
AN INTELLIGENT AGENT BASED APPROACH TO MOSAICA’S
PEDAGOGICAL FRAMEWORK
Nazaraf Shah, Jawed Siddiqi and Babak Akhgar
Informatics Research Group, Sheffield Hallam University, Sheffield, UK
Keywords: Intelligent Pedagogical Agent, Artificial Intelligence, Virtual Learning, Virtual Expeditions.
Abstract: There has been a significant amount of research in application of intelligent agent technology in virtual
training and pedagogical environments. The characteristics of intelligent agents, such as flexible behaviour,
autonomy and socialablity make them highly suitable candidates to overcome the shortcomings of the
traditional course management systems, online learning and Web resources available to learners. In this
paper we propose an agent based approach to manage virtual expeditions and learning activities in
Semantically Enhanced, Multifaceted, Collaborative Access to Cultural Heritage (MOSAICA) project. We
believe that Belief, Desire, Intention (BDI) model of intelligent agent better serve the pedagogical
requirements identified in MOSAICA project. The cognitive characteristics of MOSAICA pedagogical
framework are easy to map to mental model of BDI intelligent agents.
1 INTRODUCTION
MOSAICA (MOSAICA) is an EU-IST funded
collaborative project being carried out by a
consortium consisting of seven EU countries and
Israel. MOSAICA is envisioned as an advanced web
portal, featuring multifaceted interfaces for
knowledge based exploration and online utilities
empowering users to collaboratively author and
manage cultural resources in a globally distributed
environment.
The purpose of MOSAICA is to design a toolbox
for intelligent presentation, knowledge-based
discovery and interactive and creative educational
experience covering a broad variety of cultural
heritage resources. The initial focus of MOSAICA is
Jewish cultural heritage but the project is potentially
applicable to other cultural heritages.
MOSAICA’s proposed inovations and technical
challenges include Semantic Web technologies,
distributed content management, Geographical
Information Systems (GIS), and pedagogical
framework.
In this paper our focus will be on the
management of technical issues related to
MOSAICA’s pedagogical framework. We propose
an intelligent agent based approach for realisation of
MOSAICA’s pedagogical framework. We believe
that the objectives of pedagogical framework of
MOSAICA can be best achieved by application of
intelligent pedagogical agents.
2 MOSAICA’S PEDAGOGICAL
FRAMEWORK
MOSAICA’s pedagogical framework is based on
well know theory of knowledge known as
constructivism. The constructivist theory applied to
teaching assumes that knowledge cannot simply be
transmitted from teachers to learners: learners must
be engaged in constructing their own knowledge
(Von Glaserfeld, 1987). The focus of constructivism
is on promotion of active and inquiry-based learning
(Bruner, 1990). In constructivist environments the
learners are encouraged to create their own mental
framework and formulate their own conceptual
models to understand the learning material.
Technologies to support constructivist learning
environments require the designing of new platforms
and curricula. Effective integration of technology in
a coherent and authentic way into the curriculum is
not a trivial problem. However, judicious
implementation of educational technology may offer
means to support teaching and learning
[4],[5]
. One
way of doing this is to integrate visualizations and
virtual environments (Dori and Belcher, 2005).
Computerized visualizations and virtual worlds
are used simplify and clarify abstract concepts. The
use of textbooks presents students with two-
dimensional drawings; however, they do not
represent the true spatial nature of things. With the
development of computer graphics technology,
three-dimensional imaging has become a prominent
219
Shah N., Siddiqi J. and Akhgar B. (2007).
AN INTELLIGENT AGENT BASED APPROACH TO MOSAICA’S PEDAGOGICAL FRAMEWORK.
In Proceedings of the Ninth International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems - SAIC, pages 219-224
DOI: 10.5220/0002400902190224
Copyright
c
SciTePress

tool for representing complex structures and real-
world phenomena. Incorporating visualization as
part of the educational process has been found to
foster students' understanding of three-dimensional
structures, spatial ability, and meaningful learning
(Barnea and Bori, 1999), (Bori et al., 2003),
(Donovan and Nakhleh, 2001). In spite of the
prevalent use of visualization and virtual worlds in
the cooperative world, and the recognition of its
educational value, the integration of virtual
environments in school courses is still limited,
mostly because of lack of appropriate technology.
