
A THEORETICAL MODEL TO EXPLAIN EFFECTS OF
INFORMATION QUALITY AWARENESS ON DECISION
MAKING
Mouzhi Ge and Markus Helfert
School of Computing, Dublin City University, Dublin, Ireland
Keywords: Information Quality, Information Quality Awareness, Decision Making.
Abstract: Making high quality decision is dependent upon the quality of the information that is used to support the
decision. In most cases, decision makers are not aware of information quality issues. Decision makers
frequently believe the information they use is of high quality, however often the decision relevant
information is inaccurate and incomplete. With increasing intensity on decision making, information quality
awareness is becoming important. In order to analyse the effects of information quality awareness on
decision making, in this paper, we propose a theoretical model to address the relationship between
information quality awareness and decision quality. Our results show the effects of information quality
awareness on decision making and the importance of building IQ culture in organizations.
1 INTRODUCTION
Information Quality (IQ) is seen as a key factor in
the decision making field. Keller and Staelin (1987)
proposed a model on how decision effectiveness is
affected by IQ and information quantity. In their
model, they proposed that while retaining the same
quantity of information, increasing IQ results in an
increase on decision effectiveness. Considering
decision outcomes and decision quality, Baron and
Hershey (1988) indicated the importance of high
quality information in decision making. They
implied that IQ has a direct effect on the decision
outcomes and the quality of the decision. Regarding
the task complexity in decision making, the research
of Chengular-Smith et al. (1999) had shown that
including information about the quality of data can
impact the decision process. Considering the
experience level and time pressure in decision
making, Fisher et al. (2003) investigated that
experienced decision makers will more seriously
consider IQ than inexperienced decision makers do.
Their research implied that experts paid much more
attention to IQ because they have realized the
importance of IQ in decision making. From the IQ
management perspective, Shankaranarayan et al.
(2003) developed an IQ management framework for
dynamic decision environments. They also proposed
a virtue business environment (VBE) to address the
role of data quality management in VBE. Based on
the above literatures, we could observe the
importance of IQ in decision making.
IQ is also a key factor in information system,
which includes (group) decision support systems.
With the recognition of the importance of IQ,
recently, information system researchers have
addressed the impact of IQ in information system.
For instance, Ballou and Pazer (1985) proposed a
model to assess the impact of IQ within multi-user
information decision systems. Poor quality
information would incur the social and economic
cost. From an economic perspective, Ballou and
Pazer (1987) proposed an IQ cost model to ensure
the quality of outputs in information systems. In
order to evaluate the success of information systems,
DeLone and McLean (1992) consider IQ as one of
the key factors to the success of information
systems.
Over the last decade IQ concepts were
developed. Wang and Strong (1995) developed a
framework to address the dimensions of IQ that are
important to information consumers. Using
ontological concepts, Wand and Wang (1996)
defined IQ by the relationship between real world
and information systems. Further, Wang et al.
164
Ge M. and Helfert M. (2007).
A THEORETICAL MODEL TO EXPLAIN EFFECTS OF INFORMATION QUALITY AWARENESS ON DECISION MAKING.
In Proceedings of the Ninth International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems - ISAS, pages 164-169
DOI: 10.5220/0002368201640169
Copyright
c
SciTePress

(1998) proposed to manage your information similar
to products. Ballou et al (1998) modelled
information manufacturing systems to determine the
quality of information products. Following these
initial works, researchers and practitioners began to
concern with the IQ improvements. Wang (1998)
proposed the concept of total data quality
management (TDQM). In essence it is a systemic
methodology that assists improving IQ in
organizations. Following this concept, IQ awareness
and IQ culture are frequently mentioned elements in
a TDQM oriented organization. Furthermore
researchers have proposed various IQ assessment
methodologies such as Lee et al (2001), Kahn et al.
(2002), Bovee (2003) and Parssian (2004).
In summary, we could observe the following
essential aspects in current approaches: (1) IQ
influences decision making. (2) IQ is a crucial factor
in information systems (3) IQ awareness in
organizations is a major objective of IQ
improvement. thus IQ awareness is typically positive
related to IQ and decision making. However, at
present little research has investigated the
relationship between IQ awareness and decision
making.
