
EFFICIENT MOTION COMPENSATION ARCHITECTURE WITH
RATE-DISTORTION OPTIMIZATION FOR H.264/AVC
Tian Song and Takashi Shimamoto
Computer Systems Engineering, Institute of Technology and Science, Graduate School of Engineering
Tokushima University, Minami-Jyosanjima 2-1, Tokushima City, 770-8506, Japan
Keywords:
Motion Compensation, RDO, H.264, VLSI.
Abstract:
In this paper, a novel motion compensation architecture is proposed to support the Rate-Distortion Optimiza-
tion(RDO) in H.264/AVC. First, the scope of the motion compensation in this work is defined not only in-
cluding the half and quarter pixel motion compensation but also the deblocking filter and rate-distortion op-
timazation. Then, base on the new concept of motion compensation an efficient architecture for H.264/AVC
codec is constructed. Proposed architecture could select the best mode for INTRA macroblocks using the
lagrange function by calculating the distortion and the generated bits. It could also calculate the lagrange
function for INTER macroblocks by receiving the motion vector information and the interpolation data from
the ME(Motion Estimation) module to construct a complete rate distortion optimization architecture. Pipelined
processing structure is designed for sub-block mode selection to achieve real-time processing for up to HDTV
resolution inputs. Implementation result shows that proposed architecture could be realized with only 42,280
gates and 48,320 bits SRAM.
1 INTRODUCTION
H.264/AVC inherits a so-called MC-DCT based
structure with several new features by which can
achieve higher coding efficiency. The basic coding
tools are still the motion compensation, DCT-based
transform, and variable length coding. However, be-
sides the traditional algorithms recommended in the
traditional coding standards H.264/AVC introduced
some new features by which it achieved about 50% bit
saving. For the INTER macroblocks half and quarter
pixel precision motion estimation and up to 16 refer-
ence frames motion estimation are available. On the
other hand, for the INTRA macroblocks several new
types prediction mode are able to be used to decrease
spatial coding redundancy. An improved 5-tap filter
is also introduced to decrease subjective block noise.
Base on the trade off of the implementation complex-
ity and the coding efficiency H.264/AVC defines a set
of coding tools that can be used to generate a com-
pliant bitstream and group it into 3 profiles, baseline
profile, extended profile and main profile. Another
novel high profile is proposed recently to addict some
new coding tools for high resolution applications. To
all of these profiles, the motion compensation includ-
ing the half and quarter pixel and multi-frame motion
searching, intra block coding, deblocking filter are ba-
sic coding tools and necessary to be implemented.
Together with the achieved high coding efficiency
these new coding tools also increased the computa-
tional complexity. Another novel Rate-Distortion Op-
timization(RDO) is also introduced to always keep
the optimal trade off between the coding efficiency
and the image quality. The RDO process combining
the INTRA mode selection, INTER mode selection,
and the bit generating process to select the optimal
coding mode. However, it induces drastic computa-
tion complexity increasing due to the multiple times
exhausted pre-coding process. There are several re-
ports concerning the complexity reduction(C. S. Kim
and Kuo, 2003)-(Y. L. Xi and Hu, 2006), espe-
cially the complexity reduction for motion estima-
tion(C. S. Kim and Kuo, 2003)-(C. S. Kim and Kuo,
2006) and the mode selection algorithms for the IN-
TRA macroblocks (Y. K. Tu and Tsai, 2005)-(Y. L. Xi
and Hu, 2006) are proposed. However, all of these
proposals are not concerning the hardware implemen-
tation of the total rate distortion optimization.
There are also some works about the implemen-
tation of the H.264/AVC codec(U. J. Kapasi and
Owens, 2003)-(Y. Song and Ikenaga, 2006). There
are some single CPU or multi-CPU solutions are pro-
159
Song T. and Shimamoto T. (2007).
EFFICIENT MOTION COMPENSATION ARCHITECTURE WITH RATE-DISTORTION OPTIMIZATION FOR H.264/AVC.
In Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Signal Processing and Multimedia Applications, pages 155-160
DOI: 10.5220/0002134601550160
Copyright
c
SciTePress
posed(U. J. Kapasi and Owens, 2003)-(Y. W. Huang
and Chen, 2005). However, to fulfill the full coding
efficiency of the H.264/AVC, CPU with hardware ac-
celerator or an ASIC solution are considered as the
reasonable solution for real-time applications espe-
cially for those HDTV resolution implementations.
