
GIS QUALITY MODEL
A Metric Approach to Quality Models
Willington Libardo Siabato Vaca
Universidad Pontificia de Salamanca, Facultad de Informática, Madrid, Spain
Adriana Patricia Rangel Sotter
Universidad Pontificia de Salamanca, Facultad de Informática, Madrid, Spain
Keywords: Software Quality, ISO/IEC 9126-1, Quality Models, Metrics, GIS, Software Evaluation.
Abstract: In the past few years organizations and companies have developed new standards which have been proved
highly efficient both in the public and private sector. The most important of them is the Quality
Management System regulated by the standard ISO 9001. This standard proves how its implementation
represents sensitive improvements of the production system, optimizing the product and increasing its
quality. This phenomenon is not isolated within software engineering's frame. Many works have been
published, like Boehm and McCall, of which have raised many standards among which the ISO/IEC 9126 is
highlighted. Regarding this fact, it has been possible to create different solutions for multiple related
problems with IT. Nowadays, the Geographic Information Systems' project managers do not have a tool for
either selecting the software to implement their projects or supporting this selection in technical criteria. The
questions are: which one of the commercial software packages is appropriate to my project? Which one of
the software packages follows the requests of the project out? Which one of this software supports the needs
of the users? This article presents a quality model to support these decisions. This way, project managers
can make their decisions based on a set of metrics which are product of the deep evaluation of
characteristics, subcharacteristics and attributes of the software. These metrics has been developed to apply
for all models based on ISO/IEC 9126-1 standard. The mentioned elements allow user to know which of the
software packages is the best through a GIS Quality Indicator, generated through the model. This indicator
allows GIS’ project managers to take decisions based on a technical criterion. A model in accordance with
international standards related to product quality in software engineering such as ISO/IEC 9126-1.
1 INTRODUCTION
New trends to utilize the cartographic information
for evaluating resources and territorial planning
emerged in the sixties and seventies. It was noticed
that different coverages on the surface of the earth
were not independent, rather they kept some kind of
interdependence. The need to evaluate them in a
more efficient way was self-evident. At first, the
used methods were relatively simple namely,
transparent copies of maps were superimposed on lit
tables and points of coincidence in the distinct maps
were found. At a later time, this technique was
applied to emerging Information Technologies -IT-
and simple maps were created by means of overprint
of characters to produce different tones of grey.
Nevertheless, specialists did not find these
methods extremely useful and they were not
accepted by the professionals that produced, updated
or used cartographic information. In the late
seventies, the IT to generate cartographic
information progressed rapidly and it was tuned
many of information-technology systems for distinct
cartographic applications. In the same way, progress
was being made in related sectors namely:
photogrammetry and remote perception. Initially, the
fast development meant the duplication of efforts in
different areas relating to cartography. With constant
improvements to the systems, developers acquired
experience and the possibility to use different kind
of tools for working with spatial information had
been raised. The creation of these systems
contributed to the creation of solid Geographic
Information Systems -GIS- for general purpose. In
176
Libardo Siabato Vaca W. and Patricia Rangel Sotter A. (2007).
GIS QUALITY MODEL - A Metric Approach to Quality Models.
In Proceedings of the Ninth International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems - ISAS, pages 176-183
DOI: 10.5220/0002388701760183
Copyright
c
SciTePress

the early eighties, GIS had become a completely
operating system whilst the technology of computers
had started to grow and to develop rapidly.
Currently, GIS are being implemented in
vertiginous form on public agencies, laboratories,
research institutes, pedagogical institutions, private
and military industry. This big introduction of the
GIS has given rise to a need for the users of the
geographic information to know this technology in a
better way. Therefore, it is necessary to help them to
understand the GIS software through solid and
reliable tools which must be based on methodologies
created and developed for this specific objective.
This article describes a quality model for
selecting and verifying GIS software that will be
utilized as a platform for a specific project. This
software has to be reliable, fulfil the project
requirements analysis and satisfy the needs of both
the project and the user. This way, the paper presents
an innovative solution to help GIS professionals to
support the chose of the platform software on a
quality model created for this specific objective. A
model that solves a real problem which has not been
worked on yet, a problem that is observed in the
day-to-day routine of institutions and companies.
2 DESCRIPTION
Models are abstractions of reality and are designed
to make process easier. They offer to users the
adequate tools to interpret complex realities by
isolating and focusing on the principle components
and removing elements that do not affect the final
results meaningfully. Specifically, quality models
offer a series of elements that user must take into
consideration to insure that accomplished actions are
adequate to obtain the desired results. This way,
different kinds of variable are required in order to fit
the models up to the intrinsic and extrinsic
characteristics of the elements that will get involved
within the developed model or models.
