
BUSINESS PROCESS PRIORISATION
WITH MULTICRITERIA METHODS
Case of Business Process Reengineering
1
Elena Kornyshova and
2
Camille Salinesi
2
University Paris 1 - Panthéon Sorbonne, 90, rue de Tolbiac, 75013 Paris, France
1
Saint-Petersburg State University of Economics and Finance, 21, Sadovaia Str, 191023 Saint-Petersburg, Russia
Keywords: Business Processes Prioritisation, Multicriteria Methods, Business Process Reengineering.
Abstract: Business process (BP) engineering is used nowadays in many methods, techniques and tools. In domains such
as strategic management, reengineering, or security analysis, one particular concern is the identification of BPs
that should be dealt primarily. In practice, the number of BPs is often very large and it justifies the creation of a
priorisation mechanism. However, the number of approaches available to prioritise BPs specifically is very
limited. This paper presents a comparison of multicriteria (MC) methods, and an approach to guide the
selection and application of the MC method found as the most appropriate for BP priorisation. The approach is
illustrated with the case of selecting and applying a BP priorisation in the view of BP reengineering.
1 INTRODUCTION
Many BP engineering methods, techniques and tools
focus on “Key business processes” (Sachdeva and
Joshy, 2005) (PegaRules, 2003). BPs priorisation is
used by companies to define the most important
development axes, to increase the reaction speed to
environment changes, to optimize the expenditure,
and consequently, to improve their competitiveness.
Dealing with Key BPs supposes that decision
makers know business processes priorities or are able
to define them, at least intuitively. The intuitive
approach is viable when there is a limited number of
BPs. However in most cases, managers face problems
with a large number and large variability of BPs, and
often different versions of BPs through time. The
combination of these issues leads to a combinatory
explosion of the number of artefacts to deal with,
hence a better priorisation support is needed.
There is a limited number of researches dealing
with BPs priorisation. In our point of view, BP
priorisation can be considered as a multicriteria
decision problem, and therefore we suggest integrating
multicriteria (MC) methods into BP priorisation. Our
aim is to propose a formal approach for BP priorisation
in order to enhance decision-making (DM) in the field
of BP management and related fields such as system
engineering, or business security.
We develop our approach to achieve two main
goals: (i) selecting an appropriate MC method and (ii)
applying it to the considered BP priorisation case.
We suggest that a process allowing to guide the
selection of a DM method should take into account the
multiple aspects of the situation at hand. The presented
approach copes with these different aspects using a
structured benchmarking grid. The grid was adapted
from (Papadacci et al., 2006) to the MC methods
comparison issue and is applied to describe BP
priorisation problem, which includes the description of
alternative BPs and criteria typology for BP evaluation.
The rest of the paper is organised as follows:
section 2 gives an overview of existing approaches of
BP priorisation; section 3 presents MC approach for
defining BP priorities and justifies the selection of one
MC method; section 4 illustrates our approach with
example of BPR. The section 5 discusses possible
application domains and research's perspectives.
2 OVERVIEW OF EXISTING BP
PRIORISATION APPROACHES
This section presents an overview of existing BPs
priorisation approaches. After a brief description of
these approaches, we compare them and give some
conclusions.
138
Kornyshova E. and Salinesi C. (2007).
BUSINESS PROCESS PRIORISATION WITH MULTICRITERIA METHODS - Case of Business Process Reengineering.
In Proceedings of the Ninth International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems - ISAS, pages 138-143
DOI: 10.5220/0002381901380143
Copyright
c
SciTePress

There is only a small number of approaches that
propose to guide BP selection. Four approaches are
particularly considered in our review: (i) Hammer and
Champy’s, (ii) Robson and Ullah’s, (iii) PROSCI, and
(iv) Mazur's et al. approaches.
Hammer and Champy (Hammer and Champy,
1993) propose to analyse BPs under three different
perspectives in order to select those that need
reengineering. These are "problems", "importance"
and "feasibility". First, all processes for which a
problem can be identified are chosen. Then, the
importance of these BPs for the organization is
analysed. Last, a feasibility control is carried out in
order to verify if expected results will cover related
expenses.
