
A METHODOLOGY FOR THE DEPLOYMENT OF LIVE AUDIO
AND VIDEO SERVICES
D. Melendi, X. G. Pañeda, M. Vilas, R. Garcia and V. Garcia
Computer Science Department, University of Oviedo, Campues Viesques sn, Xixón/Gijón, Spain
Keywords: Methodology, deployment, live, audio, video, streaming.
Abstract: Since the development of the first live audio and video services in the 90s, the deployment of these services
has always been a challenging issue. Not only is it necessary to deal with the problems of the delivery of
continuous information and the high consumption of resources, but also with those imposed by the nature of
these services. Service managers do not get a second chance to broadcast live contents so it is important to
ensure that everything works as planned. Most service managers only work based on their own experience,
but they rarely follow any standardized method. With the aim of improving the current situation, the
authors have designed a methodology for the deployment of live audio and video which is presented in this
paper. The methodology tries to cover almost all the issues that may arise while putting one of these
services into operation and proposes mechanisms to deal with those issues from a management perspective.
It has been successfully used by the authors in the deployment of several live services for different
companies.
1 INTRODUCTION
Since the development of early web pages for
scientific purposes, Internet has suffered huge
changes mainly due to the improvement of access
technologies and the massive access of users from
the home environment. Many services have been
designed, developed and deployed, making the web
a vast repository of resources for entertainment,
research, study, etc. The ideas behind most of these
services have been taken from other activities, e.g.,
e-mail from snail mail, audio conference from
telephone services, etc. Audio and video have also
taken advantage of this adoption of ideas and, in the
90s, these services were deployed taking ideas from
tape and video recorders and TV and radio services.
Mainly, there are two types of audio/video
services: live and on-demand. On-demand services
are similar to a tape or video recorder, while live
services are similar to a conventional radio or TV
service. They differ in many aspects. The interaction
capabilities of their users are different. These users
even behave differently as stated in the literature
(Cherkasova and Gupta, 2004) (Veloso et al, 2002).
Live services generally require more transmission
capabilities as all the users connect at the same time
and remain connected during long periods. Also, on-
demand services use stored contents, so there is
always a chance to perform tests to ensure that
everything works as planned. On the other hand,
most live services use live information, so testing is
very limited and there is never a second chance.
Taking into account these particular problems, those
related with the delivery of continuous data and the
high consumption of resources, the design of
methodologies may be meaningful for
administrators to maintain the quality of their
services.
In this paper a methodology for the deployment
of live audio and video services is presented. It
covers almost all the issues that may arise while
putting a live service into operation and proposes
mechanisms to deal with those issues from a
management perspective. The whole process has
been defined, considering the workflow, roles,
products and techniques. It allows managers to
evaluate the feasibility of a service, develop
deployment plans, perform evaluations and deliver
evaluation reports. It has been designed following
the structure and philosophy of other methodologies
and standards such as ISO/IEC 12207 (ISO, 1995),
RUP (Kruchten, 2003) or Six Sigma (Pyzdek, 2003).
Although similar experiences have been done for
other types of services (Ginige, 1998), there are no
15
Melendi D., G. Pañeda X., Vilas M., Garcia R. and Garcia V. (2007).
A METHODOLOGY FOR THE DEPLOYMENT OF LIVE AUDIO AND VIDEO SERVICES.
In Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Signal Processing and Multimedia Applications, pages 15-21
DOI: 10.5220/0002133000150021
Copyright
c
SciTePress
deployment methodologies for live audio/video to
our knowledge, only recommendations or generic
methods. The methodology has been specifically
designed for the deployment of live audio video
services, thus, it includes elements to deal with their
particular problems.
The authors have previous experience in the
creation of analysis and configuration
methodologies. One such methodology was
specifically designed to analyze and configure video
on demand services (Pañeda et al, 2004).
Nevertheless, it did not cover issues considered in
the presented methodology. The current
methodology has been successfully applied in the
deployment of services such as the radios in the
Asturies.Com newspaper (http://www.asturies.com),
the Aula18 annual movie contest or some of the
daily conferences organized by the La Nueva
España newspaper (http://www.lne.es). Some of the
obtained results are available in (Melendi, 2006)
The rest of the paper is organized as follows.
