
REVERSIBLE AND SEMI-BLIND RELATIONAL DATABASE
WATERMARKING
Gaurav Gupta and Josef Pieprzyk
Centre for Advanced Computing - Algorithms and Cryptography
Department of Computing, Division of Information and Communication Sciences
Macquarie University, Sydney, NSW - 2109, Australia
Keywords:
Reversible, relational database, watermarking, copyright, ownership.
Abstract:
In 2002, Agrawal and Kiernan proposed a relational database watermarking scheme that modifies least sig-
nificant bits (LSBs) of numerical attributes selected using a secret key. The scheme does not address query
preservation (some queries give different results when executed on the original and watermarked relation).
Additive and secondary watermarking attacks on the watermarked relation are also possible. Such attacks can
render the original watermark undetectable. Hence, an attacker who embeds his watermark in a previously wa-
termarked relation can claim ownership of that relation. However, if the scheme is reversible, then a previous
watermark, if any, can be detected in the reversed relation. In this paper, we propose an enhanced reversible,
semi-blind and query-preserving watermarking scheme. Using this scheme, the correct owner of a relation can
be identified even if the relation has been watermarked by multiple parties. If required, the database can be
restored to it’s original state too. This finds applications in high-precision settings such as military operations
or scientific experiments.
1 INTRODUCTION
Watermarking (embedding owner information in a
multimedia object) and fingerprinting (embedding
buyer information) have received significant research
attention in the past decade. Since a multimedia ob-
ject is sold (usually) by one owner to multiple users,
each copy has the same watermark but a different fin-
gerprint. Images, audio-visual and text documents,
software, and databases are general multimedia ob-
jects considered for watermarking. Images have been
the primary focus of research in watermarking (Bors
and Pitas, 1996; Braudaway, 1997; Cox et al., 1995;
Cox et al., 1997; Cox et al., 1996) due to two main
reasons. First, the human visual system (HVS) cannot
distinguish between images with minor differences,
and second, image pixels’ LSBs can be flipped with-
out causing significant distortion in the visual quality.
Database watermarking is a relatively new field
which has seen contributions in the last five years.
A typical scenario requiring database watermarking
is when a company
C provides confidential customer
data to an external organization O (eg. call center).
To ensure that O does not exploit the information
and doesn’t sell it, C embeds it’s watermark in the
database relation. Another application is in web ser-
vices, where data provider D makes a database rela-
tion available online for remote query. An attacker
may try to steal the relation using multiple “intel-
ligent” queries. To prevent this, D watermarks the
databases before making them available online using
a blind or non-blind watermarking scheme. In a blind
watermarking model, only the watermarked media
and a secret key are required to detect/extract water-
mark whereas in a non-blind watermarking scheme,
the unmarked multimedia object is also required in
addition to the watermarked copy and secret key. This
creates a situation where one needs to store the un-
marked object at a secondary secure location. In this
paper, we present a database watermarking scheme
that is reversible and semi-blind. We call the scheme
semi-blind because it does not require the original
database to detect watermark but the insertion algo-
rithm stores the original bits selected for modifica-
tion as an embed trace
E T , which is input to the
detection algorithm. Size of E T is proportional to
283
Gupta G. and Pieprzyk J. (2007).
REVERSIBLE AND SEMI-BLIND RELATIONAL DATABASE WATERMARKING.
In Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Signal Processing and Multimedia Applications, pages 279-286
DOI: 10.5220/0002136902790286
Copyright
c
SciTePress

the number of tuples being marked. Previous wa-
termarking schemes such as (Sion et al., 2004) have
also presented similar semi-blind watermarking mod-
els. Our scheme is an enhancement of the irreversible
watermarking model proposed by Agrawal and Kier-
nan (Agrawal and Kiernan, 2002). We show that sec-
ondary watermark attacks are feasible on (Agrawal
and Kiernan, 2002). Further, we modify the model to
eliminate this shortcoming and propose an additional
algorithm to achieve identify the rightful owner from
n contenders.
1.1 Organization of the Paper
Section 2 describes related work and provides a
detailed account of database watermarking from
(Agrawal and Kiernan, 2002) to eliminate shortcom-
ings. The modified algorithms are presented in Sec-
tion 4 and Section 5 contains their analysis. The pa-
per is concluded in Section 6 with a discussion on the
added advantages provided by the new scheme.