Robson and Ullah (Robson and Ullah, 1996)
propose a methodology to sort BPs for reengineering.
In this approach, BPs are analysed in relation with
critical success factors (CSFs). First, relevant CSFs
are listed, and then each BP is estimated along a five-
grade scale according to all CSFs. A weighted sum is
generated for each process; weights represent relative
importance of CSF. It presents a complex value of
each BP for organization. Besides, the authors
suggest to analyse BP functioning (from very good to
bad according to five-grade scale). Three levels of BP
priorities are finally considered: reengineering,
improvement and supervision. BPs that contribute to
many CSFs and have bad functioning are considered
as potential for BP reengineering.
PROSCI (Crowe et al., 1997) uses a BP taxonomy
to identify reengineering opportunities. The authors
suggest that relations exist between strategic goals
and BPs. The first step of this approach consists in
establishing the taxonomy of BPs. In the second step,
the influence of each BP on every strategic goal is
taken into account. To achieve this, an influence
diagram is drawn using decision tree where every BP
is embedded in a main decision node, strategic goals
are drawn as chance nodes, and main decision nodes
are linked to each chance node. Relationships are in
the form of probability distributions, which reflect the
stochastic nature of influences that BPs have on the
strategic goals. The final BP evaluations are obtained
using weighted sums of chance nodes in which
weights are assigned to chance nodes depending on
their order of importance.
Mazur et al. (Mazur et al., 2000) propose an
approach for BP selection based on weighed sum. In
this approach, the calculation is made according to the
next criteria: influence on customer, variability,
functioning, and importance for business. Each BP is
measured towards all criteria with five-grade scale,
and then the weighted sum is calculated.
The four selected approaches are compared along
two dimensions: (i) the criteria used by the
approaches for comparing BPs and (ii) the rules
proposed to carry out BP selection. Several remarks
can be made: (i) there is only a limited set of criteria
to support BP comparison; (ii) most criteria are
abstract (e.g. problems, or importance for customers
and business), and the authors do not show how these
criteria relate to actual BP performance indicators;
and (iii) there are only two kinds of selection rules,
weighted sum and two-dimensional space. The
drawback of weighted sum is that it requires
homogeneous criteria. On the other hand, two-
dimensional space has the disadvantage of limiting
maximal number of criteria.
In order to avoid these issues, we suggest
integrating MC methods into BP priorisation.
3 MULTICRITERIA
PRIORISATION OF BP
As indicated above, our proposal consists in using
multicriteria methods in order to carry out BP
priorisation. MC methods are very different from each
other, and the result of priorisation highly depends on
the selected method. We believe that a MC method
must take into account the specific characteristics of
problems situation to provide appropriate results.
Therefore, we propose an approach that guides the
selection of a MC method consistent with the
situation at hand.
As Fig. 1 shows it, the guidance provided by our
approach is based on a 5 phases process. The process
results in applying a MC method specifically chosen
to deal with the problem at hand.
1. Define the
MultiCriteria
Problem
2. Identify
Candidate MC
Methods
4. Select a
Method
3. Evaluate
Candidate Methods
against the Problem
5. Apply the
Selected Method
Figure 1: Overview of the proposed approach.
The goal of the initiation phase is to define the
nature of the MC problem. Once the problem defined,
it is necessary to identify candidate methods (phase
2), to evaluate their ability to cope with the MC
problem (phase 3), and to select the most adequate
method(s) (phase 4). Phases 2, 3 and 4 are iterative as
several phases can match the problem at hand (in
which case a more detailed analysis is required) or on
BUSINESS PROCESS PRIORISATION WITH MULTICRITERIA METHODS - Case of Business Process Reengineering
139

the contrary none of the candidate methods matches
the problem perfectly. In this case, another cycle of
evaluation must be achieved. Several strategies are
available: either other methods are considered, or
some of the required characteristics are added or
removed, or the characteristics are ranked by order of
importance. For more details, see (Salinesi and
Kornyshova, 2006).