Addressing the drawback of current research, the
purpose of this paper is to investigate how IQ
awareness influences on decision making. In our
work, we aim to provide indications on how IQ
Awareness contributes to decision making. The
remainder of this paper is structured as follows: In
section 2, we propose a theoretical model describing
the relationship between IQ awareness, IQ and
decision quality. For facilitating the model
validation and providing an emperical scenario, in
Section 3, we outline an experiment and discuss
indicators in the experiment. Finally, we conclude
our research and summarise implications of the
necessity of establishing IQ awareness.
2 THEORETICAL MODEL
In this section, we propose a theoretical model,
which is described by three main hypotheses:
(1) IQ and decision quality
(2) IQ and IQ awareness
(3) IQ awareness and decision quality
IQ and decision quality: Many researchers
(Keller and Staelin 1987, Baron and Hershey 1988,
Chengular-Smith et al. 1999, Fisher et al. 2003,
Shankaranarayan et al. 2003) have proposed or
implied that higher IQ has a positive impact on
decision making. In order to address relationship
between IQ and decision making. Jung and Olfman
(2005) proposed an experiment to study the effects
of contextual IQ and task on decision performance.
Ge and Helfert (2006) proposed an experiment to
address the relationship between IQ and decision
quality. Based on these observations, we propose the
following hypotheses:
Hypothesis 1: Decision quality will increase with
the increasing of IQ. IQ is positively correlated with
Decision quality.
IQ and IQ awareness: Researchers have
recognized the importance of IQ awareness in
organizations. For example, Huang K.T. et al. (1999:
28) implied that top managers in organizations
should possess IQ awareness in the form of visible
continuous interest in IQ activities. Redman (2001:
197) stated the importance of advancing IQ
awareness for business process. Olson (2002: XV)
advocated increasing IQ awareness and include
building IQ awareness as one of the goals in his
book. Based on above literatures, the following
hypothesis is proposed:
Hypothesis 2: The positive effect of IQ will be
intensified by the assistance of IQ awareness.
IQ awareness and decision quality: Chengular-
Smith (1999) proposed that effective decision
makers could compensate for various deficiencies
the data may possess, especially if the decision
maker is acquainted with the data’s idiosyncrasies.
That implied decision makers would enhance the
positive effect of IQ in decision making by using
their IQ awareness. Therefore the following
hypothesis is proposed:
Hypothesis 3: IQ Awareness can enhance the
decision quality when the decision relevant
information is containing quality problems. Decision
makers who possess IQ awareness will make higher
quality decision than people who do not possess IQ
awareness.
Based on the above hypotheses, we propose the
following relationship model between IQ, IQ
awareness and decision quality.
A THEORETICAL MODEL TO EXPLAIN EFFECTS OF INFORMATION QUALITY AWARENESS ON DECISION
MAKING
165
