
EXTENDING THE EPC AND THE BPMN WITH
BUSINESS PROCESS GOALS AND PERFORMANCE MEASURES
Birgit Korherr and Beate List
Women's Postgraduate College for Internet Technologies, Institute of Software Technology and Interactive Systems, Vienna
University of Technology, 1040 Vienna, Austria
Keywords: Business process modelling, metamodel, Event Driven Process Chain, Business Process Modeling Notation.
Abstract: The Event-Driven Process Chain (EPC) and the Business Process Modeling Notation (BPMN) are designed
for modelling business processes, but do not yet include any means for modelling process goals and their
measures, and they do not have a published metamodel. We derive a metamodel for both languages, and
extend the EPC and the BPMN with process goals and performance measures to make them conceptually
visible. The extensions are based on the metamodels tested with example business processes.
1 INTRODUCTION
Business process performance measurement is an
important topic in research and industry (Casati F.,
2005). However, current conceptual Business
Process Modelling Languages (BPMLs) do not
mirror these requirements by providing explicit
modelling means for process goals and their
performance measures (List, B., Korherr, B., 2006).
The goal of this paper is to address these limitations
by
enhancing the expressiveness of the most
widely-used BPMLs, namely the Event-
Driven Process Chain (EPC) and the
Business Process Modeling Notation
(BPMN) by deriving metamodels for both,
and by
extending their metamodels with business
process goals and performance measures to
make them conceptually visible.
EPCs have become widely-used for business
process modelling in continental Europe, in
countries where SAP is a leading Enterprise
Resource Planning (ERP) system. EPCs are inspired
from Petri nets, incorporate role concepts and data
models like ER models or UML class diagrams.
The BPMN is wide spread in the US and in
countries where US companies dominate the ERP
system market. The BPMN was developed by the
Business Process Management Initiative (BPMI)
with the goal to provide a notation that is easily
readable and understandable for all business users
(BPMI/OMG, 2006), who design, implement or
monitor business processes. Thus the BPMN aims to
bridge the gap between business process design and
its implementation.
According to the evaluation in (List, B., Korherr, B.,
2006), the EPC and the BPMN belong to the most
advanced BPMLs beside the UML 2 Activity
Diagram (OMG, 2006). Although the EPC offers
notation elements for business process goals, it
does not provide elements that make performance
measures visible. BPMN does not provide
elements that make business process goals or
performance measures visible at all. In a previous
work (Korherr, B., List, B., 2006), we have
extended UML 2 Activity Diagrams with
performance measures and goals to make them
conceptually visible. We want to extend all three
languages with goals and performance measures,
but different mechanisms will be used. At UML 2
Activity Diagrams a UML profile was created,
and at the EPC we will introduce a new view, as
well as at BPMN we will establish a new
category.
The BPMN only provides notation elements and
no official metamodel published e.g. from the
Business Process Management Initiative (BPMI) or
the Object Management Group (OMG), while the
EPC provides metamodels for its views, but not an
integrated metamodel that contains all views in one
model.
We derive a metamodel for the EPC and the
BPMN based on the Meta-Object Facility (MOF),
the OMG’s meta-metamodel (OMG, 2006). We
extend the metamodels with business process goals
287
Korherr B. and List B. (2007).
EXTENDING THE EPC AND THE BPMN WITH BUSINESS PROCESS GOALS AND PERFORMANCE MEASURES.
In Proceedings of the Ninth International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems - ISAS, pages 287-294
DOI: 10.5220/0002379002870294
Copyright
c
SciTePress

and performance measures, and thus, provide the
following contributions:
Modelling goals and performance measures
allow to better structure the process design
and to better understand the broader
implication of the process design.
Performance measures quantify business
process goals, and thus help to evaluate the
process design and the operating process.
The extended EPC and BPMN make the
evaluation criteria for a business process
conceptually visible.
In the remainder of the paper, the role of
business process goals and performance measures is
briefly discussed in Section 2 and the generic
metamodel extension will be described in Section 3.
The metamodel of the EPC and the BPMN with its
extensions for process goals and performance
measures is described in Section 4 and 5. The
extension of the EPC and the BPMN is tested with
an example business process in Section 6. We close
with related work (Section 7), followed by a
conclusion (Section 8).
