
APPLYING INTEGRATED EXPERT SYSTEM
IN NETWORK MANAGEMENT
Antonio Martín, Carlos León, Juan I. Guerrero and Francisco J. Molina
Dpto. Tecnología Electrónica, Universidad de Sevilla, Avda. Reina Mercedes s/n., Sevilla, Spain
Keywords: Expert System, TMN, GDMO, Knowledge Representation, Management Information Base.
Abstract: The management of modern telecommunications networks is becoming an increasingly demanding task that
is difficult to implement using present traditional methods even assisted by conventional automation
techniques. Integration of advanced Artificial Intelligence (AI) technology into existing and future network
management system may resolve some of the difficulties. The goal of this research is to develop an
integrated expert system for management network applications. The emphasis of this research is to provide
a broad view of intelligent systems by capturing the knowledge of human experts and using a modular
approach that integrates the knowledge management and network resources specifications. For this purpose,
an extension of OSI management framework specifications language has been added and investigated. The
advantage of integrating both is that a large problem can be broken down into smaller and manageable sub-
problems/modules. Through modification of existing resources or addition of new resources, the integrated
expert system can be conveniently expanded in the future to cover the latest research findings and updated
standards of network communications.
1 INTRODUCTION
Current communications networks support a large
demand of services for which the traditional model
of network management is inadequate. The network
management has evolved: local systems with
autonomous administration, heterogeneous
management and integrated management. The
traditional expert management uses management
knowledge and management information separately.
It is necessary to develop new models, which offer
more possibilities. We propose a new evolution
called Integrated Management Expert Systems.
We propose a technique which integrates the
Expert System completely within the Management
Information Base (MIB) (Morris, 2003). Integrating
both elements is the main purpose of our work. This
task is achieved by integrating knowledge base of
expert system within the management information
used to manage a network. For this purpose, an
extension of OSI management framework
specifications language has been added and
investigated in this study. A new property named
RULE has also been added, which gathers important
aspects of the facts and the knowledge base of the
embedded expert system.
By integrating the knowledge base in resources
specifications, expert system has the power to
provide diagnosis of fault network, which can assist
civil engineering trainees, inspectorate staff and
professional. The NOMOS+ is a prototype
implemented through this thesis as a system based
on integrated expert rules.
2 NETWORK MANAGEMENT
At the moment there are two main management
models: OSI and Internet. Both network
management systems operate using client/server
architecture. Four fundamental concepts of these
models are (Clemm, 2006):
- Manager or Manager Role: In the network
management model a manager is an unit that
provides information to users, issues requests to
devices in a network, receives responses to the
requests and receives notifications.
- Agent or Agent Role: An agent is an unit that is
part of a device in the network that monitors and
maintains status about that device. It can act and
respond to requests from a manager.
- Network Management Protocols: Managers and
agents require some form of communication to issue
101
Martín A., León C., I. Guerrero J. and J. Molina F. (2007).
APPLYING INTEGRATED EXPERT SYSTEM IN NETWORK MANAGEMENT.
In Proceedings of the Ninth International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems - AIDSS, pages 101-106
DOI: 10.5220/0002361201010106
Copyright
c
SciTePress

their requests and responses. SNMP is the protocol
used to issue requests and receive responses in a
management model Internet. CMIP is the protocol
used in management model ISO.
- Management Information Base (MIB): In
addition to being able to pass information back and
forth, the manager and the agent need to agree on
and understand what information the manager and
agent receive in any exchange. This information
varies for each type of agent. The collection of this
information is referred to as the management
information base. A manager normally contains
management information describing each type of
agent the manager is capable of managing. This
information would typically include Internet MIB
definitions and ISO definitions for managed objects
and agents.
In the Open System Interconnection (OSI)
systems management the information architecture is
based on an object-oriented approach and the
agent/manager concepts that are of paramount
importance.
After this brief introduction to management
elements in common to OSI an Internet models, we
will approach our research in the integration of
knowledge management into MIB in the OSI
management model.
We are studying the way to integrate the expert
knowledge in the management Internet model.