3.1 Details of the Approach in the
Context of BP Priorisation
Our approach provides different ways of working
depending on the actual problem to deal with. The
following sections develop the approach application
in the specific context of BP priorisation.
3.1.1 Defining Multi-criteria Problem
Based on a state of the art research (Papadacci et al.,
2006), we developed a benchmarking grid that helps
defining a MC problem in detail. The grid is
composed of 15 different facets organized into four
orthogonal dimensions, namely: context, process,
form, and object.
The context dimension gathers 5 characteristics of
the situation of method use: (i) the problem is a choice
(ii) ranking, (iii) or sorting, (iv) new alternatives can
emerge, and (v) there are multiple viewpoints.
The process dimension gathers 4 characteristics of
the expected way of method applying: (i) the
approach for defining evaluations (either unique
criterion of synthesis (UCS), or outranking), (ii) for
defining the decision criteria (either without
weighting, with weighting and interdependencies, or
simple weighting), (iii) the ability to deal with
different measure scales, and (iv) easiness of use
(easy, medium or difficult).
The form dimension characterizes how the
method is described. This dimension gathers two
parameters: (i) notation (textual explanation,
mathematical formula, function), and (ii) tool (to
indicate if a software support is available).
The object dimension describes the alternatives to
be prioritized using 4 characteristics: (i) type of data
to consider (either quantitative or qualitative), (ii)
number of alternatives that will be considered with
the method (either large or small), (iii) ability to take
into account incompatibilities and conflicts between
alternatives, and (iv) hierarchicality (ability to deal
with alternatives organized within a hierarchy tree).
In the context of BP priorisation, the problem can
be a choice (application example is BPR), a ranking
(for example, the BPs must be ranked in order to
establish priorities for business security
improvement), and sorting (e.g. BPs are positioned
according to the Capability Maturity Model).
In our case, the potential actions to be considered
are the BPs of an organisation. Their number may
vary from little (if only “macroprocesses” are taken
into account) to very large (if all detailed BPs of the
BP hierarchy are considered). It is very important to
take into account the hierarchical nature of BPs.
Indeed (i) only BP of the same hierarchical level
should be compared, and (ii) BP analysis must taken
into account the nature of the hierarchical links
between BPs. Besides, the BP collection is dynamic.
New BPs emerge, some disappear, and some change
their properties. Alternative BPs have various nature
and may be evaluated according to multiple criteria.
We suggest the 9 following criteria drawn from
literature (Voyer, 1999), (PegaRules, 2003), (Shadrin,
2002), (Sachdeva and Joshy, 2005) and (Crowe et al.,
1997):
BP duration,
BP quality,
BP cost,
BP size,
BP customers satisfaction,
BP efficiency,
BP productivity,
BP contribution to strategic goals,
BP problems,
and, the 4 following criteria, developed based on
our experience with BP priorisation:
BP contribution to problems resolution (the
number of problems that can be solved by
improving the given BP),
BP lifecycle steps: creation, development,
stable functioning, regress, and destruction,
BP influence on stakeholders,
BP customer: internal or external.
These criteria have different scales: cost and value
are absolute numerical data, efficiency and
productivity are ratio, contribution to strategic
objectives, life cycle steps have nominal scales etc. In
addition, data type takes two values: quantitative and
qualitative.
Besides, the analysis involves multiple
stakeholders with different, and sometimes
contradictory, viewpoints.
This analysis allows characterizing the situation in
which BP priorisation shall be undertaken and shall
help selecting an appropriate multicriteria method.
3.1.2 Identifying Candidate MC Methods
The analysis grid was applied to the four general-
purpose MC methods: Multiattribute Utility Theory
ICEIS 2007 - International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
140

(MAUT) (Keeney and Raiffa, 1993), Analytical
Hierarchy Process (AHP) (Saaty, 1980), Outranking
methods (Roy and Bouyssous, 1993), and Weighting
methods (Keeney, 1999). For the sake of space, these
methods are not detailed here. However, table 1
shows an overview using the benchmarking grid.
Table 1: Overview of considered MC methods.