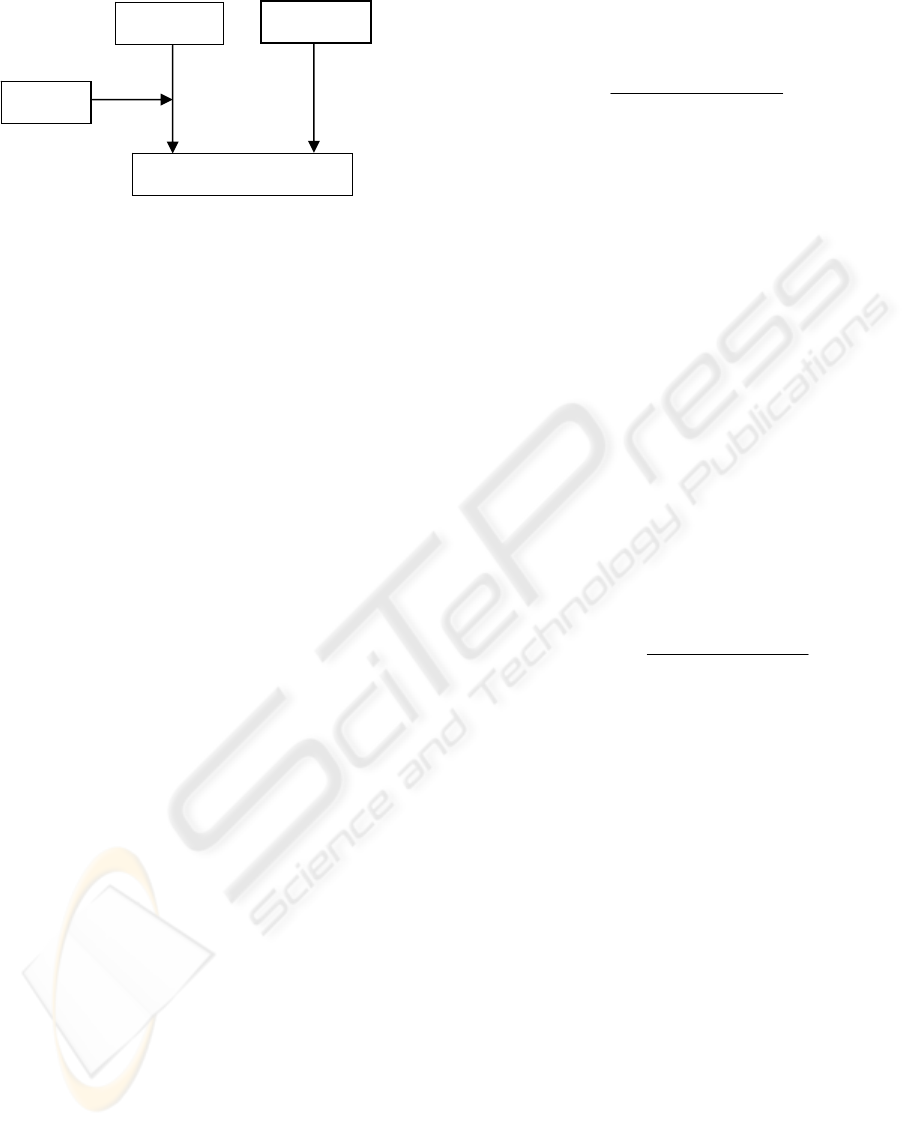
Figure 1: Effect factors on decision quality.
In this relationship model, four elements are
described: information quality (IQ), IQ Awareness
(IQA), Decision Quality and other influencing
factors. IQ has an impact on decision quality
meanwhile IQA plays as a moderating factor in
intensifying IQ. In addition, besides IQ and IQA,
decision quality is also influenced by many other
factors such as personal preference, information
quantity, task complexity, time pressure, decision
maker’s experience and so on. In our model we
consider the effects of other factors as constant
which is represented as F
N
in figure 1. The
measurements of IQ, IQA and Decision Quality are
discussed as follows:
2.1 Information Quality
Many IQ dimensions have been explored over the
last decades, such as accuracy, timeliness, relevancy
and completeness. (Zmud 1978, Fox et al. 1993,
Wand and Wand 1996, Huang K.T. et al. 1999,
Olson 2002). Among these dimensions, accuracy is
identified as crucial dimension to measure IQ. Olson
(2002) proposed the notion of “If the data is just not
right, the other dimensions are of little importance”.
He considered accuracy as a fundamental IQ
dimension. Based on the review on IQ dimensions,
Huang K.T. et al. (1999) concluded that most IQ
studies include accuracy as a key dimension.
Therefore, in the preliminary research of our model,
we focus on accuracy as one IQ dimension. There is
no commonly accepted definition of accuracy in IQ
field. For example, from a metadata view, Redman
(1996: 255) define accuracy as the nearness of the
value to the standard value, from a dataset view
Olson (2002: 29) define accuracy as correct data
values stored for an object. However, correct value
may simply be unknown or an assumed standard
may be incorrect [20]. From an ontological view,
Ballou and Pazer (1985) define accuracy as the
recorded value that is in conformity with the actual
value. In order to quantify the accuracy, we combine
the dataset view and the ontological view and
expressed the accuracy measurement as follows:
Accuracy =
n
)(dAccuracy
n
1k
k
∑
=
(1)
Where n is the total number of data item d
k
. If d
i
is the actual value, we calculate accuracy by the
following relations:
• d
k
= d
i
=> Accuracy(d
k
) = 1
• d
k
<> d
i
=> Accuracy(d
k
) = 0
2.2 Decision Quality
Decision quality could be measured by many
factors, such as decision accuracy, decision
consistency and decision consensus (Nie et al. 1975,
Libby and Blashfield 1978, Ashton 1985, Chewning
and Harrell 1990). In those decision measurements,
Chewning and Harrell (1990) reviewed the decision
measurements and proposed that the accuracy of the
decisions reached is the primary measure of decision
quality. Accordingly, we consider decision accuracy
as our decision quality measurement. In this manner,
decision quality could be measured by the following
equation:
Decision quality =
n
)Decision(d
n
1k
k
∑
=
(2)
Where d
k
is considered as the decision in the
decision collection. When the decision is right
Decision (d
k
) = 1 and when the decision is wrong,
Decision (d
k
) = 0.
