information of
a
z
. The other derivations are
similar, and thus are omitted for clarity.
In order to increase the flexibility, an organization
may adopt lenient privilege principle (LPP) as Table
2 (under LPP). The main difference between the strict
and lenient privilege principles is to loosen
SECRYPT 2007 - International Conference on Security and Cryptography
88

Table 2: Permissions of role r under strict and lenient privilege principle.
a
x
⊕ a
y
Permission on va
i
, va
i
= { a
x
, a
y
}
Permission
on a
x
Permission
on a
y
under strict privilege principle
(under SPP)
under lenient privilege principle
(under LPP)
execute
execute
manage
view
agg_view
awareness
Awareness
awareness
awareness
agg_view (if data deduction rule is satisfied)
awareness(if data deduction rule is violated)
awareness
awareness
awareness
awareness
agg_view (if data deduction rule is satisfied)
awareness(if data deduction rule is violated)
awareness
manage
manage
view
agg_view
awareness
awareness
awareness
agg_view (if data deduction rule is satisfied)
awareness(if data deduction rule is violated)
awareness
awareness
view
agg_view (if data deduction rule is satisfied)
awareness(if data deduction rule is violated)
awareness
view
view
agg_view
awareness
awareness
agg_view (if data deduction rule is satisfied)
awareness(if data deduction rule is violated)
awareness
view
agg_view (if data deduction rule is satisfied)
awareness(if data deduction rule is violated)
awareness
agg_view
agg_view
awareness
agg_view (if data deduction rule is satisfied)
awareness(if data deduction rule is violated)
awareness
agg_view (if data deduction rule is satisfied)
awareness(if data deduction rule is violated)
awareness
awareness
awareness awareness awareness
the view-view violation. Under the strict privilege
principle, if role
r has the view permission on both
base activities
a
x
and a
y
, then only the “awareness”
permission on va
i
can be authorized to role r. For the
lenient privilege principle, if role
r has the view per-
mission on both base activities a
x
and a
y
or if role r
has the
manage permission on a
x
and the view per-
mission on a
y
, then the “view” permission on va
i
can
be authorized to role
r. However, if role r has the
execute permission on both base activities a
x
and a
y
,
then only the “
awareness” permission on va
i
can be
authorized to role r, in order to achieve the constraint
of SoD.
As described in section 3.2, if the “
execute” per-
mission on
a
x
is authorized to role r, then the implied
permissions are also assigned to role
r, i.e., P(r, a
x
) =
{
execute, view, agg_view, awareness}. If role r also
has the “
execute” permission on a
y
, then the “view”
permission on
va
i
is derived for role r, according to
Table 2(under LPP), which violates the SoD principle.
To ensure no violation of SoD, the maximum privi-
lege of role
r’s permissions should be used to derive
role
r’s permissions on va
i
. The privileges of the
permissions are ranked as follows:
execute > manage
>
view > agg_view > awareness. Let
r
a
j
Pmax
denote
the maximum privilege of role
r’s permission on
activity
a
j
.
r
a
j
Pmax
= the highest ranked permission in P(r, a
j
)
For duty conflict tasks, the maximum privileges of
role
r’s permissions on base activities are used to
derive role
r’s permissions on virtual activity, ac-
cording to Table 2 (under LPP). Table 2 (under LPP)
shows the derivation of role
r’s permission on a vir-
tual activity that contains two duty-conflict activities.
The derivation for general cases that a virtual activity
may contain a set of base activities with duty-conflict
relationships is described as Fig. 2.
Algorithm The algorithm of derivation for general cases
begin
tmpVA ={}
for each pair of duty-conflict tasks a
x
⊕ a
y
and a
x
, a
y
∈ va
i
Create a temporary virtual activity tmpva
j
= { a
x
, a
y
}
P(r, tmpva
j
) = the set of permissions derived
according to Table 2 (under LPP),
by using the
r
a
x
Pmax
and
r
a
y
Pmax
tmpVA = tmpVA∪ { tmpvaj }
endfor;
for each base activity a
x
∈ va
i
if there is no a
y
∈ va
i
such that a
x
⊕ a
y
then
tmpVA = tmpVA∪ { a
x
}
endfor;
P(r, va
i
) =
I
tmpVAa
j
j
arP
∈∀
),(
if P(r, a
j
) contains agg_view permission for all
a
j
∈
r
tmpVA
S
; and the data deduction rule
is satisfied.
P(r, va
i
) = P(r, va
i
) ∪ { agg_view }
end
Figure 2: The algorithm of derivation for general cases.