Internet management model doesn’t use the Object
Oriented Programming such as it is used by the OSI
model. This is one of the reasons for the Internet
model simplicity. The definitions contain objects,
specified with ASN.1 macros.
The resources specifications can only be groups
of scalar variables and cells tables in spite of not
being an Object Oriented Programming model, we
can use the tables as classes where the attributes are
the table columns and every file contains an instance
of the class. The same as in OSI every object has an
OID associated identifier.
3 MANAGEMENT MODEL OSI
The description of management information has two
aspects. First, a Structure of Management
Information (SMI) defines the logical constitution of
management information and how it is identified and
described.
Second, the MIB, which is specified using the
SMI, defines the actual objects to be managed. The
MIB is a conceptual repository of management
information. It is an abstract view of all the objects
in the network than can be managed. In OSI, SMI
provides the Guidelines for Definition of Managed
Objects (GDMO), for definition objects contained in
the MIB (ISO, 1992).
A managed object is the OSI abstract view of a
logical or physical system resource to be managed.
These special elements provide the necessary
operations for the administration, monitoring and
control of the telecommunications network. The
managed objects are defined according to the
International Standardization Organization (ISO)
Guidelines for the Definition of Managed Objects
(GDMO), which defines how network objects and
their behaviour are to be specified, including the
syntax and semantics.
GDMO has been standardized by ITU
(International Telecommunication Union) in ITU-T
X.722 and is now widely used to specify interfaces
between different components of the TMN
(Telecommunication Management Network)
architecture (ITU-T, 1996).
GDMO is organized into templates, which are
standard formats used in the definition of a
particular aspect of the object. A complete object
definition is a combination of interrelated templates.
There are nine of these templates: class of managed
objects, package, attribute, group of attributes,
action, notification, parameter, connection of name
and behaviour.
4 STANDARD GDMO+
The elements that at the moment form the GDMO
standard do not make a reference to the knowledge
base of an expert system. To answer these questions,
it will be necessary to make changes on the template
of the GDMO standard. We present an extension of
the standard GDMO, to accommodate the intelligent
management requirements.
We describe how to achieve this goal using a
new extension called GDMO+. This extension
presents a new element RULE, which defines the
knowledge base of the management expert system.
This template groups the knowledge base supplied
by an expert in a specific management dominion. It
allows the storage of the management knowledge in
the definition of the resources that form the system
to be managed.
The standard that we propose contains the
singular template RULE and its relations to other
templates. Two relationships are essential for the
inclusion of knowledge in the component definition
of the network: Managed Object Class and Pack-
age template, Figure 1.
ICEIS 2007 - International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
102

In the standard we propose, both templates have
the new property RULES. Let us study both
relationships.
4.1 Managed Object Class Template
This template is used to define the different kinds of
objects that exist in the system. The definition of a
Managed Object Class is made uniformly in the
standard template. This way we ensure that the
classes and the management expert rules defined in
system A can be easily interpreted in system B.
<class-label> MANAGED OBJECT CLASS
[DERIVED FROM <class-label> [,<class-label>]*;]
[CHARACTERIZED BY <package-label>
[,<package-label]*;]
[CONDITIONAL PACKAGES
<package-label> PRESENT IF condition;
,<package-label>] PRESENT IF condition]*;]
REGISTERED AS object-identifier;
DERIVED FROM plays a very important role,
when determining the relations of inheritance which
makes it possible to reutilize specific characteristics
in other classes of managed objects.
This template can also contain packages and
conditional packages, including the clauses
CHARACTERIZED BY and CONDITIONAL
PACKAGES (Hebrawi, 1995).
4.2 Package Template
This template is used to define a package that
contains a combination of many characteristics of a
managed object class: behaviours, attributes, groups
of attributes, operations, notifications and
parameters. In addition to the properties indicated
above, we suggest the incorporation of a new
property called RULES, which contains all the
specifications of the knowledge base for the expert
system.