Section 2 describes the general structure of the
methodology. Section 3 details the involved actors.
Section 4 describes the designed processes. Finally,
Section 5 presents conclusions and future work.
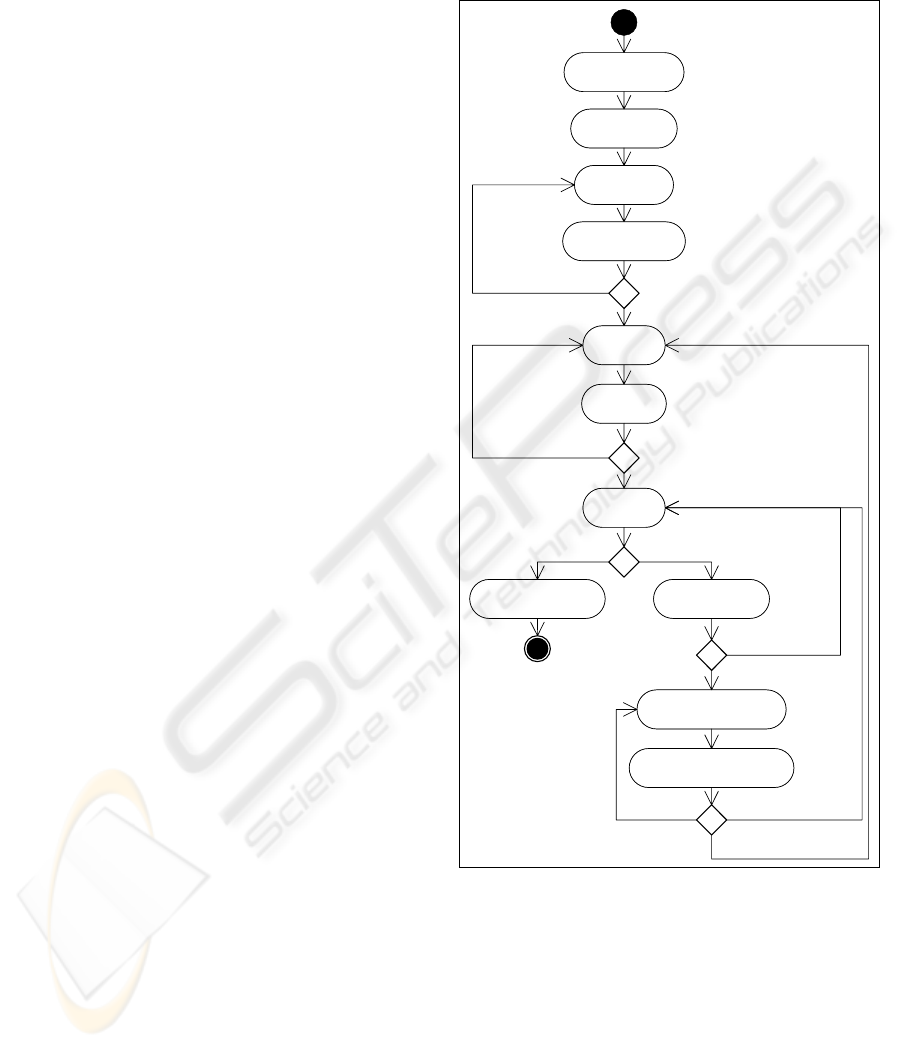
2 GENERAL STRUCTURE
Due to the broad set of tasks to be carried out during
the deployment of a live audio/video service the
methodology has been designed to have several
processes, all shown in Figure 1 in the order to be
followed. Each process groups a set of Activities
with a common purpose and is described in Section
4. Activities group tasks performed by Actors
generating Products. Products can be sections of a
document or deliverables.
3 INVOLVED ACTORS
Three types of companies intervene: Content
Provider or CP, Network Operator or NO and
Content Distribution Network Manager or CDNM.