1.2 Notations Used
The following notations will be used through the pa-
per,
• R : Relation
• r : Tuple
• A
i
: i
th
attribute
• r.A
i
: i
th
attribute in tuple r
• A
j
i
: j
th
LSB of i
th
attribute
• r.A
j
i
: j
th
LSB of i
th
attribute in tuple r
• r.P : Primary key of tuple r
• ◦ : Concatenation
•
H () : One-way hash function
• R
ins(p)
−−−→ R
w
: R is watermarked by party p to be-
come relation R
w
, or in other words, a watermark
is inserted by party p into a document R resulting
in its watermarked version R
w
• R
w
det(p)
−−−→ R : R is restored when party p’s water-
mark is detected in R
w
• |x| : Size of x in bits
• abs(x) : Absolute value of x
• ⌊x⌋: Floor value of x
• Distance for attribute r.A
i
: δ
r.A
i
=
min
˜r6=r
{abs(r.A
i
− ˜r.A
i
)}
2 RELATED WORK AND
AGRAWAL-KIERNAN SCHEME
Several relational database watermarking models
have been proposed in (Agrawal and Kiernan, 2002;
Agrawal et al., 2003; Sion et al., 2004; Gross-
Amblard, 2003; Guo et al., 2006; Li and Deng, 2006;
Li et al., 2004; Zhang et al., 2004a; Zhang et al., 2006;
Zhang et al., 2004b). These schemes are irreversible
with the exception of (Zhang et al., 2006) and except
(Gross-Amblard, 2003), do not preserve queries. Ir-
reversible watermarking implies that the original re-
lation cannot be restored from the watermarked re-
lation. Ownership disputes might be unresolved if
an attacker successfully embeds a secondary water-
mark. But if the watermarking is reversible, the orig-
inal database can be restored and the correct owner
identified using suitable algorithm (discussed in sec-
tion 4.1).
The notions of local and global distortions are
presented in (Gross-Amblard, 2003) which achieve
the property of query-preservation. Local distortion
refers to the minimum difference between values of
an attribute. For formal definitions of local and global
distortions, please refer to (Gross-Amblard, 2003). In
a nutshell, the attributes should only be modified by a
value lesser than the local distortion.
Agrawal and Kiernan (Agrawal and Kiernan,
2002) were the first to present a database watermark-
ing scheme that modifies LSBs of numerical attributes
(selected using the private key and tuple’s primary key
value). This key-based attribute selection is common
to other proposals (Agrawal et al., 2003; Li and Deng,
2006).
2.1 Agrawal-Kiernan Scheme
The watermarking scheme consists of two algorithms;
Insertion, and Detection. The bits modified during
insertion are checked for correctness in the detection
algorithm for establishment of watermark presence.
Parameters to the insertion algorithm are,
• Database Relation R containing η tuples and υ
modifiable attributes {A
0
,A
1
,...,A
υ
}
• Number of modifiable LSBs ξ
• Fraction of tuples to be watermarked 1/γ
• Private key
K
The secret parameter set is given be φ =
(
K ,γ,υ,ξ). Algorithm 1 illustrates the watermark
insertion process. Tuples are selected using mes-
sage authentication code (MAC)
F (r.P) defined as
H (K ◦ H (K ◦ (r.P)) (Schneier, 1996) and appropri-
ate bit in the tuple set to
H (K ◦ r.P)%2 till ω =
η
γ
SIGMAP 2007 - International Conference on Signal Processing and Multimedia Applications
284
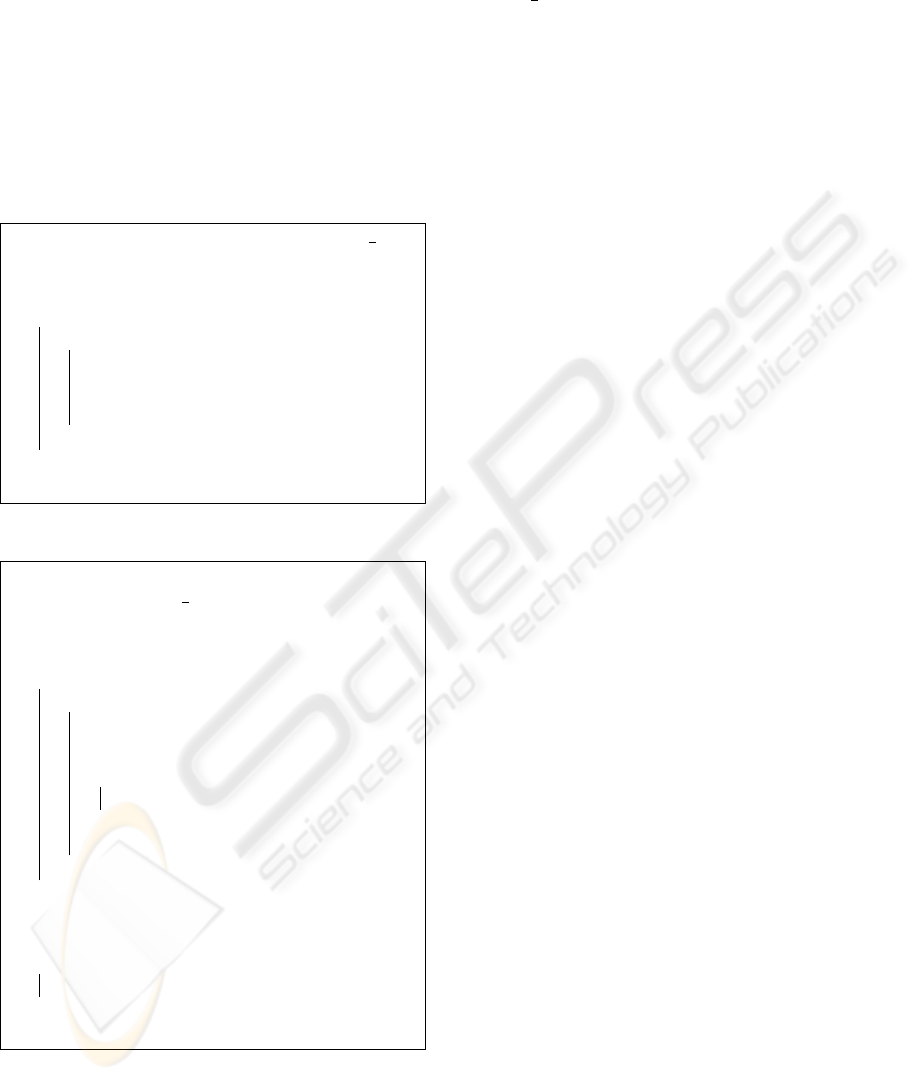
bits are marked. Converse procedure is applied on
the watermarked copy to detect the watermark (Al-
gorithm 2) by verifying the modified bit is equal