Nowadays experts and beginners engaged in
development and implementation of information
systems, have many problems to select a GIS
platform namely: the big supply of GIS products, the
multiple versions available of one product, new
products or additional extensions to have more tools
and specific functions. These are enough causes the
users become confused, this way, a simple decision
such as to select a GIS platform software turns into a
difficult job.
When GIS projects are planned, objectives are
defined and user's requirements are identified; one of
the most important stages for their design and
development is to select the platform which it will
be implemented over. This decision implicates
investment of resources, run times, accomplishment
of requirements and needs, adequate functionality
and the customer satisfaction. For GIS' domain, it
does not exist a tool, methodology or model that
permits professionals to solve this problem. They
neither have enough support to bear his decision in
theoretic well-grounded concepts. Therefore, it is
evident the need of creating some method in order
that this decision is not based exclusively on project
manager's experience or, as it occurs for the most of
the cases, taking into account the most popular GIS
software without evaluating more alternatives.
The mentioned deficiency constitutes a problem
that needs to be solved. This solution has to support
one of the most relevant processes in the project
cycle, due to the fact that it affects deeply the
success or failure of the project.
Taking into consideration what's been said up to
this point, it is possible to define the main objective
of this article. Of course, it is to define a quality
model for GIS software packages, that permits
identifying through robust metrics which is the best
GIS software for an specific project and its
implementation within a frame of specific conditions
and under a set of specific requirements. Three
fundamental points would be mitigated with this
model: (i) speeding up the process of selection of
platforms and tools of the system, (ii) offering a safe
methodology to guarantee that the selected tool
fulfils the minimal requirements of system and user,
(iii) bearing the development of information systems
on standards and quality models designed and
developed specifically for this objective.
2.1 Quality Models
The first topic that must be discussed in this article it
is what quality means and how this characteristic is
integrated in information systems and software
packages. Just as quality has evolved, its concept has
borne several transformations over the time. Thus,
different definitions have been emitted by working
groups dedicated to its study. Formal meanings that
take into account the human dimension are
suggested by Dr. Joseph M. Juran (Juran, 1995):
quality consists in freedom after deficiencies; quality
refers to the absence of deficiencies itself; quality
consists in the product’s characteristics that are
based on the customer's needs. Other important
definitions are (Crosby, 1991), (Feigenbaum, 1991),
(Taguchi, 2004) and (ISO, 2000), that defines
quality as “set of properties or characteristics of
something (product, service, process) that made it
GIS QUALITY MODEL - A Metric Approach to Quality Models
177

apt to satisfy needs.” This definition not only refers
to the characteristics of the product or services itself,
rather introduces other aspects that can be shown in
the final service.
Analyzing the above definitions the quality
concept that will be taken into account to develop
the model exposed in this paper is the set of product
or service’s characteristics that have the ability to
satisfy the user's needs and expectations, permitting
to judge its value based in a set of attributes and
intrinsic properties, within a frame of reference well
defined.
2.1.1 Software Quality
Nowadays it is clear how computers and software
are utilized for a wide range of fields and
applications. That is why, development and selection
of high-quality software products are relevant, even
though it is considered that its development and
implementation in a right way implies the success or
failure of the processes that are borne on these tools.
Thus, the specification and the extensive evaluation
of the software quality is a key factor to ensure an
adequate quality and the success of the tasks based
on software products.
ISO (ISO & IEC, 2001) suggests that it is
important that each relevant characteristic of
software quality be specified and evaluated, using
valid and widespread metrics as far as possible.
Software producers are responsible for that these
characteristics are identified in order to define the
metrics that will permit to know whether an element
or attribute of the product is acceptable. Thus,
several elements will be considered both in the
process of development and the use of software.
ISO/IEC 9126 and ISO/IEC 14598 have been
developed considering these characteristics; in
addition associated metrics can be used not only for
evaluating software products but also to define
quality requirements and other uses. ISO/IEC 9126
was created for the specification and extensive
evaluation of the software product quality taking
into account metrics, specifying relevant quality
characteristics and describing a model for
production of software products from the point of
view of internal and external use. ISO/IEC 14598 is
related with the software product evaluation.