2 PERFORMANCE MEASURES
With business process reengineering Davenport,
Hammer and Champy encouraged a new discipline
at the beginning of the 1990s and provided the
theoretical background for business process
modelling. In the business process modelling
community attention has so far only been given to
the modelling of certain aspects of processes (e.g.
roles, activities, interactions) rather than goals or
measures. The former theoretical aspects are
mirrored in several business process modelling
languages (BPMLs), i.e., in BPMN (BPMI/OMG,
2006), EPC (Scheer, A.-W., 1999), the UML 2
Activity Diagram (OMG, 2006), etc.
A business process is defined as a “group of
tasks that together create a result of value to a
customer” (Hammer, M., 1996). Its purpose is to
offer each customer the right product or service, i.e.,
the right deliverable, with a high degree of
performance measured against cost, longevity,
service and quality (Hammer, M., 1996). Although
process goals and performance measures lack the
visibility in conceptual BPMLs, they are used in
process theory.
According to Kueng and Kawalek (Kueng, P.,
Kawalek, P., 1997), the modelling of goals is a
critical step in the creation of useful process models,
for the following reasons:
We need to be able to state what we want to
achieve so that we are then able to define the
necessary activities which a business process
should encompass.
A clear understanding of goals is essential in
the management of selecting the best design
alternative.
A clear understanding of goals is essential
for it to be possible to evaluate the operating
quality of a business process.
A clear expression of goals makes it easier to
comprehend the organisational changes that
must accompany a business process redesign.
For all the reasons described above, we capture
the business process goals and represent them
graphically in a conceptual BPML, namely the EPC
and BPMN. Furthermore, Kueng and Kawalek
recommend in (Kueng, P., Kawalek, P., 1997) to
define to which extent the process goals are fulfilled,
to measure the achievement of goals either by
qualitative or quantitative measures, and to define a
target value for each measure. Target values are also
very important for Service Level Agreements
(SLAs) as well as for business process improvement.
3 GENERIC METAMODEL
EXTENSION
As a first step according to the missing concepts
found out in the evaluation of List et al., we capture
goals as well as measures and represent them
graphically in two conceptual BPMLs, namely EPCs
and BPMN.
The metamodel of the EPC and the BPMN will
be extended by a small generic metamodel of goals
and performance measures shown in Figure 1. The
big advantage of that generic metamodel is that it
can be integrated in every BPML at that point where
it is needed. It contains two core concepts, namely
Measure and Process Goal. While these two
concepts do not appear as notation elements in
BPMN, the process goal is a part of EPC. Often it
does not appear in the graphical notation of a
business process modelled with EPCs, and there are
no measures available for quantifying a goal.
A process goal describes the specific intension of
a business process and is quantified by at least one
measure. Furthermore the goal can be refined by one
or more sub goals. A measure is an abstract
metaclass, and can be classified and implemented as
Quality, Cost or Cycle Time. A measure is
responsible for the concrete quantification of
different goals as well as for measuring the
