
A MULTI-AGENT ARCHITECTURE FOR ENVIRONMENTAL
IMPACT ASSESSMENT
Information Fusion, Data Mining and Decision Making
Marina V. Sokolova
1,2
and Antonio Fernández-Caballero
1
1
Universidad de Castilla-La Mancha, Departamento de Sistemas Informáticos &
Instituto de Investigación en Informática de Albacete, Campus Universitario s/n, 02071-Albacete, Spain
2
Kursk State Technical University, ul.50 let Oktiabrya, 94, Kursk, 305040, Russia
Keywords: Environmental impact, Multi-agent system, Data fusion, Data handling, Conceptual hierarchy, Decision
support system.
Abstract: The paper introduces an approach to creating a multi-agent architecture for environmental impact
assessment upon human health. As the indicators of the environmental impact we assume water pollution,
indexes of traffic and industrial activity, wastes and solar radiation; and as the human health indicator we
take morbidity. All the data comprise multiple heterogeneous data repositories. The general structure of the
architecture is represented. Thus, the proposed system is logically and functionally divided into three layers,
solving the tasks of information fusion, pattern discovery through data mining, and decision support
making, respectively, which are discussed. The discovered patterns will be used as a foundation for real-
time decision making, which should be of great importance for adequate and effective management by
responsible municipal and state government authorities.
1 INTRODUCTION
The convenience of our research is stated by the fact
that environmental pollution as a result of energy
production, transportation, industry, or lifestyle
choices adversely affects health. The term
“environmental pollution” includes such factors as
ambient and indoor air pollution, water pollution,
inadequate waste management, pesticides, noise and
radiation (Turunen & Latola, 2005; Carrillo &
González-Chávez, 2006). In addition, people usually
face a deteriorated environment which affects their
health and provokes its degradation within a
population due to their life styles and the aggressive
ecological impact. This is demonstrated by
increasing number of endogenous diseases (such as
birth defects, chromosome diseases, etc) and some
classes of exogenous diseases (diseases of the skin
and subcutaneous tissue, endocrine and metabolic
diseases, neoplasm and some others).
The complete set of pollution and health data
forms a complex system, which inhabits all the
necessary characteristics to de modeled by means of
multi-agent systems (MAS) approach, e.g.
modularity, decentralization, changeability, ill
structure and weak predictability (Bradshaw, 1997;
Wooldridge, 2002; López-Jaquero et al., 2005).
Multi-agent approach is to our opinion the best
technique that can help reducing the complexity of
the system by creating module components, which
solve private subtasks, constituting together the
whole goal.
In this paper we introduce our proposal for a
multi-agent architecture for environmental impact
assessment, structured into three levels: Information
Fusion, Data Mining and Decision Making.
2 RELATED WORKS
Multi-agent systems have been in the center of
active research for more than ten years and resulted
in many successful applications. There is a range of
works dedicated to environment and human health,
as described next. Furthermore, the application of
Data Mining (DM) techniques for environmental
monitoring, medicine, social issues is also quite
common. In one of the related works (Athanasiadis
& Mitkas, 2004) it is reported about applying the
219
V. Sokolova M. and Fernández-Caballero A. (2007).
A MULTI-AGENT ARCHITECTURE FOR ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT ASSESSMENT - Information Fusion, Data Mining and Decision Making.
In Proceedings of the Ninth International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems - AIDSS, pages 219-224
DOI: 10.5220/0002346802190224
Copyright
c
SciTePress

software agent paradigm to environmental
monitoring informational system embodied by
MAS. In another paper (Gorodetski et al., 2005) an
approach to agent-based situation assessment system
development for security-related applications is
presented. DM techniques for knowledge
discovering and early diagnostics were utilized to
early intervention to developmentally-delayed
children (Chang, 2006). In the work by Chen and
Bell (2002) the MAS, which is aimed to reveal
correlations between human health and
environmental stress factors (traffic activity,
meteorological data and noise monitoring
information) using wide range of DM methods is
reported about.
Although all the works have demonstrated novel
and promising practical and theoretical outcomes, it
seems to be important to create a MAS for
knowledge discovering and assessment of
environmental tension upon the population by detail
analysis of endogenous and exogenous diseases
cases.
3 THE PROBLEM AREA
The main practical aim of the project is to create an
agent-based system for state situation assessment,
monitoring the environment pollution and following
the corresponding changes in human health,
generating a set of alternatives for successful and
sustainable situation management.