Mental operations elicited by virtual
environments differ from those occurring in
traditional instructional settings that allow learners
to experience physical properties of objects and
events, such as shape, size, distance and time, and
realize the actual implications of such properties.
The virtual pedagogical environments have limited
benefits of cooperation and coordination as
compared to physical learning environments.
The learning experience in both worlds is
essentially different. Real world learning
environments offer myriad opportunities for
observations and interactions. Real world learning
incorporates body and mind experience, including
all five senses. Learners physically walk amongst
the observed objects, touch them (in most cases),
listen to surrounding sounds, sense odours, and
communicate with a guide or fellow learners to
enhance the learning experience.
Transfer of the real world into a virtual
environment is certainly not merely a one-to-one
mapping, but must follow a complex logic of
transformation. Learning in virtual worlds must be
specifically designed for virtual environments. Our
research will address problems of accessibility and
complexity, aiming at developing an educational
framework, and a platform for interactive inquiry
and exploration. We intend to research how to do it
efficiently, but through entertaining exploration.
Within this general research direction, a special
track will be directed toward development of the
methodology and the technology for Virtual
Expeditions. Virtual Expeditions are a specific
educational instrument based on conceptual
modelling, and designed specifically for learning
through exploration of virtual worlds. The Virtual
Expedition methodology must devise a step-by-step
procedural approach to the thematically driven
conceptualisation of cultural resources aiming at
long-term educational impact. Such a methodology
will include:
1. Selection and design of pedagogical themes,
2. Development of educational content,
including: (a) the general site in which the
virtual expedition takes place, (b) the three-
dimensional images learners will encounter,
(c) their attached textual and vocal
description, (d) the conceptual relationships
between the images and potential exploration
paths,
3. Implementation of the virtual expeditions,
including short assignments and/or extensive
projects, as well as individual and/or
collaborative learning, and
4. Documentation, including “tutorial” and
“help” buttons, and the instructions for their
use to various purposes and age groups.
Each virtual expedition will be triggered by a
driving question, riddle or problem that needs
solving. The students will be asked to make
assumptions, hypothesize, or problem-solve an
authentic issue that confronts the real world. One of
the objectives is that students respond to problems
that prompt higher-order thinking. Built into the
virtual expedition process are the strategies of
cognitive psychology and constructivism. The
problems posed to students cannot be answered
simply by collecting and retrieving information. In
order to engage students in higher-order thinking,
virtual expedition methodology will use scaffolding
or prompting, that is, breaking tasks into meaningful
“chunks” and steer students through a thinking
process that is used by expert learners.
The Virtual Expedition methodology will offer
two ways for implementing collaborative learning:
(1) by assigning group assignments, and (2) by
utilizing an online forum for informal text-based
discourse. As part of the group assignments, students
take on roles. Each student will focus on a certain
aspects of the large and complex problem and
become an expert in it. By running several Virtual
Expedition groups in the same class, students will
also see different solutions chosen by different
teams.
Thus, Virtual Expedition is an innovative
approach to learning in virtual environments. It
offers a structured way to guide users through
virtuality. Therefore, our methodology will be
designed, developed and researched, so that it could
be followed by other, less expert users to construct
their own Virtual Expeditions.
In addition to the pedagogical research,
technological research is also required, in order to
develop a framework enabling design, recording and
automatic execution of Virtual Expeditions. This
effort must provide an online editing tool
empowering end users with the ability to create and
record their own Virtual Expeditions.