2.3 Information Quality Awareness
Meager et al. (2002) define awareness as
“Awareness occurs when an individual is
sufficiently informed about a subject for him/her to
be conscious of its existence and its broad subject
matter”. We adopt this definition to our context. IQ
awareness occurs when the decision maker is
sufficiently informed about IQ for him/her to be
conscious of IQ problems. If People possess IQ
awareness, he/she will benefit from the IQ
awareness to avoid the decision risk when the
quality of decision related information is low.
People who do not possess IQ awareness will ideally
trust the information they use even if the information
is of low quality. Thus IQ awareness is considered
as one of the key factors influencing the decision
quality.
IQ
Decision Quality
IQA
F
N
ICEIS 2007 - International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
166

In order to measure IQ awareness, we could
implement a survey or semi-structured interviews. In
the survey, some IQ concepts and cases, which are
failed because of IQ problems, are used. By testing
the understanding level of IQ concepts and the
ability of locating the IQ problems, we could
initially distinguish whether testers possess IQ
awareness or not.
2.4 Model Formulation
Based on the above discussion, our model is
proposed as follows,
Decision Quality = d (IQ
α
) + f (F
N
) (3)
Where IQ represents the quality of the provided
information. The exponent α is used to express the
awareness of IQ. F
N
represents other factors
influencing the decision quality, such as decision
makers’ subjective preference or experience. d (⋅)
and f (⋅) reflect functions that have an impact on
decision quality.
Once we only initially consider accuracy as the
IQ dimension, equation (3) becomes:
Decision Quality=d{[
n
)(dAccuracy
n
1k
k
∑
=
]
α
}+f (F
N
)
In order to facilitate the model validation and
estimate function d(⋅), following we propose an
application scenario with several experiment
indicators.
3 EXPERIMENT
In our earlier research (Ge and Helfert 2006), we
proposed an experiment to address the relationship
between IQ and decision quality. Here, we extend
this approach and develop an experiment, which is
characterised in the following sections.
3.1 Participants
After the IQ awareness survey, we could divide the
participants into two groups. One group possess IQ
awareness, and the other group do not. In this way,
we can compare the decision quality of the two
groups and can approximate the IQ awareness
function in decision making. Those participants who
possess IQ awareness will be referred as Group A,
while those participants who do not possess IQ
awareness will be referred as Group B. This research
focuses on decision quality difference between
Group A and Group B. Group A members may use
their IQ awareness to complete a subjective IQ
assessment whereas Group B members may ignore
the IQ problems that are in the decision relevant
information.
In order to reduce the effects of other factors, (1)
Participants are selected to have the same decision
experience on the decision tasks. (2) Constructions
(age, male and female proportion, education
background, etc.) of the group who possess IQ
awareness should be similar as that of the
participants who do not possess IQ awareness. (3)
Participants will not obtain any IQ hints in the
experiment.
3.2 Decision Scenario
The participants are required to complete a number
of decisions using the provided information. For
instance, the participants are instructed to complete
six decision tasks and all six decision tasks are Yes
or No questions in relation to investment issues. One
decision task could be, “Are we going to invest on
this bank project?” The six decision tasks are
different in the content but with the same format on
investment issues. Participants make their decisions
according to available information. The information
is limited by providing answers to the following ten
questions:
What sort of investment is this?
Who is involved in providing it to me?
How much do I pay?
What are the charges?
What returns will I get?
What are my risks?
Can the investment be altered?
How do I cash in my investment?
Is there anyone to whom I can complain if I
have problems with the investment?
What other information can I obtain?
Besides the above information, a virtual financial
setting is provided for the participants. According to
the above decision environment, participants will
process the provided information and make six
investment decisions. In addition, because time
pressure decreases decision accuracy [28] and can
impair the decision performance [1]. There is no
time pressure on the decision making tasks.
However communications among participants are
forbidden. Finally participants will submit their
decisions via our server based software system.