There are some architectures(Y. Song and Ikenaga,
2006)-(Y. W. Huang and Chen, 2003) proposed to de-
crease the computation complexity with parallel pro-
cessing method. However, all of these proposals so
far are concerning the mode selection for INTRA and
INTER macroblocks. For example, Chen’s architec-
ture(Y. W. Huang and Chen, 2005), Huang’s architec-
ture(Y. W. Huang and Chen, 2003) for INTRA frame
and Song’s architecture (Y. Song and Ikenaga, 2006)
for motion estimation are designed individually with-
out consideration of the RDO. From the viewpoint of
the system implementation of H.264/AVC the mode
selection for INTRA and INTER macroblocks, the In-
teger DCT transform, Quantization and CAVLC cod-
ing are not able to be considered separately.
In this paper, we firstly construct a new concept of
the motion compensation with some coding tools em-
bedded to achieve high performance hardware imple-
mentation for high resolution applications. Then an
efficient total architecture with RDO implementation
will be proposed. After the discussion on the architec-
ture the details of the proposed MC architecture will
be described. Section 2 introduces the concept and
the scope of the proposed motion compensation and
the proposed RDO architecture. In section 3 the pro-
posed architecture of MC is outlined with several sub-
sections to discuss the proposed INTRA mode selec-
tion methods and the detail of proposed architecture.
In section 4 the implementation results are shown and
in section 5 the conclusion remarks are addressed.
2 PROPOSED ARCHITECTURE
FOR RDO
To fulfill the efficient architecture of motion compen-
sation we expend the concept of motion compensation
which make it not only include half and quarter con-
cise compensation but also include deblocking filter,
INTRA mode selection and a RDO calculation func-
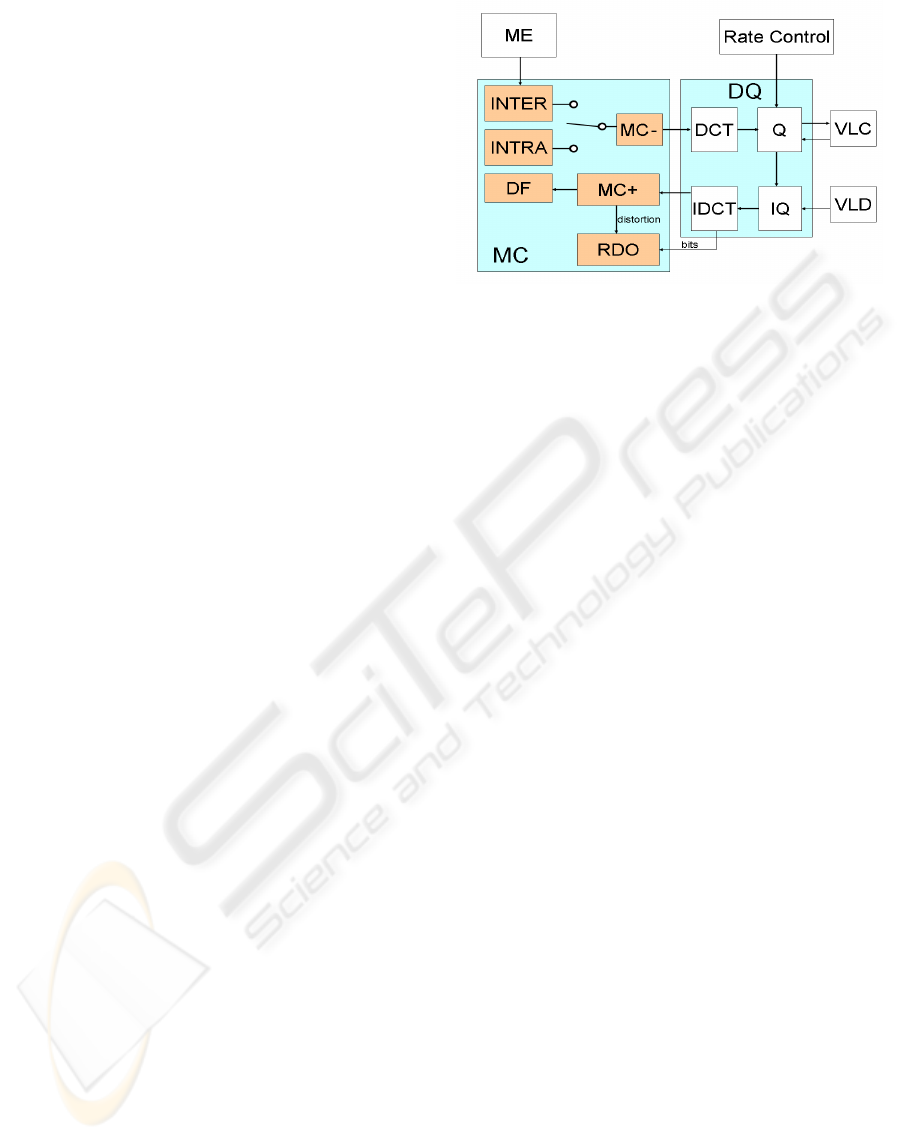
tion. Fig. 1 shows the proposed total codec architec-
ture to perform MB-based pipeline real-time encod-
ing.