performance of a business process.
Quality has the aim to measure the quality of a
business process, which can be expressed e.g., by a
low number of complaints or a high customer
ICEIS 2007 - International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
288
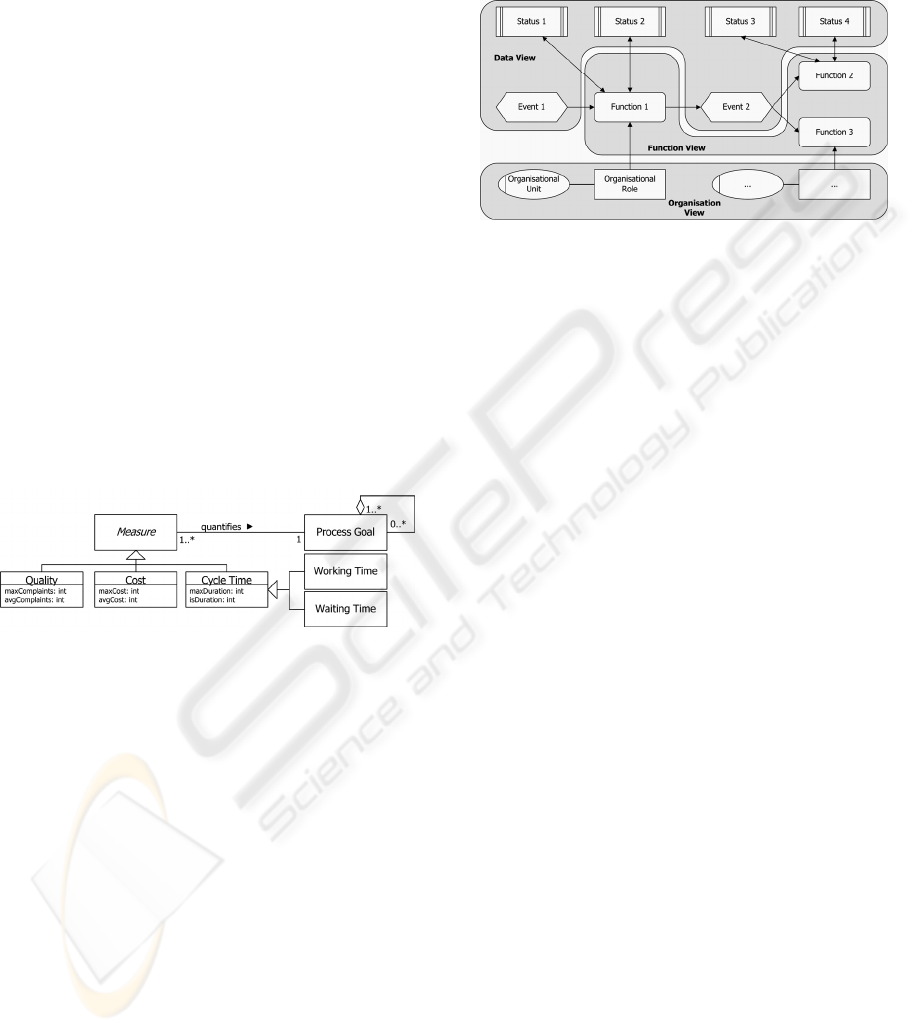
satisfaction, described in Fig. 1 through the
attributes maxComplaints as well as avgComplaints.
The attribute maxComplaints shows the total
number of complaints, and the attribute
avgComplaints shows the average allowed number
of complaints measured for instance during the time
period of a month.
Cost represents the expenses a business process
requires for instance for its execution. Its attributes
maxCost and avgCost are necessary for comparing
for example the average values like the total and
monthly average cost of a certain process. The
performance measures of quality and cost are in
contrast to the measures of the cycle time often more
focused on the type level of a process, as the
required data is often not available on instance level.
The measure cycle time presents a time based
measure and defines the processing duration of a
business process instance, or part of it. Cycle Time
can be specialised as Working Time or Waiting Time.
Working time presents the actual time a business
process instance is being executed by a role. Waiting
time shows the time the process instance is waiting
for further processing. Moreover, cycle time has two
attributes maxDuration and isDuration for
representing the target value and the actual value of
the process duration or a part of it.
Figure 1: Generic metamodel of goals and performance
measures.
4 THE EPC
The EPC (Scheer, A.-W., 1999) has been developed
within the framework of the Architecture of
Integrated Information System (ARIS) and is used
by many companies for modelling, analysing, and
redesigning business processes. The ARIS concept
(Scheer, A.-W., 1999) divides complex process
models into separate views, in order to reduce the
complexity. The views can be handled
independently as well as related. There are three
views focused on functions, data, and the
organisation (see Fig. 2), and an additional view
focused on their integration.
The Data View contains events and statuses. The
Function View contains the description of the
activities that have to be performed. The
Organisation View represents the organisational
structure. This includes organisational units,
employees and roles as well as their relationships.
The Control View links functions, organisation and
data. It integrates the design results, which were
initially developed separately.
Figure 2: ARIS Views.
4.1 The EPC Metamodel
The metamodel of the EPC is described in Figure 4.
An EPC consists of functions, events, control flow
connectors, logical operators, and additional process
objects. Each EPC consists of one or more Functions
and two or more Events, as an EPC starts and ends
with an event and requires at least one function for
describing a process. A function can be either an
Elementary Function or a Complex Function, and
the latter is refined by at least one function. A
function is connected with two Control Flow
Connectors and has to fulfil at least one Process
Goal. A process goal can be refined by one or more
sub goals. Control flows link events with functions,
but also events or functions with Logical Operators,
which can be either an XOR, OR or AND. It is
connected at least with 3 control flows, one or more
incoming as well as outgoing connectors.
