
IMPRECISE EMPIRICAL ONTOLOGY REFINEMENT
Application to Taxonomy Acquisition
V
´
ıt Nov
´
a
ˇ
cek
DERI, National University of Ireland, Galway, IDA Business Park, Lower Dangan, Galway, Ireland
Keywords:
Ontology engineering, ontology learning, taxonomy acquisiton, uncertainty.
Abstract:
The significance of uncertainty representation has become obvious in the Semantic Web community recently.
This paper presents new results of our research on uncertainty incorporation into ontologies created automat-
ically by means of Human Language Technologies. The research is related to OLE (Ontology LEarning) – a
project aimed at bottom-up generation and merging of ontologies. It utilises a proposal of expressive fuzzy
knowledge representation framework called ANUIC (Adaptive Net of Universally Interrelated Concepts). We
discuss our recent achievements in taxonomy acquisition and show how even simple application of the princi-
ples of ANUIC can improve the results of initial knowledge extraction methods.
1 INTRODUCTION
This paper builds on a novel representation of uncer-
tain knowledge in the scope of automatic ontology
acquisition, which was introduced in (Nov
´
a
ˇ
cek and
Smr
ˇ
z, 2006). The main objective of the ontology ac-
quisition platform OLE
1
is to implement a system that
is able to automatically create and update domain spe-
cific ontologies for a given domain. Ontologies are
used for many different tasks in the Semantic Web –
mainly for annotation of the web content, formal de-
scription of specific domains and reasoning on them.
As the amount of data on the Internet is vast and
dynamically growing and changing, we we empha-
sise an empirical approach to the ontology construc-
tion by means of bottom-up acquisition of concepts
from the domain-relevant resources (documents, web
pages, corpus data, etc.). The acquisition process
is incrementally boosted by the integration with the
knowledge already stored in the ontology.
The ontology engineering process is a difficult
task. Manual efforts of collaborative ontology de-
sign (Gomez-Perez et al., 2004; Zhdanova et al.,
2005) lead to development of relatively precise and
complex ontologies, however, it is infeasible to cover
data intensive domains (e. g. medicine or computer
science) using only this approach to knowledge engi-
neering.
1
The project’s web page can be found at URL:
http:
//nlp.fi.muni.cz/projects/ole/
.
Therefore, automatic techniques (ontology learn-
ing (Buitelaar et al., 2005; Staab and Studer, 2004))
are needed to be applied in line with the collaborative
efforts. But they have another drawback – they are
not 100% correct, though they are generally broad in
coverage of the domain. There is obvious need for
tools that can refine the possibly incorrect statements
in such ontologies before presenting them to users.
One way is to incorporate uncertainty into the learned
ontologies and select only the most important parts
according to the adopted uncertainty measure.
Besides the simple threshold-based refinement of
the learned ontologies, there are also important cog-
nitive motivations of the utilisation of uncertainty in
our empiric ontologies that led us to the proposal of
a novel
ANUIC (Adaptive Net of Universally Interre-
l
ated Concepts) framework for representing uncertain
knowledge. This format can be easily applied in very
simple, yet effective refinement of the results of on-
tology acquisition methods. The main contribution of
this paper is the presentation of initial results of appli-
cation of the ANUIC-based refinement by integration
to taxonomy acquisition.
The structure of rest of the paper is as follows. We
briefly recall the ANUIC model features in Section 2.
W
e go on describing the progress in our current re-
search in the meaning of new taxonomy acquisition
techniques implemented and more elaborate results
achieved (Sections 3 and 4). Section 5 briefly resumes
related work. We conclude the paper in Section 6.
31
Novác
ˇ
ek V. (2007).
IMPRECISE EMPIRICAL ONTOLOGY REFINEMENT - Application to Taxonomy Acquisition.
In Proceedings of the Ninth International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems - AIDSS, pages 31-38
DOI: 10.5220/0002391800310038
Copyright
c
SciTePress
2 DATA-DRIVEN ASSIGNMENT
OF FUZZY RELEVANCE
MEASURES IN ANUIC
Uncertain, and especially fuzzy semantics is consid-
ered as very important for the future development of
the Semantic Web (Sheth et al., 2005; Sanchez, 2006).
We work on development of such (formal) seman-
tics model within the
ANUIC framework. Currently,
a very initial proof of concept concerning the (auto-
matic) assignment
2
of reasonable fuzzy measures has
been implemented for our experiment in taxonomy
acquisition.
The implementation is based on a function that
assigns the relevance measure to a relation between
terms according to the frequency of the particular re-
lation in input data. The function definition is de-
scribed as follows.