<package-label> PACKAGE
[BEHAVIOUR <behaviour-label>
[,<behaviour-label>]*;]
[ATTRIBUTES
<attribute-label>propertylist[,<parameter-label>]*
[,<attribute-label>propertylist[,<parameter-label>]*]*;]
[ACTIONS <action-label> [<parameter-label>]*
[<action-label> [<parameter-label>]*]* ;
[NOTIFICATIONS
<notification-label> [<parameter-label>]*
[<notification-label> [<parameter-label>]*]* ;]
[RULES <rule-label> [,<rule-label>]*;]
REGISTERED AS object-identifier;
All the properties that we define in the package
will be included later in the Managed Object Class
template, where the package is incorporated. A same
package can be referenced by more than one class of
managed objects.
The property RULES allows a treatment similar
to the other properties, including the possibility of
inheritance of rules between classes. Like the rest of
the other properties defined in a package, the
property RULES need a corresponding associated
template.
4.3 Expert Rule Template
Knowledge is represented in production rules or
simply rules. Rules are expressed as IF-THEN
statements which are relatively simple, very
powerful as well as very natural to represent expert
knowledge. A major feature of a rule-based system
is its modularity and modifiability which allows for
incremental improvement and fine tuning of the
system with virtually no degradation of
performance. The structure of the RULE template is
shown here:
<rule-label> RULE
[PRIORITY <priority>;]
[BEHAVIOUR <behaviour-label>[,<behaviour-label>]*;]
[IF occurred-event-pattern [,occurred-event-pattern]*]
[THEN sentence [, sentence]* ;]
REGISTERED AS object-identifier;
In our study case the template RULE permits the
normalized definition of the specifications of the
expert rule to which it is related. This template
allows a particular managed object class to have
properties that provide a normalized knowledge of a
management dominion.
The following elements compose a normalized
definition of an expert rule.
- <rule-label>: This is the name of the management
expert rule and RULE, a key word indicates the type
of template.
- BEHAVIOUR: This construct is used to extend
the semantics of previously defined templates.
Figure 1: Relations between proposed standar
d
templates.
APPLYING INTEGRATED EXPERT SYSTEM IN NETWORK MANAGEMENT
103
- PRIORITY: This represents the priority of the rule,
that is, the order in which competing rules will be
executed.
- IF: It contains all the events that must be true to
activate a rule. Those events must be defined in the
Notification template. We can add a logical
condition that will be applied on the events occurred
or their parameters.
- THEN: This gives details of the operations
performed when the rule is executed. Those
operations must be previously defined in the Action
template. These are actions and diagnoses that the
management platform makes as an answer to
network events occurred.
- REGISTERED AS is an object-identifier: A clause
identifies the location of the expert rule on the ISO
Registration Tree. The identifier is compulsory.
5 APPLICATION OF GDMO+
To show the viability of our proposal, we proceed to
the study and building of a management Expert
System, so that the corresponding knowledge base
begins to belong to the normalized proprieties
information defined by the managed resources. For
this we use an expert system developed for the
management of a data network belonging to an
electrical company. The definitions of the employed
resources and the expert knowledge base use an
unique specification. To define these specifications
we will use the syntax and rules investigated in
GDMO+ standard.
We present a rule-based expert system applied to
the fault diagnosis in telecommunication system of a
power utility. The communications systems
employed to implement the integrated intelligent
management prototype belongs to the SEVILLANA-
ENDESA (CSE) a major Spanish power utility. The
current management and control of that network is
based on an Expert System called NOMOS
developed by the Electronic Technology Department
in the University of Seville (Leon, 1999). Our tool
understands transceivers and multiplex equipment.
The knowledge base of this system is integrated
in the specifications of the resources using for that
purpose our GDMO+ proposal. These new
specifications contain management information of
managed resources and include also the set of expert
rules that provides the knowledge base of the expert
system.
5.1 Related Work
Part of SEVILLANA-ENDESA's long-distance
traffic is controlled by a wireless System distributed
throughout the CSE network. Expert systems are
part of the system dedicated to the management of a
power utility's communications system, which we
call NOMOS+ (Martin, 2006). It has been employed
a Sun Blade 150 Workstation to program the expert
system. The resultant expert system has about 200
rules. NOMOS+ is an extension for intelligent
decision-making and diagnostic reasoning controlled
by its own integrated expert system. NOMOS+ is the
first production software written and integrated in
GDMO+.