ROLE AND TASK BASED AUTHORIZATION MANAGEMENT FOR PROCESS-VIEW
89

The algorithm creates a temporary virtual activity,
tmpva
j
for each pair of duty-conflict tasks a
x
and a
y
in
va
i
, where tmpva
j
= { a
x
, a
y
}. Then role r’s permis-
sions on tmpva
j
are derived according to Table 2
(under LPP)
by using the maximum privilege of P(r, a
x
)
and P(
r, a
y
) (i.e.
r
a
x
Pmax
and
r
a
y
Pmax
), respectively.
Once role
r’s permissions on duty-conflict tasks are
derived, the algorithm then uses Equation (1) de-
scribed in Section 3.3 to derive role
r’s permissions
on the virtual activity
va
i
.
4 CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE
WORKS
Authorization management and access control are
essential in supporting secure workflow management
systems. Process-view is a good solution that differ-
ent workflow participants acquire different needs and
types of authority. This work analyzes the grouping
and aggregate function of a virtual activity; and fur-
ther, explains the permissions of a virtual activity in a
process-view. Moreover, this work discusses the
permissions for a role on a virtual activity aggregated
from duty-conflict base activities.
Our future work will address two themes. First,
duty-conflict relationships are essential to design SoD
constraints. Further work is necessary to explore
more kinds of duty-conflict relationships. Second,
inter-organization workflows are gaining importance
in B-to-B commerce. Although some works have
addressed access control in this aspect, they disregard
the coordination behavior in inter-organizational
workflows (
Schulz and Orlowska, 2004). Future re-
search will be to investigate the authorizations and
access control in inter-organizational workflows.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors would like to thank the National Science
Council of the Republic of China for financially
supporting this research under contract no. NSC
94-2416-H-216 -004.
REFERENCES
Ahn, G-J, Sandhu, R., Kang, M., Park, J.(2002). Injecting
RBAC to Secure a Web-based Workflow System, In
Proceedings of 5th ACM Workshop on Role-Based Ac-
cess Control.
Atluri, V., Huang W-K (1996). An Authorization Model for
Workflows, Proceedings of the fifth European Sympo-
sium on Research in Computer Security, Rome, Italy,
44 – 64.
Bertino, E., Ferrari, E., Atluri, V. (1999). Specification and
Enforcement of Authorization Constraints in Workflow
Management Systems, ACM Transactions on Informa-
tion and System Security, Vol. 2, No. 1, 65 – 104.
Ferraiolo, D.F., Cugini, J., Kuhn, R. (1995). Role-Based
Access Control (RBAC): Features and Motivations,
Proceedings of 11th Annual Computer Security Appli-
cation Conference, IEEE Computer Society Press,
241-248.
Ferraiolo, D.F., Kuhn, R. (1992). Role-Based Access Con-
trol, In Proceedings of 15th NIST-NCSC National
Computer Security Conference, 554-563.
Georgakopoulos, D., Hornick, M., Sheth, A. (1995). An
Overview of Workflow Management: From Process
Modeling to Workflow Automation Infrastructure, Dis-
tributed and Parallel Databases, 119-153
Gligor, V.D., Gavrila, S.I., Ferraiolo, D. (1998). On the
Formal Definition of Separation-of-Duty Policies and
Their Composition, Proceedings of IEEE Symposium on
Security and Privacy, IEEE Computer Society.
Huang, W-K, Atluri, V. (1999). SecureFlow: A secure
web-based workflow management system, In Proceed-
ings of 4th ACM Workshop on Role-Based Access Con-
trol, 83-94.
Nash, M.J., Poland, K.R. (1990). Some Conundrums Con-
cerning Separation of Duty, Proceedings of IEEE
Computer Society Symposium on Security and Privacy,
IEEE Computer Society Press.
Sandhu, R.S., Coyne, E.J., Feinstein, H.L., Youman C.E.
(1996). Role-Based Access Control Models, IEEE
Computer, 29(2), 38-47.
Schulz, K.A., Orlowska, M.E. (2004). Facilitating cross-
organizational workflows with a workflow view ap-
proach, Data & Knowledge Engineering, 51, p109-147.
Shen, M., Liu, D.R. (2004). Discovering role-relevant
process-views for disseminating process knowledge,
Expert Systems with Applications, 26, 301–310.
Simon, R.T., Zurko, M.E. (1997). Separation of Duty in
Role-Based Environments, 10
th
Computer Security
Foundations Workshop.
SECRYPT 2007 - International Conference on Security and Cryptography
90