A THEORETICAL MODEL TO EXPLAIN EFFECTS OF INFORMATION QUALITY AWARENESS ON DECISION
MAKING
167

3.3 Decision Complexity
Yes or No decisions questions are employed in the
experiment for the following reasons. First the Yes
or No questions are the most common. Second, the
decision makers will not invest much time on option
trade-off. This is also the approach to protect the
participants from using their own experiences on the
option evaluation. Third, Yes or No questions are
easy to measure and friendly to the participants. In
order to decrease the effect of other personal factors
such as subjective experience and preference, an
investment decision scenario is employed because
we can choose participants who have principle in the
same knowledge level on the investment issues.
Consequently, participants will make decision only
according to the provided information, and other
influence factors are highly decreased. We will use
the following table to evaluate the decision from the
participants:
Table 1, Decision evaluating specification
In the decision row of table 1, Yes represents
decision makers will invest on the project whereas
No represents decision makers will not invest on the
project. Before we carry out our experiment, we
have already identified the best practice answer to
each decision task. The best practice decisions are
set as the objective column. In the decision part, they
are decisions that come from the decision makers. If
the decision part conforms to the objective part, it is
the right answer. Otherwise it is the wrong answer.
3.4 Information Accuracy
According to the decision tasks, we could use
information points to calculate the information
accuracy. Information points are the metadata whose
status can be changed between accurate and
inaccurate. Continuing the example in task section,
the information is the answers to the corresponding
10 questions. In each answer, we develop 10
information points to calculate the accuracy.
Information point is the word or number in each
answer, whose state could be changed between
accurate and inaccurate. Thus we could obtain 100
information points in each decision task. Based on
Ballou and Pazer’s accuracy definition, accuracy in
our experiment is defined as the ratio of the correct
information points in relation to the provided
information points. For instance, when we set 20
accurate information points in the decision task, the
information accuracy is 20 percent.
3.5 Limitations
Guarantee on Participants’ Encouragement
In order to guarantee all the participants will
seriously consider the decision relevant information,
we could use an award to encourage the participants.
For example, we could use an iPod award to
encourage and motivate the participants. Those who
made the highest quality decisions will win the iPod
award in the end.
Reducing the Human Learning
When participants make decisions on different
tasks, they may learn the task scenarios and IQ
problems and then use this experience to finish the
following tasks. Thus decision makers’ experiences
will influence decision quality through learning. In
order to protect human learning in the experiment,
we could develop several decision environments and
IQ levels. For example, six decision environments
and six IQ levels are developed. Those decision
environments are related to IT project investment,
Banking project investment, Hotel project
investment, Tourism project investment, Education
project investment and Healthcare project
investment. Six IQ levels are 10%, 20%, 40%, 60%,
80% and 90%. We will provide different decision
environments with different IQ levels to each
participant. So to a single participant, he/she will
experience six different decision environments as
well as different IQ levels. In this manner, we could
reduce the human learning on decision environments
and IQ problems.
4 CONCLUSION
As IQ awareness becomes more and more important,
it is increasingly valuable to assess the effects of IQ
awareness in the context of decision making. In this
paper, we propose three hypotheses which are
demonstrating the relationships among IQ, IQ
awareness and decision quality. Then we propose a
theoretical model to address that relationship. Four
variables are shown in the model: IQ, IQ awareness,
decision quality and other influencing factors. For
Yes- Invest
No − No investment is done
Decision
Objective
Yes No
Yes Right Wrong
No Wrong Right
ICEIS 2007 - International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
168

each variable, we propose a measurement
methodology. The main contribution of this model is
to address the moderating functionality of IQ
awareness in the relationship of IQ and decision
quality.
Based on the model, we provide an empirical
scenario to facilitate the model validation. In the
application scenario, we point out several
experimental indicators such as human learning,
decision issue selection and measurement
calculation.
The model in this paper has several possible
extensions. First, more IQ dimensions could be
included in the IQ measurement. For example, we
could include completeness, relevancy, consistency
etc.. Second, more decision quality measurements
could be taken into consideration, such as decision
consistency and decision consensus. Third, more
experiment indicators could be included to a more
comprehensive and concrete application scenario.
For instance, we could develop a concrete finance
situation for each decision maker or increase the task
complexity of the decision environments. Overall
future work of this research is improving the
theoretical model and building a comprehensive
empirical scenario.
