
INTEGRATING IDENTIFICATION CONSTRAINTS
IN WEB ONTOLOGY
Thi Dieu Thu Nguyen and Nhan Le-Thanh
I3S laboratory (CNRS - UNSA)
Les Algorithmes - Euclide B Building, 2000 route des Lucioles – B.P. 121
F-06903 Sophia Antipolis Cedex, France
Keywords:
Integrating relational data sources, Web ontology languages, Semantic Web, Description Logics, Identification
constraints.
Abstract:
In recent years, there has been a growing interest in semantic integration in the Semantic Web environment,
whose goal is to access, relate and combine knowledge from multiple sources. The need of integrating the
semantics from relational data sources into this environment, therefore, has also emerged. However, there is
one important aspect of database schemas that OWL up to now has not captured yet, namely identification
constraints. To address this problem, this paper introduces a decidable extension of OWL-DL, namely OWL-
K, that supports such constraints.
1 INTRODUCTION
In recent years, the problem of interoperability and
semantic integration of heterogeneous data sources in
the Web environment has attracted distinctive atten-
tion of many researchers in various domains, which
can be brought together to the so-called Semantic
Web (SW). One of the main features of the SW is
the ability to describe data sources on the Web by
declarative annotations. The latter should be ex-
pressive enough to deal with the problem of hetero-
geneity of sources and well formalized to be used
in automated reasoning. OWL-DL (Ontology Web
Language-Description Logic) is a popular resource
description language proposed by W3C
1
for this pur-
pose. Particularly, to integrate relational data sources
on the Semantic Web environment, OWL-DL must
be capable of expressing the notion of Identification
Constraints (ICs), which is so called (primary and
foreign) keys in relational models. However, up to
now this important feature of database schemas has
not been fully captured yet.
Motivated by this problem, we introduce ICs into
OWL-DL, resulting in a new Web ontology language
OWL-K. This extension is a decisive step to integrate
1
World Wide Web Consortium, http://www.w3.org/
relational data sources into the SW.
2 OVERVIEW OF OWL-DL
In order to support desirable computational proper-
ties for reasoning systems, OWL-DL is designed with
the same set of constructors as for OWL (Bechhofer
et al., 2004), but restricted to be used in a way sat-
isfying decidable inference. What making OWL-DL
a Semantic Web language, however, is not its seman-
tics, which are quite standard for Description Logics
(DLs), but its RDF/XML exchange syntax besides an
abstract frame-like syntax.
The abstract syntax, DL syntax and semantics
of OWL-DL descriptions and axioms can be seen
in table 1 and 2, where A is a class URI refer-
ence; C,C
1
,...,C
n
are class descriptions; S is an ob-
ject property (whose value is an individual) URI ref-
erence; R, R
1
,...,R
n
are object property descriptions;
o,o
1
,...,o
n
are individual URI references; d is a data
range; U is a datatype property (whose value is a
data literal); ♯ denotes cardinality; I is the interpre-
tation function; ∆
I
is the individual domain and ∆
D
is
the domain of data values. The semantics of OWL-
DL is based on S H O I N (D) DL, an extension of
S H O Q (D) (Horrocks and Sattler, 2001) with inverse
338
Dieu Thu Nguyen T. and Le-Thanh N. (2007).
INTEGRATING IDENTIFICATION CONSTRAINTS IN WEB ONTOLOGY.
In Proceedings of the Ninth International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems - DISI, pages 338-343
DOI: 10.5220/0002397803380343
Copyright
c
SciTePress

Table 1: OWL-DL class, property descriptions.
