
AN ORDER ALLOCATION MODEL IN VIRTUAL ENTERPRISES
BASED ON INDUSTRIAL CLUSTERS
Fangqi Cheng, Feifan Ye
School of Mechanical Engineering, Shanghai JiaoTong University, 800 Dongchuan Street, Shanghai, P. R. China
Faculty of Engineering, Ningbo University, 818 Fenghua Street, NingBo, P.R. China
Jianguo Yang
School of Mechanical Engineering, Shanghai JiaoTong University, 800 Dongchuan Street, Shanghai, P. R. China
Keywords: Industrial Cluster, Virtual Enterprise, Order Allocation, Evolutionary Programming, Partner Selection.
Abstract: To build virtual enterprise based on an industrial cluster is one of the most important ways to improve the
agility and competitiveness of manufacturing enterprises. One of the key factors towards the success of
virtual enterprises is the correct selection of cooperative partners. The approach proposed for order
allocation and partner selection is composed of two stages: task-resource matching and quantitative
evaluation. In the first stage the potential candidates are identified and in the second stage evolutionary
programming is applied. The architecture for information evaluation and order allocation is studied for the
proposed approach. The target function, in which the load rate of candidate enterprise is taken as the main
variable, is developed, and a simplified example is used to verify the feasibility of the proposed approach.
The result suggests that the proposed model and the algorithm obtain satisfactory solutions.
1 INTRODUCTIOIN
The manufacturing industry in the 21st century is
faced with a rapidly changing market demands and
global competition. Customers require that
manufacturing companies make more products with
high quality, low cost, quick delivery, short lead
time, perfect service, as well as the personalization
of the products. From the early 90s of last century,
agile manufacturing has become a popular
philosophy and an important enabling tool.
Partner selection and order allocation are very
important problems in virtual enterprise. Early
literatures on partner selection have been mainly
qualitative and focused on methodological aspects.
Then quantitative methods are employed to study
partner selection problem. Tulluri and Baker (Talluri
S and Baker R.C, 1996) proposed a two-phase
mathematical programming approach for partner
selection by designing a virtual enterprise where the
factors of cost, time and distance were considered.
Zhao Fuqing (Zhao Fuqing et al, 2005) proposed a
multi-objective optimization model and took into
account the factors of cost, due date, and the risk of
failure at the same time. Order allocation problem in
virtual enterprise is attracting increasing attention in
recent years. A. Hammami proposed a method to
calculate satisfying routes for customers’ orders
within manufacturing networks of small-medium
enterprises (A. Hammami et al, 2003). Ruengsak
Kawtummachai et al constructed an algorithm to
deal with order allocation and minimize the total
purchasing cost in a supply chain (Ruengsak
Kawtummachai et al, 2005).
The above literatures studied partner selection and
order allocation separately. However, order
allocation is sometime coupled with partner
selection in a virtual enterprise. Moreover,
production load rate of each entity in virtual
enterprise is one of most important factors for
partner selection and order allocation problems.
Industrial clusters are generally defined
as geographic concentration of interconnected
companies and institutions in particular business
field according to the relationship of specialization
445
Cheng F., Ye F. and Yang J. (2007).
AN ORDER ALLOCATION MODEL IN VIRTUAL ENTERPRISES BASED ON INDUSTRIAL CLUSTERS.
In Proceedings of the Ninth International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems - DISI, pages 445-448
DOI: 10.5220/0002350304450448
Copyright
c
SciTePress
and collaboration. In China, there are many typical
industrial clusters, such as plastics injection machine
industry in Ningbo, shoe making companies in
Wenzhou, Zhejiang province, and so on.
2 ORDER ALLOCATION
2.1 Problem Description
When one of the companies in an industrial cluster
gains an order, and if it is too large for its own
capacity, a good way for this company (dominant
company) is to allocate order among a group of
manufacturing companies in the cluster. The
dominant company needs to review the core
competencies and the production load of the
candidates in the cluster and decide how to allocate
the order. An order allocation oriented to the
horizontal virtual enterprise model based on
evolutionary programming is proposed according to
the above two aspects of information in this paper.
This approach consists of two stages:
task-resource matching and quantitative evaluation.