For demonstration purposes, research will develop
few exemplifying Virtual Expeditions. These
ICEIS 2007 - International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
220
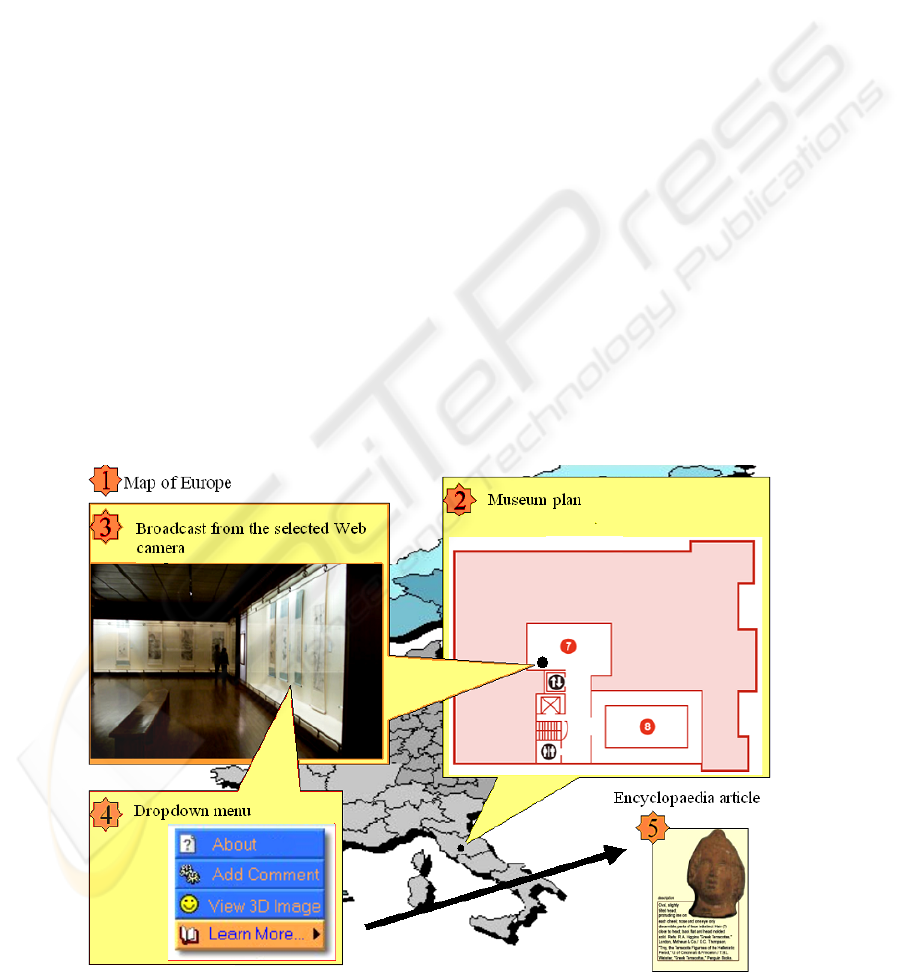
demonstrators will be also used as tutorials and
instructional material to guide end users in designing
their own Virtual Expeditions. MOSAICA's
repository will contain ready-to-use educational
material designed for the educational personnel to
use them in instruction and
teaching, but also for
students and other visitors to use them for individual
studies. A mock up screen shot of a 1
MOSAICA’s virtual expedition is shown in
Figure 1 All navigational interfaces will be tightly
interconnected enabling users to seamlessly move
between them. For example, by selecting a certain
item from the search results, users will be able to
move to the GIS empowered map with related
locations automatically marked on it, or to the
MOSAICA directory displaying the relevant
concepts and their semantic relations, etc.
3 INTELLIGENT AGENT
The definition of an intelligent agent is still subject
of controversy. However, it is generally accepted
that an agent can be viewed as “an encapsulated
computer system that is situated in some
environment and is capable of flexible and
autonomous actions in that environment in order to
meet its design objectives” (Wooldridge, 2000).
Wooldridge and Jennings (Wooldridge and
Jennings, 1995) argue that the term agent can be
used to denote a hardware or (more usually)
software-based computer system that has following
properties:
Autonomy: Agents can operate without the
direct intervention of humans or other agents, and
have control over their individual actions and
internal state.
Social Ability: Agents are able to interact with
other agents (and possibly humans) via an agent
communication language.
Reactivity: Agents perceive their environment,
and should respond in a timely fashion to changes
that occur in it.
Pro-activeness: Agents do not simply act in
response to their environment; rather they are able to
exhibit goal-directed behaviour by taking the
initiative.
Franklin et al. provide a useful taxonomy of the
agents based on agent definitions arising from their
functional characteristics and attributes (Stan and
Graesser, 1996).
Multi-agent systems can be viewed as a
collection of autonomous problem solving entities,
capable of achieving their goals through interaction,
coordination, cooperation and collective intelligence
(Jennings et al., 1998).