Considering that the proposed model aims
supplying a tool that permits users to select among
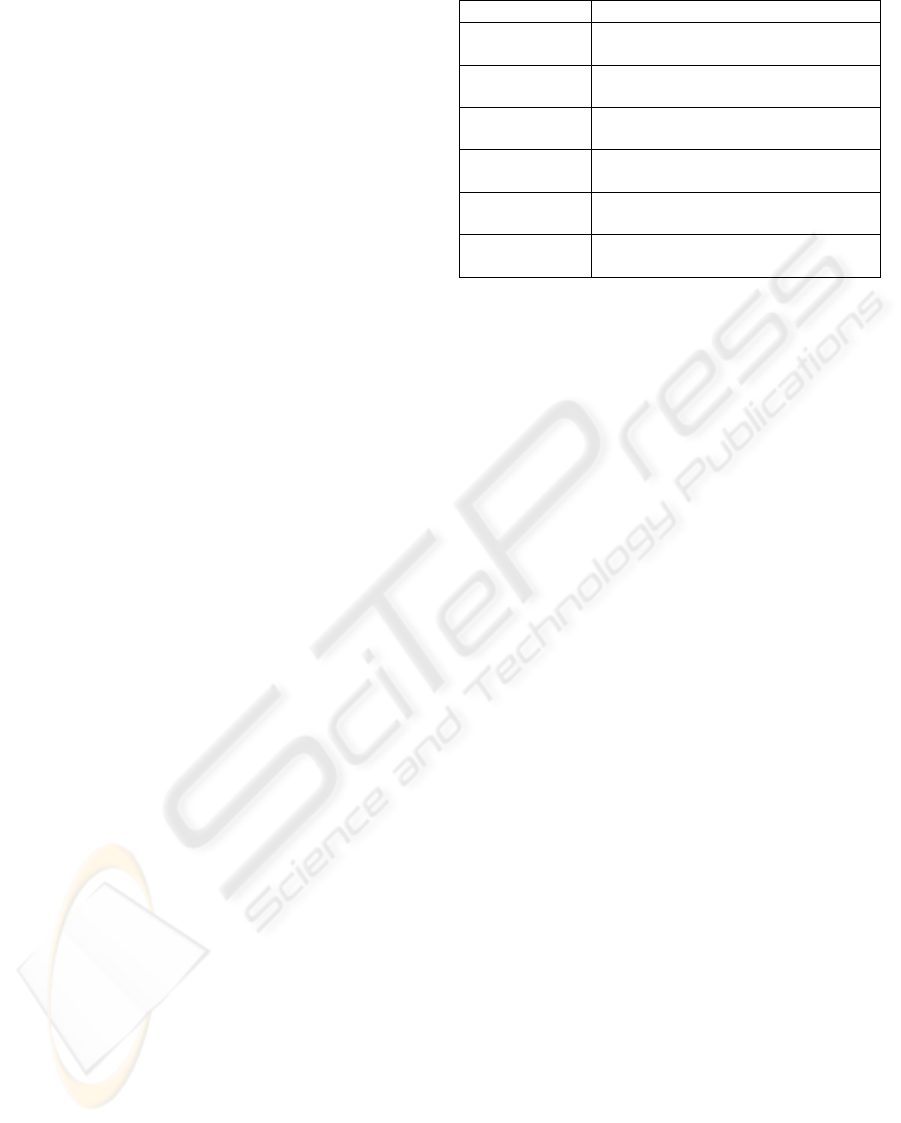
Table 1: Standard ISO/IEC 9126.
Standard Objective
ISO/IEC 9126-1 Quality model
ISO/IEC 9126-2 External metrics
ISO/IEC 9126-3 Internal metrics
ISO/IEC 9126-4 Quality in use metrics
the different bidding of the market, the software
which adjusts to specific user needs and fulfils the
entire quality requirements for GIS projects in a
specific domain. The developed model relies on the
ISO/IEC 9126 family standard and specifically in
the ISO/IEC 9126-1 quality standard due to the fact
that it lets to create hierarchies of quality features,
which are essential for building structured quality
models besides that it is a widespread standard.
2.1.2 ISO/IEC 9126 Quality Standard
ISO/IEC9126 is a family of standards that regulates
the software product quality taking into account:
models which are conformed by, internal and
external characteristics, the method to measure these
characteristics and the functionality of the proposed
model. The standard is conformed by four parts that
share the same general title: Information
technologies – Software engineering – Product
quality.
Xavier Franch (Franch, 2003) says that ISO/IEC
9126-1 specifically addresses quality model
definition and its use as a framework for software
evaluation. A 9126-1 quality model is defined by
means of general software characteristics, which are
further refined into subcharacteristics, which in turn
are decomposed into attributes, yielding a multilevel
hierarchy. At the bottom of the hierarchy are
measurable software attributes, whose values are
computed using some metrics, which are defined
and regulated by ISO/IEC 9126-2 and ISO/IEC
9126-3 standards. Internal metrics quantify the
software’s characteristics, while external metrics
measure the general behaviour and performance
implicating the system in which the software is
implemented. Finally, quality in use quantifies the
effects of using a software package in a specific
context; this is regulated by the standard ISO/IEC
9126-4 taking into consideration characteristics and
subcharacteristics.