Continuous processing and maintenance of the
information requires essential efforts from the
practitioners and professionals not only while
handling and storing data, but fundamentally when
interpreting it. Actually, it seems very hard to handle
all the data without using DM methods, which can
autonomously dig out all the valuable knowledge
that is embedded in a database without human
supervision, providing a full life-cycle support of
data analysis.
Working with public health information puts on
restrictions caused by the methodologies of data
measurement, the standards currently in use, data
availability, etc. For instance, it is known that
International Statistical Classification of Diseases
and Related Health Problems (ICD) was reviewed
10 times, International Classification of Functioning
and Disability (ICIDH) – 2 times, and local
standards were also reviewed relatively.
In recent years, the tendency to use products and
energy life-cycle indicators in order to assess
ecological impact has appeared. This approach
seems to be effective when evaluating quota of
industrial, chemical and traffic activity impact and
we accept to follow it in our work.
The concept hierarchy was created using
ontology editor Protégé 3.2, and includes the
information about the regions of interest and the
examining indicators of our current study. The
ontology contains the diseases classes in accordance
with the ICD-10 and environmental pollution
indicators: water pollution, dangerous wastes,
transport activity, and industrial activity parameters
revealing dangerous emissions during energy life-
cycle. All this has been detailed by years and other
sub-indexes. In the ontology we have made accent in
regions, which are characterized with some
environmental pollution and human health level.
4 SYSTEM ARCHITECTURE
Fig.1 shows the layout of the model where system
goals and agent roles are indicated. The system
consists of three levels; the first is aimed for meta-
data creation, the second one is responsible for
hidden knowledge discovering, and the third level
provides real-time decision support making, data
distribution and visualization.
4.1 Analysis of the System with Gaia
Methodology
There are many alternative agent-oriented software
engineering methodologies, including MaSE
(DeLoach et al., 2001), Gaia (Wooldridge, 2000),
Agent ULM, Prometheus (Padgham and Winikoff,
2002), Tropos (Giunchiglia et al., 2002), INGENIAS
(Gómez-Sanz & Pavón, 2003) and some others. In
our study analysis was performed following Gaia
methodology.
The analysis has led to the identification of two
roles on the first level, three roles on the second
level and also three roles on the third level of the
MAS. The roles show the detailed functionality of
the system. Agents are responsible for execution of
the extracted activities.
All the protocols are named in a similar way to
indicate that they carry out related functions
consisting in transmission of processed data and
information from one agent to another. The safety
responsibilities for the roles are specified by means
of a list of predicates and states that the activities
have to bring up as results and notify them.
ICEIS 2007 - International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
220

Support in
Decisiуn
Making
Knowledge
discovery
Meta-data
creation
Level 3– “Decision making”
Simulation, Decision making, Alarm generation and Data Distribution
Simulation agents, Decision making agents, Distribution agents
Level 1 – “Information Fusion”
Data Aggregation and Clearing
DB handling agents, DB aggregation agents
Level 2 – “Data Mining”
Impact assessment, Decomposition and Function Approximation
Analysing agents, Evaluation agents
user
web
document
Expert
knowledge
Data Sources
Decision
maker
preferences
Figure 1: The general system schema with main tasks and agent roles.
4.1.1 Level 1: Information Fusion
The first level, as detailed in Fig. 2, is named
“Information fusion” and it acquires data from
diverse sources and in different format types. The
input to this level is through protocol ReturnEI,
which incorporates all the expert knowledge. The
aims of this level include data monitoring,
validation, clearing and fusing into a common meta-
data scheme. These tasks are grouped into two roles:
“Data Fusion” and “Data Clearing”. There are two
general types of agents at this level: DB handling
agents and DB aggregation agents (see Fig.1, level
1), fully controlling data maintenance and executing
all the necessary pre-processing functions at the
every step.
There are two general types of agents at this
level: DB handling agents and DB aggregation
agents (see Fig.1, level 1), fully controlling data
maintenance and executing all the necessary pre-
processing functions at the every step.According to
the scheme of level 1, firstly we fuse incoming raw
data and form a meta-data base, consisting in time
series, which then pass throw the sequential data
processing steps: noise reduction, outlier elimination
and doubling, and inconsistent and missing values
checking. The role “Data Fusion” supposes the
following logical steps:
Vocabulary creation: Create a vocabulary for
the domain of interest.
Hierarchy creation: Create a conceptual
hierarchy by assigning weights to each class
of concepts and by determining relations
among classes.
DB transformation with Ontology Algebra:
Select data from different sources with respect
to hierarchy using ontology algebra.