Abstract syntax DL Syntax Semantics
Class(A) A A
I
⊆ ∆
I
Class(owl:Thing) ⊤ owl:Thing
I
= ∆
I
Class(owl:Nothing) ⊥ owl:Nothing
I
=
/
0
intersectionOf(C
1
...C
n
) C
1
⊓ ... ⊓C
n
(C
1
⊓ ... ⊓C
n
)
I
= C
I
1
∩ ... ∩C
I
2
unionOf(C
1
...C
n
) C
1
⊔ ... ⊔C
2
(C
1
⊔ ... ⊔C
n
)
I
= C
I
1
∪ ... ∪C
I
2
complementOf(C) ¬C (¬C)
I
= ∆
I
\C
I
oneOf(o
1
...o
n
) {o
1
} ⊔... ⊔ {o
n
} ({o
1
} ⊔... ⊔ {o
n
})
I
= {o
I
1
,..., o
I
n
}
restriction(R someValuesFrom(C)) ∃R.C (∃R.C)
I
= {x ∈ ∆
I
|∃y.hx,yi ∈ R
I
∧ y ∈ C
I
}
restriction(R allValuesFrom(C)) ∀R.C (∀R.C)
I
= {x ∈ ∆
I
|∀y.hx,yi ∈ R
I
→ y ∈ C
I
}
restriction(R hasValue(o)) ∃R.{o} (∃R.{o})
I
= {x ∈ ∆
I
|hx,{o}
I
i ∈ R
I
}
restriction(R minCardinality(n)) ≥ nR (≥ nR)
I
= {x ∈ ∆
I
|♯{y.hx,yi ∈ R
I
} ≥ n}
restriction(R maxCardinality(n)) ≤ nR (≤ nR)
I
= {x ∈ ∆
I
|♯{y.hx,yi ∈ R
I
} ≤ n}
restriction(U someValuesFrom(d)) ∃U.d (∃U.d)
I
= {x ∈ ∆
I
|∃y.hx,yi ∈ U
I
∧ y ∈ d
D
}
restriction(U allValuesFrom(d)) ∀U.d (∀U.d)
I
= {x ∈ ∆
I
|∀y.hx,yi ∈ U
I
→ y ∈ d
D
}
restriction(U hasValue(v)) ∃U.v (∃U.v)
I
= {x ∈ ∆
I
|hx,vi ∈ U
I
}
restriction(U minCardinality(n)) ≥ nU (≥ nU)
I
= {x ∈ ∆
I
|♯{y.hx,yi ∈ U
I
} ≥ n}
restriction(U maxCardinality(n)) ≤ nU (≤ nU)
I
= {x ∈ ∆
I
|♯{y.hx,yi ∈ U
I
} ≤ n}
ObjectProperty(S) S S
I
⊆ ∆
I
× ∆
I
inverseOf(S) S
−
(S
−
)
I
= {hx, yi|hy,xi ∈ S
I
}
DatatypeProperty(U) U U
I
⊆ ∆
I
× ∆
D
roles and restricted to unqualified number restrictions.
See (Horrocks and Patel-Schneider, 2004) for more
details of OWL-DL.
As shown in table 1 and 2, OWL-DL can declare
classes and organize them in a subsumption (subclass)
hierarchy. OWL classes can be specified as logical
combinations (intersections, unions, or complements)
of others, as enumerations of specified objects or as
restrictions on a particular property so that all the val-
ues for the property in instances of the class must be-
long to a certain class (or datatype); at least one value
must come from a certain class (or datatype); there
must be at least certain specific values; there must be
at least or at most a certain number of distinct val-
ues. OWL-DL can also declare properties with their
domains and ranges, can organize them into a sub-
property hierarchy. It can also state that a property is
transitive, symmetric, functional, or inverse w.r.t an-
other.
3 OWL-DL WITH ICS
3.1 Limitations of OWL-DL in
Representing ICs
Although supporting considerable expressive power
to the Semantic Web, the mechanism to express ICs
in OWL-DL is seriously limited. In particular, OWL-
DL provides two constructors
Functional and Inverse-
Functional
to link individuals together.
If a property P is tagged as
Functional then ∀ x, y,
z: P(x,y) and P(x,z) implies y = z. For example, if the
property
hasFlag is characterized as Functional, then
each nation has at most one flag. Vice versa, if P is
tagged as
InverseFunctional then ∀ x, y and z: P(y,x)
and P(z,x) implies y = z. For example, if character-
izing
hasFlag as InverseFunctional, then two nations
could be inferred to be identical based on having the
same flag. See the illustration of Functional and In-
verseFunctional
in figure 1.