The proposed quality model has been developed
exclusively taking into account the external quality
elements, because it is there where the end user
interacts directly with the final product and it is from
this that the user defines his quality perception. In
other reference frames, this perception can feed back
to the internal quality and create an ever improving
ICEIS 2007 - International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
178
cycle of product. Nevertheless, this element was not
considered within the development of this work due
to the fact that it is focused exclusively on the end
user. The objective is to reach the necessary quality
to satisfy the real users’ needs.
2.2 Referenced Models
The software product quality should be evaluated
using a well defined quality model. In practice it is
not possible to measure all the software's internal
and external subcharacteristics due to the fact that
software products are normally too big. Also, it is
not practical to measure the quality in use for all of
the possible user-task scenarios. The resources for
evaluation must be assigned to the different kinds of
measurements depending on the objectives of the
business and the nature of the product or the design
process. ISO proposes evaluating the software
products quality based on a set of characteristics and
subcharacteristics of general interest.
Table 2 shows the six quality characteristics
defined in the ISO/IEC 9126-1 quality standard and
their decomposition into subcharacteristics. In
addition, subcharacteristic compliance is included
for all of the characteristics. These elements support
the proposed model. Combining this model with the
one proposed by Franch, it is possible to define an
adequate evaluation frame for GIS.
Quality models considered for the development
of this article are the ones that for its aim permit to
evaluate the performance of any application or to
create some kind of metric.
In the study accomplished by Chirinos (Chirinos
et al, 2003), he intends a requirements classification
which takes into account the quality views from the
first stages of development to provide the quality
requirements identification. The authors develop a
requirements classification model based on views of
quality with the aim of providing the quality
requirements identification.
Another interesting work is developed by
(Losavio, 2002). She proposes a form to specify the
relevant quality attributes implicated in the design of
architectonic process. An additional model to take
into account was carried out by (Calero et al, 2004),
whom developed the Web Quality Model –WQM–.
The main referenced model is developed by
Franch and Carvallo (Franch, 2003), quality models
in software package selection. This work proposes a
specific methodology to make structured quality
models to select software package involving
software's description and functionality. The model
Table 2: ISO/IEC 9126-1 standard.
Characteristics Subcharacteristics
Functionality Suitability, Accuracy,
Interoperability, Security.
Reliability Maturity, Fault tolerance,
Recoverability.
Usability Understandability, Learnability,
Operability, Attractiveness
Efficiency Time behaviour, Resource
utilization.
Maintainability Analyzability, Changeability,
Stability, Testability.
Portability Adaptability, Installability,
Coexistence, Replaceability
comprises six steps: defining the domain,
determining quality subcharacteristics, defining a
hierarchy of subcharacteristics, decomposing
subcharacteristics into attributes, decomposing
derived attributes into basic ones, stating
relationships between quality entities and
determining metrics for attributes.
It is in the determination of metrics for attributes
where the proposed model focuses its develop and
underlies one of the main contributions (since
current methodologies does not define real metrics),
and further on, a global quality indicator which
defines an absolutely quantification for the package
software quality evaluation.
3 MODEL DEFINITION
Through the proposed model, it is possible to know
which of the available software packages fulfil
minimal and necessary requirements in desired
conditions, and which of they get the higher
evaluation for each characteristic (dimensions)
defined in the model. This evaluation will permit
discarding those tools that not fulfil minimal
conditions, as well as reducing the possibilities to
determine a final decision based on another kind of
criteria like the cost-benefit ratio, because it is
possible that tools with a huge difference in their
cost, supply the same functionalities and guarantee
the same reliability in some designing conditions.