A Deliverable, an Information Object, an
Organisational Structure as well as Process Goals
are called additional process objects and are
connected with functions. All these types of
additional process objects are assigned to one or
more functions.
4.2 The Extended EPC Metamodel
The metamodel is extended by introducing a new
view, the so called performance measure view. It is
shown with the performance measure elements high-
lighted in grey in Figure
4. The relationship between
goals and measures in a so called goal measure tree
is illustrated in Figure 3 in the context to the
examples in section 6. A goal can have several sub
goals, and each goal has at least one measure and is
connected with one or more Measure Flow
Connectors. Its main process goal is good process
performance. This goal has three sub-goals: low
EXTENDING THE EPC AND THE BPMN WITH BUSINESS PROCESS GOALS AND PERFORMANCE MEASURES
289
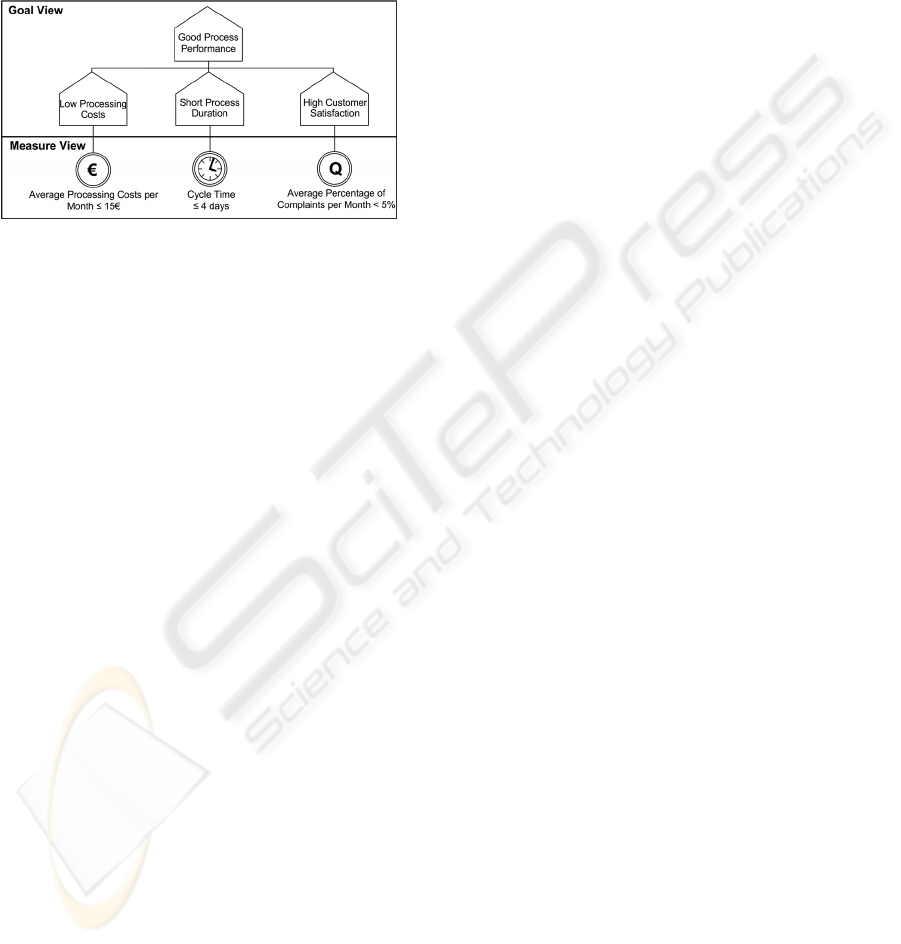
processing costs, short process duration, and high
customer satisfaction. Furthermore each goal is
refined by measures. The goal low processing costs
is fulfilled, when the average processing costs per
month are under 15 Euros. The measure cycle time
indicates that the process duration has to be less than
four days. Moreover the goal high customer
satisfaction is achieved, if the average percentage of
complaints per month is less than five percent.
Figure 3: Goal Measure Tree.