As shown in Fig. 1, there are INTRA mode opti-
mization loop and INTER mode optimization loop in-
dividually. For INTER macroblock the process start
from the motion estimation process. After calculat-
ing each mode the ME(Motion Estimation) module
Figure 1: The concept of proposed architecture.
generates motion vector and the interpolation data
for the sub-pixel motion compensation, then the dis-
tortion is calculated by the following local decode
process which includes the MC-(Motion Compensa-
tion differential), DCT(Discrete Cosine Transform),
Q(Quantization), IQ(Inverse Quantization) and the
MC+(Motion Compensation construction) process.
Together with the generated bits information the RDO
module could calculate the coding cost for this mode.
After repeating this process for each mode, the best
coding mode will be selected. On the other hand,
for the INTRA mode selection loop, it starts from
the calculation of the distortion for each I16x16 and
I4x4 mode by the same local decoding process. The
generated bits information which is generated by the
VLC(Variable Length Coding) is also sent to the RDO
module to select the best mode for all INTRA modes.
In the end the coding cost is compared with the best
mode for INTRA and INTER mode to decide the final
mode for one macroblock. After the mode selection
and the motion compensation process, the deblocking
filter process is performed. This proposed architec-
ture extremely balances the ME and the RDO pro-
cess at the computation complexity. In this paper, our
design interest emphasizes on the design of an effi-
cient MC(Motion Compensation) module to realize
high performance coding.
3 PROPOSED ARCHITECTURE
OF MC
MC is one of the important processes in the MB
pipelined codec. Carefully considering the coopera-
tion with the ME and the DQ modules, we proposed
an efficient MC architecture. Fig. 2 shows the details
of the proposed architecture.
As described in the Fig. 2, proposed architecture
consists of a arithmetic logic unit(ALU), a register
SIGMAP 2007 - International Conference on Signal Processing and Multimedia Applications
160
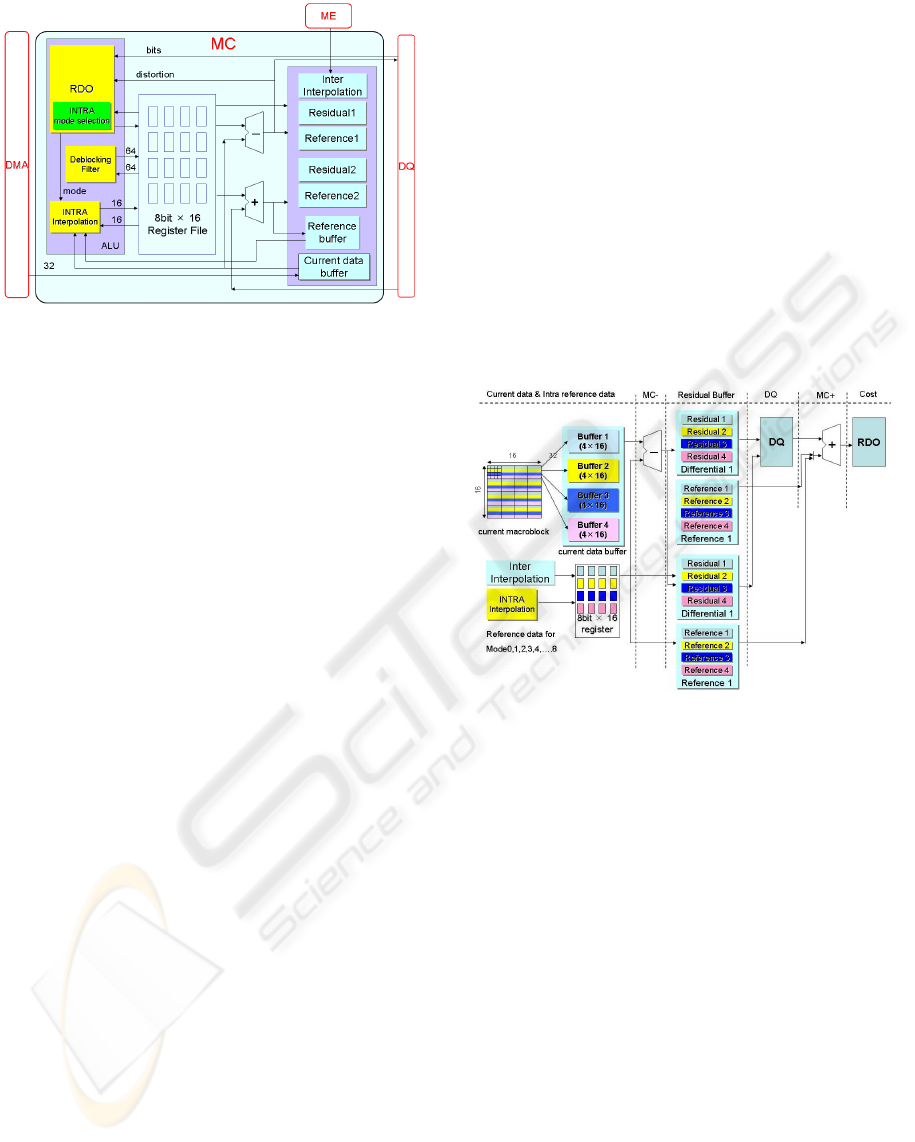
Figure 2: Proposed MC architecture.