The CP wishes to broadcast the contents. They
provide the materials but they do not have the
infrastructure or even the knowledge. Its CEO (or
Chief Executive Officer) is the person approving
money expenditures based on the information
provided by the Manager, who is responsible for a
particular deployment, has to report to the CEO and
has to take decisions based on the information
provided by other companies and the Production
Designer. The Production Designer designs the
contents, the look and feel, etc. The Operator deals
with the generation of contents and the tasks to be
carried out on a day to day basis.
Figure 1: Processes in the methodology.
The CDNM manages the hardware and software
used in the service. This implies having proxies,
servers and other devices with the most adequate
peripherals and software. The infrastructure can be
installed ad-hoc or reused. The Technical Director is
the person in charge, plays an assessment role and
takes decisions based on the requirements or the
evolution of the service. The Service Analyst
analyzes the needs of each service, designs the
architecture, ensures the fulfilment of all the Service
Feasibility Analysis
Service Analysis
Service Design
System Test
Operation
Post-mortem Analysis Evolution Analysis
Desing of Improvements
[End of Service ]
Validation of Improvements
[
A
nalysis Cycle ]
[Prototype Accepted ]
[Prototype Rejected ]
[Tests succeeded ]
[Tests failed ]
[Detected
Improvements ]
[ No Improvements ]
[ Tests succeeded ]
[Tests failed ] [ Improvements Rejected]
Service Prototyping
Deployment
SIGMAP 2007 - International Conference on Signal Processing and Multimedia Applications
16

Level Agreements or SLAs (Lee and Ben-Natan,
2002), etc. The Systems Administrator manages the
devices of the CDNM, applies the changes approved
by the Technical Director, generates reports, etc.
Finally, the NO provides the communication
infrastructure. The Technical Director is the person
in charge, plays an assessment role, and takes
decisions based on the requirements.
There might be scenarios where only one or two
of these companies appear. For instance, a NO may
have deployed several devices, so both the NO and
CDNM roles are played by this company. Also, all
the roles may be played by the same company, such
as the case of a cable operator offering contents and
owning devices and networks. Regarding the
interactions between these companies, CP and NO
interact with the CDNM, but rarely interact with
each other. These interactions will be defined later.
4 DETAILS OF THE PROCESSES
4.1 Feasibility Analysis
The goal of this process is to establish if it is feasible
or not to deploy a service. A deliverable document
called Feasibility Report will be generated,
containing a set of requirements, a first approach to
the solution and a preliminary evaluation of costs.
First, the Manager of the CP must define the
service, preparing a document providing a
description, its type and important dates and times.
Also, some goals need to be included with potential
groups of users, number of expected accesses,
business and productivity profits, strategic goals,
brand improvements, etc. If he has organized other
events, the goals can be adjusted with their results.
After that, the Manager and Production
Designer of the CP must set their initial
requirements. The requirements should be provided
to the Technical Director of the CDNM, and
discussed to check their feasibility. Also, the
Technical Director provides his requirements and,
once they have all been discussed, a list of
preliminary requirements is obtained. Then they
need to establish the risks which may affect the
deployment, such as failure to reach the goals.
Now, the Technical Director of the CDNM must
meet the Manager of the CP to check if the latter
has infrastructure which can be reused. Through
meetings, a document must be generated stating
everything suitable to be used including available
communications, servers, software products,
licenses and any audiovisual equipment. UML
deployment diagrams and anchored notes (OMG,
2006) can be used to describe how and where each
element is.
After this activity, the Technical Directors of the
CDNM and the NO need to establish the deployment
plan for each of the available alternatives. At this
point it is very important to estimate the required
infrastructure as this may have a strong impact on
the final cost. To this end, they can use the access
expectations stated by the CP to estimate the
consumption of resources and the needs of this
deployment. The more accurate the expectations are,
the better the design of the service will be. To
achieve this activity, the Technical Directors need to
discuss hardware, software and communication
needs and the final architecture. A document
describing the alternatives needs to be produced,
with a schedule and an estimation of costs. UML
deployment diagrams and Gantt Charts can be used.