3.1 Characteristics &
Subcharacteristics
The flexibility of the methodology proposed by
9126-1 standard is unequivocal, their components
are not a straightjacket for the definition of the
model in a specific dominion but they constitute a
good starting point. This way, when the components
GIS QUALITY MODEL - A Metric Approach to Quality Models
179
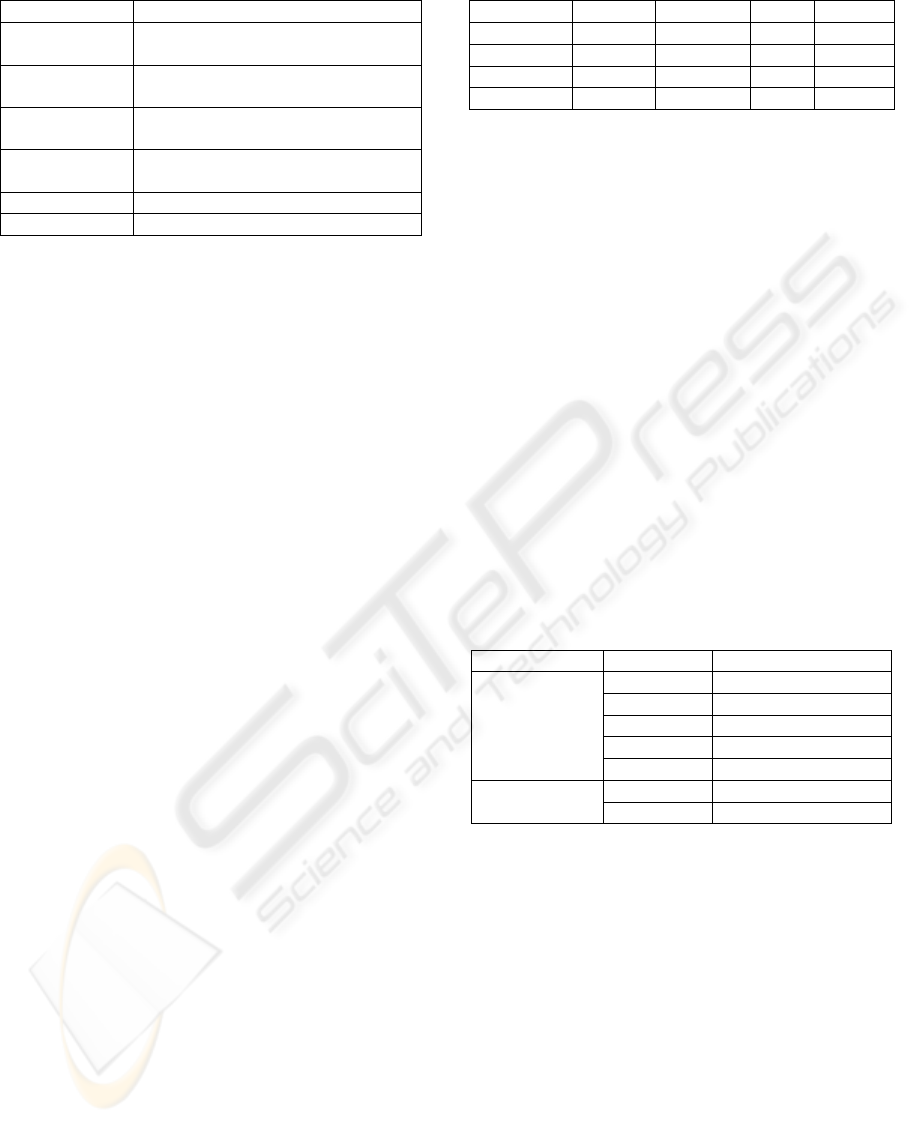
Table 3: Modified characteristics and subcharacteristics.
Characteristics Subcharacteristics
Functionality Compatibility.
Availability.
Reliability Quality data verification.
Scalability.
Usability Complexity of personalization.
Usability compliance.
Efficiency Data protection.
Efficiency compliance.
Maintainability Maintainability compliance.
Portability Portability compliance.
and the modifying dimensions are examined
according to the needs of GIS software, some
subcharacteristics have been eliminated, others have
changed its meaning and others have been created
defining new concepts according to GIS software
packages. The result is showed in Table 3.
In general all the subcharacteristics definitions
are according to what is indicated by ISO/IEC 9126-
1. The subcharacteristics compliance for usability,
efficiency, mantainability and portability are
eliminated for being considered irrelevant for GIS
software. The six new incorporated elements try to
refine the model for a complete evaluation.
For the dimension functionality, the
subcharacteristic compatibility is defined like the
capability of the software to interchange data and to
maintain projects with others software package of
the same type. The subcharacteristic availability
evaluates the licenses and license administrator to
verify if the software guarantees the license service.
Data verification permits to verify input and output
of data quality. Scalability checks the software
capability to be adapted without problems to a
harder work as a result of new users addition,
increment of the traffic or execution of new
transactions. An important GIS subcharacteristic is
the complexity of personalization, defined like the
set of software attributes that determine the
capability and facility of software's personalization
for specific tasks. Finally, data protection compiles
the attributes for users’ administration and how the
data access is administrated in the main system.