to
H (K ◦ ˜r
w
.P)%2. The primary key value is un-
changed. Parameters to the watermark detection algo-
rithm are watermarked database relation R
w
contain-
ing η tuples and υ attributes {A
0
,A
1
,...,A
υ
}, number
of LSBs modified ξ, fraction of tuples watermarked
1/γ, upper bound on probability of falsely detecting
watermark α, minimum number of correctly marked
attributes for successful detection τ, and private key
K .
Input: Relation R, private key K, fraction
1
γ
,
LSB usage ξ
Output: Watermarked relation R
w
forall tuple r ∈ R do1
if F (r.P)%γ = 0 then2
i = F (r.P)%υ;3
j =
F (r.P)%ξ;4
r.A
j
i
=
H (K ◦ r.P)%2;5
end6
end7
return R;8
Algorithm 1: Agrawal-Kiernan watermark in-
sertion algorithm.
Input: Watermarked Relation
˜
R
w
, private key
K, fraction
1
γ
, LSB usage ξ
Output: Detection Status ∈ {true, false}
totalcount = matchcount = 0;1
forall tuple ˜r
w
∈
˜
R
w
do2
if F (r.P)%γ = 0 then3
i = F (r.P)%υ;4
j =
F (r.P)%ξ;5
if ˜r
w
.A
j
i
=
H (K ◦ ˜r
w
.P)%2 then6
matchcount = matchcount +1;7
end8
totalcount = totalcount + 1;9
end10
end11
τ = min{θ :
B (θ,totalcount,1/2) < α} ;
//
B12
defined in Equation 1
if matchcount ≥ τ then13
return true;14
end15
return f alse;16
Algorithm 2: Agrawal-Kiernan watermark de-
tection algorithm.
Equation 1 gives the binomial probability of hav-
ing at least k successes from n trials where probability
of success in a single trial is p. During detection, at
least τ bits need to be detected correctly in order to ex-
tract the correct watermark or in other words the prob-
ability of τ out of ω bits matching by sheer chance
B(τ,ω,
1
2
) should be less than the upper bound of false
positive α.
B (k, n, p) =
n
∑
i=k
n
i
p
i
(1− p)
n−i
(1)
2.2 Security Provided by
Agrawal-Kiernan Scheme
While discussing the security of the scheme, Agrawal
and Kiernan consider the following collection of at-
tacks,
A1: Bit attack: Updating some bits in numerical at-
tributes.
A2: Randomization attack: Assigning random values
to some bits.
A3: Rounding attack: Rounding off a fixed number of
bits.
A4: Translation attack: Transforming numerical val-
ues to another data type.
A5: Subset attack: Removing a small subset of tuples/
attributes.
A6: Mix and match attack: Applying A4 on multiple
relations and merging them.
A7: Additive attack: Re-watermarking an already wa-
termarked relation.
A8: Invertibility attack: Checking if detection returns
true for a random key.
Inserting new tuples to destroy watermark will not
succeed as
F (r.P) identifies marked tuple and two tu-
ples cannot have the same primary key. Success of
removing the watermark by deleting tuples depends
on the parameter γ. Probability of destroying water-
mark by deleting a few tuples is extremely low when
the fraction of tuples marked when γ is high. If γ is
high for a fixed n, 1/γ is low and hence the fraction
of tuples marked are low. Thus the probability of the
attacker modifying the watermarked tuples is low. Bit
flipping attacks (A1–A3) are probabilistically ineffec-
tive since the identification of correct tuples, attributes
and LSBs is dependent on MAC. Additive and invert-
ibility attacks are still feasible.
REVERSIBLE AND SEMI-BLIND RELATIONAL DATABASE WATERMARKING
285

3 ANALYSIS OF
AGRAWAL-KIERNAN
WATERMARKING SCHEME
Based on our observations, Agrawal and Kiernan
scheme has three weaknesses.