Thus, one can think of
InverseFunctional as defin-
ing a unique key in the database sense. However,
it does not require that all elements of the domain
have values. Furthermore, two values may infer to
the same element. Essentially,
InverseFunctional does
not represent a 1-1 but 1-n relation between elements
of the domain and those of the range of a prop-
erty. Therefore, this constructor does not fully capture
the meaning of ICs (which will be more explained
in the next section). Similarly to
InverseFunctional,
Functional does not represent the notion of ICs but a
functional dependency. One can think of using both
of these constructors to represent the notion of ICs.
However, the relations are not compulsory to all ele-
ments of the domain. So that the meaning of ICs is
not fully described. Figure 1 illustrates the relations
put by these constructors.
nation1
nation2
nation3
nation4
flag1
flag2
flag3
Funtional: n-1 relation InverseFuntional: 1-n relation
hasFlag
nation1
nation2
nation3
nation4
flag1
flag2
flag3
hasFlag
Figure 1: Limitations of OWL-DL in representing ICs.
INTEGRATING IDENTIFICATION CONSTRAINTS IN WEB ONTOLOGY
339
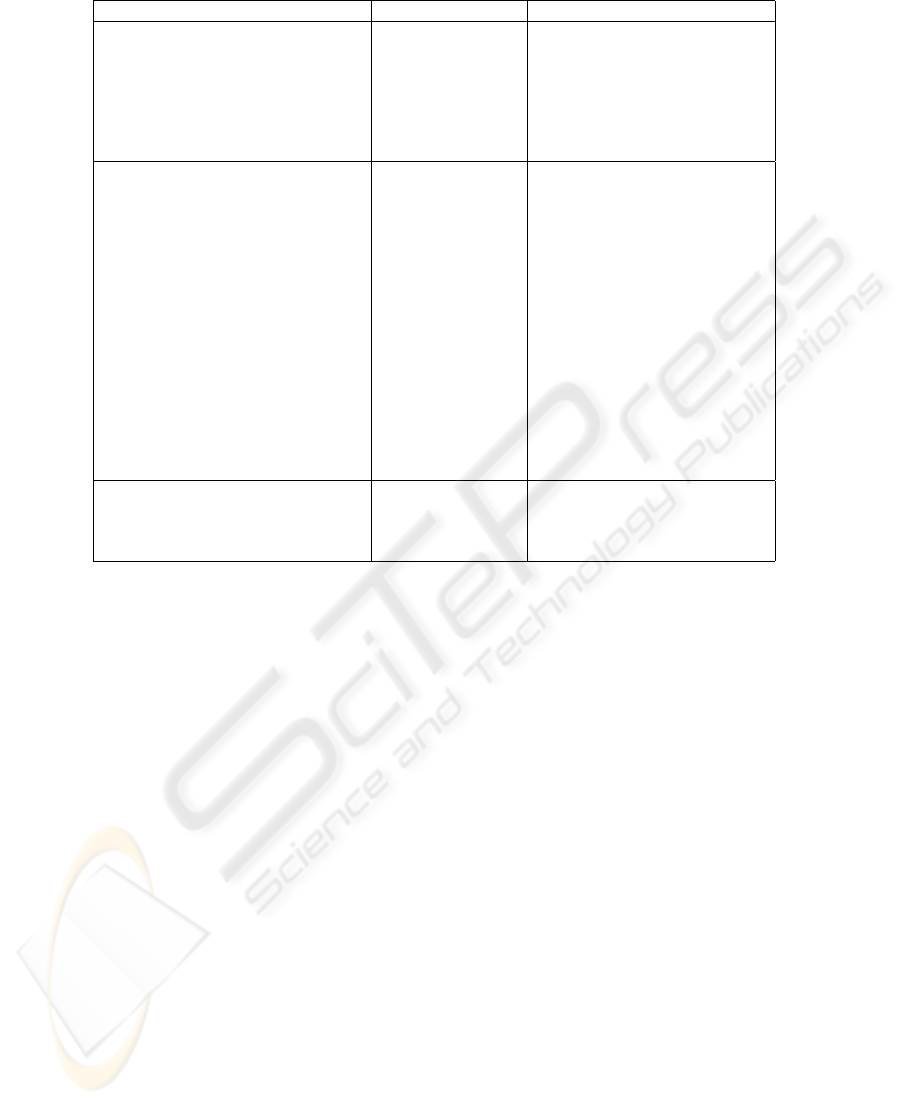
Table 2: OWL-DL axioms.