NOMOS+ is implemented in Brightware's
ART*Enterprise, an expert system shell. The
experience with NOMOS+ is that ART*Enterprise is
a useful tool for developing expert systems.
5.2 The System Features
NOMOS+ operations, uses a supervision system
called SSC (Communication Supervisory System).
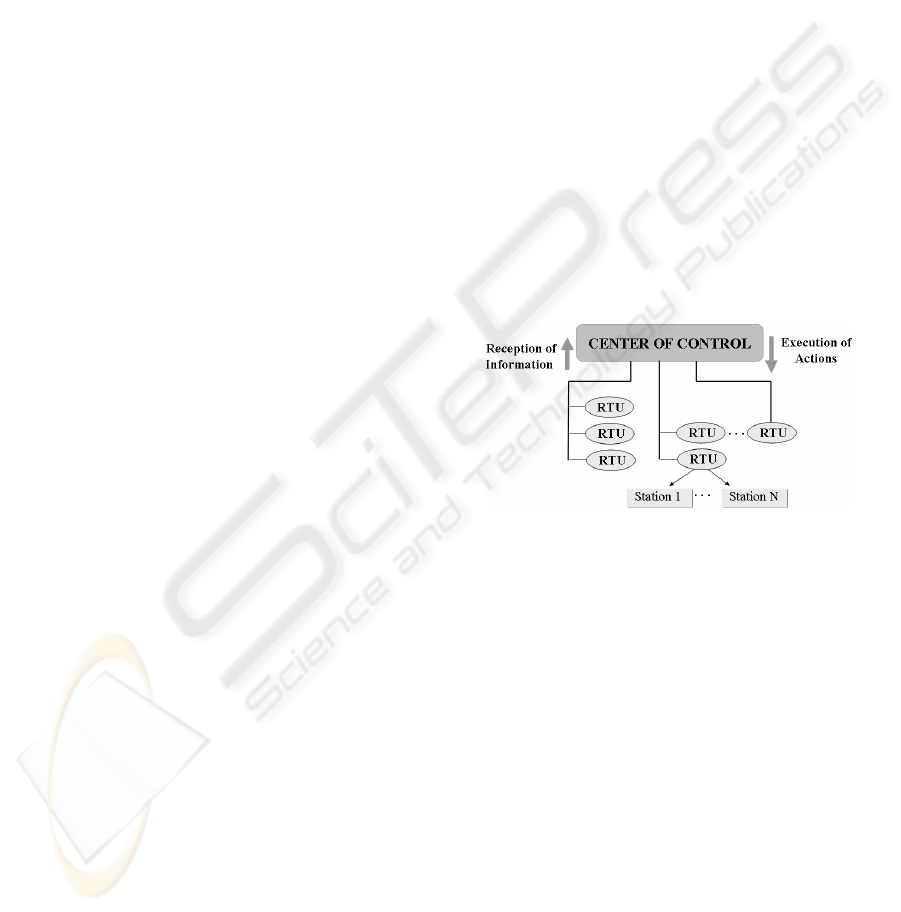
Figure 2: Communication Supervisory System.
This system can monitor, in real time, the
network's main parameters, making use of the
information supplied by a Supervisory Control and
Data Acquisition (SCADA), formed by a Control
Centre (placed on the main CSE building), and
Remote Terminal Units (RTUs) installed into
different stations. The use of a SCADA system is
due to the management limitations of network
communication equipment.
The SSC allows the operator to acquire
information, alarms or digital and analogical
parameters of measure, registered on each RTU.
Starting from the supplied information, the operator
is able to undertake actions through the SSC in order
to solve the failures that could appear or to send a
technician to repair the stations equipment (Garcia,
2001).