1. Susceptibility of secondary watermarking:
Secondary watermarking refers to an attacker
who is trying to insert his watermark in an
already watermarked relation. The scheme does
not protect against secondary watermarking as
the attacker can choose his/her own parameter
list
˜
φ and insert a new watermark in the original
watermarked relation. The new watermark will
establish the ownership of the attacker over
the relation and might also destroy the original
watermark. If the watermarking is reversible, the
actual owner’s watermark can be recovered from
the reversed relation.
2. Lack of query-preservation: If an attribute
r.A
i
= x
1
is modified to x
2
, then query “Select r
from R where r.A
i
= x
1
” cannot be preserved.
Thus, it is obvious that not all queries are preserv-
able in watermarked database. Distance δ
r.A
i
, that
refers to the minimum difference between value
of r.A
i
from values of A
i
in other tuples, is not
considered in (Agrawal and Kiernan, 2002), due
to which queries might not be preserved. If we
change value of an attribute beyond it’s distance,
the ordering of the tuples is modified when the
relation is sorted on that attribute and hence query
results change. Consider the following relations
that contains foreign exchange rate data of some
countries against 100 US Dollars. Table 1 is the
original relation and Table 2 is the watermarked
relation.Result of queries “Select Nation from
ForEx where Selling rate<130” and “Select
Currency from ForEx where Buying rate is
maximum” are different when executed on the
original and watermarked relations.
3. Lack of tolerance of attributes: The number of
LSBs that can be used for watermarking are not
dependent on the tolerance of the attributes. This
results in the possibility that the relation becomes
unusable from a user’s perspective. Tolerance is
different from distance. For example, even if pop-
ulation of the two countries differ by millions,
modifying population values beyond a couple of
thousands might render the data useless. Hence,
the number of bits that one can change does not
depend only on distance, but also on tolerance.
Table 1: Original ForEx relation.
Currency Nation Buying Selling
code rate rate
AUD Australia 133 125
INR India 4500 4300
THB Thailand 3740 3510
SLR Sri Lanka 4430 4210
NZD New Zealand 151 134
Table 2: Watermarked ForEx relation.
Currency Nation Buying Selling
code rate rate
AUD Australia 133 125
INR India 4500 4300
THB Thailand 3740 3510
SLR Sri Lanka 4530 4310
NZD New Zealand 151 124
We propose the following modifications to eliminate
each of these weaknesses.
1. Secondary Watermarking
To defeat secondary watermarking attacks, the
step r.A
j
i
=
H (K ◦ r.P)%2 in Algorithm 1 is
changed to
E T = E T ◦ r.A
j
i
r.A
j
i
=
H (K ◦ r.P◦ r.A
j
i
)%2,
r.A
j
i
is concatenated to embed trace
E T and
then modified. The scheme is semi-blind and re-
versible, since the original values can be restored
from
E T . The size of E T is proportional to
n
γ
.
At the detection time, the value of matchcount is
incremented only if
˜r
w
.A
j
i
==
H (K ◦ ˜r
w
.P◦ E T [totalcount])%2
(i, j,totalcount,matchcount are counters updated
during the detection)
The owner stores
E T at a secondary location.
(
E T ,K ) is the watermark detection key. Sub-
section 4.1 discusses how the rightful owner is
identified if multiple parties watermark a relation
in some sequence. Implementation is given in
Algorithm 5.
2. Query preservation
The value of an attribute r.A
i
should be modi-
fied by less than the distance δ
r.A
i
. Thereby, the
number of bits available for watermarking are
⌊log
2
(δ
r.A
i
)⌋ (For example, if the smallest differ-
ence between values of an attribute in two rows is
SIGMAP 2007 - International Conference on Signal Processing and Multimedia Applications
286

57.68, then only 5 bits can be used for watermark-
ing as log
2
(57.68) = 5.85 and ⌊5.85⌋ = 5). This
would guarantee query-preservation for the exist-
ing relation. Since the watermarking scheme is re-
versible, it facilitates incremental watermarking.
The steps involved in incremental watermarking
are,
(a) Restore relation to unmarked version.
(b) Add (or delete) required tuples (or attributes).
(c) Re-watermark the updated relation.
3. Tolerance
Since each attribute has a different tolerance limit
beyond which it should not be modified, it is rec-
ommended that the number of LSBs to utilize
for watermarking should be a function of toler-
ance of the attributes. Hence, ξ
i
LSBs of attribute
A
i
can be modified. The list of all these values
Ξ = {ξ
1
,ξ
2
,...,ξ
υ
} where υ attributes are avail-
able for watermarking.
4 MODIFIED ALGORITHMS
With the above modifications, the secret param-
eter list for watermark detection becomes φ =
(
K ,E T , γ, υ, Ξ). We present a reversible and
semi-blind watermarking scheme that comprises
of three algorithms; Insertion, Detection, and
(1,n)identification. The algorithms are presented
in Algorithm 3, Algorithm 4, and Algorithm 5 re-
spectively. They contain comments illustrating the
purpose served by various steps. The acronym WM
refers to “watermark” in the three algorithms.