Fuzzy appropriateness of a relation’s R element
(c
1
, c
2
) ∈ R, where c
1
, c
2
are respective terms, is given
by a special function µ (derived from standard sig-
moid):
µ((c
1
, c
2
) ∈ R) =
1
1+ e
−s( f
r
((c
1
,c
2
)∈R)−β)
where f
r
((c
1
, c
2
) ∈ R) =
f(O((c1,c2)∈R))
∑
c∈V
f(O((c1,c)∈R))
is the rela-
tive frequency of relation observations in input data
3
,
s is a parameter regulating the “steepness” of the func-
tion and β influences the placement of the inflexion
point. The domain of the function is real interval
(0, 1i (but only rational numbers obviously appear as
an input). The range is real interval (0, 1).
This function maps relative frequencies of respec-
tive observations in input data to the fuzzy appropri-
ateness measure of the relation. It can model various
natural characteristics of human mind like conserva-
tiveness, open-mindness (in the meaning of influence
of major or minor observations to the overall convic-
tion) and so forth
4
.
The function is continuous and thus can be im-
plemented in a very straightforward way. However, it
can easily imitate discontinuous jumps in the shape of
the curve, which is also very useful. Examples show-
2
Which was considered as an open problem to some ex-
tent in (Sheth et al., 2005).
3
This is rather an abstract, yet intuitive notation — the
O(Fact) expression stands for an observation of the Fact
in input data; the frequencies are absolute. The frequency
measure is not generally symmetric, as the relations them-
selves do not have to be symmetric.
4
One can, for example, fix the meaning of a specific
group of terms and allow meaning variations for another
one.
ing shapes of the conviction function are displayed in
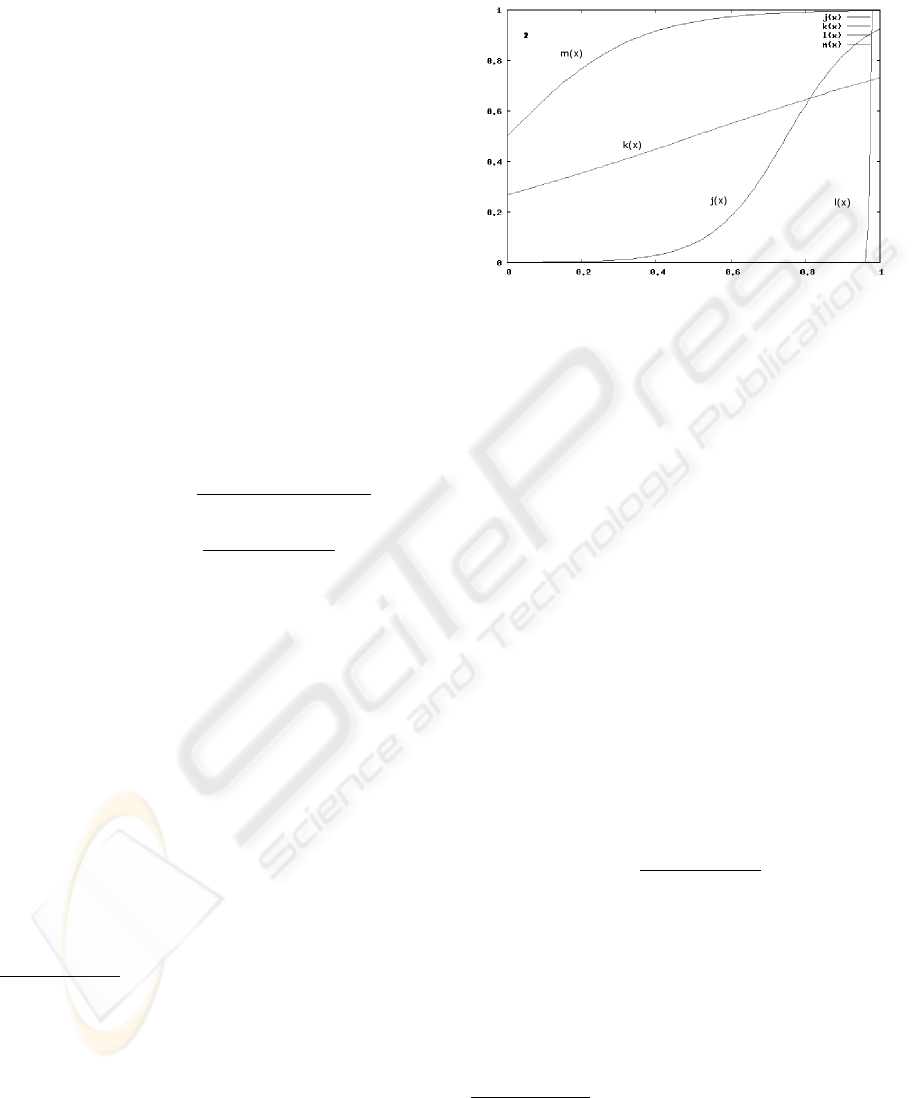
Figure 1
5
.