Abstract syntax DL Syntax Semantics
Class(A partial C
1
...C
n
) A ⊑ C
1
⊓ ... ⊓C
n
A
I
⊆ C
I
1
⊓ ... ⊓C
I
n
Class(A complete C
1
...C
n
) A ≡ C
1
⊓ ... ⊓C
n
A
I
≡ C
I
1
⊓ ... ⊓C
I
n
EnumeratedClass(A o
1
...o
n
) A ≡ {o
1
} ⊓... ⊓ {o
n
} A
I
≡ {o
I
1
,..., o
I
n
}
SubClassOf(C
1
,C
2
) C
1
⊑ C
2
C
I
1
⊆ C
I
2
EquivalentClasses(C
1
...C
n
) C
1
≡ ... ≡ C
n
C
I
1
= ... = C
I
n
DisjointClasses(C
1
...C
n
) C
i
⊑ ¬C
j
, C
I
i
∩C
I
i
=
/
0,
(1 ≤ i < j ≤ n) (1 ≤ i < j ≤ n)
DatatypeProperty(U super(U
1
) ... super(U
n
)) U ⊑ U
i
,(1 ≤ i ≤ n) U
I
⊆ U
I
i
,(1 ≤ i ≤ n)
domain(C
1
) ... domain(C
m
) ≥ 1U ⊑ C
i
,(1 ≤ i ≤ m) U
I
⊆ C
I
i
× ∆
D
I
,(1 ≤ i ≤ m)
range(d
1
) ... range(d
k
) ⊤ ⊑ ∀U.d
i
,(1 ≤ i ≤ k) U
I
⊆ ∆
I
× d
I
i
,(1 ≤ i ≤ k)
[Functional] ⊤ ⊑≤ 1U {hx,yi|♯{y.hx,yi ∈ U
I
} ≤ 1∀x ∈ ∆
I
}
SubPropertyOf(U
1
,U
2
) U
1
⊑ U
2
U
I
1
⊆ U
I
2
EquivalentProperties(U
1
...U
n
) U
1
≡ ... ≡ U
n
U
I
1
= ... = U
I
n
ObjectProperty(R super(R
1
) ... super(R
n
)) R ⊑ R
i
,(1 ≤ i ≤ n) R
I
⊆ R
I
i
,(1 ≤ i ≤ n)
domain(C
1
) ... domain(C
m
) ≥ 1R ⊑ C
i
,(1 ≤ i ≤ m) R
I
⊆ C
I
i
× ∆
I
,(1 ≤ i ≤ m)
range(C
1
) ... range(C
k
) ⊤ ⊑ ∀R.C
i
,(1 ≤ i ≤ k) R
I
⊆ ∆
I
×C
I
i
,(1 ≤ i ≤ k)
[Symmetric] R ≡ R
−
R
I
= (R
−
)
I
[Functional] ⊤ ⊑≤ 1R {hx,yi|♯{y.hx,yi ∈ R
I
} ≤ 1∀x ∈ ∆
I
}
[InverseFunctional] ⊤ ⊑≤ 1R
−
{hx,yi|♯{y.hx,yi ∈ (R
−
)
I
} ≤ 1∀x ∈ ∆
I
}
[Transitive] Trans(R) R
I
= (R
I
)
+
SubPropertyOf(R
1
,R
2
) R
1
⊑ R
2
R
I
1
⊆ R
I
2
EquivalentProperties(R
1
...R
n
) R
1
≡ ... ≡ R
n
R
I
1
= ... = R
I
n
AnnotationProperty(R)
Individual(o type(C
1
) ... type(C
n
) o ∈ C
i
o
I
∈ C
I
i
value(R
1
o
1
)...value(R
n
o
n
)) ho,o
i
i ∈ R
i
ho
I
,o
I
i
i ∈ R
I
i
SameIndividual(o
1
...o
n
) o
1
= ... = o
n
o
I
1
= ... = o
I
n
DifferentIndividuals(o
1
...o
n
) o
i
6= o
j
o
I
i
6= o
I
j
Another limitation of OWL-DL is that these con-
structors relate only two elements while in database
schemas, ICs can be put on a set of elements as shown
in the next section.