Dimension
Facets
MAUT AHP
Outran-
king
Weigh-
ting
Context
Problematic, choice Yes Yes Yes Yes
Problematic, ranking Yes Yes Yes Yes
Problematic, sorting No No Yes No
Treatment of a new
alternative
Yes No Yes Yes
Taking into account
multiple viewpoints
No No Yes No
Process
Approach for defining
evaluations
UCS UCS Out-
ranking
UCS
Approach for decision
criteria weighting
Yes, no
interd
Yes,
interd
Yes,
interd
Yes, no
interd
Taking into account
various scales of criteria
Yes No Yes No
Easiness of use Difficult Easy Medium Easy
Form
Notation Utility
func-
tion
Weigh-
ted sum
Textual Weigh-
ted sum
Tools No Yes Yes Yes
Object
Data type quan,
qual
quan,
qual
quan,
qual
quan
Number of alternatives to
be treated
Great Small Great Great
Treatment of
incompatibility,
alternatives conflicts
Yes No Yes No
Hierarchicality No Yes No No
3.1.3 Evaluating Candidate Methods
The goal of this step is to identify which candidate
method satisfies all the characteristics which are at
step 1.
In our example: (i) all the considered methods
deal with the choice and ranking problems, and only
outranking methods allow alternatives sorting; (ii)
two methods (MAUT and outranking) supports
various scales of criteria and deal with a great
alternatives number; (iii) AHP is not able to treat the
apparition of new alternatives, and (iv) only
Outranking is able to deal with multiple viewpoints.
3.1.4 Selecting and Applying a Method
Both MAUT and outranking methods satisfy majority
of characteristics. Nevertheless, outranking methods
exceed MAUT regarding to two criteria: sorting
problematic and ability to take into account the
multiple viewpoints. If the last criteria are not
significant, then two methods are equivalent. In such
a case, we must extend analysis to other criteria.
Besides characteristics elicited on step 1, these
methods differ according to approach for defining
evaluations, easiness of use and tool presence. The
approach by outranking gives a more exact result then
unique criterion synthesis. Moreover, outranking
methods are more easy to use and are supported by
tools.
Thus, our recommendation is to use outranking
methods for defining BP priorities.
4 CASE STUDY WITH ELECTRE
This section presents a case study undertaken at a
company in the electronics industry. The purpose of
the experiment was to choose BP to be reengineered.
As a result of this experience, the enterprise expected
to identify one or two processes which reengineering
would bring maximal value with minimal drawbacks.
As shown in the former section, an outranking
method should be considered to deal with this issue.
The family of ELECTRE methods was found
particularly interesting by the enterprise. The
ELECTRE I method intended for choice problems
(Roy and Bouyssous, 1993) was finally chosen. In
order to apply ELECTRE I, one must (i) define the
problem (potential BP and criteria) and evaluate BP
according to selected criteria, and (ii) apply the
method.
4.1 Problem Definition
The problem definition includes specifying (i) a list of
BP, (ii) a list of criteria, (iii) criteria construction and
preference rules, and (iv) criteria weights.
The set of BPs was developed based on the
"Process classification framework" proposed by
APQC (Process Classification Framework, 1996). It
included:
BP1.Understand Markets and Customers,
BP2.Design Products,
BP3.Market and Sell,
BP4.Produce and Deliver,
BP5.Invoice and Service Customers,
BP6.Develop and Manage Human Resources,
BUSINESS PROCESS PRIORISATION WITH MULTICRITERIA METHODS - Case of Business Process Reengineering
141
BP7.Manage Information Resources,
BP8.Manage Financial and Physical Resources.
The collection of criteria to be considered while
applying ELECTRE I was defined based on the
enterprise requirements:
Cr.1. BP contribution to strategic goals presents
the degree of influence of BPs on organizational
performance. Within the framework of Balanced
Scorecard, strategic goals are divided into two
categories: "results" that concern financial
performance and customers, and "leverages" that
concern internal processes, learning and growth.
Weights were distributed within these categories: 2 –
"results" and 1 – "leverages". The final evaluation
was based on weighted sum. The preference rule was
maximum.