Figure 1: Examples of various shapes of the conviction
function.
One of the key properties of the
ANUIC format
is that it allows to naturally merge ontologies from
the same domain. When we have a large amount of
ontologies gained from a vast number of domain re-
sources, we can join them simply using their mutual
insertion into one complex
ANUIC structure. After
proper configuration of the aforementioned function
parameters s, β, we obtain qualitatively different rep-
resentation of the domain – many formerly incorrect
relations are mostly marginalised, whereas the empir-
ically more valid relations obtain high relevance mea-
sures, signalising strong belief in their appropriate-
ness.
After several experiments with configuration of
ANUIC parameters, we have found that a very good
heuristic for configuration of the function parame-
ters is dynamic setting of the β inflexion point value.
The steepness parameter s was set to 100, which per-
formed best among various other settings.
The β for a term c and relation R is set as:
β =
1
|{ ˆc|(c, ˆc) ∈ R}|
.
Moreover, any relative frequency f higher than 0.5 is
adjusted by modifying the β parameter with 1− ( f −
0.5) expression. Only thus we obtain, for example,
natural conviction of (almost) 1 when we deal with
a single relation instance. Thus we can discriminate
very well between the relation instances with signifi-
cant and insignificant frequencies due to the shape of
the conviction function
6
.
5
With the relative frequency and relevance measure on
the horizontal and vertical axes respectively.
6
Supposing that the higher the relation frequency is with
respect to the average relative frequency for relation edges
ICEIS 2007 - International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
32

The process of integration of newly coming facts
is similar to the process of how people construct their
conceptual representations – first they have almost
crisp evidence of a relation between objects (for ex-
ample that dogs have four legs). This opinion is
strengthened by further observations of four-legged
dogs, but one day they see a cripple dog having only
three legs. So they have to add another instance of the
“have-number-of-legs” relation, but with much more
decreased relevancy (unless they keep seeing other
and other different three-legged dogs). And this is a
simplified example of what we call continuous mean-
ing refinement of conceptual models and what is hap-
pening also when the new resources are integrated
within the
ANUIC framework.
3 APPLICATION OF EMPIRICAL
REFINEMENT TO TAXONOMY
ACQUISITION
The technical description of application of our frame-
work in the taxonomy acquisition from English nat-
ural language texts is presented here
7
. We use the
well-known pattern-based technique (Hearst, 1992)
for creation of miniontologies from each input re-
source. These ontologies are
ANUIC-integrated then
in order to build a reference ontology that is exploited
by the consequent steps of complex taxonomy acqui-
sition. Section 3.1 elaborates our method based on ap-
proximate clustering that ensures significant enhance-
ment in coverage. And eventually, the meta-algorithm
of conceptual refinement is introduced in Section 3.2.
3.1 Clustering and Autonomous
Annotation
The clustering is very tempting in the scope of ac-
quisition of taxonomy of an ontology. The main idea
of this approach is to gain clusters of similar terms
and induce a hierarchical structure upon these terms
somehow. However, these approaches usually do not
offer a reliable automatic mechanism of annotation
of the resulting clusters that naturally correspond to
classes in an ontology.
coming from the c term, the more the relation is significant
and vice versa.
7
We have concentrated on extraction of single general
terms in the presented experimental settings, but other tech-
niques of acquisition of more specific and multi-word terms
(like those in (Ryu and Choi, 2005)) can be easily incorpo-
rated as well.
We can obtain an initial domain ontology ontology
by integration of ontologies gained from particular re-
sources by pattern-based methods into the
ANUIC for-
mat (see Section 3.2 for details). Thus we obtain a
reference ontology that can be used for annotation of
clusters obtained from the same resources. The con-
tribution of such technique is obvious – we will dra-
matically increase the ontology coverage by incorpo-
ration of all significant terms from the resources. We
have designed a method similar to k-means one-level
clustering, tuned to suit our demands in order to iden-
tify rough clusters in the input data.
3.1.1 Preprocessing Specialties
We require our platform to be scalable even for ex-
treme amounts of data. Therefore we are interested
also in efficiency of the clustering. The clustering
speed is significantly influenced by the dimension of
the feature space.
We use quite a simple and standard metric of term
similarity given by a cosine distance between vec-
tors that represent their contexts. Given a set F =
{ f
1
, . . . , f
n
} of features, the vector V
T
= (v
1
, . . . , v
n
)
for term T is constructed this way:
• assign w
d−1
to v
i
, if feature f
i
is contained within
a vicinity of ⌈
CS
2
⌉ from T; w ∈ (0, 1i is a prede-
fined weight, CS is the relevant context size and d
is distance of the respective feature from T
8
;
• assign 0 to v
i
otherwise.