3.2 Motivation of Adding ICs
In the sense of OWL-DL, ICs can be defined as to
state that a certain set of properties uniquely identi-
fies instances of a given class. Essentially, these con-
straints put a 1-1 relation between sets of values of
properties and instances of a class. Example 1 shows
that ICs cannot be represented in OWL-DL.
Example 1:One would like to state that instances
of the class
NationHistory are uniquely identified by
a couple of properties (
hasFlag, onDate), where has-
Flag
is an ObjectProperty whose values are flags and
onDate is a DatatypeProperty whose values are of
datatype date.
However, OWL-DL has no constructors to de-
scribe that an “instance” of the couple (hasFlag, on-
Date
) uniquely identifies an instance of the class Na-
tionHistory
. It is even impossible to describe this
expression with any combination of constructors in
OWL-DL.
From the example, we can see that properties in
the set identifying instances of a concept are relations
between either instances of concepts or instances of
a concept and values of a datatype, showing that ICs
allow to express the relations not only between indi-
viduals but also between individuals and values.
As a result, to express ICs, a new mechanism is
required to support both datatype and object proper-
ties. The next section will introduce a such mech-
anism which results in an extended language called
OWL-K.
4 MODELING ICS IN OWL-K
4.1 Vocabulary
The representation of ICs in OWL-DL, as shown in
section 3.1 cannot express the constraints in exam-
ple 1. Therefore we extend OWL-DL with IC asser-
tions resulting in OWL-K. In this language, IC as-
sertions are modeled as entities. They are neither
classes (or concepts) nor properties (or roles). Hence
we define IC assertions as instances of a new class
owl:ICAssertion, which is a subclass of rdfs:Resource
(see figure 2).
Figure 2 shows the class hierarchy using a “nodes
and arcs” graph representation of the RDF data
ICEIS 2007 - International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
340

rdfs:Resource
rdfs:Class
s
rdf:Propertys
owl:Classs
owl:ICAssertion
s
owl:Restrictions
rdf:ObjectProperty
rdf:DatatypeProperty
s
s
t
t
t
t
t
t
t
s= rdfs:subClassOf
t= rdf:type
Figure 2: Class Hierarchy for OWL-K.
model. If a class is a subset of another, then there is
an rdfs:subClassOf arc from the node representing the
former class to the node representing the latter. Simi-
larly, if a resource is an instance of a class, then there
is an rdf:type arc from the resource to the node repre-
senting the class. (Note that not all resources, classes
and such arcs are shown. We only show the principle
resources, classes and arcs relating to our extension.
The rest remains the same as for OWL-DL.)
An IC puts a constraint on a set of properties.
Let us see how OWL-DL provides property restric-
tions. First, property restrictions are defined as classes
while ICs do not create new classes. Second, OWL-
DL distinguishes two kinds of property restrictions:
value and cardinality constraints. Value constraints
put constraints on the range of a property when ap-
plied to a particular class description. Cardinality
constraint puts constraints on the number of values a
property can take, in the context of a particular class
description. So restriction constructs in OWL-DL put
restrictions on only one property while an IC puts
a restriction on a collection of properties. Restric-
tion constructs in OWL-DL, therefore, do not agree
with ICs. To express IC assertions, we introduce new
kinds of restriction constructs, namely
owl:onClass
and owl:byProperty. The former is used to specify
the class an IC is applied to. The latter is used to
specify the property in the collection of properties
identifying the instance of a given class. Since ICs
can be applied both to datatype and object proper-
ties,
owl:byProperty
is designed to have range both
of them. Table 3 shows the vocabulary extension of
OWL-K compared with OWL-DL.
4.2 Abstract Syntax
The abstract syntax is used to facilitate access to and
evaluation of the language. It is specified by means
of a version of Extended BNF, which is defined in
section 2 of (Horrocks and Patel-Schneider, 2004).
IC assertions in OWL-K ontologies must be iden-
tifiable and referable. Hence as for classes, proper-
ties and instances in OWL-DL ontologies, we asso-
ciate with each IC assertion in an OWL-K ontology
an identifier, which is a URI reference.
As the axioms modeled in OWL-DL, a new kind
of axioms to express IC assertions is added as follows.