An MAS is a system composed of a population
of autonomous agents, which cooperate with each
other to reach common objectives, while
simultaneously each agent pursues individual
objectives " (Jacques, 1999), (Wooldridge, 2000).
Figure 1: A Mock-up Screen Shot of MOSAICA’s Virtual Expedition.
AN INTELLIGENT AGENT BASED APPROACH TO MOSAICA’S PEDAGOGICAL FRAMEWORK
221

4 PROPOSED APPROACH
The original proposal of MOSAICA’s pedagogical
framework does not propose the use of intelligent
agent technology in realisation of the framework. It
leaves the technological issues involved in
realisation of framework for further investigation.
Our past experience of working in intelligent agent
area and a growing number of research efforts
related to application of pedagogical agent in online
learning environment (Blanchard et al., 2006),
(Conati, 2004), (Baylor, 2001) motivate us to
investigate the suitability of agent technology in
realisation of MOSAICA’s pedagogical framework.
Intelligent agent technology provides promising
approaches for modelling high level abstractions and
high level reasoning. We propose the use of BDI
agents in as enabling technology for MOSICA’s
pedagogical framework.
BDI agent model (Rao and Georgeff, 1995) is
one of the most popular approaches towards the
design and development of intelligent agents. The
defining characteristic of this model is that the
generation of agent behaviour is driven by mental
attitudes such as belief desire and intentions. It aims
to be a model that is a functional abstraction of high
level reasoning carried out by human mind.
Our proposed approach makes use of two types
of intelligent agent know as Virtual Expedition
Agent and User Agents are shown in figure 2. These
agents use various software components attachments
in order to support their low level system
functionality.
Abstract descriptions of these agents are given
below.
4.1 User Agent
A User Agent sits between a user and Virtual
Expedition Agent (VEA). It is responsible for
managing user interaction with VEA during a virtual
expedition. It obtains user input and, formulates and
sends an expedition request to VEA. This agent acts
as a tutor/coach for its user and provides proactive
help whenever necessary.
User agent uses two different set of rules for
managing its learning and coaching functionality.
These rules will be realised in the belief component
of user agents. The implementation of rules set as
agent beliefs enables context sensitive reasoning
during presentation of an expedition to user and
coaching service whenever a user needs it.
User Agent has a set plans for carrying out
expeditions and coaching tasks. Each plan in agent’s
plan library is a recipe of actions that it executes in
response to achievement of a specific goal.
Figure 2 depicts User Agent and collaborative
user agent group. These all agents are essentially the
same, but they operate in different mode.
a) A single user mode, where a User Agent is
serving a single user during a virtual
expedition without any regard to other agents
interacting with VEA. In this mode user
agent uses the request-response interaction
protocol to manage interaction with VEA.
Figure 2: Agent Based Framework for MOSAICA Pedagogical Framework.
ICEIS 2007 - International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
222

Collaborative mode, where user agents interact with
VEA and with each other for the purpose of
collaborative learning. Each User Agent in a group
of users agents involved in collaborative learning
will focus on certain aspects of a complex problem.
The group needs to be aware of contribution of each
remember in order to progress toward overall
solution. The agents in this mode use teamwork
interaction protocol for managing interaction among
group members in addition to request-response
interaction protocol.
4.2 Virtual Expedition Agent
Virtual Expedition Agent is at the heart of our
proposed approach. It manages interactions with
user agents and Web resources. MOSAICA proposes
the use of Service Oriented Architecture (E. Ort) for
the integration of different systems components. An
Agent-WS gateway is proposed to manage seamless
interaction between intelligent agents and Web
Services (WS). This gateway will provide a
translation service that will convert message in agent
communication language (FIPA, 2000) to Web
Services Description Language (WSDL)
(Christensen et al., 2001) and vice versa.
VEA respond to User Agent’s requests using an
expedition from its libraries of static or dynamic
expeditions or preparing a new virtual expedition if
not already present in expedition library.
VEA expedition libraries contain two types of
virtual expeditions known as static and dynamic
expedition.
a) Static Expeditions are few exemplifying those
that will be used as tutorials and instructional
material to guide end users in designing their
own Virtual Expeditions. These also contains
ready-to-use educational material designed for
the educational personnel to use in instruction
and teaching, but also for students and other
visitors to use them for individual studies.
b) Dynamic Expeditions are expeditions that a
VEA agent complies in response to requests
received from User Agent. VEA compiles
these expeditions by interacting with resources
via an Agent-WS gateway. It also maintains a
record of dynamic expeditions and uses them
in order to serve identical request coming from
different User Agents.