Following the main idea of the meta-algorithm pre-
sented in Section 3.2, we extract the initial concepts
from single resources of relatively small size and re-
fine them further by empirical integration of the re-
sulting ontologies.
Therefore we can select features only from the
particular resources. We have tested several mea-
sures (like TF/IDF) for feature selection on the whole
domain as well as on the isolated resources, but we
have found out that a specific heuristics performs best
for our method. We simply discard hapax legomena
(terms with frequency equal to 1) from the resource’s
dictionary (without application of a stop-list, because
we would like to have the functional words in our
contexts as well). Thus we obtain a feature space
of dimension in range from 500 to 1, 500 for most
of the resources, which is satisfactory. The terms
8
When w = 1, the contexts are represented as bag of
words. When w < 1, their distance from term T is pro-
jected into the vector characteristics. The context size was
set to 14 – an average length of sentence in the resource
sets. Lower or higher context sizes were tried as well, but
without any significant contribution. All the other parame-
ter settings used are further specified in Section 4.
IMPRECISE EMPIRICAL ONTOLOGY REFINEMENT - Application to Taxonomy Acquisition
33

themselves are extracted in a similar way – a gen-
eral English stop-list is applied and the terms with
frequency above a given threshold are considered as
terms. Frequency of 5 was found to be reasonable for
it does not eliminate any domain-specific words and
does not bring too many unwanted garbage-words in
most cases.
3.1.2 Simplified Rough Clustering
Several variants of k-means clustering are discussed
and briefly analysed for example in (Kanungo et al.,
2002). General characteristic of all algorithms of this
kind is that they find k points (centres) in the data
space that minimise average square distance of all
points in the data-set from these centres. Then the
clusters are usually defined as a k-sized set of bal-
anced groups of points that are nearest to particular
centres.
Many algorithms find a local minimum for the
problem in an iterative manner. We have found usual
implementation of k-means clustering unsuitable for
our reasons mainly due to their speed. We are not
very interested in optimality of our clusters. More-
over, the points in our data space are quite uniformly
distributed in most cases because of the restricted size
of the feature space and characteristics of natural lan-
guage that lay beyond the feature selection.
We have implemented a non-optimal (even lo-
cally), but very efficient technique that provides us
with rough clustering of the initial resources that is
further utilised within the refinement of ontologies
gained from particular resources
9
.
The method of simplified rough clustering is de-
scribed
10
in Algorithm 3 (given in Appendix).
3.1.3 Annotation
The consequent annotation of the clusters using the
reference ontology is sketched in Algorithm 1 (given
in Appendix).
3.2 Refinement by Integration
The conceptual refinement idea lies in integration of
small ontologies into bigger ones, smoothing many
9
The sub-optimality of clusters obtained by the tech-
nique is balanced by the efficiency and further empirical
refinement in the resulting ontology model. However, the
technique presented here could be used for preparing rea-
sonable initial means and related reduction of iterations for
the classical k-means clustering methods, if needed.
10
Certain parts of the algorithm are put rather informally
due to simplicity of the description.
of the crisp and possibly incorrect relations by uncer-
tain empirical evidence from large number of obser-
vations. It is inspired by a simple analogy of human
mind and utilises the inherent dynamics and uncer-
tainty of the
ANUIC framework. Note that for the op-
timal performance of the
ANUIC-based integration, it
is needed to process at least tens of relevant resources
of a sufficient size (hundreds or more words). We
should not await reasonable refinement results when
providing only few documents with size of a couple of
sentences – even human learners cannot process such
small amounts of data in order to create a valuable
opinion about the domain’s conceptual structure.
Concrete application of the above mechanism to
the taxonomy acquisition is quite straightforward and
conforms to the abstract description in Algorithm 2
(given in Appendix).
We can easily update the domain ontology when
keeping the track of how a relation was obtained.
Thus we can still identify the more precise “refer-
ence” relations in the domain ontology D. We add
the new resource by processing it first by the pattern-
based technique. Then we integrate the result into the
domain ontology and process the resource again by
clustering-based method, annotating the classes using
reference subset of D. The result of this step in then
integrated in D as well – the new resource is com-
pletely covered then.
4 SELECTED RESULTS OF
TAXONOMY ACQUISITION
In the following we describe some of the experiments
with taxonomy extraction in OLE and show their re-
sults. The improvement of the integration within the
ANUIC knowledge representation format is then illus-
trated in Section 4.2.
4.1 Extraction Phase and its Initial
Results
We tested the taxonomy acquisition on a sample of
3, 272 computer science articles, automatically down-
loaded from the web. The compound size of the re-
sources was 20, 405, 014 words. For the approximate
manual evaluation we randomly chose five ontologies
for respective resources from the whole set for each
run of a method.