3.2 Definition of Types of Measures
Once the model’s dimensions have been defined and
before defining the attributes that describe them, it is
necessary to indicate the types of measures that the
user will use to quantify attributes. For its definition
some points must have considered:
Types of measures have to be represented by
quantitative elements to be able for operations.
Table 4: Type of measures for attributes quantification.
Measure Type Dominion Unit Symbol
Eyewitness Boolean 0-1 P
Time Integer s/d/m T
Level Integer 0-4 N
Ratio Integer 0-100 % R
If the type of measure is represented by
qualitative elements, it has to be changed to
quantitative elements.
For some types of attributes it is not enough to
express the measure of his behaviour with
single elements like boolean or integer, in this
case the attribute require a function to express
in a best-suited form its behaviour.
Taking into account Vallecillo and Bertoa’s work
(Vallecillo & Bertoa, 2002), the proposed model will
use the types of measures defined in Table 4. Each
one of these types will be utilized to quantify the
model defined attributes in following cases:
Eyewitness (P) indicates if an attribute exists.
Time (T) measures spans.
Ratio (R) expresses a specific percentage.
Level (N) indicates a grade of effort, ability.
The model establishes a five-level classification
method for the Level type according to Table 5. The
Eyewitness type is defined through a boolean value.
Table 5: Measures description.
Measure Value Scale
0 Very low
1 Low
2 Medium
3 High
Level
4 Very high
0 – False Exist Eyewitness
1 – True Not exist
Time and Ratio types are expressed in seconds
and percentage respectively. The percentage shows
how much the software gets close to the fulfilment
of a requirement. In cases like installation times and
configuration as well as capacitating and learning
can change the time unit second to day or month.
For operations of attributes quantified through
Time type, it is necessary to transform from Time to
Level, this way the metrics operation becomes more
efficacious. This transformation is done according to
Table 6. Each attribute needs to be transformed in a
different way. The attributes A, B, C & D
correspond to: duration of the product in the market,
efficient use, adequate configuration and efficient
administration. The values correspond to the same
scale defined in the Table 5.
ICEIS 2007 - International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
180

Table 6: Attribute reclassification for Time measures.
Value Atributte
A (Year)
Atributte
B (Mth)
Atributte
C (Day)
Atributte
D (Mth)
0 < 5 < 7 > 5 < 4.5
1 5 - 10 6 - 7 5 4 - 4.5
2 11 - 20 5 - 6 4 3.5 – 4
3 21 - 30 4 - 5 3 3 – 3.5
4 > 30 < 4 <= 2 < 3
Once the dimensions and types of measure have
been defined it is possible to start the definition of
attributes, the main component of the GIS quality
model. The attributes correspond to the way that the
model's characteristics are described and a quality
property which is possible to assign a measure.
Through an analysis of GIS tools, compiling GIS
experts’ concepts and experiences as well as the
observation of projects, 370 attributes have been
defined for the dimensions. The complete list can be
consulted in the physical model or (Siabato, 2005).
3.3 Metrics Definition
The measures, which rate the attributes that describe
the dominion defined for the characterization of the
model, are computed through metrics. Two kinds of
metrics have become established in the model:
specific and general metrics. Specific metrics are
defined to deliver a general evaluation of the
evaluated software, in this sense, it will be a metric
which will compute not measured but other metrics
derived of the model such as general metrics, which
are defined as the elements that will be utilized to
quantify each one of the dimensions of the model.
3.3.1 GIS Quality Indicator
As was said, the model intends to show an indicator
that represents in a simple way the GIS software
quality evaluated, a specific metric is established (1).
∑
=
=
6
1i
ii
WNI
(1)
Where Ni represents each one of the dimensions
which conforms the model and Wi is their weight. In
order to define the Wi weights a group of GIS
experts replied to an opinion poll which tried to
classify the level of the dimensions. From the
obtained values and pondering the results the Wi
weights are described in Table 7.
Considering that grades granted by experts are
rated in the range 0–10 and they must be normalized
to the model's dominion (0-1); it is necessary to use
the relation described in (2).
Table 7: Weights for dimensions.
Dimension Value Weight
Functionality 0.26 W
1
Reliability 0.21 W
2
Usability 0.17 W
3
Efficiency 0.10 W
4
Maintainability 0.16 W
5
Portability 0.10 W
6
∑
=
=
6
1i
iii
W
χχ
(2)
3.3.2 Subcharacteristics Evaluation
To define the metrics of the dimensions it is
necessary to take into account each one of the
subcharacteristics which compose them. Unlike the
definition of the indicator I, each subcharacteristic
will be calculated with the same weight.