In task-resource matching stage the dominant
company search for the candidates according to the
product’s manufacturing features and the candidates’
resources information. In the light of the parameters
in the model, evolutionary programming is applied
to optimize partner selection and order allocation in
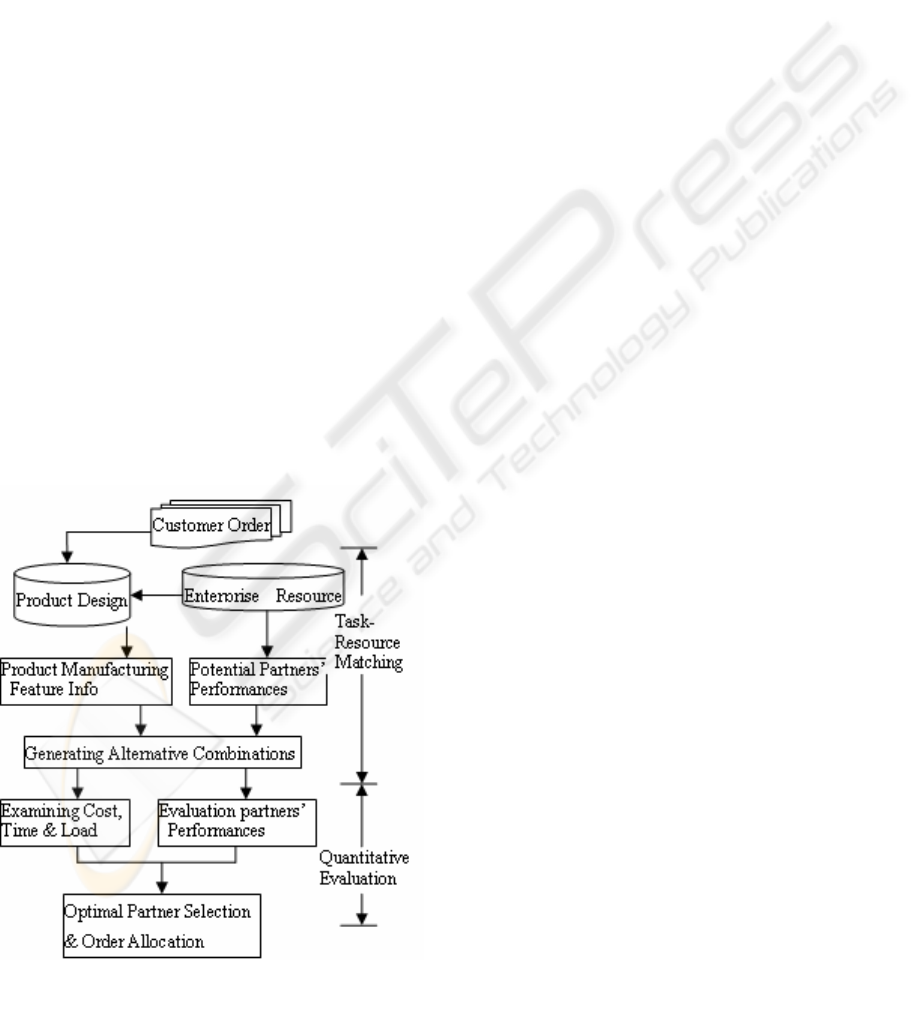
the second stage. Figure 1 illustrates the relationship
of two stages.
2.2 Task-Resource Matching
Task-resource matching means that products’
features should match companies’ manufacturing
capacities. By using definite search algorithm, all the
potential companies that are qualified for the
manufacturing tasks will be found. For achieving the
above procedure, companies’ manufacturing
resources database should be built to improve the
efficiency and effectiveness of the search and match.
The requirements of search and match are that the
manufacturing capacities of companies’ combination
cover the requirements of collaboration tasks.
2.3 Quantitative Evaluation
To identify the proper partners and assign
corresponding volume of orders is the key task of
the second stage. An evolutionary programming
method is used to gain the results.
The problem can be described as follows. There are
n candidates in an industrial cluster, and the target
function and the constraints are modeled as follows:
=
infM max{
n21
T,,T,T " } •
i
n
1i
i
Cnum
∑
=
(1)
.t.s =
∑
=
n
1i
ii
xnum 100
(2)
))1(CP/(numT
i
iii
ρ−•=
(3)
Where:
n,,2,1i "
=
;
i
T is the lead time of candidate
i ;
i
num is the volume of products corresponding
candidate
i ;
i
C is the cost of each product in
candidate
i ;
i
x is the candidate which is selected to
combine into the virtual enterprise;
i
CP is the
competences of candidate
i ;
i
ρ is the production
load rate of candidate
i .