Due to problems with evaluation of automatic
ontology acquisition (as expressed, for example,
in (Brewster et al., 2004)) we performed only a lim-
ited evaluation within the initial experiments. For
ICEIS 2007 - International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
34
each selected ontology corresponding to a resource,
we computed precision as the ratio of “reasonable” re-
lations compared to all extracted relations
11
. The rea-
sonability of a relation was judged by a committee of
computer science experts and students after analysing
the respective resources.
The coverage was computed as the ratio of num-
ber of extracted significant terms (nouns for the sim-
ple experimental settings) to all significant terms
present in the resource. For all the measures of preci-
sion (Pr.) and coverage (Cov.), an average value was
computed. We present these results in Table 1, pro-
vided with respective average original resource size
and number of all concepts extracted.
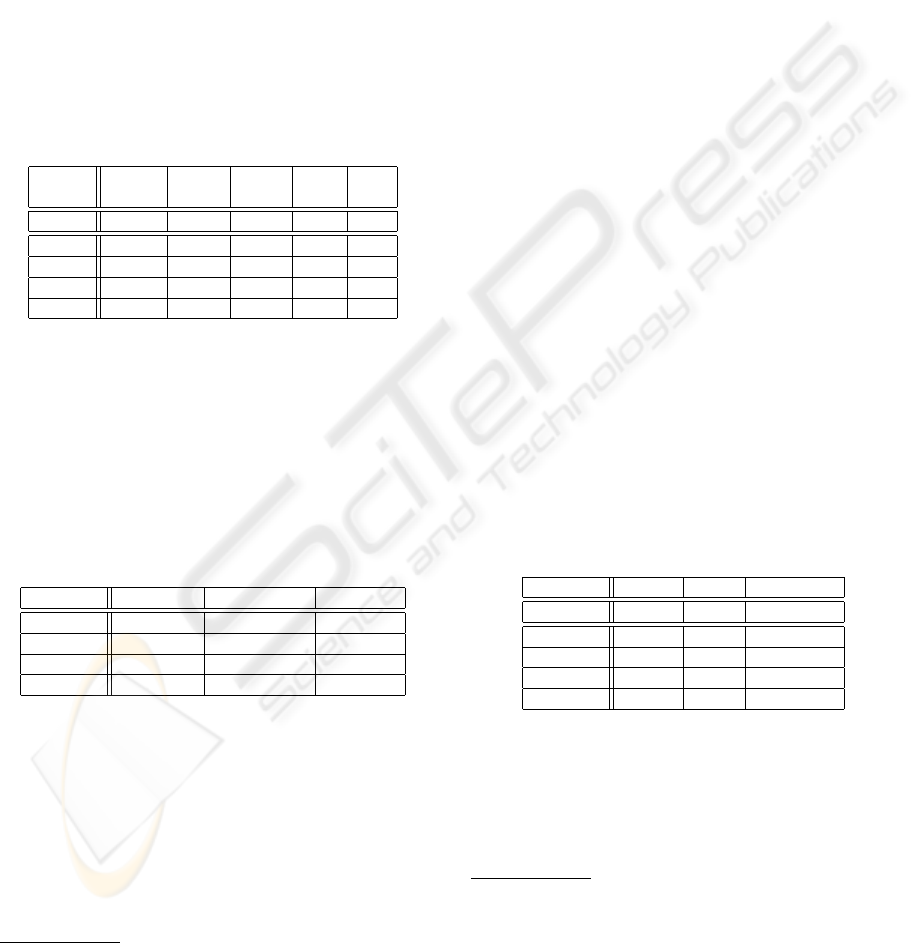
Table 1: Selected results of initial taxonomy extraction.
Method Res. sz. No. of No. of Pr. Cov.
(wrd.) conc. rel. (%) (%)
M1 4275 20.6 15.2 61.73 1.83
M2/S1 5777 138.4 1191.8 45.78 100
M2/S2 4669 106.2 494 33.11 100
M2/S3 4827 136.6 1336.2 46.13 100
M2/S4 5339 128.25 680 41.52 100
The M1 row contains results of pattern-based ex-
traction. The M2 rows contain results of clustering-
based method for respective parameter settings given
in Table 2. The rows’ headings present settings ID, in
the columns there are values of the respective param-
eters. The cluster size is used for derivation of the k
parameter for clustering algorithm.
Table 2: Settings for clustering-based method.
Settings ID Context size Position weight Cluster size
S1 14 1.0 10
S2 14 1.0 5
S3 14 0.7 10
S4 14 0.7 5
4.2 Improvement Obtained by
Uncertain Conceptual Refinement
In order to produce reference ontology for the au-
tonomous cluster annotation, we generated ontologies
for each resource by pattern-based OLE module and
merged them into one
ANUIC structure. We used the
11
For the clustering-based acquisition only 50 randomly
selected relations were evaluated for each ontology, because
the average number of all relations was too high for manual
evaluation.
heuristics described in Section 3.2 for configuration
of the parameters.