ICEIS 2007 - International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
104

5.3 The System Architecture
Our tool has three major components:
- The inference engine: This is the processing unit
that solves any given problems by making logical
inferences on the given facts and rules stored in the
knowledge base. In our tool we used the
ART*Enterprise. By using an existing general
purpose tool we were able to build a standard and
extensible platform with proven performance and
quality.
- The knowledge base: This is a collection of expert
rules and facts expressed in the ARTScript
programming language ART*Enterprise.
The knowledge base contains both static and
dynamic information and knowledge about different
network resources and common failures. The
knowledge base of our system can be extended by
adding new higher level rules and facts. To this
purpose we can employ user interface.
- The user interface: This controls the inference
engine and manages system input and output. The
user interface of our tool contains a preprocessor for
parsing GDMO+ specification files, a set of input
and output handling routines for managing the
system. Also, the user interface components allow
administrators to inspect the definitions of
management object classes interactively. The user
interface allows to modify and to include new expert
management rules in the managed objects definition.
5.4 A Management Expert Rule
Next paragraph shows an example of expert rules
integration in the GDMO+ proposed standard. This
defines a Managed Objects Class:
radioTransceptorCTR190, which defines the
properties corresponding to the radio transceiver
devices. This class includes all the specifications
corresponding to the resource.
radioTrasnceptorCTR190 MANAGED OBJECT CLASS
DERIVED FROM “rec.X721”:top;
CHARACTERIZED BY transceptorPackage;
RULES powerErrorCTR190, linkCTR190
REGISTERED AS {nm-MobjectClass 1};
powerErrorCTR190 RULE
PRIORITY 3;
BEHAVIOUR powerErrorCTR190Behaviour;
IF (?date ? ?local 7_F_ALIM_2 ?remote ALARM)
THEN (“Severity:" PRIORITY),
(“Diagnostic: It damages in the electric feeding
of the station” ?local),
(“Recommendation:
To revise the electric connection”, ?local);
REGISTERED AS {nm-rule 1};
linkCTR190 RULE
PRIORITY 4;
BEHAVIOUR linkCTR190Behaviour;
IF (?date ?time1 ?local 7_TX_C2 ?remote ALARM
(?date ?time2 ?local 7_TX_C2 ?remote ALARM
& : (<(ABS(? ?time1 ?time2)) 1.00))
THEN (“Severity:" PRIORITY) ,
(“Diagnostic: “Mistake in transmission ”, ?local),
(“Recommendation “Revise transceiver”);
REGISTERED AS {nm-rule 2);
The most important properties that we can
indicate are the two expert rules that have been
associated with the defined class by means of the
RULES clause. The two rules are defined by using
the RULE template.
When there are alarms in the network, the
integrated expert system makes a study of the events
produced.
...
(31/01 1115.1836 Station1 7_TX_C2 Station4 ALARM) n
(31/01 1116.2142 Station1 7_TX_C2 Station4 ALARM) n+1
...
After an analysis, the management actions in the
expert rules are executed. The connection error
returns the following error messages, indicate
problems that require corrective action.
The first rule powerErrorCTR190, is in charge of
detecting failures in the power supply of the device;
the second rule linkCTR190, is devoted to the
detection of errors in the data transmission module.
FIRE 1: linkCTR190 f-2
Severity 4.
Diagnostic: Mistake in transmission Station4.
Recommendation: Revise transceiver.
1 rules fired.
Run time is 0.074 seconds, 27.0270 Rules/Sec.
6 PROTOTYPE VALIDATION
Validation is essential to the decision-making
success of NOMOS+ and to its continued use.
Validation constitutes an inherent part of the
knowledge based expert system development for
NOMOS+ and is intrinsically linked to the
development cycle (Giarratano, 2005).
To verify the system we feed it with an alarms
arbitrary amount. NOMOS+ has been validated with
respect to the following aspects: system validation
using test cases, validation by case studies,
validation against human experts, validation against
tough cases and validation on site, etc. The result of
this proof is included in Table 1.
APPLYING INTEGRATED EXPERT SYSTEM IN NETWORK MANAGEMENT
105

Table1: Prototype Testing Results.