For the evolutionary programming, the natural
Figure 1: An outline of the approach for optimal model.
ICEIS 2007 - International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
446

number string is selected as the gene description.
Let
}w,,w,w{w
n21
"= , where
i
w is a natural
number between 0 and
i
m . That stands for the
number of volume of orders corresponding
candidate
i .
2.4 System Architecture
Based on the order allocation oriented to the
horizontal virtual enterprise model mentioned above,
the system architecture was proposed for
information evaluation and order allocation system
(IEOAS) as shown in Figure 2, which contains five
function modules, and a knowledge base and
partners’ databases.
Figure 2: Architecture of IEOAS.
3 NUMERICAL EXAMPLE
To illustrate the approach presented in this paper, a
simplified example by using evolutionary
programming is described below.
There are the parameters of the numerical example.
Six candidates and the corresponding parameters
were given shown in Table 1.
Table 1: Performance index of each candidate.
CCN
Items
1 2 3 4 5 6
i
C
0.75 0.35 0.98 1.05 2.00 1.56
i
CP
10 30 24 37 9 45
i
ρ
0.30 0.80 0.75 0.65 0.12 0.97
Note: CCN: candidates code number in Table 1.
The total number of orders is 100 units;
The population size is 20;
The condition to end iterative process is 10000.
The evolutionary programming can obtain the
second-optimal solution and cost less time than
many other programming methods such as integer or
mixed integer programming if the size of problem is
very large. The target function converges 0.8981
when the iterative number is 1930, and the quantum
of each candidate is allocated. The result is shown in
Figure 3.
Figure 3: Target function value change curve.
Since our optimal target is the lead time and cost, the
lead time of each enterprise is almost equal shown as
Table 2. From comparing the lead time of each
candidate, it is evident that the deviation among the
candidates is very small. The biggest value is 2.57
and the smallest value is 2.02.
Table 2: The results of order & Time.
Items 1 2 3 4 5 6
i
ρ
0.30 0.80 0.75 0.65 0.12 0.97
i
num
18 15 15 33 16 3
i
T
2.57 2.50 2.50 2.55 2.02 2.22
AN ORDER ALLOCATION MODEL IN VIRTUAL ENTERPRISES BASED ON INDUSTRIAL CLUSTERS
447

4 CONCLUSIONS
In order to improve the agility and competitiveness
of manufacturing companies with similar products in
industrial clusters, horizontal virtual enterprises are
suggested to be an effective enabler. During the
development and operation of the virtual enterprises
based on industrial clusters, a two-stage approach is
employed, in which there are a task-resources
matching and a quantitative evaluation stages. In the
second stage, evolutionary programming is applied.
Meanwhile, the architecture of network system is
studied in relation with the algorithm. The study
shows that production load rate should be considered
as a very important factor in partner selection and
order allocation to achieve the equilibrium of
production load in all the involved enterprises. Then
the overall improvement of agility and
competitiveness can be obtained within the
enterprises.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This paper is based upon work funded by Zhejiang
Provincial Natural Foundation of China under Grant
No. Z604342
REFERENCES
A. Hammami, P. Burlat, J.P. Campagne, 2003. Evaluating
orders allocation within networks of firms.
International Journal of Production Economics. vol. 86,
pp. 233-249.
Ruengsak Kawtummachai, Nguyen Van Hop, 2005. Order
allocation in a multiple-supplier environment.
International Journal of Production Economics. 93-94,
pp. 231–238.
Talluri S, Baker R.C., 1996. Quantitative framework for
designing efficient business process alliances. In:
Proceedings of the 1996 International Conference on
Engineering and Technology Management.
Piscataway. pp. 656–661.
Zhao Fuqing, Hong Yi, Yu Dongmei, 2005. A
multi-objective optimization model of the partner
selection problem in a virtual enterprise and its
solution with genetic algorithms. International Journal
of Advanced Manufacturing Technology.
ICEIS 2007 - International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
448