ICAssertionID ::= URIreference
axiom ::= ‘ICAssertion(’ ICAssertionID
description
propertyID {propertyID}‘)’
propertyID ::= datavaluedPropertyID |
individualvaluedPropertyID
The IC in example 1 is then written in the abstract
syntax as follows:
ICAssertion(NatHisIC NationHistory hasFlag onDate)
4.3 Semantics
The semantics of the abstract syntax above is de-
fined by definition 4.1. Actually, this definition is
provided by a constructor called Idfor, which is
added to S H O I N (D), the underpinning of OWL-
DL, producing the underpinning of OWL-K, the DL
S H O I N K (D) (see section 5). Note that in DLs
we talk about concepts, abstract roles and concrete
roles while in Web ontology languages we usually call
them classes, object properties and datatype proper-
ties respectively.
Definition 4.1 (Identification constraint) An iden-
tification constraint is defined as:
(R
1
,...,R
n
IdforC) (1)
where C is a concept, R
i
is a simple role (abstract
or concrete) ∀1 ≤ i ≤ n, Idfor is the constructor spec-
ifying the constraint. The semantics of this definition
is formally defined by an interpretation
I that sat-
isfies the definition (R
1
,...,R
n
IdforC) iff ∀s, s
′
∈ C
I
and ∀1 ≤ i ≤ n, hs,t
i
i,hs
′
,t
′
i
i ∈ R
I
i
, we have t
i
= t
′
i
then
s = s
′
.
Intuitively, this definition indicates that two in-
stances of a concept C never have the same partici-
pation in these n roles. To ensure the decidability of
the reasoning algorithm, the roles must be simple (see
Table 3: Vocabulary extension for OWL-K.
rdfs:Class rdfs:subClassOf
owl:ICAssertion rdfs:Resource
Property name Type
owl:onClass rdf:ObjectProperty
owl:byProperty rfd:Property
Property name rdfs:domain rdfs:range
owl:onClass owl:ICAssertion owl:Class
owl:byProperty owl:ICAssertion owl:Property
INTEGRATING IDENTIFICATION CONSTRAINTS IN WEB ONTOLOGY
341

Table 4: Mapping OWL-K abstract syntax to DL syntax
and semantics.
Abstract syntax DL syntax Semantics
ICAssertion
(ICAssertionID
C R
1
...R
n
)
(R
1
,...,R
n
Idfor C)
I |= (R
1
,...,R
n
IdforC)
iff ∀s,s
′
∈ C
I
and
hs,t
i
i,hs
′
,t
′
i
i ∈ R
I
i
∀1 ≤ i ≤ n, t
i
= t
′
i
∀1 ≤ i ≤ n then s = s
′
section 5). The abstract, DL syntax and semantics of
ICs are presented in Table 4.
For example, the constraint in example 1 will be
represented in DL as the definition: (hasFlag, onDate
Idfor NationHistory), where hasFlag is the abstract
role, onDate is the concrete role, NationHistory is the
concept.
4.4 RDF Graphs
An OWL ontology is an RDF graph, which is in
turn a set of RDF triples. Hence it is necessary to
relate specific abstract syntax ontologies with spe-
cific RDF/XML documents and their correspond-
ing graphs. We provide a mapping from the ab-
stract syntax for OWL-K to the exchange syntax, i.e.
RDF/XML syntax. Since OWL-K is the extension
of OWL-DL, it inherits the mapping from OWL-DL
(Horrocks and Patel-Schneider, 2004). Thus, we in-
troduce here only the mapping for IC assertions (see
table 5). As a result, our extension preserves the nor-
mative relationship between the abstract syntax and
the exchange syntax. The IC in example 1 is repre-
sented in the exchange syntax as follows:
<owl:ICAssertion rdf:ID = "NatHisIC">
<owl:onClass rdf:resource = "NationHistory" />
<owl:byProperty rdf:resource = "#hasFlag"/>
<owl:byProperty rdf:resource = "#onDate"/>
</owl:ICAssertion>
5 DECIDABILITY OF OWL-K
Now we show that OWL-K is decidable by presenting
its underpinning
S H O I N K (D) language (Nguyen
Table 5: Transformation of IC assertion to triples.