Meta-data base aggregation: Combine data
together.
Then protocol ReturnDF delivers meta-data base
to agents of role “Data Clearing”, that is to say, to
DBHandling Agents (see Fig.1, level 1). The
DBHandling Agents check data for outliers, smooth
time series and interpolate missing values with
weighted moving averages.
The final meta-data base consists of sequences of
ordered indicator values, measured at equal time
intervals (time-series). It is delivered to the next
layer for knowledge discovering through the
ReturnDC protocol.
A MULTI-AGENT ARCHITECTURE FOR ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT ASSESSMENT: Information Fusion, Data
Mining and Decision Making
221

Level 1
Role Schema
Data Clearing
Role Schema
Data Fusion
Vocabulary
creation
Hierarch
y
creation
DB transformation
with Ontology
Algebra
Protocol
ReturnEI
Expert
Informa
tion
expert
Protocol
ReturnDC
to Level 2
Meta-data base
aggregation
Protocol
ReturnDF
Outliers
clearing
Weighted
moving
avera
g
es
Missing
Values
correction
Figure 2: Layout of the first level.
Level 2
Role Schema
Decomposition
Decomposition
into groups
Correlation
Analysis
Protocol
ReturnD
Role Schema
Function Approximation
Models
acceptance
Library of Data Mining methods
Data Mining method 1
Data Mining method 2
Data Mining method N
. . . . .
Approximation
acceptance
Role Schema
Impact Assessment
PCA
to Level 3
Protocol
ReturnFA
Protocol
ReturnIA
Protocol
ReturnDC
Figure 3: Layout of the second level.
4.1.2 Level 2: Data Mining
The second level is responsible for knowledge
mining from meta-data base (Fig. 3.). There will be
a number of techniques to can be used for data
analysis, all of them provided by Analysis agents.
There are three roles at this level: “Decomposition”,
“Impact Assessment” and “Function
Approximation”, which will be performed by
Analyzing agents and Evaluation agents (as
previously shown in Fig.1, level 2).
Through the role “Impact Assessment”, which
apply the procedure of principal component analysis
(PCA), we aim to reveal interconnections between
health and pollution indicators and qualitatively
evaluate the influence of the latter. The procedure is
sequentially delivered for every class of diseases and
to the totality of environmental pollution indicators
(Sokolova, Rashad & Skopin, 2006).
The other roles solved at level 2 are
“Decomposition” and “Function approximation”.
We will require models for computer simulation,
forecasting and decision making. In order to
decrease the number of simultaneously processed
indicators and be saved from intercorrelation and
multi-colinearity between them, Analyzing agents
initiate a procedure of factor space decomposition by
calculating the correlation matrix and its further
decomposition (Artemenko, et al, 2004). We will
receive a set of independent variables and those that
do not correlate significantly between them and with
certain class of diseases and can be used as factors
for modeling this class of diseases. The protocol
ReturnD transfers information about decomposition
to Analyzing agents.
Then, for every indicator we will extract models
revealing their tendencies by Analyzing agents,
executing the procedure of function approximation,
are based on different methods, which are stored in
ICEIS 2007 - International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
222
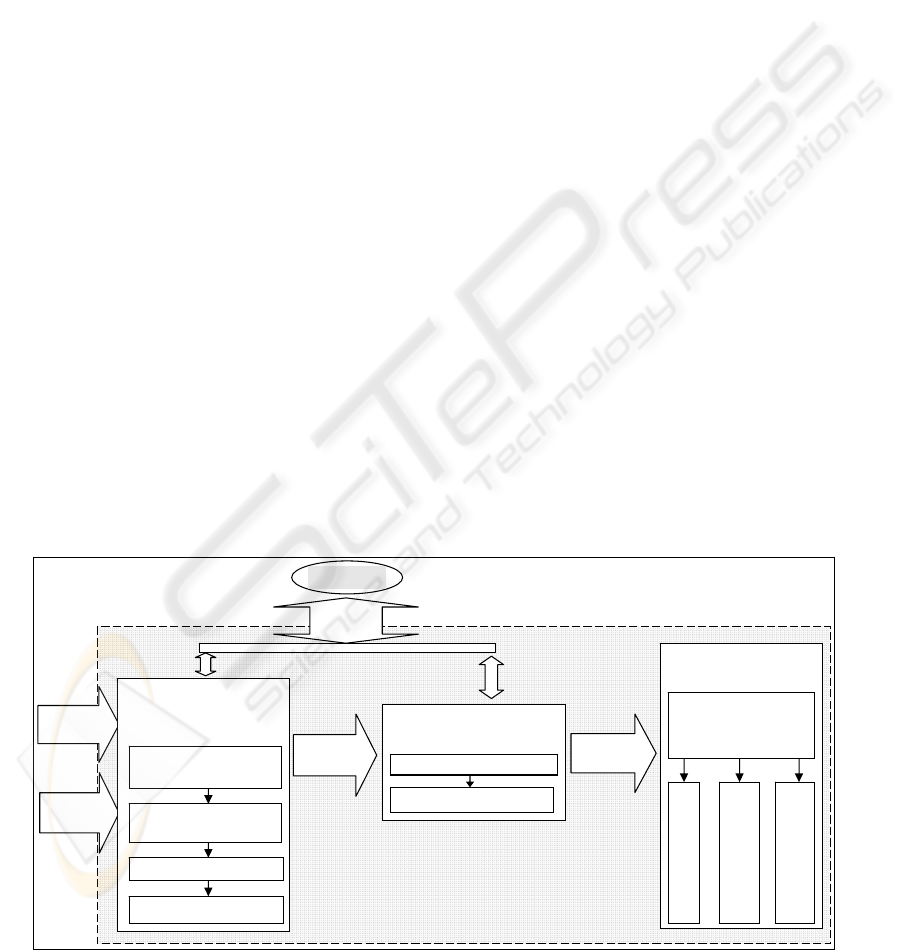