4.1 Identifying Rightful Owner
In this additional algorithm, ownership disputes can
be resolved through backtracking. If R
ins(p
1
)
−−−−→ R
1
is
followed by R
1
ins(p
2
)
−−−−→ R
2
, then R
2
det(p
2
)
−−−−→ R
1
will
show that the restored relation R
1
has already been
watermarked by another party (p
1
) and hence p
2
is
not the original owner. For all potential owners u
i
,
we compare relations restored R
restored
after detect-
ing watermark of party u
i
, and if it matches any other
party’s watermarked relation R
w
within a preset tol-
erance limit ε, then u
i
is eliminated from the list of
possible owners. Each party supplies its secret pa-
rameter list φ. and the relation R
w
on which it claims
ownership. A limitation is that each party that has wa-
termarked the relation should participate in the owner-
identification process. If this condition is not satisfied,
we might not be able to associate the restored relation
with another user, in which case the algorithm will
fail.
Input: Relation R, private key K, fraction γ, number of
markable attributes υ, LSB usage
Ξ = {ξ
1
,ξ
2
,. .. ,ξ
υ
}
Output: Watermarked relation R
w
, Embed Trace E T
count = 0 ;
// index in WM to be generated
1
forall tuples r ∈ R do2
if F (r.P)%γ = 0 then3
i = F (r.P)%υ;
// identify attribute
4
j = F (r.P)%ξ
i
;
// identify bit
5
if j < ⌊log
2
(δ
r.A
i
)⌋ then6
E T [count] = r.A
j
i
;
// store old value
7
in WM
count = count + 1;
// next watermark
8
bit’s index
r.A
j
i
= H (K ◦ r.P ◦ r.A
j
i
)%2 ;
// modify
9
bit in relation
end10
end11
end12
Algorithm 3: Watermark insertion.
5 ANALYSIS
According to (Agrawal and Kiernan, 2002), the at-
tacker Mallory needs to flip at least
¯
τ = ω − τ + 1
marked bits to carry out a successful attack, where
ω =
η
γ
. Let us assume that Mallory somehow knows
the values of ξ and υ and randomly chooses ζ tuples.
The probability that this attack will succeed when
Mallory flips A
ξ
i
for all υ attributes in all randomly
selected ζ tuples is given in Equation 2 (Agrawal and
Kiernan, 2002), and the values are provided in Ta-
ble 3. For our modified watermarked scheme, ξ =
∑
υ
i=1
ξ
i
υ
. Note that if the attacker flips more than 50%
bits, the watermark will be detected when the entire
bits in the relation are flipped. This also gives us a
fair idea about the value of γ that should be chosen.
It should be fairly low and somewhere in between 10
and 100 as the attack is ineffective for values in this
range.
P (A ) =
n
∑
i=
¯
τ
ω
i
η− ω
ζ− i
η
ζ
(2)
Without the knowledge of ξ,γ,υ, Mallory’s task is
much tougher. To compensate for the lack of knowl-
edge, Mallory might need to choose an estimated
ξ
′
and flip that bit of each of the attribute which
degenerates the data quality. The security analysis