The Technical Directors also need to agree on the
best alternative. The alternatives and the proposal
are delivered to the Manager of the CP who needs
to decide if it is suitable or not. If he disagrees, he
must meet the Technical Directors to reach an
agreement.
At this point, and apart from the costs reported
by NO and CDNM, the Manager of the CP needs to
estimate the costs derived from the use of his own
resources. These costs are mainly capital expenses
(Pisello, 2001) including the costs of reutilized
infrastructure and staff. With the estimations, the
alternative and the goals, the Manager analyzes the
expected
ROI (return on investment) of the
deployment. This requires the calculation of the
ROI, net present value savings, internal rate of
return and breakeven point (Pisello, 2001).
Finally, the Manager puts all the products in a
single document called Feasibility Report and
delivers it to its CEO for its review and approval.
4.2 Service Analysis
Once the deployment has been approved, it is
necessary to analyze its needs. A deliverable called
Analysis Report will be generated, with a description
of the service, necessary prior to its final design.
First, the Manager of the CP and the Service
Analyst of the CDNM must meet to further define
the service. This includes stating technologies,
actors, laws, standards and recommendations. A
high-level description of the technologies involved
forms the technological environment: encoding
formats, software and hardware products, protocols
and distribution technologies. Also, a section with
A METHODOLOGY FOR THE DEPLOYMENT OF LIVE AUDIO AND VIDEO SERVICES
17

the involved actors should be included stating who
is responsible for what. Finally, it is necessary to
reflect standards, laws and recommendations,
including business, modelling and notation
standards and procedures as well as related
legislation such as intellectual property rights
(EPCEU, 2004) or personal information protection
(EPCEU, 2002).
Once the service has been described in detail the
Manager and the Production Designer of the CP
must meet the Service Analyst of the CDNM to
obtain a final catalogue of requirements. All the
requirements associated with the selected alternative
must be added to the previous catalogue, such as
product requirements (efficiency, reliability, etc.),
high-level broadcast requirements (expected quality)
and requirements obtained from the description of
the service (business standards, legislation, etc.).
SLAs also need to be defined around measurable
events so they can be easily monitored.
It is also necessary to refine the risks identified
in the previous process. The Manager of the CP and
the Technical Director of the CDNM must consider
failures in the network, hardware, software, third
companies, an unexpected demand, lack of staff,
other business risks, delays in the deployment, etc.
Now, for each risk a list of possible occurrences
must be developed. This will permit to establish a
priority for each of the risks. The risks need to be
detailed using Ishikawa diagrams (Ishikawa, 1976).
At this point, the Service Analyst of the CDNM
must identify the subsystems to be considered. First,
the architecture of the service must be depicted,
identifying each subsystem (encoders, servers, etc.).
This can be done using UML deployment diagrams.
Each subsystem must be described providing a
name, description, details of the action performed,
inputs, outputs, origin and destination subsystems,
preconditions and post conditions and actor in
charge. It is necessary to distinguish between new
and reused subsystems. Subsystems not managed by
the CP or the CDNM need to be put on an Interfaces
with External Subsystems list.
Meanwhile, the Production Designer of the CP
must define the user interface. First, it is necessary
to identify the rules used to decide how the contents
should be offered depending on the user device. It is
necessary to document screen heights and widths,
bandwidths, interaction capabilities and other
constraints. For each combination, the Production
Designer must provide a draft of the layout and a
summary of the expected user interactions, if any.
After this activity, the Manager and the
Production Designer of the CP must meet the
Technical Director of the CDNM to design a test
plan to be used prior to the execution of the service.
With the catalogue of requirements, several test
cases must be designed, such as checking that all the
required subsystems exist, the correctness of their
configuration and the compatibility between their
outputs and inputs (Myers, 2004). For each test case,
it is necessary to provide an id, description, list of
affected subsystems, related requirements, expected
results and a priority.
Using all the products generated in this process
and the previous definition of the service, the
Manager of the CP generates a document called
Analysis Report which is delivered to its CEO
.
4.3 Service Design
Several deliverable documents will be produced in
this process: a Deployment Plan defining how
everything needs to be done, a Quality Plan to
ensure that the initial requirements are met and a
Maintenance Plan with maintenance routines.