the library of DM methods. For example, for the role
“Function Approximation” several kinds of agents
may be called: statistical ones utilizing regression
modeling for activities DataMiningMethod1 and
DataMiningMethod2, and decision trees techniques
for activity DataMiningMethod3, and another
technique for activity DataMiningMethodN. The
agents execute in interleaved mode. As a result, we
have several different models for every indicator and
we will choose the best one.
The Evaluation agents check if the models are
adequate to data sets. Then Evaluation agents select
the models which best fulfill the requirements. All
the results of data transformations are distributed to
the next level for decision making through protocols
ReturnIA and ReturnFA.
4.1.3 Level 3: Decision Making
The third level carries out a set of procedures
including model evaluation, computer simulation,
decision making and forecasting based on the
models created on the previous level (ReturnFA) and
the results of the PCA (ReturnIA).
The structural schema of this level is given in
Fig. 3. There are three roles: “Computer Simulation
and Forecasting”, “Decision Making” and “Data
Distribution”. Protocols ReturnFA (which delivers
the output of “Function Approximation”) and
ReturnIA (delivering results of “Impact
Assessment”) come from the previous level.
Protocols ReturnCS and ReturnDM deliver
simulation and decision making results for further
processing. The end-user (person making decisions)
interacts with the MAS through the SUI (System-
User Interaction) protocol. The user chooses the
indicator he wants to examine and initiates a
computer simulation.
He may choose the independent variables and
state their values and forecasting period. Then the
information is delivered to Simulation agents (see
Fig.1, level 3) that perform computations for every
model and repeats it until the outputs for all the
models are received. Then SUI protocol delivers
results to the end-user for future decision making.
The Decision making agents (see Fig.1, level 3),
in agreement with their believes, recommend the
most optimal variants of computer simulation, which
are selected by standard decision making criteria
(Bayes, minimax, Hurvitz, etc) to the user. Decision
making agents also control the forecasted values. In
case they exceed or are likely to exceed the
permissible levels, an alarm message will be
generated, visualized and sent to the user.
At the last step, the information is delivered to
the final destination – end-users and applications in
the form of web messages, textual files, e-mails and
visual presentations. This level transforms the
revealed information including results of computer
simulation, forecasting and decision making into
understandable and multiple forms. These tasks are
realized by the Distribution agents, which operate
on combining textual and graphical descriptions of
recommendations.
User
Level 3
Protocol
SUI
Protocol
ReturnIA
Protocol
ReturnFA
Role Schema
Decision Making
Protocol
ReturnCS
Role Schema
Computer Simulation
and Forecasting
Protocol
ReturnDM
Role Schema
Data Distribution
Generate alarm alert
Making forecast
Simulating every
model
Stating values for
simulation
Choising the models
Calculating criterias
Create module with
textual and graphical
information
Create document
Create web-
p
a
g
e
Create e-mail
Figure 4: Layout of the third level.