files and data buffers. The ALU makes the role of
the calculation of INTRA interpolation, deblocking
filter and RDO cost. The register files are used as a
temporary data buffer for calculating and memory ac-
cess. The data buffers include a Current data buffer
which is provided to keep the pixel data of current
macroblock. The Reference buffer is to save the ref-
erence pixel data which is used to make the INTRA
interpolation data. To alternately keep the differential
and the residual data, a double buffer is used. An-
other Inter interpolation buffer is embedded to receive
the interpolation data from the sub-pixel motion com-
pensation for the INTER macroblocks. Based on the
proposed architecture, the MC process timing could
be concluded by Fig. 3.
As described in the Fig. 3, proposed architecture
could accomplish the coding and decoding process.
The motion compensation process starts from the data
input of the current coding macroblock and the refer-
ence data and ends at the completion of the data out-
put after the deblocking filtering process. The major-
ity processes are the mode selection loop for both IN-
TRA and INTER macroblocks. For the INTRA type
macroblocks there are 9 times pre-codings for the 4x4
blocks and 4 times pre-coding for the 16x16 block.
Depending on the ME processing, there are maximum
16 times pre-coding for INTER type macroblocks
with differential block size. For both INTER and IN-
TRA type macroblocks, the pre-coding for the RDO
process includes MC-(Motion Compensation differ-
ential), DQ(DCT, Q, IQ and IDCT), MC+(Motion
Compensation reconstruction) and COST(Cost calcu-
lation for RDO) steps. Therefore, it is obvious that
to realize high throughput motion compensation the
implementation key point is on how to decrease the
coding mode for both INTER and INTRA type mac-
roblocks and the design of the pipeline processing ar-
chitecture.
Because the strong correlation between the adja-
cent macrobloks and sub-blocks, it is difficult to re-
alize sub-MB pipelined architecture. Proposed archi-
tecture designs a pipeline architecture for the mem-
ory input/output, Intra interpolation calculation and
the MC routine process. Together with this pipeline
architecture, the candidate modes reduction method
and the high performance DQ module are proposed
and it will be described in the next subsection.
3.1 MC Encoding Routine Process
The mode selection process is mainly a loop for the
MC-, DQ, MC+ and the cost calculation. Fig. 4 shows
the core of the MC process includes a MC-, DQ, MC+
and Cost calculation for each mode.
Figure 4: Motion compensation routine process.
As the Fig. 4 shows, before the MC process, the
INTRA or INTER interpolation data has to be pre-
pared by the INTRA Interpolation module and the
ME module. The current MB data is pre-prepared in
the current data buffer which is constructed by four
distributed SRAM with the size of 64 words individu-
ally. This four distributed SRAMs ensure the 16 pixel
data could be read out in the same cycle. After the
MC- process, the residuals and the interpolation data
are saved into the Differential and Reference buffers
individually. Two sets of the Differential and Refer-
ence buffers are available to be alternately used ac-
complish the sub-block pipeline encoding. Each Dif-
ferential and Reference buffer is also consisted of 4
SRAMs to ensure the parallel data access. Then the
residuals of MC are sent to DQ module for the lo-
cal decoding process. The reconstructed residuals are
added back to the interpolation data to reconstruct the
decoded pixel data by the MC+ process and the cod-
ing distortions are calculated as well. At the last stage
the RDO module gathers the distortion and the gener-
ated bits to select the best coding mode.