5 THE BPMN
The BPMN was developed by the Business Process
Management Initiative (BPMI) with the goal to
provide a notation that is easily readable and
understandable for all business users (BPMI/OMG,
2006), who design, implement or monitor business
processes including a transformation into an
execution language, namely the Business Process
Execution Language, (BPEL) (IBM, 2003). Thus the
BPMN aims to bridge the gap between business
process design and its implementation. The main
concepts of BPMN are similar to UML 2 Activity
Diagrams (AD) (OMG, 2006). But in contrast to
ADs, the BPMN has no official metamodel, just a
mapping to the Business Process Definition
Metamodel (OMG, 2004) which is not fully
developed yet.
5.1 The BPMN Metamodel
We derived the BPMN metamodel from the core
elements of BPMN ((BPMI/OMG, 2006)) which is
shown in Figure
5. It includes process goals and
performance measures (in grey). The metamodel
was developed according to the specification of
BPMN. The BPMN metamodel consists of four
different categories: Flow Objects, Connecting
Objects, Swimlanes, Artifacts and the newly
introduced Performance Measures.
The elements Activity, Process, Sub-Process,
Task as well as Events and Gateways are Flow
Objects, which define the behaviour of a business
process. A process consists of one or more activities.
The activity is the main part of a BPMN, and is
specialised through sub-processes that consist of at
least one task. An event is something that “happens”
during the execution of a business process. There are
three types of events, based on when they affect the
flow: Start, Intermediate, and End. Also the Time
Event, which can be a start or an intermediate event,
is part of the metamodel because it is required for
presenting the measure of time. It belongs to the
complete set of elements, which displays a more
extensive list of the business process concepts that
could be depicted through BPMN. A Gateway is
used to control the divergence and convergence of a
sequence flow. Markers within a gateway show the
type of that flow object, it will determine between
the logical operators XOR, OR, and AND, which
stand for the Exclusive (XOR), Inclusive (OR) and
Parallel (AND) gateway. Furthermore the type
Complex indicates complex conditions and
situations, for instance that three paths out of five
have to be chosen.
The connecting objects Sequence Flow, Message
Flow and Association describe the ways of
connecting the flow objects to each other. A
message flow can be connected to at most two
activities, or occur between an activity and a pool, or
between two pools to illustrate the exchange of
messages. A sequence flow shows the order in
which activities are performed in a process, and
relates activities, gateways and events to each other.
An association is used to associate information to
activities, and associates a Data Object to a flow or
connects it to an activity.
Data objects as well as a Group and Text
Annotations belong to the category of artefacts.
They do not have any effect on the process flow at
all. A data object can be used to represent many
different types of objects, both electronic and
physical, and provides information about what the
process does. A group groups elements of a business
process informally, and it is also used to assign
process goals to a business process. A text
annotation is a mechanism for a modeller to provide
additional information for the reader of a BPMN
Diagram, and is not integrated in the metamodel for
sake of simplicity.
A Pool represents a participant in a process and
belongs to the category of swimlanes, and it groups
a set of activities for identifying activities that have
some characteristic in common. A pool can be
connected with other pools or activities by a
message flow. A Lane is a sub-partition within a
pool.
ICEIS 2007 - International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
290

5.2 The Extended BPMN-Metamodel
The metamodel is extended with performance
measures as a new category according to the
specification (BPMI/OMG, 2006), with regard to the
fact that an extension is not allowed to change the
basic shape of the defined graphical elements and
markers. The extensions are marked with the term
"is presented through" in the metamodel, to sign that
an extended metaclass is graphically described
through a core element of BPMN.
The Organisational Structure explicitly
describes Organisational Units and Roles within a
business process. This could be for example the
department or an employee of a company. They are
presented through a pool, because they are a
concrete specification of a pool and so far also part
of the category swimlanes. An organisational unit
has one or more roles, and a role belongs to at most
one unit. The metamodel extended with the new
introduced category of performance measures are
highlighted in grey in Figure
5. A Measure is
distinguished between a measure on Type Level or
Instance Level, because the type level of BPMN can
be executed with a mapping to BPEL according to
the specification ((BPMI/OMG, 2006). Since the
EPC is not executable, therefore the BPML does not
need a distinction in its metamodel between type or
instance level. Cost and Quality belong to the type
level, and cycle time to instance level. Cost and
quality are in contrast to cycle time more focused on
the type level of a process, as the required data is
often not available on instance level. A measure is
represented by a pool, because an organisational
structure has to act on measures. If the measure is
Cycle Time, then it is represented through a Time
Event. Furthermore an organisational structure can
be triggered by an event alert, if an action or a group
of actions is not executed within its performance
measures.