Cr.2. BP contribution to problems resolution
means that BPR should help to resolve some decision
problems. The problem at hand was to select a BP
which improvement would bring the greatest result.
We defined improvement by the contribution of
processes to problems that could be solved by process
reengineering. To make the analysis closer to reality
the frequency of occurrence and threat degree were
used as weights. For frequency, the scale was: 0 –
never, 1 – sometimes, 2 – often, 3 – regular. For threat
degree, the scale was estimated on a three-level grade:
1 – low, 2 – medium, 3 – high. This function was
maximum.
Cr.3. BP costs were defined as the number of
persons, working on the BP. Preference rule was
minimum.
Cr.4. BP sizes were defined by the quantity of
sub-processes, which we believed would reflect their
importance in the company. The preference function
was aimed at a maximum.
Cr.5. The purpose of BP life cycle steps was to
define the administrative influences required for
process reforming. Indeed, it was found that process
reengineering was needed or at least acceptable for
processes in the state of development, regression or
stable functioning. Reengineering was felt less
preferable for BPs in state of creation, destruction and
stable functioning. Therefore, the preference rule was
defined as: (development = regress) ≥ stable
functioning > (creation = destruction).
Cr.6. BP customers could be external or internal.
External processes add value for organization's
customers, therefore they were considered as more
important. The preference rule is: external ≥ internal.
To define criteria weights, we used the SWING
method (Keeney, 1999). The decision maker (DM)
chose the most important criterion and affected a
value of 100 to it. Then, the DM chose the most
important criterion and affected a lower value to it.
The same principle was applied recursively until a
value was affected to all criteria. Normalisation
produced weights as shown in Table 2.
Table 2: Criteria Weighting.
Criteria Cr.1 Cr.2 Cr.3 Cr.4 Cr.5 Cr.6
Value 80 100 20 20 60 50
Weight 0.24 0.30 0.06 0.06 0.19 0.15
The two first criteria were general; that is they
included "sub-criteria". In order to define the partial
evaluations we attributed “1” to BPs, which affected
either strategic goals (in our case, the data on strategic
goals were taken from Balanced Scorecard (BSC)) or