EFFICIENT MOTION COMPENSATION ARCHITECTURE WITH RATE-DISTORTION OPTIMIZATION FOR
H.264/AVC
161
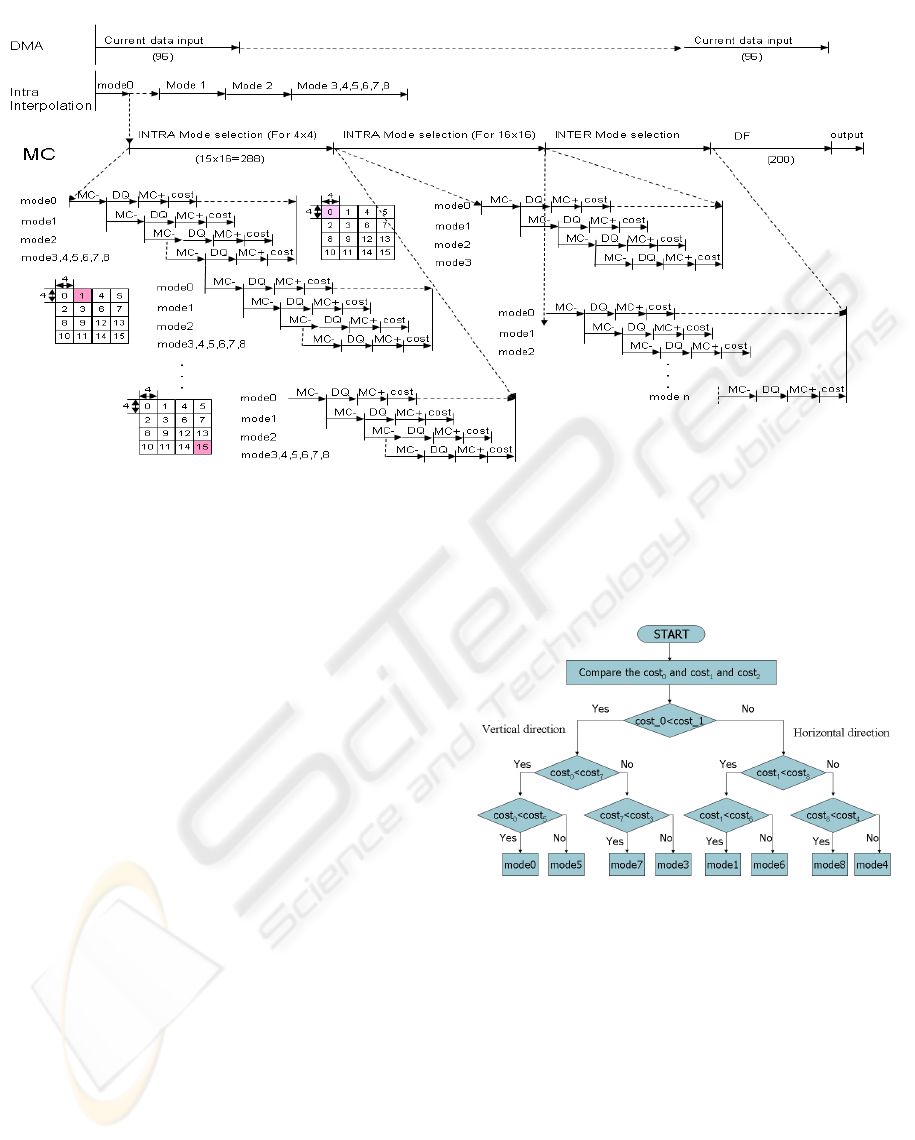
Figure 3: The pipeline timing of the proposed architecture.
3.2 Intra Mode Selection
In this paper a new mode selection algorithm is pro-
posed included with a 3-step mode selection method
and a adaptive compensation process. Proposed
method first focuses on the features of the 9 modes for
the 4x4 blocks. The 9 modes for the 4x4 blocks could
be classified into two groups, one group includes the
mode0, mode7, mode5 and mode3 representing the
vertical direction components and the other group in-
cludes the mode1, mode 4, mode6 and mode8 rep-
resenting the horizontal direction components. The
proposed 3-step mode selection method is described
in Fig. 5.
As described in Fig. 5, proposed method first cal-
culates the coding cost of the mode0 and mode1.
Based on the comparison of these two coding costs,
the next possible coding mode is selected in the next
step. At the third step another selection of possible
mode is performed to choose the best mode. As a re-
sult the coding cost for mode0, mode1 and mode2 is
always calculated. However, only the coding costs of
the 2 modes in the left 6 modes are calculated.
However, sometimes the possible coding mode es-
timation in the step2 and step3 could make mistake.
To overcome this mis-estimation another compensa-
tion process is proposed. The flow-chart of this pro-
cess is described in Fig. 6.
Figure 5: Proposed 3-step mode selection algorithm.
As the Fig. 6 shows, proposed method sets a
threshold value SH which is the average of the min-
imum cost of the top and the left blocks. Then after
calculating the best mode, using the proposed 3-step
algorithm the minimum cost(cost
min
) is compared
with the T H. If the cost
min
is bigger than the T H,
the left mode will be selected as the candidate coding
mode again to search a better mode.