A method according to the type of measure P, T,
N or R is determined for the evaluation of each
subcharacteristic. The dominion of evaluation is
established in the range 0 -1, 1 represents a total
fulfilment of the subcharacteristic and 0 represents
its absence. Taking into account these premises,
metrics M
TP
, M
TT
, M
TR
and M
TN
are defined
according to the type of measure.
For evaluation of the type P attributes the
expression (3) has been defined, where Xi is the
grade P established by the user and n corresponds to
the number of attributes for the evaluation of each
subcharacteristic. With this metric is possible to
evaluate attributes such as applicability, accuracy,
interoperability, security and availability.
nM
n
i
iTP
∑
=
=
1
χ
(3)
For quantification of type R measures, the
previous method is valid if it is considered that the
dominion of evaluation R: 0-100 is comparable with
P: 0-1. The expression (4) defines the metric for the
evaluation of type R attributes. Subcharacteristics
such as compatibility and functionality compliance
are quantifiable with this method.
100
1
n
M
n
i
i
TR
∑
=
=
χ
(4)
For type N measures, the method to calculate the
grades is more complex. Due to the evaluation scale
(Table 5) it is possible to define the work dominion
in R5. Therefore, the best-suited the way of
quantifying attributes related to this type of measure
is applying the Euclidean rule. The expression (5)
represents the metric for type N measures. Where, Xi
GIS QUALITY MODEL - A Metric Approach to Quality Models
181

represents the grade N established by the user
between 0-4 and the element n, just like (3), is the
number of attributes for each subcharacteristic.
nM
n
i
iTN
4
2
1
2
∑
=
=
χ
(5)
Finally, for the quantification of type T measures
and keeping in mind the reclassification showed in
Table 6, which the dominion of evaluation for N is
homologate to type T measure, it is also possible to
apply the expression (5) to type T measures, taking
into account the respective reclassification process.
The metrics defined until now allows finding
values in ideal conditions in which all attributes are
graded with the same type of measure. Nevertheless,
there are some subcharacteristics that combine three
or more types of measures, this force to define a new
method for computing a single value for each
subcharacteristic. Ad hoc, it must be taking into
account that the final result belongs to the dominion
of the model, defining a general case that allows
finding the final value independently if the
subcharacteristic is quantified with two or more type
of measures. The expression (6) is the best suitable
relation to solve this problem.
n
M
n
i
i
TG
2
1
2
∑
=
=
χ
(6)
Where M
TG
, defined as the metrics of general
type, is the general evaluation of the
subcharacteristics. Xi represents the metrics N, R, T
ó P established for the attributes that define the
subcharacteristic and n is the number of different
measures N, R, T ó P implicated in the evaluation.
3.3.3 Quantification of Dimensions
When the defined metrics are applied to the
subcharacteristics that compose the dimensions of
the model, a value between zero and one is obtained.
This value represents the level of quality for each
quantified item. This information can be useful for
some user that requires comparing a
subcharacteristic in particular. However, this
information is only an intermediate product utilized
for the final purpose, the presentation of the GIS
quality indicator (1). Once the sub-characteristics
were defined, the last step is to define Ni. Keeping in
mind that each one of obtained elements has been
normalized, in order to obtain each Ni it is necessary
to average the subcharacteristics which compose it.
(7) represents the expression to obtain each Ni value.
nN
n
i
ii
∑
=
=
1
θ
(7)
Where, u
i
represents each one of the dimension
subcharacteristics, and n is the number of related
subcharacteristics. This way, the metric for each
dimension is obtained and the user will be able to
evaluate the result according to his needs and the
ones belonging to the project. In addition, we have
all of the elements to calculate the Indicator (I)
useful to determine which of the evaluated software
adjust better to the project.
3.4 Metrics Representation
The elements that must be represented are the GIS
quality Indicator and each one of the metrics which
are utilized to evaluate the dimensions. Two
methods of presentation have been established in
order to show the obtained results to the user:
Numerical method. A numerical value that will
be utilized to represent the GIS Indicator (1)
and to compare the general evaluation of each
software package evaluated.
Graphical method. A six-branch graphic that
will be utilized to represent each dimension.
The user will be able to evaluate which one of
the dimensions has the biggest evaluation.
4 SOFTWARE EVALUATION
There are multiple companies which offer different
solutions for the implementation of GIS projects.
The most outstanding are Intergraph
®
, MapInfo
®
,
Autodesk
®
, MicroImages
®
, Smallworld
®
, Bentley
®
and ESRI
®
. Once the model has been defined, three
GIS software will be evaluated in order to validate
the proposed model. The three evaluated GIS
package are ArcGIS
TM
ArcInfo 9.0 from ESRI
®
TNT 6.9 from MicroImages
®
and Geomedia
TM
Professional from Intergraph
®
.