Abstract
syntax S
Transformation - T(S)
ICAssertion(
ICAssertionID
description
propertyID
1
...
propertyID
n
)
ICAssertionID rdf:type owl:ICAssertion.
ICAssertionID rdf:type rdfs:Resource.
[opt]
ICAssertionID owl:onClass
T(description).
ICAssertionID owl:byProperty
T(propertyID
1
). ...
ICAssertionID owl:byProperty
T(propertyID
n
).
and Le-Thanh, 2007; Nguyen and Le-Thanh, 2006),
which is an extension of
S H O I N (D) by combining
it with ICs. We show
S H O I N K (D)-concept satisfi-
ability w.r.t a knowledge base, guaranteeing the decid-
ability of OWL-K. Note that in DLs, domain of data
values is called concrete domain.
5.1 S H O I N K (D)
5.1.1 Datatypes
Datatypes are used to represent literal values such as
numbers or strings. They compose a concrete domain
D as introduced for
S H O Q (D) (Horrocks and Sat-
tler, 2001). Each datatype d ∈ D is associated with a
set d
D
⊆ ∆
D
, where ∆
D
is the domain of interpreta-
tion of all datatypes. For example, a datatype ≥
21
in
D defines a set ≥
21
D
of integer values greater than or
equal to 21.
5.1.2 Syntax and Semantics
As for any DL language, the basic syntactic build-
ing blocks of
S H O I N K (D) are atomic concepts,
atomic roles, and individuals. Concepts are inter-
preted as sets of individuals (subsets of the interpreta-
tion domain) and roles as sets of pairs of individuals.
Expressions are then built from these basics by using
several kinds of constructors. For example, the con-
junction of concepts C⊓ D denotes the set of individ-
uals obtained by intersecting the sets of individuals
belonging to C and D.
S H O I N K (D) syntax and semantics can be seen
in table 1, 2 and 4, where C and D are concept
descriptions; o is nominal, i.e. singleton concept;
R,R
1
,...,R
n
, S are roles; ∆
I
is the interpretation do-
main disjoint from the concrete interpretation domain
∆
D
. The inclusion relationship is denoted by ⊑. In
number restrictions, i.e. ≤ nR and ≥ nR, R is a
simple role which does not have transitive subroles.
The formal definition of
S H O I N K (D) can be found
in (Nguyen and Le-Thanh, 2007; Nguyen and Le-
Thanh, 2006).
5.2 S H O I N K (D) Reasoning
The decidability of OWL-K is addressed by propos-
ing a decision procedure for
S H O I N K (D). This is
an extension of the algorithm introduced in (Horrocks
and Sattler, 2005) by adding new expansion rules to
support ICs with some refinement techniques. The
algorithm is proved to be decidable (Nguyen and Le-
Thanh, 2007; Nguyen and Le-Thanh, 2006).
Theorem 5.1 The
S H O I N K (D)-concept satisfia-
bility problem w.r.t a knowledge base is decidable.
ICEIS 2007 - International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
342

Since OWL-K corresponds to S H O I N K (D)
DL, we have the following corollary.
Corollary 5.1 The OWL-K concept satisfiability
problem w.r.t a knowledge base is decidable.
According to Tobies (Tobies, 2001), if L is a
DL that provides the nominal constructor, knowledge
base satisfiability can be polynomially reduced to the
concept satisfiability w.r.t a knowledge base. So that
we obtain the following theorem.
Theorem 5.2 The knowledge base satisfiability prob-
lem of OWL-K is decidable.
6 DISCUSSION AND
PERSPECTIVES
We have proposed OWL-K as a decidable extension
of OWL-DL. This language supports ICs, which can-
not be represented in OWL-DL. The underpinning
DL of the latter,
S H O I N (D), is already known
with the complexity of NExpTime-complete (Tobies,
2000). Consequently, OWL-K has a difficult entail-
ment problem. The extension of the language pre-
sented here, therefore, are built like detachable com-
ponents for various needs.
Considering recent works adressing the same
problem, (Dou et al., 2006) introduced an ontology-
based framework, OntoGrate, using the web ontol-
ogy language Web-PDDL to incorporate database
schemas. This language allows IC representation.