After the mode decision for all the 4x4 blocks, 16
best modes are available. By using this data the best
mode for 16x16 is also predictable. Simulation re-
sults show that if most of the 4x4 blocks select the
same mode, there is high possibility to select the same
SIGMAP 2007 - International Conference on Signal Processing and Multimedia Applications
162
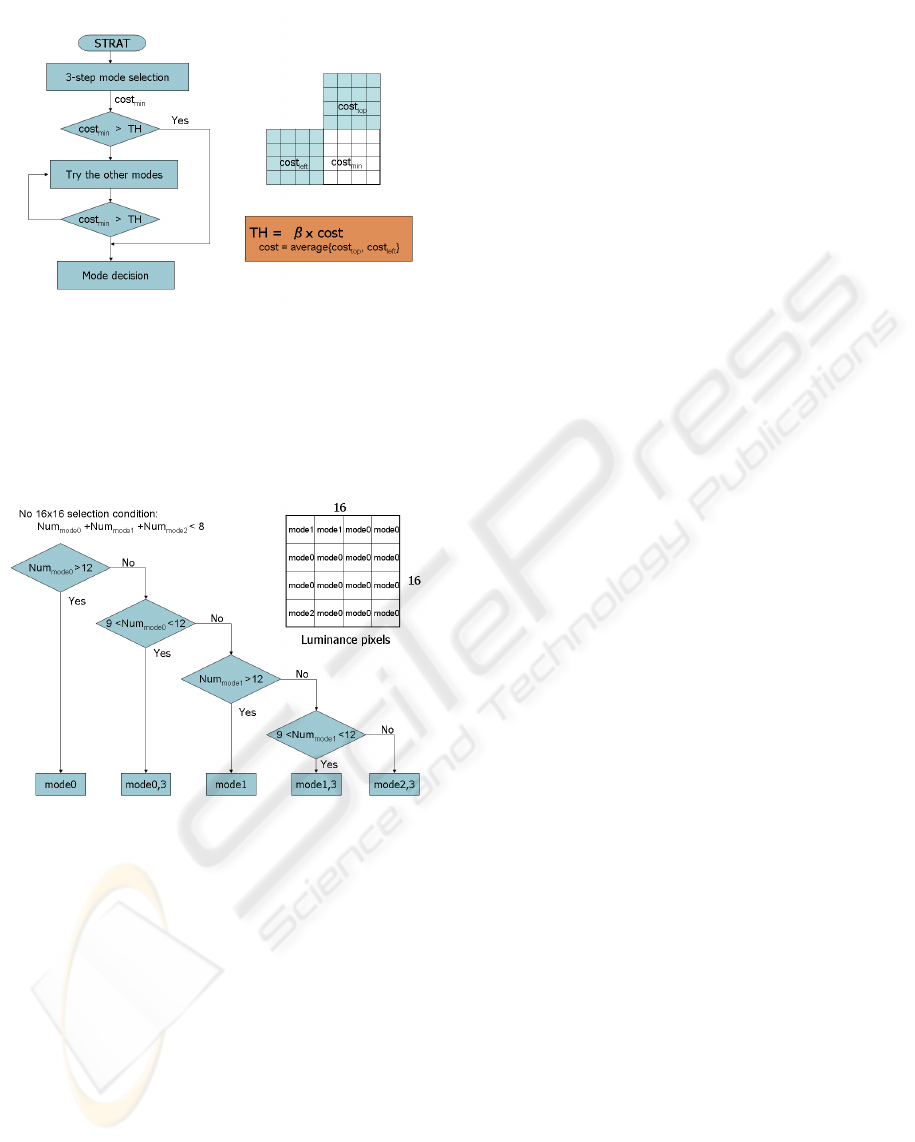
Figure 6: Proposed mode selection algorithm for 4x4
blocks.
mode for 16x16 block. Utilizing this feature an IN-
TRA mode prediction method for the 16x16 blocks is
proposed. The detail of this method is described in
Fig. 7.
Figure 7: Proposed mode selection algorithm for 16x16
blocks.
If the selected mode for 4x4 blocks is concentrated
in mode0 or mode1, there is a high possibility for the
mode0 or mode1 to be the best mode for the 16x16
block too. In proposed method, if the number of the
mode0 or mode1 is over 12, it is selected as the fi-
nal mode without other mode selection processings.
When the number of the same mode0 or mode1 is
smaller than 12 but bigger than 9, it is set to be an
candidate. Otherwise, it isn’t thought to be estimated.
Then all the modes have to be calculated as an candi-
date.
3.3 Dq Architecture
The DQ module is constructed by DCT, Q, IDCT and
IQ module. There are some works concerning the effi-
cient DCT and Quantization architectures(H. S. Mal-
var and Kerofsky, 2003)-(Q. Wang and Ma, 2005).