To validate the model the set of metrics have
been implemented in a Microsoft
®
Office Excel
book. In this book, the user rates each attribute in the
dominion that has been defined for each type of
measure. Each sheet has the changes of scale and the
necessary operations to generate the metrics.
The results of the finished evaluation for the
mentioned software are shown in Table 8 and Figure
1. The showed metrics will permit project managers
make the best decision based on the metrics for each
subcharacteristic and the GIS Quality Indicator.
ICEIS 2007 - International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
182

Figure 1: Metrics representation.
The results indicate that the best performed
software is ArcGIS
TM
, followed by TNT and
Geomedia
TM
. It is necessary to underline that this is
a general evaluation and takes into account the
global performance of the evaluated software and it
is not an evaluation based on specific conditions.
However, offers a good idea about which of the
evaluated software has the best performance. But it
is not possible to say that ArcGIS
TM
is better than
the other ones. Figure 1 shows such the software
with the best functionality is TNT. This implicates
that if the user is looking for a package with specific
functions and properties to satisfy his needs, the
adequate election is TNT. This type of analysis is
possible because of the independent evaluation of
each dimension, e.g. if the user needs a highly
adaptable software the right election is ArcGIS
TM
.
5 CONCLUSIONS
It is evident how any GIS project must select each
one of its components in the right way. This project
has covered this problem for the software platform
on which the project will be implemented. Taking
into account that exists many kinds of products, the
aforementioned platform must be selected with
technical criteria and keeping in mind users’ needs.
The proposed model constitutes an advance for the
definition and selection of GIS software packages,
based on international standards and focused on the
fulfilment of users and project requirements. This
model helps to GIS managers to select the platform
based on technical criteria and a safe methodology.
This a pioneer model, even though it is based on
existing methodologies, it does not exist quality
models related in the GIS dominion. Besides that,
this work proposes a set of completely innovative
metrics which can be applicable to any quality
model derived from ISO/IEC 9126-1.
Table 8: Results of the finished evaluation.
Dimension ArcGIS
TM
Geomedia
TM
TNT
Functionality 0,900 0,892 0,968
Reliability 0,932 0,811 0,840
Usability 0,918 0,850 0,856
Efficiency 0,855 0,862 0,868
Maintainability 1,000 0,809 0,676
Portability 0,772 0,780 0,905
Indicator (I)
0,909 0,840 0,859
The developed model considers the typical
evolution between measure, metric and indicator.
Each one of the attributes derived from the GIS
software analysis is quantified through a measure.
These measures are processed through a set of
algorithms which let to know an overview of the
evaluated software. Finally, each metric generated
for each dimensions is processed to generate the GIS
Quality Indicator, main objective of this work.
This paper had defined a new methodology
which can be used to support the GIS projects design
process on international standards, incorporating this
type of projects to international quality standards.
REFERENCES
Calero, C., Ruiz, J. & Piattini, M. (2004) "A web metrics
survey using WQM", In: Fourth International
Conference on Web Engineering, Munich - Alemania
Chirinos, L. (2003) "Una clasificación de requisitos
basada en vistas de calidad", In: Jornadas Chilenas.
Crosby, P. B. (1991) La organización permanece exitosa,
Mc. Graw Hill, México D.F. – México.
Feigenbaum, A. V. (1991) Total Quality Control, Mc.
Graw Hill, New York – USA.
Franch, X. & Carvallo, J. (2003) "Using Quality Models in
Software Package Selection", IEEE Software, 20 (1)
ISO (2000) International Standard ISO 9001:2000 Quality
systems - Model for quality assurance
ISO, IEC, (2001) International Standard ISO/IEC 9126-1.
Software engineering -Product quality- Part 1:
Quality Model, ISO/IEC 9126.
Juran, J. M. (1995) Juran y la planificación para la
calidad, Diaz de Santos, Madrid – España.
Losavio, F. (2002) "Quality Models to Design Software
Architecture", Journal of Object Technology, 1 (4) 165
Siabato, W. (2005) Modelo de calidad para paquetes de
software SIG, MSc. Tesis. U. Pontificia de Salamanca.
Taguchi, G., Chowdhury, S. & Wu, Y. (2004) Taguchi's
Quality Engineering Handbook, Wiley-Interscience,
New York – USA.
Vallecillo, A. & Bertoa, M. (2002) "Atributos de calidad
para componentes COTS", In: IDEAS 2002, La
Habana - Cuba 352-363
GIS QUALITY MODEL - A Metric Approach to Quality Models
183