Using the
ANUIC-integration we gained a tax-
onomy with 5, 538 classes, 9, 842 individuals
12
and
61, 725 mutual is-a relations.
It is very hard to formally decide what is the repre-
sentation’s exact improvement when compared to the
knowledge stored in the former crisp ontologies. But
we can again give at least a rough picture – when we
considered only the relations with the highest fuzzy
relevance for a particular concept
13
, we can compute
an approximate ratio of “reasonable” relations simi-
lar to the one presented in Section 4.1. We computed
the ratio on a random sample of 50 relations from the
whole merged ontology and obtained the value 84 %,
which definitely shows an improvement.
The ontology gained by incorporation of results
of pattern-based method into
ANUIC was used as the
reference for clustering-based method. The results of
the
ANUIC merge of the source crisp ontologies for
both methods and various settings of the algorithms
are in Table 3 below.
We used the same merging parameters and crite-
ria of reasonability as for the creation and evaluation
of the reference ontology. Only the relations with the
highest conviction(s) were taken into account for eval-
uation. The precision computed on random sample of
50 relations from the merged ontology is given in the
Pr
latter
column. The average crisp precision for re-
spective source ontologies is in the Pr
former
column.
The improvement (in percents) is in the Improvement
column.
Table 3: Results of merging for clustering-based method.
Settings ID Pr
former
Pr
latter
Improvement
M1 61.73 84.0 136.08
M2/S1 45.78 65.52 143.12
M2/S2 33.11 65.38 197.46
M2/S3 46.13 63.16 136.92
M2/S4 41.52 64.07 154.31
The ontology with the best characteristics (gained
with S1 configuration) was experimentally merged
with the reference ontology. Resulting ontology has
much higher range than the reference one – it contains
1, 584 classes
14
and 30, 815 individuals, intercon-
12
We empirically assume that a concept is an individual
as long as it has no hyponyms.
13
Which is by the way a very strong restriction, the range
of possible interpretations of the concrete conviction values
is much higher.
14
Some of the former classes were turned into individuals
– this is a direct consequence of the annotation algorithm.
IMPRECISE EMPIRICAL ONTOLOGY REFINEMENT - Application to Taxonomy Acquisition
35

nected by 1, 293, 998 relations in the taxonomy. The
approximate precision of the 50 randomly selected re-
lations with the highest conviction was 71.05 %. It is
of course slightly lower than the similar measure for
the reference ontology, but this is not a big drawback
when we consider the widely increased coverage of
the domain.
A sample from the resulting extended uncertain
domain ontology is given in Figure 2. The ovals rep-
resent classes, squares are individuals and arrows go
from sub-concept to its super-concept, labelled by re-
spective fuzzy relevance measures.
5 RELATED WORK
Our work is to some extent similar to the one pre-
sented in (Haase and V
¨
olker, 2005) paper on uncer-
tainty handling in Text2Onto (Cimiano and V
¨
olker,
2005). Text2Onto also utilises initial automated
knowledge extraction methods and integrates them
into so called Learned Ontology Model. It incorpo-
rates uncertain rating annotations of the gained re-
lations. A DL-consistent model is selected then as
a subset of the statements in the learned model ac-
cording to these annotations. On the other hand, we
deal with the inconsistencies internally and allow to
reason generally among all the gained knowledge un-
der different well-defined perspectives. This provides
us with very valuable option of contextualised infer-
ences, among other things.
The reasoning perspectives of our paper are re-
lated to the work on fuzzy extension of OWL, which
is presented in (Stoilos et al., 2005). However, our
current research in automated
ANUIC-based reason-
ing with learned ontologies is somehow different from
this logical approaches and is motivated rather by the
more general AI paradigms of analogical (Paritosh,
2006; Hobbs and Gordon, 2005) and heuristic (Koki-
nov and French, 2003) reasoning. The transforma-
tions of
ANUIC into the current standard and fuzzy on-
tology representation formats (namely OWL (Bech-
hofer et al., 2004) and fuzzy-OWL (Stoilos et al.,
2005) have to be studied in more detail before we can
make proper conclusions and proceed with compar-
isons with traditional reasoning paradigms.
6 CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE
WORK
The main contribution of this paper rests with the pre-
sented boost of initial ontology acquisition methods
by very simple application of the
ANUIC-based empir-
ical integration of learned knowledge. In this exper-
iment, we have provided an initial proof of concept
and groundwork for a novel ontology learning and
reasoning paradigm we are currently working on. The
full implementation of the related framework aims at
extension of ontology learning with robust, though
heuristic reasoning routines, that would enable rich
and meaningful inferences even for large learned on-
tologies. Thus we can help to shift on-line knowl-
edge acquisition, management and decision support
in data-intensive domains (such as medicine) to a
qualitatively different level.