5 REFERENCE
Ahituv, N., Igbaria, M., and Stella, A., “The Effects of
Time Pressure and Completeness of Information on
Decision Making,” Journal of Management
Information Systems, (15:2), 1998, pp. 153-172.
Ballou, D. P. and Pazer, H. L. Modelling data and process
quality in multi-input, multi-output information
systems. Manage. Science. 31, 2 (1985), pp. 150-162.
Ballou D. P., Wang R. Y., Pazer H. L., Tayi G. K.,
Modeling Information Manufacturing Systems to
Determine Information Product Quality, Management
Science, v.44 n.4, p.462-484, April 1998.
Baron J. and Hershey J. C.. Outcome bias in decision
evaluation, Journal of Personality and Social
Psychology. Apr Vol 54(4) , 1988, pp: 569-579.
Chengalur-Smith I. N., Ballou D. P., Pazer H. L.: The
Impact of Data Quality Information on Decision
Making: An Exploratory Analysis. IEEE Trans.
Knowl. Data Eng. 11(6): 853-864 (1999)
Cinzia C., Chiara F., and Barbara P., Time-Related Factors
of Data Quality in Multichannel Information Systems,
Journal of Management Information Systems Vol. 20
No. 3, pp. 71 – 91, 2004
Fisher C. W., Chengalur-Smith I., Ballou D. P.. The
Impact of Experience and Time on the Use of Data
Quality Information in Decision Making, Information
Systems Research/Vol. 14, No. 2, 2003.
Ge M., Helfert M.. A Framework to Assess Decision
Quality Using Information Quality Dimensions, 11th
International Conference on Information Quality,
MIT. November 10-12, 2006
Huang K., Lee Y. W., Wang R. Y.. Quality Information
and Knowledge Management, Prentice Hall, 1st
edition, ISBN: 0130101419, 1999.
Jung W., Olfman L., An Experimental Study of the Effects
of Contextual Data Quality and Task Complexity on
Decision Performance, Information Reuse and
Integration, Conf, 2005. IRI -2005
Keller K.L. and Staelin R. Effects of Quality and Quantity
of Information on Decision Effectiveness, Journal of
Consumer Research, volume 14, page 200
Lee Y. W., Strong D., Kahn B., and Wang R.Y., AIMQ: A
Methodology for Information Quality Assessment,
Information & Management, December 2002, Volume
40, Issue 2, pp. 133-146.
Matthew B., Raiendra S. P.; Brenda M.; A conceptual
framework and belief-function approach to assessing
overall information quality, International journal of
intelligent systems, 2003, vol. 18, no 1 (42 ref.), pp.
51-74
Meager N., Tyers C., Perryman S., Rick J. Willison R.,
Awareness, knowledge and exercise of individual
employment rights, Employment Relations Research
Series No.15
Olson J. E., Data Quality: The Accuracy Dimension,
Publisher: Morgan Kaufmann (December 26, 2002),
ISBN: 1558608915
Redman, T. Data Quality: The Field Guide, Publisher:
Digital Press (January 15, 2001), ISBN: 1555582516
Redman, T. Data Quality For The Information Age,
Publisher: Artech House Publishers (December 1996),
ISBN: 0890068836
Parssian A., Sarkar S., Jacob V. S., Assessing Data
Quality for Information Products: Impact of Selection,
Projection, and Cartesian Product, Management
Science Volume 50, Issue 7, July 2004.
Shankaranarayan G., Ziad M., Wang R.Y.. Managing Data
Quality in Dynamic Decision Environments: An
Information Product Approach, Journal of Data
Management, 2003.
Wand Y., Wang R. Y., Anchoring data quality dimensions
in ontological foundations, Communications of the
ACM, v.39 n.11, p.86-95, Nov. 1996
Wang, R. Y. and Strong, D. M. Beyond accuracy: What
data quality means to data consumers. J. Manage. Info.
Syst. 12, 4 (1996), pp. 5-34.
Wang R.Y., Lee Y. W., Pipino L., Strong D.M., Manage
Your Information as a Product," Sloan Management
Review, Summer 1998, Volume 39, No. 4. pp. 95-105.
Wang R. Y., A Product Perspective on Total Data Quality
Management, Communications of the ACM, February
1998, pp. 58-63.
A THEORETICAL MODEL TO EXPLAIN EFFECTS OF INFORMATION QUALITY AWARENESS ON DECISION
MAKING
169