VEA uses different kind of interaction protocols in
order to maintain interactions between various User
Agents and resources. It also supports User Agents in
their collaborative expeditions.
5 RELATED WORK
In this section we present literature review in
relation to the use of intelligent agents as
pedagogical agents in order to make the case for
suitability of agent technology in realisation of
MOSAICA’s pedagogical framework.
Johnson (Johnson, 1998) purpose the definition
of pedagogical agent as special purpose
agent:“Pedagogical agents are autonomous agents
that support human learning, by interacting with
students in the context of interactive learning
environments. They extend and improve upon
previous work on intelligent tutoring systems in a
number of ways. They adapt their behaviour to the
dynamic state of the learning environment, taking
advantage of learning opportunities as they arise”.
Blanchard (Blanchard et al., 2006) propose an
intelligent tutoring system in which pedagogical
agents have ability to evolve. This evolution process
allows producing agents whose behaviours are
fitting the learner motivational and cultural needs.
They have used rule based methodology for
evolution process.
Conati (Conati et al., 2006) propose intelligent
pedagogical agents that can provide individualised
instructions integrated with the entertaining nature
of the games. They describe different ways of
improving learning using intelligent agents in
educational games.
Baylor (Baylor, 2001) proposes the cognitive
requirements for agent based learning environments
and identifies four dimension of control that must be
considered in designing agent based learning
environments.
Rickel (Rickle, 1998) introduce a pedagogical
agent STEVE for virtual reality learning
environment. STEVE handles high level cognition
processing and sensor motor processing as two
separate but related processes.
The cognitive process interprets the state of the
world and executes plans to achieve its goals. The
sensory motor process deals with its interface with
virtual world.
Hamburger (Hamburger and Tecui, 1998)
propose architecture for pedagogical agents that can
learn from human tutor and then teach to human
learners. They used machine learning and
knowledge acquisition approaches in their proposed
architecture.
Johnson (Johnson et al.) propose the integration
of pedagogical agents into virtual environment.
These pedagogical agents monitor the trainees’
behaviour in virtual environment and provide them
instructions by interaction with them. This
integration enables trainees to get guidance and
coaching in virtual environment.
AN INTELLIGENT AGENT BASED APPROACH TO MOSAICA’S PEDAGOGICAL FRAMEWORK
223

Although none of these approaches deal directly
with the issues related to virtual expedition
discussed in MOSAICA’s pedagogical framework.
But these approaches do make a case for the use of
intelligent agent as enabling technology in
pedagogical applications. We believe that these
approaches provide foundational building blocks for
realisation of MOSAICA’s pedagogical framework.
6 CONCLUSION
In this paper we have presented MOSAICA’s
pedagogical framework and proposed an intelligent
agent based approach for the realisation of this
framework. Intelligent agents provide an intelligent
virtual learning environment, where user will engage
in learning individually and collaboratively with the
help of their agents. Our future work will focus on
design and implementation of User Agent and VEA.
We have also provided discussion of related
literature in order to justify the use of intelligent
agent technology in realisation of MOSAICA’s
pedagogical framework.
REFERENCES
MOSAICA - Semantically Enhanced, Multifaceted,
Collaborative Access to Cultural Heritage,
Information Society Technologies,
http://cordis.europa.eu/ist/digicult/mosaica.htm
Von Glaserfeld, E. “The Construction of Knowledge:
Contributions to Conceptual Semantics”, Seaside, CA:
Intersystems Publications, (1987).
Bruner, J.S. “Acts of Meaning”, Cambridge: Harvard
University Press. (1990).
Barak, M. and Dori, Y.J. “Enhancing Undergraduate
Students’ Chemistry Understanding Through
Project-Based Learning in an IT Environment”.
Science Education. 89(1), (2005), 117-139.
Dori, Y.J., Barak, M. and Adir, N. A Web-based
chemistry course as a means to foster freshmen
learning. Journal of Chemical Education, 80(9), 1084-
1092. (2003).