First, the Service Analyst of the CDNM and the
Technical Director of the NO need to define the
architecture of the service. This can be done by
reusing products from the previous processes. It is
necessary to place every subsystem in a device in a
specific location. Again, UML deployment diagrams
and anchored notes can be used. Physical devices
must be defined providing, a description, the list of
subsystems running on it, its configuration and the
actors in charge. Also, the configuration of each
subsystem needs to be added to its definition: it is
necessary to define how the inputs and outputs are
formatted, reflecting the number of audio and video
streams to be generated and their details (codecs,
frames per second, bitrate, height and width). The
Catalogue of Risks needs to be considered here as
most of the risks can be minimized and even
avoided with an appropriate architecture. Aspects
such as fault tolerance and detection need to be
considered. It is necessary to develop a fault
recovery and repair document which includes
documenting how the system will recover once a
failure has happened and what needs to be done to
solve it. For each of the failures in the Catalogue of
Risks it is necessary to define the involved devices,
actors in charge, contact information, workflow to
be followed, expected recovery time, loss of
capabilities during the failure and equipment and
tools utilized. The last product to be generated is a
summary of needs including hardware, software and
communication needs.
Meanwhile, the Production Designer of the CP
SIGMAP 2007 - International Conference on Signal Processing and Multimedia Applications
18
needs to work on the design of the contents and user
interface. Depending on the type of service, it is
necessary to establish how the contents will be
broadcast. If the service is deployed for a particular
event and works with live information, the contents
are conditioned by the event. On the other hand, if
the service is continuous (24x7) and works with
stored information, it is necessary to define the order
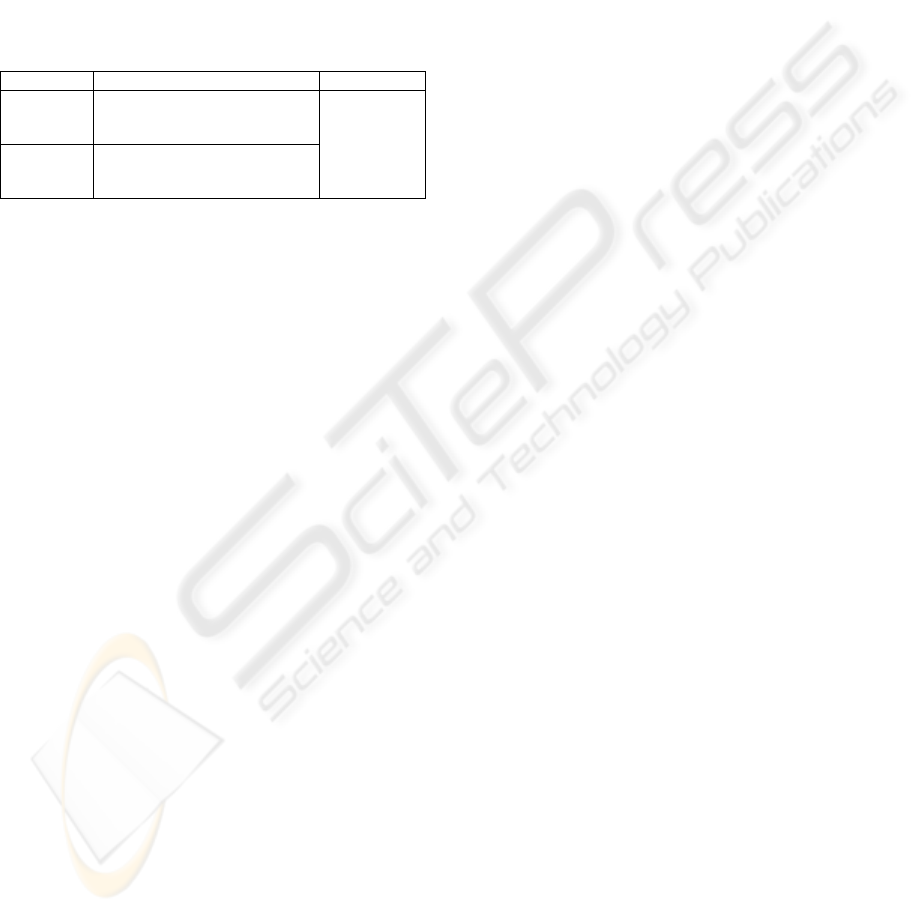
of the contents. Table 4 shows the minimum set of
information to be determined depending on the type
of service and contents.