6 EXAMPLES
We demonstrate the practical applicability of the
extension of the EPC and the BPMN with business
process goals and performance measures in Figure 4
and 5 with the example business process of an
insurance company: the Processing of Automobile
Claims business process (Fig. 6). The business
process in both diagrams is decomposed into three
hierarchical levels to improve the structure and
clarity. The main difference in the graphical notation
of the extension of both BPMLs is that EPC uses
new graphical notation elements for presenting the
performance measures, while BPMN uses no
graphical notation elements and integrates them into
the existing elements. In BPMN, extensions to
notation elements can be made by means of new
markers or indicators associated with the current
graphical elements. It is recommended to use the
existing graphical notation elements, and to keep
away from changing them. In the examples in Figure
6 we introduce additional labels to the graphical
elements of BPMN, for instance for a pool the label
“Organisational Role” which corresponds to the
homonymous metaclass in the metamodel.
At the first hierarchy level, the overall goal of
the complex function of the EPC and the collapsed
sub-process in BPMN with the label Process of
Automobile Insurance Claims is to fulfil the process
goals High Customer Satisfaction, Short Process
Duration and Low Processing Costs. The process
has to meet three measures, costs, cycle time and
quality. The average processing costs per month
have to be 15€ maximum and the number of
complaints should not exceed five percent. In case of
the BPMN it is also possible to introduce alerts in a
diagram with time events (BPMI/OMG, 2006). In
our example, if the cycle time is over four days, then
the Claim Manager receives an alert, and gets a
report about that specific case.
At the second hierarchy level the organisational
role Financial Claim Specialist is responsible for the
complex function in EPC and for the collapsed sub-
process in BPMN respectively, labelled with
Assertion of the Claim. The organisational role of
the Claim Administrator is responsible for the
Compensation of the Claim in both BPMLs.
Furthermore assertion of the claim has to fulfil its
tasks within a cycle time of one day, and
compensation of the claim within three days.
At the beginning of the process at the third
hierarchy level, the organisational role Financial
Claim Specialist is responsible for the
functions/tasks Record the Claim and Calculate the
Insurance Sum. After a waiting time of two days
maximum, the organisational role of the Claim
Administrator has to follow up with the process.
If the insurance sum is a major amount, then the
claim administrator has to Check History of the
Customer.
Otherwise, when the insurance sum is a minor
amount, then no additional function for EPCs
respectively task for BPMN is required and the
organisational role of the claim administrator starts
immediately to Contact the Garage. After contacting
the garage for the reparation, the Examination of
Results has to begin with the decision whether the
payment for the damage is positive or negative. If
the examination is positive, then the insurance has to
Pay for the Damage, and the case is closed.
EXTENDING THE EPC AND THE BPMN WITH BUSINESS PROCESS GOALS AND PERFORMANCE MEASURES
291

Figure 4: Extended EPC metamodel with performance measures.
Figure 5: Extended BPMN metamodel with performance measures and goals.
Figure 6 shows that a business process in EPC
and BPMN with its hierarchical levels based on
extended metamodels can be grasped at a glance.
The extensions of the metamodel illustrate the
requirements of a certain business process better and
enhance the expressiveness of the model.
7 RELATED WORK
Several approaches exist in the global area of goal-
oriented business process modelling. A couple of
works will be presented here.
Korherr et al. (Korherr, B., List, B., 2006)
presented a UML 2 profile for integrating business
process goals and performance measures time, cost,
and quality into UML 2 Activity Diagrams.
Furthermore, it is possible to show the
organisational structure that is concerned with alerts
that belong to a measure. The profile also is mapped
to BPEL.
Neiger et al. (Neiger, D., Churilov, L., 2004))
focus on the problem that business process
management frameworks are able to represent
various aspects of the business process, but they do
not meet the requirements of goal-oriented business
process modeling.
ICEIS 2007 - International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
292

EPC BPMN
First Hierarchy Level
Second Hierarchy Level
Third Hierarchy Level
Figure 6: Example business process of Processing of Automobile Claims for EPCs and BPMN.
EXTENDING THE EPC AND THE BPMN WITH BUSINESS PROCESS GOALS AND PERFORMANCE MEASURES
293

To solve this problem, the authors establish links
between EPCs and its additional goals with the
“value focused thinking” (VFT) framework to
address the gaps in the existing methodologies and
tools, without looking at the measurement of the
goals.