Dori, Y.J. and Belcher, J.W. “How does Technology-
Enabled Active Learning Affect Students'
Understanding of Scientific Concepts?” The Journal
of the Learning Sciences. 14(2), (2005), 243-279.
Barnea, N. and Dori, Y.J. “High-School Chemistry Pre-
service teacher's Performance and Gender Differences
in a Computerized Molecular Modeling Learning
Environment”
Journal of Science Education and
Technology, 8(4), (1999),257-271.
Dori, Y.J., Barak, M. and Adir, N. A Web-based
chemistry course as a means to foster freshmen
learning. Journal of Chemical Education, 80, 1084-
1092, (2003).
Donovan, W.J. and Nakhleh, M.B, “Students' use of Web-
based Tutorial Materials and their Understanding of
Chemistry Concepts”, Journal of Chemical Education,
78, (2001), 975-980
Wooldridge, M. Reasoning about Rational Agent, The
MIT Press, 2000.
Wooldridge M., and Jennings, N. R., “Intelligent Agent:
Theory and Practice”, Knowledge Engineering
Review, 10(2), (1995), 115-152.
Franklin Stan and Art Graesser, “Is it an Agent, or just
Program?: A taxonomy for Autonomous Agents”,
Proceeding of third International Workshop on Agent
Theories, Architecture, and Language, Springer-
Verlag 1996.
Jennings N. R., Sycara K. and Wooldridge M., “A
Roadmap to Agent Research and Development”,
Autonomous Agents and Multi-Agent Systems,
(1998). 7-38.
Ferber Jacques, Multi-agent Systems: An Introduction to
Distributed Artificial Intelligence. Addison-
Wesley, 1999
Rao A. S. and Georgeff M. P., “BDI Agents: From Theory
to Practice”, Proceedings of the First Intl. Conference
on Multiagent Systems, San Francisco (1995).
E. Ort, Service-Oriented Architecture and Web Services:
Concept, Technologies, and Tools. Available:
http://java.sun.com/developer/technicalArticles/WebS
ervices/soa2/soa2.pdf.
FIPA Communicative Act Library Specification,
www.fipa.org/specs/fipa00037/SC00037J.pdf, 2000.
E. Christensen, F. Curbera, G. Meredith, and S.
Weerawarana, “Web Services Description Language
(WSDL) 1.1,” W3C, 15th Mar., 2001, Available:
http://www.w3.org/TR/2001/NOTE-wsdl-20010315
Johnson, W.L. (1998) Pedagogical Agents. In Chan, T.-
W., Collins, A. & Lin, J. (eds.) Global Education on
the Net Vol 1, Proceedings of ICCE ’98, the Sixth
International Conference on Computers in Education,
Beijing, China, 14 – 17 October 1998. Beijing: China
Higher Education Press and Springer-Verlag
Emmanuel Blanchard, Claude Frasson, Motivation and
Evolutionary Pedagogical Agents, Workshop on
Motivational and Affective Issues in ITS. 8
th
International Conference on ITS 2006, pp 54-61,
2006.
Cristina Conati, Xiaohong Zhao, Building and Evaluating
an Intelligent Pedagogical Agent to Improve the
Effectiveness of an Educational Game, IUI-CADUI
’04, January 13-16, 2004, Island of Madeira, Portugal
Copyright 2004 ACM.
Amy L. Baylor, Cognitive Requirements for Agent-Based
Learning Environments, Proceedings of the IEEE
International Conference on Advanced Learning
Techniques (ICALT’01), 2001.
Jeff Rickle, W. Lewis Johnson; “STEVE: A Pedagogical
Agent for Virtual Reality”, Proceedings of the Second
International Conference on Autonomous Agent,
ACM, 1998,
Henry Hamburger, Gheorghe Tecui, Architecture of
Pedagogical Agent for Human-Computer Learning
and Tutoring; In Proceedings of the ITS-98 Workshop
2 – Pedagogical Agents, San Antonio, TX, 1998.
W. Lewis Johnson, Jeff Rickel, Randy Stiles, Allen
Munro, “Integrating Pedagogical Agents into Virtual
Environments”; Teleoperators and Virtual
Environments (76): 5
ICEIS 2007 - International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
224