problems to be solved. The final evaluations are the
weighted sums of the partial ones (the weights are
described above).
We proceeded by simply assigning values to BP
evaluation according to next four criteria. The
summary of BP evaluation is presented in Table 3.
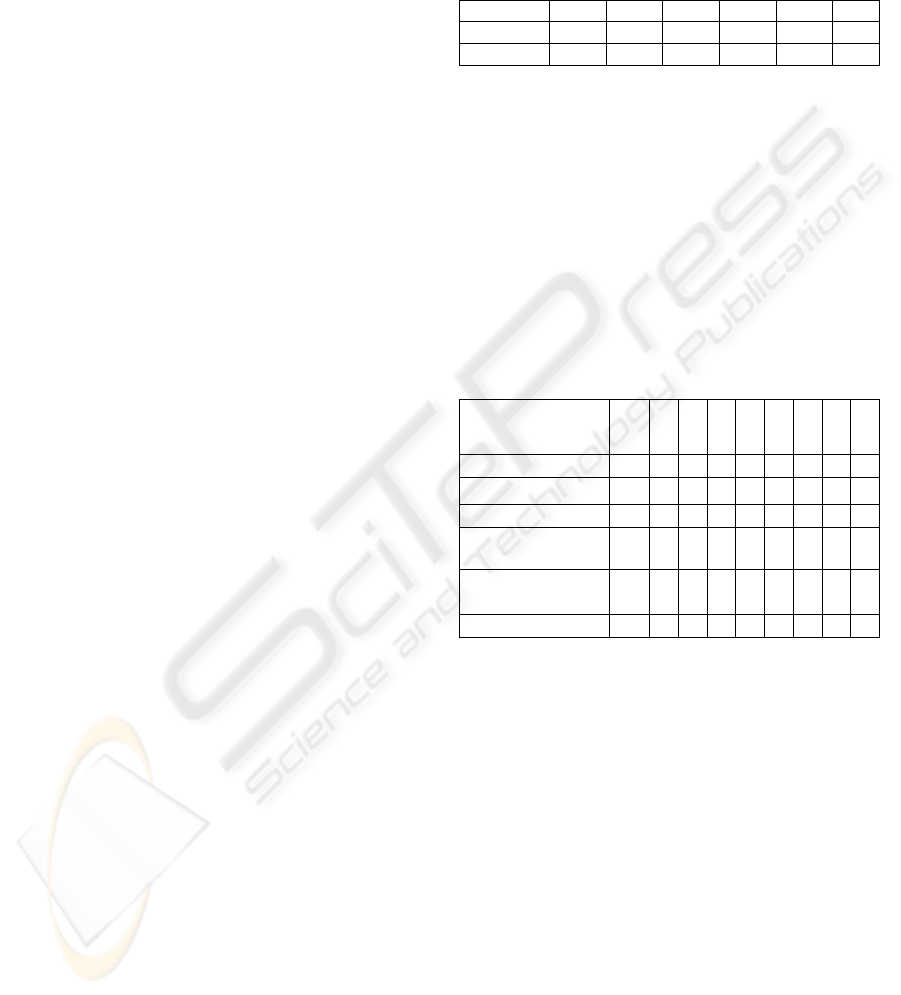
Table 3: BP evaluation summary.
Criteria
weights
BP1
BP2
BP3
BP4
BP5
BP6
BP7
BP8
Cr.1 (in points)
0,24 18 5 12 18 2 2 1 9
Cr.2 (in points)
0,30
3 4 13 13 4 4 4 26
Cr.3 (in persons)
0,06 4 8 5 29 2 1 3 2
Cr.4 (sub-processes
number)
0,06 6 1 1 5 2 2 3 4
Cr.5 (nominal)
0,19 st.
fun.
st.
fun.
st.
fun.
reg. reg. st.
fun.
cre-
at.
reg.
Cr.6 (nominal)
0,15 ext. int. ext. ext. ext. int. int. int.
4.2 ELECTRE Application
ELECTRE I is based on the principles of concordance
and discordance (see Roy and Bouyssous, 1993).
The method starts by a calculation of concordance
and discordance indices. These indices define
concordance and discordance with the assumption that
alternative A is preferred to alternative B. Concordance
and discordance were established using the following
principle: if a DM declared that alternative A is at least
as good as B for the majority of attributes then a
concordance was defined. Discordance was defined
based on the other attributes according to which A was
not strong enough compared with B. All calculations
are not shown here for the sake of space. The
concordance and discordance matrices developed in
our case study are shown in Table 4 and Table 4.
Using a threshold of 0,55 to highlight BPs in the
concordance and discordance tables revealed that BP8
ICEIS 2007 - International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
142

(Manage Financial and Physical Resources)
dominated the others on average without any
particular shortcoming in terms of discordance. A
qualitative analysis of this choice revealed that the
enterprise agreed with it. A reengineering of the
financial and physical resources management
processes was thus undertaken.
Table 4: Concordance matrix.
BP1 BP2 BP3 BP4 BP5 BP6 BP7 BP8
BP1 0,70 0,70 0,51 0,45 0,64 0,64 0,45
BP2 0,49 0,25 0,06 0,54 0,88 0,88 0,15
BP3 0,64 1,00 0,51 0,69 0,88 0,88 0,39
BP4 0,88 0,94 0,94 0,94 0,94 0,94 0,64
BP5 0,70 0,76 0,46 0,40 1,00 0,94 0,40
BP6 0,55 0,76 0,31 0,06 0,66 0,94 0,21
BP7 0,36 0,57 0,12 0,06 0,36 0,51 0,15
BP8 0,55 1,00 0,61 0,55 0,79 0,94 1,00
Table 5: Discordance matrix.