REVERSIBLE AND SEMI-BLIND RELATIONAL DATABASE WATERMARKING
287
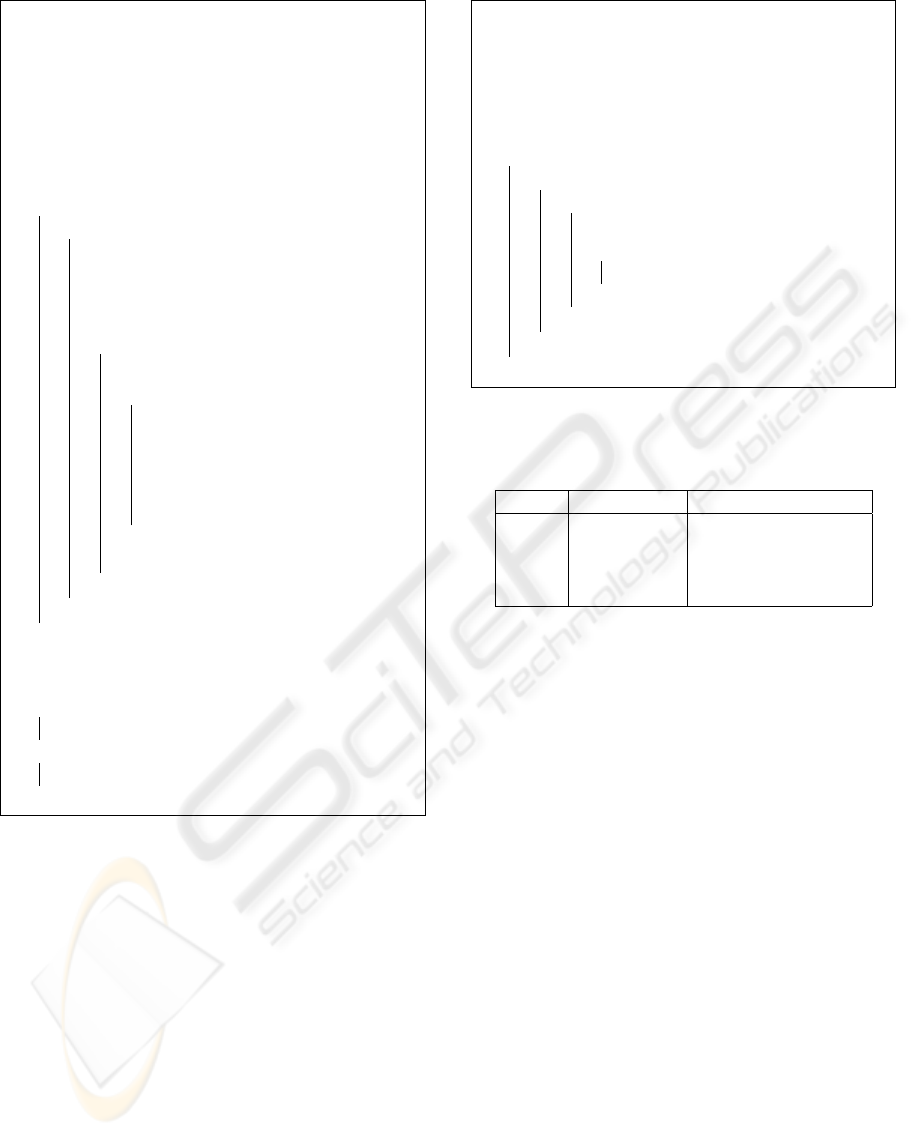
Input: Watermarked Relation
˜
R
w
, Secret
parameter list φ = (
K ,E T , γ, υ, Ξ)
Output: {Watermark Status ∈ {true, false},
Restored Relation R}
R =
˜
R
w
;1
matchcount = 0 ;
// matching WM bits
2
counter
totalcount = 0 ;
// total WM bits counter
3
forall tuples ˜r
w
∈
˜
R
w
do4
if F (r.P)%γ = 0 then5
i = F (r.P)%υ;
// identify marked
6
attribute
j = F (r.P)%ξ
i
;
// identify marked
7
bit
if j < ⌊log
2
(δ
r.A
i
)⌋ then8
if H (K ◦ ˜r
w
.P) ⊕9
E T [totalcount]%2 = ˜r
w
.A
j
i
then
matchcount = matchcount +1;10
// bit authenticated
r.A
j
i
= E T [totalcount];11
// restore bit in
relation
end12
totalcount = totalcount + 1;13
end14
end15
end16
τ = min(θ) : B(θ,totalcount,1/2) < α;17
// threshold check
if matchcount ≥ τ then18
return {true,R};19
else20
return { false,
˜
R
w
};21
end22
Algorithm 4: Watermark detection.
for (Agrawal and Kiernan, 2002) also holds for our
scheme as the underlying operations are retained.
The advantages of our reversible watermarking
scheme as compared to (Agrawal and Kiernan, 2002)
are,
1. Ownership resolution amongst n parties
This is not possible in the absence of a reversible
watermarking scheme. Consider a situation in
Figure 1 where a company C and five data servers
d
1
,d
2
,d
3
,d
4
,d
5
are contesting for ownership over
a relation, each party having a slightly different
version of the same relation. The dotted line
represents a relation being distorted by a party
in an attempt to destroy any watermark it con-
Input: Potential owners U = {u
1
,u
2
,...,u
n
}.
Secret parameter list of each u
i
,
φ
u
i
= {
K
i
,
E T
i
,γ
i
,υ
i
,Ξ
i
}, tolerance ε,
Potential owners’ versions of the
watermarked relation {
˜
R
u
1
w
,
˜
R
u
2
w
,...,
˜
R
u
n
w
}
Output: Owner O
forall u
i
∈
U do1
if detect(
˜
R
u
i
w
,I
u
i
) == {true,R
′
} then2
forall u
j
∈ U do3
if (difference(
˜
R
u
j
w
,R
′
) < ε) OR4
(detect(R
′
,u
j
) == true) then
U = U \ u
i
;5
end6
end7
end8
end9
Algorithm 5: (1,n)identification.
Table 3: Probability of success for bit flipping attack.
γ bits flipped success probability
10000 40% 0.64
1000 46% 0.44
100 48% 0.11
10 >50% ≈ 0
tains. We assume that γ < 100 for all the par-
ties who have watermarked the relation, which
gives a high probability of the watermark be-
ing preserved if the relation is distorted or re-
watermarked (Table 3). Hence, C’s watermark is
also detected in
˜
R
1
,
˜
˜
R
1
and d
1
’s watermark is also
detected in
˜
R
2
,
˜
˜
R
2
,
˜
˜
˜
R
2
. When we execute Algo-
rithm 5, the relation restored upon detecting wa-
termark of each party matches another party’s re-
lation (except when C’s watermark is detected).