(H. S. Malvar and Kerofsky, 2003) gives the concept
of the low complxity DCT and the Quantization pro-
cess for H.264/AVC and the (K. H. Chen and Wang,
2006) gives the most high throughput performance
DCT architecture which make the 4x4 DCT could
be performed in two cycles. (D. M. Zhang and Yu,
2007) proposes a complexity reduction method for
DCT. Observing that many blocks obtain all-zero co-
efficient after the quantization process, (H. L. Wang
and Kok, 2006) proposes an all-zero check method to
omit the DCT-Q-IQ-IDCT routine. This work adopt
these excellent methods and architectures which make
the DQ process accomplished within 2 cycles for one
4x4 sub-block.
3.4 Deblocking Filter Architecture
There are several architectures proposed to process
the deblocking filter faster with efficient memory ac-
cess and small register arrays(Y. W. Huang and Chen,
2003)-(T. M. Liu and Lee, 2005). In the latest pro-
posal Shih’s architecture achieves the DF in about
200 cycles for one macrobock(S. Y. Shih and Lin,
2006). Similar processing method as described in
Shih’s work is adopted in the architecture.
4 SIMULATION RESULTS
First, we evaluate the proposed INTRA mode selec-
tion method from the viewpoint of the complexity de-
crease and the image quality. Simulation results show
that the average hit rate is about 90%. Then, the im-
proved 3-step algorithm is also evaluated. Several
simulation results show that the parameter β gives the
best performance when it is equal to 1. When using
this β average 54% of the computation complexity
could be reduced with almost no PSNR decrease.
4.1 Cycle Consumption
The proposed architecture is evaluated from the view-
point of the cycle consumption and the implementa-
tion cost. The cycle consumption for one macroblock
is concluded in the Tab. 1
This simulation results show that even at the worst
case the architecture could fulfill the real-time encod-
ing for HDTV(720p) applications.
EFFICIENT MOTION COMPENSATION ARCHITECTURE WITH RATE-DISTORTION OPTIMIZATION FOR
H.264/AVC
163
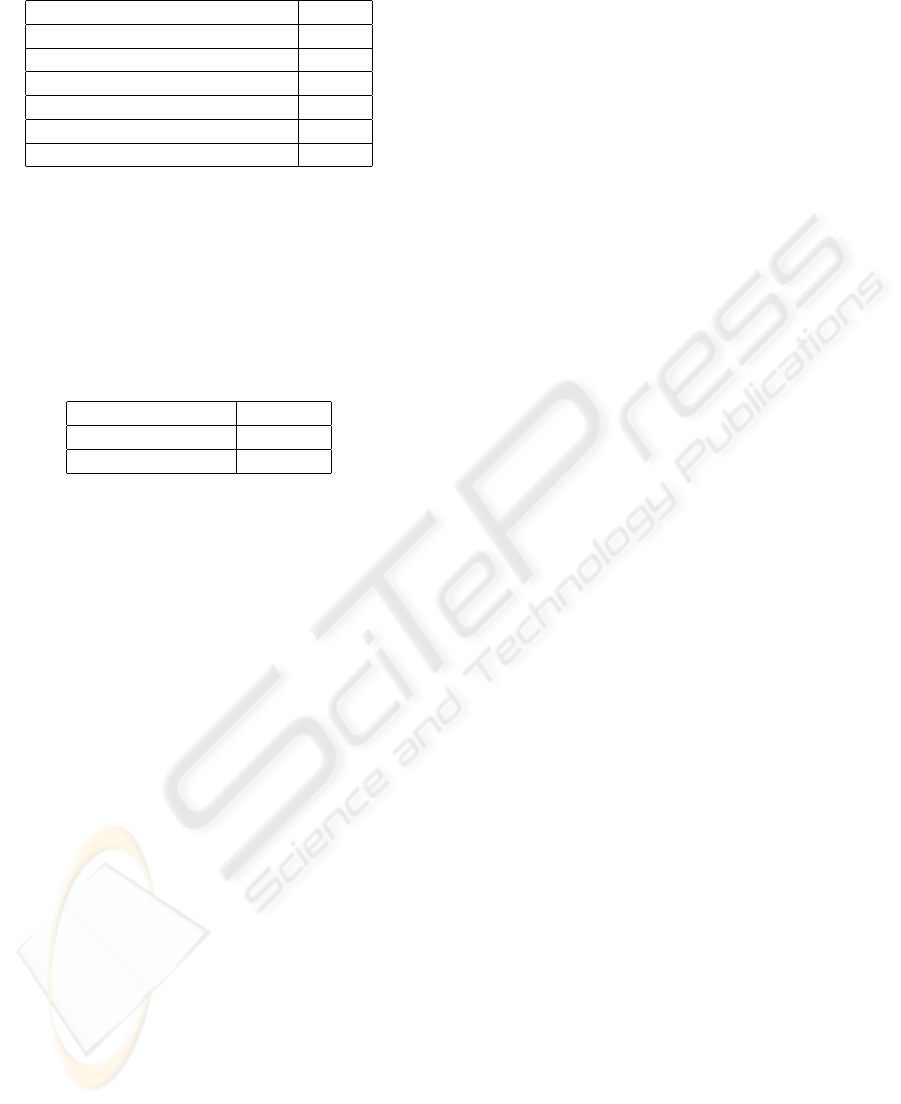
Table 1: Cycle consumption.