Alarms
Initial Number
Number
After Filtration
Filtered
Alarms
Fired Rules
Proceeding
time
Rules/Sec.
Indications
to the Operator
100 1 99 51 0,118 Sec. 432,2034 1
200 10 95 102 0,412 Sec. 247,5728 6
300 31 89,6 155 1,250 Sec. 124,0000 20
400 31 92,25 201 1,438 Sec. 139,7775 16
500 32 93,6 254 2,975 Sec. 85,3782 19
600 38 93,66 293 5,249 Sec. 55,8202 16
700 44 93,71 346 17,982 Sec. 19,2415 18
800 55 93,125 394 26,938 Sec. 14,6262 23
From these result we can establish the following
conclusions:
- The expert system, with over 200 operation rules,
has produced excellent results which, after extensive
field-testing, proved to be capable of filtering 90%
of produced alarms with a precision of 95% in
locating them.
- As noted above, the NOMOS+ performs
satisfactorily with about a 95% rate of success in
real cases.
- The speed of the system improves diminishing the
number of alarms on which the rest of rules act.
It is noted that the performance of NOMOS+
depends considerably in the facts happened. In the
same way the more information is input, chances of
diagnosing the likely causes of the problems in the
network is increased.
7 CONCLUSIONS
Current networks are very complex and demand
ever-increasing levels of quality, making their
management a very important aspect to take into
account. Network management systems are based on
Client/Server architecture, and consist of a Manager
(offering user interface for the network
administrator), Agents (on managed network
devices), a protocol (in between the Manager and the
Agents) and a Management Information Base
(describing the properties of the managed device).
The traditional model of network administration has
certain deficiencies that we have tried to overcome
by using a model of intelligent integrated
management. To improve the techniques of expert
management in a communications network, we
propose the possibility of integrating and
normalizing the expert rules of management within
the actual definition of the managed objects.
Through the integration of the knowledge within the
new extension the GDMO+ standard, we can
simultaneously define the management information
and knowledge. Thus, the management platform is
more easily integrated and allows a better adaptation
for the network management.
To achieve this goal we build a prototype, an
expert system integrated is developed as a rule-based
expert system which is a computer program using
integrated IF-THEN rules.
We conclude pointing out an important aspect of
the obtained integration: by using only and
exclusively the extended GDMO specification, the
administration platform will be able to obtain the
management information necessary with respect to
the managed objects as well as the expert rules of
management that make up the knowledge base of the
expert system.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The work described in this paper has been supported
by the Spanish Ministry of Education and Science
(MEC: Ministerio de Educación y Ciencia) through
project reference number DPI2006-15467-C02-02.
REFERENCES
Morris, S. B., (2003). Network Management, MIBs and
MPLS: Principles, Design and Implementation.
Prentice Hall
Clemm, A., (2006). Network Management Fundamentals.
Cisco Press.
ISO/IEC. (1992). Structure of management information -
Part 4: Guidelines for the definition of managed
objects. CCITT X. 722 / ISO 10165-4. Geneva.
ITU-T. (1996). Principles for a Telecommunications
Management Network (TMN). Rec. M.3010.
Hebrawi, B. (1995). GDMO, Object modeling and
definition for network management. Technology
appraisals
Leon, C., Mejias, M., Luque, J., Gonzalo, F. (1999).
Expert System for the Integrated Management of a
Power Utility's Communication System. IEEE Trans
on Power Delivery, Vol. 14, No. 4, 1208-1212
Martín, A., León, C., Monedero, I. (2006). The Evolution
of OSI Network Management by Integrated the Expert
Knowledge. Publisher Springer Berlin / Heidelberg.
LNCS, 402-409.
Garcia, R.C.; Cannady, J. (2001). Boundary expansion of
expert systems: incorporating evolutionary
computation with intrusion detection solutions.
SoutheastCon. IEEE, 96-99.
Giarratano, J. C., Riley, G. D., (2005). Expert Systems:
Principles and Programming. Book, Brooks/Cole
Publishing Co.
ICEIS 2007 - International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
106