BP1 BP2 BP3 BP4 BP5 BP6 BP7 BP8
BP1 0,04 0,43 0,43 0,14 0,14 0,04 1,00
BP2 0,76 0,39 0,76 0,25 0,25 0,14 0,96
BP3 0,35 0,00 0,35 0,18 0,18 0,07 0,57
BP4 0,86 0,75 0,82 1,00 1,00 0,89 0,93
BP5 0,94 0,18 0,59 0,94 0,00 0,20 0,96
BP6 0,94 0,18 0,59 0,94 0,50 0,20 0,96
BP7 1,00 0,24 0,65 1,00 0,11 0,11 0,96
BP8 0,53 0,00 0,18 0,53 0,07 0,07 0,00
5 CONCLUSIONS
This paper shows how to choose and to apply a
MCDM method. In the particular domain of BP
priorisation, it shows that outranking methods should
be used. Based on an analytical comparison, this
claim is confirmed by a case study of BP priorisation
for the purpose of reengineering in an electronic
company.
Besides BPR, BP priorisation could be achieved
in others contexts such as: ERP implementation,
business continuity plan elaboration, or improvement
of Information System strategic alignment. We
believe that other case studies in these domains and
comparative analyses should be undertaken to fully
validate our approach.
Defining BP priorities with a structured MC
method has advantages: (i) time for decision-making
and implementing decreases thanks to less analysis
mistakes in the BP, (ii) expenses decrease, (iii) degree
of goals achievement grows by targeting the most
important BPs, and (iv) stakeholders confidence in
results and in the overall project grows owing to their
participation in the definition of priorities.
We intend to proceed this research in two
directions: improving our approach to multicriteria
methods selection and developing new practical cases
to obtain more precise evaluations.
REFERENCES
Crowe, T.J., Rathi, K. and Rolfes, J.D., (1997), Applying a
Taxonomy of Business Processes to Identify
Reengineering Opportunities,
http://www.prosci.com/rathi.htm, October 15, 2005.
Hammer, M. and Champy, J., (1993), Le reengineering:
Réinventer l'entreprise pour une amélioration
spectaculaire de ses performances, Dunod, Paris.
Keeney, R.L., (1999), Foundations for Making Smart
Decisions, IIE Solutions, 31, No. 5.
Keeney, R.L. and Raiffa, H., (1993), Decisions with
Multiple Objectives: Preferences and Value Trade-Offs.
Cambridge University Press.
Mazur, I., Shapiro, V., Titov, S. and Elkina, L., (2000),
Companies restructuring, Moscow, Ed. High school.
Papadacci, E., Salinesi, C. and Sidler, L., (2006) Panorama
des approches d’arbitrage dans le contexte de
l'urbanisation du SI, Revue des sciences et techniques de
l'information (RSTI), Hermes, France.
PegaRULES Process Commander. Business Activity
Monitoring: Empowering BPM, (2003),
http://www.insurancenetworking.com/assets/article/4/B
AM%20White%20Paper.pdf, October 19, 2005.
Process Classification Framework (1996),
http://www.apqc.org/, February 28, 2006.
Robson, M. and Ullah, P., (1996), A Practical Guide to
Business Process Reengineering, Gower Publishing
Limited.
Roy, B. and Bouyssous, D., (1993), Aide Multicritère à la
Décision: Méthodes et Cas, Economica, Paris.
Saaty, T.L., (1980), The Analytic Hierarchy Process. NY,
McGraw Hill.
Sachdeva, N. and Joshy, J., (2005), On demand business
process life cycle, Part 8: Business process monitoring
– Create key performance indicators, http://www-
128.ibm.com/developerworks/webservices/library/ws-
odbp8/, October 19, 2005.
Salinesi, C. and Kornyshova, E. (2006), Choosing a
Prioritization Method – Case of IS Security
Improvement. In Forum Proceedings of the 18th
International Conference on Advanced Information
Systems Engineering, Luxembourg.
Shadrin, A., (2002), Process approach: Foundation and
implementation methods, All about Quality, N 16-17.
Moscow, Ed. Trek.
Voyer, P., (1999), Tableaux de bord de gestion et
indicateurs de performance, Presse Universitaire du
Québec.
BUSINESS PROCESS PRIORISATION WITH MULTICRITERIA METHODS - Case of Business Process Reengineering
143