Anderson et al. (Andersson B., Bider I.,
Johannesson P., Perjons, E., 2005) developed a
formal definition of goal-oriented business process
patterns for making a formal comparison of business
processes. This approach is very high level, because
the authors focus on business processes, and not on a
specific business process modeling language.
Aguilar et al. (Aguilar, E. R., Ruiz, F., Garcia,
F., Piattini M., 2006) developed a set of measures to
evaluate the structural complexity of business
process models on the conceptual level. The authors
use BPMN for their evaluation. The evaluation of
performance measures like time or cost is not
important for their work, the focus lies on measuring
the complexity of BPMN.
8 CONCLUSION
EPC as well as BPMN belong to the most well-
known languages, but both are not able represent
performance measures. In this paper, we have
presented the metamodels with its extension to
integrate business process goals and performance
measures into these languages. The extension of
both languages provides an explicit illustration of
the goals a business process must achieve, as well as
an integration of the performance measures time,
cost, and quality, because without measuring the
process goals it is not possible to assess if a goal is
fulfilled or not. These extensions better illustrate the
requirements of a certain business process and
enhance the expressiveness of a model. Furthermore
the organisational structure – a concept that is
already available in EPCs – is integrated in BPMN,
which is concerned with alerts that belong to a
measure for a possible transformation to BPEL. The
extensions of both languages were tested with an
example business process.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This research has been funded by the Austrian
Federal Ministry for Education, Science, and
Culture, and the European Social Fund (ESF) under
grant 31.963/46-VII/9/2002.
REFERENCES
Aguilar, E. R., Ruiz, F., Garcia, F., Piattini M., 2006.
Evaluation Measures for Business Process Models,
Proceedings of the 21st ACM Symposium on Applied
Computing (SAC'06), ACM Press.
Andersson B., Bider I., Johannesson P. and Perjons E.,
2005. Towards a Formal Definition of Goal-Oriented
Business Process Patterns. Business Process
Management Journal (BPMJ), Emerald, V11(6).
BPMI/OMG, Inc., 2006. Business Process Modeling
Notation. Version 1.0, February 6, 2006,
http://www.bpmn.org/.
Casati F., 2005. Industry Trends in Business Process
Management – Getting Ready for Prime Time,
Proceedings of the 1st International Workshop on
Business Process Monitoring & Performance
Management (BPMPM 2005), August 2005,
Copenhagen, Denmark, IEEE Press.
Hammer, M., 1996. Beyond Reengineering – How the
process-centered organization is changing our work
and our lives. Harper Collins Publishers.
IBM, 2003. BPEL4WS Version 1.1, www.ibm.com/
developerworks/library/ws-bpel/, (07/03/02)
Kueng, P., Kawalek, P., 1997. Goal-based business
process models: creation and evaluation. Business
Process Management Journal, Vol. 3, No. 1, April
1997.
Korherr, B., List, B., 2006. Extending the UML 2 Activity
Diagram with Business Process Goals and
Performance Measures and the Mapping to BPEL,
Proceedings of the 2
nd
International Workshop on Best
Practices of UML (ER 2006), Tucson, Arizona, USA,
Springer Verlag, 2006.
List, B., Korherr, B., 2006. An Evaluation of Conceptual
Business Process Modelling Languages. In
Proceedings of the 21
st
ACM Symposium on Applied
Computing (SAC’06), ACM Press.
Neiger, D., Churilov, L., 2004. Goal-Oriented Business
Process Modeling with EPCs and Value-Focused
Thinking, In Proceedings of Business Process
Management: Second International Conference (BPM
2004), Springer Verlag.
OMG Inc., 2004. Business Process Definition Metamodel.
Version 1.0.2, http://www.bpmn.org.
OMG Inc., 2006. MOF Core Specification v2.0,
http://www.omg.org.
OMG Inc., 2006. UML 2.1 Superstructure convenience
document, http://www.omg.org.
Ould, M. 1995. Business Processes – Modelling and
Analysis for Re-engineering and Improvement. John
Wiley & Sons.
Scheer, A.-W., 1999. ARIS – Business Process Modeling.
Springer Verlag.
ICEIS 2007 - International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
294