Table 1: Minimum data for the design of contents.
Type Stored contents Live
Eventual
Files to be used and their details,
order to be followed, length of
transmission
Continuous
Files to be used and their details,
initial order to be followed and
policy of change
Main
source of
contents and
interruptions
Now the previous user interface guidelines need
to be complemented with a detailed description. For
each user device set of characteristics, it is necessary
to define the type of interface to be used, types of
media, encoding qualities and formats for audio,
encoding qualities, formats and frames per second
for video and a general picture of the layout. If users
can perform interactions, these also need to be
documented with a description, the place where they
can be performed, the expected result, the input
device to be used and the set of data associated.
With the previous summary of needs, the design
of the user interface and the design of the contents,
the Manager of the CP and the Service Analyst of
the CDNM need to establish which components need
to be acquired or need to be developed. These can
be developed by the CDNM or by an external
company.
Now the Manager of the CP must meet the
Technical Directors of the CDNM and the NO in
order to agree on the schedule of the deployment.
The following needs to be considered: acquisition,
installation and configuration of hardware devices
and software tools, installation and configuration of
network infrastructure, development, installation
and configuration of new components, initial
generation of contents and satisfaction of legal
requirements (EPCEU, 2002) (EPCEU, 2004). Each
task needs to be assigned to one or more actors,
finish within a predetermined period and shows
dependencies with other tasks. They can be
represented using Gantt charts. It is very convenient
to consider in the project schedule the Service
Prototyping and System Test processes of the
methodology.
At this point, the Service Analyst of the CDNM
must design the measures to be applied in case some
of the previously identified risks occur. If possible,
it is necessary to prepare a plan of action with
alternatives to apply for each of the avoidable risks,
providing contact information for the actors with
technical and management responsibilities, tasks to
be achieved and reports to be generated.
During the life of the service, it is
recommendable to perform frequent analyses as they
permit the fulfilment of business goals to be
checked, make the error identification process easier
and allow administration staff to generate reports.
Thus, the Manager of the CP must agree with the
Technical Director of the CDNM on a frequency to
perform analyses and the set of metrics and analyses
to carry out: behaviour of the users, perceived
quality, consumption of resources, etc.
Now, the Manager of the CP can develop the
Deployment Plan with the definition of the
architecture, the design of the user interface,
contents and components and the project schedule;
the Maintenance Plan with the fault recovery and
repair mechanisms, the design of analysis and
improvement cycles, the design of contingency
plans and, depending on the service, the policy of
updates; and the Quality Plan with the analysis of
profitability, the refined requirements and risks and
the design of analysis and improvement cycles.
4.4 Service Prototyping
After the Deployment Plan, a prototype needs to be
developed. It needs to be as realistic as possible to
perform tests and discover limitations in the service.
Two deliverables are produced: Prototype Report,
with the results of the prototype, and Change
Proposal, when changes need to be applied.
First, the Service Analyst of the CDNM, the
Technical Director of the NO and the Manager of
the CP need to agree on the design of the prototype,
setting its scope and limitations.
The tests to be performed need to be designed as
well. They can be extracted from the test plan or
agreed between the Manager of the CP and the
Technical Director of the CDNM.
Now, the Operator of the CP needs to produce a
set of contents or set up an environment where they
can be generated. At the same time, the Systems
Administrator of the CDNM deploys the architecture
on a controlled environment provided by the NO.
After the installation and configuration of devices,
the contents or the set up can also be installed.