A MULTI-AGENT ARCHITECTURE FOR ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT ASSESSMENT: Information Fusion, Data
Mining and Decision Making
223

5 CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE
WORK
In this paper we have introduced an approach to
developing an intelligent environmental situation
monitoring and evaluation decision support through
MAS, which uses software and works with
heterogeneous data sources. We discussed the nature
and peculiarities of experimental data and expert
knowledge used in our system, described an
ontology and presented a general system
architecture. In accordance with requirements of
Gaia methodology we extracted and explained in
detail the roles and associated set of interactions.
The supposed approach to environmental impact
assessment through multy-agent system enables to
identify and evaluate quantitatively which certain
type of pollutants affects health, approximate and
forecast the tendencies of situation development and
allows a user to exploit the inherent potentialities of
real-time simulation. The software agents use data
mining methods for knowledge discovery, which
will be used as a foundation for support in decision
making and recommendation generating. This
should be of great importance for adequate and
effective management by responsible municipal and
state government authorities.
The system developed is being used as a pilot
project in Spanish University of Castilla-La Mancha
and Institute of Regional Development of Albacete.
In our future work we will concentrate on working
out the MAS and its implementation into practical
use.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Marina V. Sokolova is the recipient of a
Postdoctoral Scholarship (Becas MAE) awarded by
the Agencia Española de Cooperación Internacional
of the Spanish Ministerio de Asuntos Exteriores y de
Cooperación.
REFERENCES
Agent UML: http://www.auml.org/
Athanasiadis, I.N., Mitkas, P.A. (2004). An agent-based
intelligent environmental monitoring system. In:
Management of Environmental Quality, 15, 238-249.
Artemenko, M., Hudec, O., Lapina, T. and Sokolova,
M.V, (2004). The information-analytical program tool
for regional decision making in social sphere. In:
Telecommunications, 9, 42-44.
Bradshaw, J.M. (1997). Software Agents. The MIT Press.
Carrillo González, R., and González-Chávez, M.C.A.
(2006). Metal accumulation in wild plants surrounding
mining wastes. Environmental Pollution, 144, 84-92.
Chang, C.L. (2006). A study of applying data mining to
early intervention for developmentally-delayed
children. Expert Systems with Applications. In press.
Chen, H., Bell, M. (2002). Instrumented city database
analysts using multi-agents. Transportation Research,
Part C, 10, 419–432.
DeLoach, S.A., Wood, M.F., and Sparkman, C.H. (2001).
Multiagent systems engineering. International Journal
of Software Engineering and Knowledge Engineering,
11, 231-258
Giunchiglia, F., Mylopoulos, J., and Perini, A. (2002). The
Tropos software development methodology:
Processes, models and diagrams. In: Third
International Workshop on Agent-Oriented Software
Engineering, Juna.
Gómez-Sanz, J., and Pavon, J. (2003). Agent oriented
software engineering with INGENIAS. Lecture Notes
in Computer Science, 2691 394–403.
Gorodetsky, V., Karsaeyv, O., Samoilov, V. (2005).
Multi-agent and data mining technologies for situation
assessment in security-related applications. In: Dunin-
Keplicz, B., Jankovski, A., Skowron, A., and Szczuka,
M. (eds.), Monitoring, Security, and Rescue
Techniques in Multi-agent Systems, 411-422.
International Classification of Diseases (ICD):
http://www.who.int/classifications/icd/en/
López-Jaquero, V., Montero, F., González, P., and
Fernández-Caballero, A. (2005). A multi-agent system
architecture for the adaptation of user interfaces.
Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence, 3690, 583-586.
Padgham, L. and Winikoff, M. (2002). Prometheus: A
pragmatic methodology for engineering intelligent
agents. In: Proceedings of the OOPSLA 2002
Workshop on Agent-Oriented Methodologies, Seattle.
Protégé: http://protege.stanford.edu/
Sokolova, M.V., Rashad J. Rasras, and Skopin, D. (2006).
The artificial neural network based approach for
mortality structure analysis. In: American Journal of
Applied Science, 3, 1698-1702.
Turunen, M., and Latola, K. (2005). UV-B radiation and
acclimation in timberline plants. Environmental
Pollution, 137, 390-403.
Wooldridge, M. (2002). An Introduction to Multiagent
Systems. John Wiley & Sons.
Wooldridge, M., Jennings, N.R., Kinny, D. (2000). The
Gaia Methodology for Agent-Oriented Analysis and
Design. Journal of Autonomous Agents and Multi-
Agent Systems, 3, 285-312.
ICEIS 2007 - International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
224