For example, the relation
˜
R
2
restored upon detect-
ing d
3
’s watermark in R
4
matches R
2
within tol-
erance limit ε. But the relation R restored upon
detecting the watermark of the authentic owner C,
does not match any other party’s relation, which
establishes C’s ownership.
Line 4 of Algorithm 5 maximizes the probability
of identifying if the restored relation has been pre-
viously marked by another party. If the attacker
only slightly modifies the relation before water-
marking, the value of difference(
˜
R
u
j
w
,R
′
) is less
than ε, and even if the attacker changes the rela-
tion extensively, the value of detect(R
′
,u
j
) is true
with a high probability (by Equation 2).
If some of the parties do not participate in the
owner identification process, the algorithm might
SIGMAP 2007 - International Conference on Signal Processing and Multimedia Applications
288

fail. If we model parties watermarking relations as
nodes of a tree where the actual owner is the root
of the tree, then the probabilities with which the
owner will be correctly identified despite nodes
from n levels of the tree abstaining from participa-
tion is given by (1−
P (A ))
n
. These probabilities
are calculated taking into consideration the mod-
ifications the attacker might make in the relation
before watermarking it. The probability that an
attacker will succeed in destroying the watermark
is
P (A ) and hence the probability of the relation
surviving an attack is 1 −
P (A ). The probabil-
ity of a relation surviving n sequential attacks is
(1 − P (A ))
n
. It is extremely rare that the rela-
tion will be distributed beyond three or four lev-
els as there usually a few companies dealing with
similar data. It is shown in (Agrawal and Kier-
nan, 2002) that the attacker has a probability of
11% success if he changes 48% of the tuples as-
suming γ = 100. Hence, if only C and d
3
par-
ticipate in the correct algorithm, C will be iden-
tified as the correct owner with a probability of
89% since parties from only one level (d
1
,d
2
) ab-
stain. This probability is 100% if C,d
1
partici-
pate or C,d
2
participate. In general, successful
detection of the correct watermark occurs with the
probability of 0.89
n
where n levels abstain from
participation for γ = 100. Thus the probability
of finding rightful owner if two levels abstain is
0.89∗ 0.89 = 0.7921.
R
insert(C)
R
1
d
1
d
2
˜
R
1
insert(d
1
)
˜
˜
R
1
insert(d
2
)
R
2
d
3
d
4
d
5
R
3
˜
R
2
insert(d
3
)
˜
˜
R
2
insert(d
4
)
˜
˜
˜
R
2
insert(d
5
)
R
4
R
5
R
6
Figure 1: Dotted lines denote relation manipulated and
solid lines denote relation watermarked.
2. Situations requiring original dataset
Often, companies require precise data where a dif-
ference of even one bit might be disastrous such
as stock markets and military operations. Once
a relation is watermarked in (Agrawal and Kier-
nan, 2002), it cannot be restored to it’s original
state if needed. Since our watermarking scheme
is reversible, the original data can be restored by
executing the detection algorithm. It is also possi-
ble to distribute low-quality data free of cost and
users can then purchase the key to extract original
data.
5.1 Semi-blindness
As mentioned in the introduction, the two alter-
natives to facilitate reversibility are 1) Store orig-
inal bits at a secondary location before modifying
(This is the implemented solution in our paper or
2) Original bits and watermark bits should be re-
coverable from modified bits.
There are a few ways of implementing the second
option,
Algorithm 3, statement 9 can be replaced by
r.A
j
i
=
H (K ◦ r.P) ⊕ r.A
j
i
%2. But an attacker
A can run the insertion algorithm with inputs
(R
w
,K
′
,γ
′
,υ
′
,Ξ
′
) and get output R
′
,W
′
such that
R
′
ins(A )
−−−→ R
w
. Also R
ins(C )
−−−→ R
w
, thus making it
impossible to decide who (owner/ attacker) wa-
termarked the relation first. Thus the this solution
is vulnerable to pre-image attacks.
There have been reversible watermarking algo-
rithms, primarily for images (Alattar, 2004; Tian,
2003). These schemes facilitate watermarking by
encoding watermark bit and original value in the
modified value at at the cost of watermarking ca-
pacity. Another option is to use lossless compres-
sion to first compress the original bits, append wa-
termark bits and embed resulting bitstream (Celik
et al., 2002). Since lossless compressions are sen-
sitive to modifications, such schemes are not very
resilient as suggested in (Jen-Bang Feng and Chu,
2006).
The first challenge in designing a blind reversible
scheme for database relations is that lossless com-
pression technique is not resilient against attacks.
The second problem is that adapting reversible
image watermarking schemes is harder because
neighboring attributes or tuples do not have cor-
relation unlike images, which is a prerequisite
for schemes such as (Alattar, 2004). Our next
research endeavor is to implement a fully blind
REVERSIBLE AND SEMI-BLIND RELATIONAL DATABASE WATERMARKING
289

database watermarking model by working around
these two limitations.