However, it is written in RDF, an older formalism
with a lower capability than that of OWL. Even wrap-
ping one more layer translating Web-PDDL to OWL
syntax to facilitate worldwide use, the language is un-
decidable because its semantics is based on First Or-
der Logic (FOL), which is well known to be undecid-
able.
Some other works are discussed in (Chen et al.,
2006; Kalfoglou et al., 2005). However, to the best of
our knowledge, there exists no integrating framework
at the database schema level that provides a formal se-
mantic web ontology language, supporting OWL and
IC representation, and at the same time affording a
decidable reasoning procedure.
Our work comes within the perspective of a global
project to construct a methodology of integration of
relational data sources into the Semantic Web envi-
ronment. This integration will be realized through the
model ORM (Object Role Modeling) (Halpin, 2006).
The project consists of the study of the mapping with-
out loss of semantics of ORM schemas to a Web on-
tology language, i.e. OWL-K introduced here. Future
work will turn towards the research on the automated
translation of requests from OWL-K to SQL by using
the above mentioned mapping.
REFERENCES
Bechhofer, S., van Harmelen, F., Hendler, J., Horrocks, I.,
McGuinness, D. L., Patel-Schneider, P. F., and Stein,
L. A. (2004). OWL Web Ontology Language Refer-
ence.
Chen, H., Wang, Y., Wang, H., Mao, Y., Tang, J., Zhou,
C., Yin, A., and Wu, Z. (2006). Towards a Seman-
tic Web of Relational Databases: a Practical Semantic
Toolkit and an In-Use Case from Traditional Chinese
Medicine. In 4th International Semantic Web Con-
ference (ISWC’06), LNCS, pages 750–763, Athens,
USA. Springer-Verlag. Best Paper Award.
Dou, D., LePendu, P., Kim, S., and Qi, P. (2006). Inte-
grating Databases into the Semantic Web through an
Ontology-Based Framework. In ICDEW ’06: Pro-
ceedings of the 22nd International Conference on
Data Engineering Workshops (ICDEW’06), page 54,
Washington, DC, USA. IEEE Computer Society.
Halpin, T. (2006). Object-role modeling (ORM/NIAM). In
Handbook on Architectures of Information Systems,
2nd edition, pages 81–103. Springer, Heidelberg.
Horrocks, I. and Patel-Schneider, P. F. (2004). OWL
Web Ontology Language, Semantics and Ab-
stract Syntax. http://www.w3.org/TR/2004/REC-owl-
semantics-20040210/syntax.html.
Horrocks, I. and Sattler, U. (2001). Ontology Reasoning in
the S H O Q (D) Description Logic. In Proc. of the 17th
Int. Joint Conf. on Artificial Intelligence (IJCAI 2001),
pages 199–204. Morgan Kaufmann, Los Altos.
Horrocks, I. and Sattler, U. (2005). A Tableaux Decision
Procedure for S H O I Q . In Proc. of the 19th Int. Joint
Conf. on Artificial Intelligence (IJCAI 2005), pages
448–453.
Kalfoglou, Y. Hu, B., Reynolds, D., and Shadbolt, N.
(2005). Semantic Integration Technologies survey.
Technical report.
Nguyen, T. D. T. and Le-Thanh, N. (2006). La con-
trainte d’identification dans la Logique de descrip-
tion S H O I N (D). ISRN I3S/RR- 2006-34-FR, Lab-
oratoire I3S, Universite de Nice Sophia-Antopolis,
France.
Nguyen, T. D. T. and Le-Thanh, N. (2007). Identification
constraints in S H O I N (D). In Proc. of the 1th Int.
Conf. on Research Challeges in Information Science
(RCIS 2007). Accepted to publish.
Tobies, S. (2000). The Complexity of Reasoning with Car-
dinality Restrictions and Nominals in Expressive De-
scription Logics. Journal of Artificial Intelligence Re-
search, 12:199–217.
Tobies, S. (2001). Complexity Results and Practical Algo-
rithms for Logics in Knowledge Representation. PhD
thesis, Rheinisch-Westfalischen Hochschule Aachen.
INTEGRATING IDENTIFICATION CONSTRAINTS IN WEB ONTOLOGY
343