Note that we have also implemented SOLE – a
web interface demonstrating the basic functionalities
of the current state of our OLE ontology acquisi-
tion framework. It processes documents (in plain
text, HTML, PDF or PostScript) uploaded by users
and creates (fuzzy) ontologies from them. It uses
the techniques described here. Users can also de-
fine their own patterns for extraction of different se-
mantic relations than the taxonomical ones. The sys-
tem can be accessed at URL:
http://nlp.fi.muni.
cz/projects/ole/web/
. One can download a brief
manual for the system there. The preview credentials
for a testing public account with few pre-defined rela-
tion patterns are test for user-name and test for pass-
word.
Our future work will focus on incorporation of re-
sults of another extraction methods to increase the re-
call and number of kinds of extracted relations. A
formal development and validation of a specific cal-
culus for
ANUIC-based reasoning engine is needed
then. The mutual correspondence and transformation
possibilities between ontologies in ANUIC format and
formats like OWL or fuzzy-OWL must be examined
as well, in order to thoroughly evaluate and compare
the framework to other similar tools and provide an
inter-operation layer by means of the Semantic Web
standards.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work has been supported by the Academy
of Sciences of the Czech Republic, ‘Informa-
tion Society’ national research program, the
grant AV 1ET100300419, and by the EU IST
6th framework’s Network of Excellence ‘Knowledge
Web’ (FP6-507482). We would also like to thank
to Pavel Smr
ˇ
z, who supported our research by his
general senior experience during the initial course of
our work within a master thesis.
ICEIS 2007 - International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
36

Figure 2: Sample from the merged computer science ontology.
REFERENCES
Bechhofer, S., van Harmelen, F., Hendler, J., Horrocks, I.,
McGuinness, D. L., Patel-Schneider, P. F., and Stein,
L. A. (2004). OWL Web Ontology Language Refer-
ence. Available at (February 2006):
http://www.w3.
org/TR/owl-ref/
.
Brewster, C., Alani, H., Dasmahapatra, S., and Wilks, Y.
(2004). Data driven ontology evaluation. In Proceed-
ings of LREC 2004.
Buitelaar, P., Cimiano, P., and Magnini, B., editors (2005).
Ontology Learning from Text: Methods, Evaluation
and Applications. IOS Press.
Cimiano, P. and V
¨
olker, J. (2005). Text2Onto - a framework
for ontology learning and data-driven change discov-
ery. In Proceedings of the NLDB 2005 Conference,
pages 227–238. Springer-Verlag.
Gomez-Perez, A., Fernandez-Lopez, M., and Corcho, O.
(2004). Ontological Engineering. Advanced Informa-
tion and Knowledge Processing. Springer-Verlag.
Haase, P. and V
¨
olker, J. (2005). Ontology learning and rea-
soning - dealing with uncertainty and inconsistency.
In da Costa, P. C. G., Laskey, K. B., Laskey, K. J.,
and Pool, M., editors, Proceedings of the Workshop on
Uncertainty Reasoning for the Semantic Web (URSW),
pages 45–55.
Hearst, M. A. (1992). Automatic acquisition of hyponyms
from large text corpora. In Proceedings of the 14th
conference on Computational linguistics, pages 539–
545, Morristown, NJ, USA. Association for Compu-
tational Linguistics.
Hobbs, J. R. and Gordon, A. S. (2005). Toward a large-
scale formal theory of commonsense psychology for
metacognition. In Proceedings of AAAI Spring Sym-
posium on Metacognition in Computation, pages 49–
54, Stanford, CA. ACM.
Kanungo, T., Mount, D., Netanyahu, N., Piatko, C., Silver-
man, R., and Wu, A. (2002). An efficient k-means
clustering algorithm: analysis and implementation.
Kokinov, B. and French, R. M. (2003). Computational mod-
els of analogy making. In Nadel, L., editor, Encyclo-
pedia of Conginitve Science, volume 1, pages 113–
118. Nature Publishing Group, London.
Nov
´
a
ˇ
cek, V. and Smr
ˇ
z, P. (2006). Empirical merging of
ontologies – a proposal of universal uncertainty repre-
sentation framework. In LNCS, volume 4011, pages
65–79. Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg.
Paritosh, P. K. (2006). The heuristic reasoning manifesto.
In Proceedings of the 20th International Workshop on
Qualitative Reasoning.
Ryu, P.-M. and Choi, K.-S. (2005). An information-
theoretic approach to taxonomy extraction for on-
tology learning. In Buitelaar, P., Cimiano, P., and
Magnini, B., editors, Ontology Learning from Text:
Methods, Evaluation and Applications, pages 15–28.
IOS Press.
Sanchez, E., editor (2006). Fuzzy Logic and the Semantic
Web. Capturing Intelligence. Elsevier.