To execute the tests, the Systems Administrator
A METHODOLOGY FOR THE DEPLOYMENT OF LIVE AUDIO AND VIDEO SERVICES
19

of the CDNM can configure and run a workload
loader (Melendi et al, 2005). Its configuration can be
obtained from the literature (Veloso et al, 2002) or
from the analyses of other events. These parameters
also need to be documented. At least, in the tests it is
necessary to verify the evolution of the accesses, the
maximum number of connections, the evolution of
the consumption of resources and transmission
problems or bottlenecks. These results, along with
the description of the contents, prototype and load,
need to be placed in a document called Prototype
Report by the Manager of the CP, who also needs to
take a decision on the approval of the prototype.
4.5 Deployment
The Deployment Plan is executed and, after its
completion, the service is ready to operate.
4.6 System Test
It is now necessary to perform the tests designed in
the Test Plan developed in the Service Analysis. A
document called Test Report will be generated,
providing information about the obtained results.
The Systems Administrator of the CDNM needs
to proceed with the tests generating a Test Report
containing, a table summarizing the results, a
description of the execution of each test case and a
list of the incidences detected.
The Test Report is provided to the Manager of
the CP who needs to take a decision. If no
incidences are detected, the service can be put into
operation. On the other hand, he can decide to
cancel the service, to request the CDNM or the NO
to solve the incidences or to ignore the problems.
4.7 Operation
After the System Test process, the service is put into
operation and the users of the service may access the
offered contents. If any problem is detected the
Maintenance Plan needs to be followed.
4.8 Evolution Analysis
This process is part of the analysis and improvement
cycles designed during the Service Design process.
The analyses were designed and recorded in the
Maintenance Plan. Thus, it is only necessary to
follow what was stated there. In the end, two
deliverable documents, called Evolution Report and
Improvement Proposal, are generated.
The analyses in the Maintenance Plan need to be
executed by the Service Analyst of the CDNM and
the results written in a preliminary report with some
conclusions. With this report, the Manager of the
CP checks the fulfilment of the ROI and SLAs in the
Quality Plan by calculating the proper metrics.
The Manager of the CP and the Technical
Director of the CDNM need to check if
improvements can be performed, producing a list of
items which may be improved and their priority.
With all the products generated in this process,
the Manager of the CP produces a document called
Evolution Report which is delivered to the CEO of
the CP for its review and approval.
4.9 Design of Improvements
If some improvements were identified, these need to
be defined in detail. This requires the Technical
Directors of the CDNM and NO to meet and select
the proper solutions. Improvements may require
changes in the architecture, in the configuration of
the devices, in the network or in the contents. The
implantation of these changes requires a new
Deployment Plan. The structure of this document is
similar to that defined in the Service Design process
so the activities to be performed are the same and
depend on the type of improvement.
Once all the activities have been completed
another Project Schedule is planned and the
Manager of the CP puts all the products in a new
Deployment Plan which is delivered to his CEO.
4.10 Validation of Improvements
Now it is necessary to ensure that the improvements
will have the desired effects. Again, following the
new Deployment Plan, a prototype needs to be
developed. Note that it is very useful to reuse the
prototype developed in the Service Prototyping
process. The activities, actors and products of this
process are the same as those in the Service
Prototyping process, so they will not be commented
on here. Only the goals change: now the Manager of
the CP needs to know if the service will benefit
from the improvements, and if the improvements
may cause a deterioration of other aspects of the
service.
All the results, along with the description of the
contents, the prototype and the load, need to be
placed in a Prototype Report document by the
Manager of the CP who must decide if the tests are
not satisfactory and improvements need to be
redesigned, if the tests are not satisfactory and
improvements will not be applied or if the tests are
SIGMAP 2007 - International Conference on Signal Processing and Multimedia Applications
20

satisfactory and improvements will be deployed.
If the results of the prototype are accepted, the
Manager delivers the Prototype Report to the CEO
of the CP and the designed improvements can be
deployed in another Deployment process. Otherwise,
it is necessary to return to the Design of
Improvements with the proposals of the Manager of
the CP in a Change Proposal document.