6 CONCLUSION
The watermarking scheme proposed by Agrawal and
Kiernan is irreversible, resulting in problems during
owner identification in case of additive or secondary
watermarking attacks. Our modified scheme is re-
versible and thus the rightful owner can be identified
from n candidates. The major advantages of our pro-
posed scheme are 1)It provides query preservation, 2)
It identifies rightful owner if relation is watermarked
by multiple parties, and 3) It facilitates reversibility.
The current model requires modified bits to be
stored at a secondary location (
E T ). Our future re-
search is directed towards eliminating this require-
ment and formulate a reversible blind watermarking
scheme. The second enhancement is watermarking
relations that do not contain a primary key. Concate-
nated attributes in a tuple can act as a primary key
in such cases. However, the possibility of duplicate
attributes makes identification of marked tuples diffi-
cult. One possibility is to treat tuples with duplicate
attributes as a single tuple.
REFERENCES
Agrawal, R., Haas, P. J., and Kiernan, J. (2003). Water-
marking relational data: framework, algorithms and
analysis. The VLDB Journal, 12(2):157–169.
Agrawal, R. and Kiernan, J. (2002). Watermarking rela-
tional databases. In Proceedings of the 28th Interna-
tional Conference on Very Large Databases VLDB.
Alattar, A. (2004). Reversible watermark using the dif-
ference expansion of a generalized integer transform.
IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 13(8):1147–
1156.
Bors, A. and Pitas, I. (1996). Image watermarking using
dct domain constraints. In Proceedings of IEEE Inter-
national Conference on Image Processing (ICIP’96),
volume III, pages 231–234.
Braudaway, G. W. (1997). Protecting publicly-available im-
ages with an invisible image watermark. In Proceed-
ings of IEEE International Conference on Image Pro-
cessing (ICIP’97), Santa Barbara, California.
Celik, M. U., Sharma, G., Tekalp, M. A., and Saber, E.
(2002). Reversible data hiding. In Proceedings of
International Conference on Image Processing, vol-
ume 2, pages 157–160.
Cox, I., Kilian, J., Leighton, T., and Shamoon, T. (1995).
Secure spread spectrum watermarking for multimedia.
Technical Report 128, NEC Research Institute.
Cox, I., Kilian, J., Leighton, T., and Shamoon, T. (1997).
Secure spread spectrum watermarking for multimedia.
IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 6(12):1673–
1687.
Cox, I. J., Killian, J., Leighton, T., and Shamoon, T. (1996).
Secure spread spectrum watermarking for images, au-
dio, and video. In IEEE International Conference on
Image Processing (ICIP’96), volume III, pages 243–
246.
Gross-Amblard, D. (2003). Query-preserving watermark-
ing of relational databases and xml documents. In
Proceedings of the 20th ACM Symposium on Princi-
ples of Database Systems, pages 191–201.
Guo, F., Wang, J., and Li, D. (2006). Fingerprinting rela-
tional databases. In SAC ’06: Proceedings of the 2006
ACM symposium on Applied computing, pages 487–
492, New York, NY, USA. ACM Press.
Jen-Bang Feng, Iuon-Chang Lin, C.-S. T. and Chu, Y.-P.
(2006). Reversible watermarking: Current status and
key issues. International Journal of Network Security,
2(3):161–171.
Li, Y. and Deng, R. H. (2006). Publicly verifiable ownership
protection for relational databases. In Proceedings of
the ACM Symposium on Information, computer and
communications security, pages 78–89, New York,
NY, USA. ACM Press.
Li, Y., Guo, H., and Jajodia, S. (2004). Tamper detection
and localization for categorical data using fragile wa-
termarks. In DRM ’04: Proceedings of the 4th ACM
workshop on Digital rights management, pages 73–
82, New York, NY, USA. ACM Press.
Schneier, B. (1996). Applied Cryptography. John Wiley,
second edition.
Sion, R., Atallah, M., and Prabhakar, S. (2004). Rights
protection for relational data. IEEE Transactions
on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 16(12):1509–
1525.
Tian, J. (2003). Reversible data embedding using a differ-
ence expansion. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and
Systems for Video Technology, 13(8):890–896.
Zhang, Y., Niu, X.-M., and Zhao, D. (2004a). A method
of protecting relational databases copyright with cloud
watermark. Transactions of Engineering, Computing
and Technology, 3:170–174.
Zhang, Y., Yang, B., and Niu, X.-M. (2006). Reversible
watermarking for relational database authentication.
Journal of Computers, 17(2):59–66.
Zhang, Z. H., Jin, X. M., Wang, J. M., and Li, D. Y. (2004b).
Watermarking relational database using image. In
Proceedings of 3rd International Conference on Ma-
chine Learning and Cybernetics, volume 3, pages
1739–1744.
SIGMAP 2007 - International Conference on Signal Processing and Multimedia Applications
290