Sheth, A., Ramakrishnan, C., and Thomas, C. (2005). Se-
mantics for the semantic web: The implicit, the formal
and the powerful. International Journal on Semantic
Web & Information Systems, 1(1):1–18.
Staab, S. and Studer, R., editors (2004). Handbook on
Ontologies. International Handbooks on Information
Systems. Springer-Verlag.
Stoilos, G., Stamou, G., Tzouvaras, V., Pan, J., and Hor-
rocks, I. (2005). Fuzzy owl: Uncertainty and the se-
mantic web. International Workshop of OWL: Expe-
riences and Directions, Galway, 2005.
Zhdanova, A. V., Krummenacher, R., Henke, J., and Fensel,
D. (2005). Community–driven ontology management:
Deri case study. In Proceedings of IEEE/WIC/ACM
International Conference on Web Intelligence, pages
73–79. IEEE Computer Society Press.
IMPRECISE EMPIRICAL ONTOLOGY REFINEMENT - Application to Taxonomy Acquisition
37

APPENDIX
Algorithm 1 Cluster annotation with super-class
term.
Require: C — set of clusters
Require: t
h
hyperonymy confidence threshold, 0.7 is reasonably discrimi-
native
Require: R reference ontology
Require: hyper(t,R, t
h
) — function that returns all hypernyms of t in R with
hypernymy relation relevance higher than t
h
Require: onto(C) — functions that returns an internal ontology representa-
tion equivalent to the annotated clusters
1: for c ∈ C do
2: H ←
/
0 {* hypernymic relation “stubs” *}
3: for term t ∈ c do
4: if t ∈ R then
5: h ← hyper(t, R,t
h
)
6: H ← H ∪ h
7: end if
8: end for
9: annotate all terms in c with the hypernyms from the set H
10: end for
11: return onto(C)
Algorithm 2 Empirical refinement.
1: process the resources by the pattern-based method and produce a set of
ontologies S
p
2: merge the ontologies in S
p
into one ontology R
3: process the resources by the clustering-based method (Alg. 1 and Alg. 2)
using R as a reference ontology in Alg. 2 and produce set of ontologies
S
c
4: merge the ontologies in S
c
and produce ontology C
5: join the R and C in order to produce domain taxonomy in ontology D
6: return D
Algorithm 3 Simplified rough clustering.
Require: V — set of feature-vectors mapped to respective terms
Require: k — number of desired clusters
Require: r — number of optimisation repeats, value 5 was found to be suf-
ficient
Require: centroid(V) — function that computes centroid of the vector set
V
Require: dist(u, v) — cosine distance of two vectors u,v
Require: pickBal(d
i
,V) — abstract (due to simplicity of the description)
function, which pops a subset S from set V; S is characterised by these
conditions: (1) all v ∈ S all the closest possible vectors to d
i
, and (2) all
the sets picked fromV are balanced in size after a sequence of pickBal()
applications that makes V empty
1: M
init
← random v ∈ V {* initial means *}
2: V
tmp
← V
3: repeat
4: c ← centroid(M
init
)
5: v ← u such that dist(u,c) is maximal for u ∈ V
tmp
6: M
init
← M
init
∪ {v}
7: V
tmp
← V
tmp
− {v}
8: until |M
init
| < k
9: FACT ← {} {* empty map *}
10: V
tmp
← V
11: j ← 0
12: for d
i
∈ M
init
do
13: S
balanced
← pickBal(d
i
,V
tmp
)
14: j ← j + 1
15: FACT[ j] ← S
balanced
16: end for
17: C ←
/
0
18: for j ∈ FACT.keys() do
19: C ← C ∪ centroid(FACT[ j])
20: end for
21: VECT2SCORE ← {} {* empty map *}
22: for v ∈ V do
23: VECT2SCORE[v] ← {(c
0
, 0), . . . , (c
k−1
, k − 1)} such that
{c
0
, . . . , c
k−1
} is a sequence of centroids from C ordered by the
increasing distance from v
24: end for
25: CLUST ←
/
0 {* clustering structure *}
26: S ← {} {* empty map *}
27: for j ∈ {1, . . . , r} do
28: S
tmp
← random shuffle of V
29: initialize clustering c
j
with clusters given by pivotal centroids from
C
30: sequentially process S
tmp
and assign each vector to the nearest avail-
able cluster from c
j
, keeping the clusters as balanced in size as pos-
sible
31: compute the score S[j] for the obtained clustering by summing up
the numbers pointed by respective centroids in VECT2SCORE for
each vector in each cluster in c
j
32: CLUST ← CLUST ∪ c
j
33: end for
34: return c
x
∈ CLUST with lowest score S[ j], s ∈ {1, . . . , r} associated
ICEIS 2007 - International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
38