4.11 Post-mortem Analysis
Depending on the type of service, this will finish
after a certain time. Eventual services are associated
to a particular event and once the event finishes, the
service finishes. Even a continuous service may end
after some time. Thus, it is necessary to analyze
what has happened during the service to improve
future deployments and generate reports. The CP
will want to know how the service has evolved. The
CDNM and NO may be interested in the results in
order to improve their services. The analyses to
carry out are those from the Maintenance Plan, also
used in the analysis and improvement cycles.
As happened in the Evolution Analysis process,
the analyses in the Maintenance Plan are executed
by the Service Analyst of the CDNM. Their results
and a set of conclusions are provided to the
Manager of the CP, who checks the fulfilment of
the ROI study and SLAs established in the Quality
Plan.
With all the obtained information, the Manager
of the CP produces a document called End-Of-
Service Report adding a description of the service,
the initial goals and requirements and a summary of
the changes performed during the analysis and
improvement cycles.
5 CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE
WORK
In this paper, a methodology for the deployment of
live services is presented. It defines the processes,
the roles, the staff, the tasks, the techniques and the
products to be generated. It is flexible enough to be
used in the deployment of almost any type of live
audio and video service, ranging from Internet
radios to conventional TV channels. It can be an
essential tool for companies interested in the
delivery of live contents, offering broadcasting
infrastructure or looking for new lines of business.
The authors have used the methodology in several
live services.
The methodology can be further improved by
adding new products to each of its processes and
different techniques to make its usage easier. Also,
specific metrics can be included to accurately define
the analysis activities included in the methodology.
REFERENCES
A. Ginige, “Web Engineering: Methodologies for
developing large and maintainable web based
information systems,” Proc. IEEE Int. Conf.
Networking India and the World (CNIW 98), 1998
D. Melendi, M. Vilas, X.G. Pañeda, R. García, V. García,
“Test environment for performance evaluation of an
Internet radio”, in Proc. 2nd Int. Conf. on E-Business
and Telecomunication Networks, Reading, UK, 2005.
D. Melendi, M. Vilas, R. García, X.G. Pañeda, V. García,
Characterization of a real Internet Radio Service, In
Proc. of 32
nd
EuroMicro Conf. SEAA Croatia, 2006
Directive 2002/58/EC of the European Parliament and of
the Council of 12 July 2002 concerning the processing
of personal data and the protection of privacy in the
electronic communications sector.
Directive 2004/48/EC of the European Parliament and of
the Council of 29 April 2004 on the enforcement of
intellectual property rights.
E. Veloso, V. Almeida, W. Meira, A. Bestavros, S. Jin, “A
hierarchical characterization of a live streaming media
workload,” ACM SIGCOMM Internet Measurement
Workshop, France, 2002
G.J.Myers, The art of software testing, 2nd edition, John
Wiley and Sons, Inc. 2004. Information Technology –
Software life cycle processes, ISO/IEC standard
12207:1995
J. J. Lee and R.. Ben-Natan, Integrating Service Level
Agreements, Wiley Publishing, Inc. 2002.
K. Ishikawa, Guide to Quality Control, Asian Productivity
Organization, 1976.
L. Cherkasova, M. Gupta, “Analysis of enterprise media
server workload: access patterns, locality, content
evolution and rates of change” IEEE/ACM
Transactions on Networking, 2004.
P. Kruchten, The Rational Unified Process An
Introduction, 3rd edition, Addison-Wesley, 2003
T. Pisello, Return on investment for information
technology providers, using ROI as a selling and
management tool, Information Economics Press, 2001.
T. Pyzdek, The Six Sigma Handbook: The Complete
Guide for Greenbelts, Blackbelts, and Managers at All
Levels, McGraw-Hill, 2003
Unified Modeling Language: superstructure, version 2.1,
Object Management Group Standard, April 2006.
X.G. Pañeda, D. Melendi, R. Bonis, M. Vilas, I.
Rodríguez, R. García, “Fesoria, an integrated tool for
performance and contents analysis, SLA evaluation,
management and smart presentation for video-on-
demand services,” in Proc. Int. Conf. on E-Business
and Telecom. Networks, Setúbal, Portugal. 2004.
A METHODOLOGY FOR THE DEPLOYMENT OF LIVE AUDIO AND VIDEO SERVICES
21