Functions cycles
INTRA mode selection(4x4) 288
INTRA mode selection(16x16) 332
INTER mode calculation 97
For Cb,Cr 230
Deblocking Filter 200
Total 1137
4.2 Hardware Cost
Proposed architecture is described by Verilog-HDL
and synthesized using synopsis CAD tools. The sim-
ulation results are shown in Table 2.
Table 2: Implementation results.
#Gates 42,280
#SRAM(bits) 48,320
#Max Clock Freq. 128MHz
From these simulation results, it is obvious that
the proposed architecture could be obtained with ac-
ceptable hardware cost.
5 CONCLUSION
In this paper, a novel motion compensation archi-
tecture with the embedded RDO for H.264/AVC is
proposed. Proposed method can be realized by only
about 42,280 gates and 48,320 bits SRAM.
REFERENCES
C. S. Kim, H. H. S. and Kuo, C. C. J. (2006). Fast h.264
intra-prediction mode selection using joint spatial and
transform domain features. In Journal of Visual Com-
munication and Image Representation. Springer.
C. S. Kim, Q. L. and Kuo, C. C. J. (2003). Fast intra-
prediction model selection for h.264 codec. In SPIE
International Symposium ITCOM.
D. M. Zhang, S. X. Lin, Y. D. Z. and Yu, L. J. (2007). Com-
plexity controllable dct for real-time h.264 encoder.
In Journal of Visual Communication and Image Rep-
resentation.
H. L. Wang, S. K. and Kok, C. W. (2006). Efficient predic-
tion algorithm of integer dct coefficients for h.264/avc
optimization. In IEEE transactions on circuits and
systems for video technology.
H. S. Malvar, A. Hallapuro, M. K. and Kerofsky, L.
(2003). Low-complexity transform and quantization
in h.264/avc. In IEEE transactions on circuits and
systems for video technology.
K. H. Chen, J. I. G. and Wang, J. S. (2006). A high-
performance direct 2-d transform coding ip design for
mpeg-4 avc/h.264. In IEEE transactions on circuits
and systems for video technology.
Q. Wang, D. B. Zhao, W. G. and Ma, S. W. (2005). Low
complexity rdo mode decision based on a fast coding-
bits estimation model for h.264/avc. In Proceedings of
IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Sys-
tems.
S. Y. Shih, C. R. C. and Lin, Y. L. (2006). A near optimal
deblocking filter for h.264 advanced video coding. In
Proceedings of ASP-DAC 2006.
T. M. Liu, W. P. Lee, T. A. L. and Lee, C. Y. (2005). A
memory-efficientdeblocking filter for h.264/avc video
coding. In Proceedings of IEEE International Sympo-
sium on Circuit and Systems.
U. J. Kapasi, S. Rixner, W. J. D. B. K. J. H. A. P. M. and
Owens, J. D. (2003). Programmable stream proces-
sors. In IEEE Computer.
Y. K. Tu, J. F. Yang, M. T. S. and Tsai, Y. T. (2005). Fast
variable block-size block motion estimation for effi-
cient h.264/avc encoding. In Journal of Signal Pro-
cessing: Image Communication. Springer.
Y. L. Xi, C. Y. Hao, Y. Y. F. and Hu, H. Q. (2006).
A fast block-matching algorithm based on adaptive
search area and its vlsi architecture for h.264/avc. In
Journal of Signal Processing: Image Communication.
Springer.
Y. Song, Z. Liu, S. G. and Ikenaga, T. (2006). Scalable vlsi
architecture for variable block size interger motion es-
timation in h.264/avc. In IEICE tran. on Fundamen-
tals.
Y. W. Huang, T. W. Chen, B. Y. H. T. C. W. T. H. C. and
Chen, L. G. (2003). Architecture design for deblock-
ing filter in h.264/jvt/avc. In IEEE International Con-
ference on Multimedia and Expo.
Y. W. Huang, B. Y. Tsieh, T. C. C. and Chen, L. G. (2005).
Analysis, fast algorithm, and vlsi architecture design
for h.264/avc intra frame coder. In IEEE transactions
on circuits and systems for video technology.
SIGMAP 2007 - International Conference on Signal Processing and Multimedia Applications
164
