
KNOWLEDGE FLOW ANALYSIS TO IDENTIFY KNOWLEDGE
NEEDS FOR THE DESIGN OF KNOWLEDGE MANAGEMENT
SYSTEMS AND STRATEGIES
A Methodological Approach
1,2
Oscar M. Rodríguez Elias,
2
Ana I. Martínez García,
2
Jesús Favela Vara
1
UABC, Facultad de Ciencias, Km 103, Carretera Tijuana-Ensenada, Ensenada, B.C., Mexico, 22860
2
CICESE, Computer Science Department, Km 107, Carretera Tijuana-Ensenada, Ensenada, B.C., Mexico, 22860
Aurora Vizcaíno, Juan Pablo Soto
UCLM, Escuela Superior de Informática, Paseo de la Universidad No. 4, Ciudad Real, Spain, 13071
Keywords: Knowledge Management, Knowledge Flow Analysis, Process Engineering.
Abstract: This paper presents a methodological approach to identify knowledge needs in organizational processes.
The methodology is oriented to facilitate obtaining requirements to design knowledge management systems
and/or strategies. This approach has been applied for different purposes, including identifying relationships
between the knowledge and sources involved in the activities of a process, the mechanisms used for
managing knowledge in those processes, and the main problems affecting the flow of knowledge. In order
to exemplify the usefulness and applicability of the proposed approach, a case study is described, in which
the methodology was successfully applied to analyze a software development group. From this case study
different possible solutions to some problems observed in the maintenance process were proposed.
1 INTRODUCTION
Many Knowledge Management (KM) initiatives fail
when they are implemented in organizations
(Stewart, 2002). One of the causes of this is that
those initiatives do not consider the real needs of the
knowledge workers (Wiig, 2004), that means, the
people that will use the knowledge to better
accomplish their actual work. In order to a KM
system or strategy be succesful, it must be aligned to
the real work processes of the organization where it
will be implemented (Maier & Remus, 2002).
KM systems (KMSs) must facilitate knowledge
workers to obtain the knowledge they require from
where it is created or stored; or to capture and store
the knowledge created in the activites performed by
those workers, to make it avalable for future use.
From this view, we must first understand how
knowledge is actualy flowing in the work processes,
to later identify possible improvements to facilitate
the knowledge flow (Nissen, 2002). Once identified
the different forms in which knowledge is flowing
through a process, it should be easier to identify the
problems affecting that flow, and, as a consequence,
to propose possible solutions to improve the flow.
This paper presents a methodology that has been
succesfully applied to identify knowledge
management needs in work processes, through the
identification and analysis of knowledge flows. The
remains of this paper is organized as follows: in the
next section the methodology is described. Later,
section three presents a case study that exemplify the
applicability and usefulness of the methodology.
Section four discusses some lessons learned from the
case study, to finally conclude in section five.
2 A KNOWLEDGE FLOW
ANALYSIS METHODOLOGY
To define successful KM strategies is important to
take care of the real work processes of organizations,
and the technical infrastructure used to support them
(Jennex & Olfman, 2005; Maier & Remus, 2002).
Therefore, before defining KMSs or strategies, it is
492
M. Rodríguez Elias O., I. Martínez García A., Favela Vara J., Vizcaíno A. and Pablo Soto J. (2007).
KNOWLEDGE FLOW ANALYSIS TO IDENTIFY KNOWLEDGE NEEDS FOR THE DESIGN OF KNOWLEDGE MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS AND
STRATEGIES - A Methodological Approach.
In Proceedings of the Ninth International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems, pages 492-497
Copyright
c
SciTePress

important to understand how knowledge is involved
in those processes. Based on this, we have defined a
methodology to identify and analyze knowledge
flows in work processes, first introduced in
(Rodríguez-Elias et al., 2005b). The methodology is
called KoFI (Knowledge Flow Identification), and is
based on process engineering techniques, such as
process modeling (Curtis et al., 1992).
Process modeling can be used as a means to
analyze and understand the knowledge that is used
or generated in organizational processes, and the
mechanisms through which that knowledge flows
(Bera et al., 2005; Hansen & Kautz, 2004).
However, process models are not just to understand
the process, they are also useful to obtain
requirements for approaches focused on improving it
(Cox et al., 2005).
The KoFI methodology was defined to help in
three main forms: 1) to identify, structure, and
classify the knowledge base of the studied process,
2) to identify the technological infrastructure that
support the process and that is affecting the
knowledge flow, and 3) to identify requirements to
improve the knowledge flow in the process.
2.1 Description of KoFI
The KoFI methodology is oriented to help analyze
specific work processes. Therefore, before applying
KoFI, is required to define the specific process to be
analyzed. To help on this analysis, the process must
be modeled. Those models should be done with a
Process Modeling Language (PML) that allows the
explicit representation of the knowledge and
knowledge sources involved in the activities of the
process. The process models are later analyzed
following a four step process, as is shown in figure
1. The first step is focused on identifying the main
knowledge sources involved in the process. The
second step is oriented to identify the knowledge
that is used or generated in the activities of the
process. Later, in step three the flow of knowledge
between activities, and sources is identified and
analyzed. Finally, the problems that are affecting the
well flow of knowledge are defined.
The process followed for applying the
methodology is iterative, since each stage may
provide information useful for the others before it.
As well, the process model can be evolving while it
is being analyzed in the different stages of KoFI.
Next we provide some directions about how each
stage can be carried out.
The KoFI methodology
To identify
problems in the
knowledge flow
To identify
knowledge flows
To identify kinds of
knowledge
To identify
knowledge sources
To specify the process
to be analyzed
Knowledge focused
process modeling
Figure 1: Stages of the KoFI methodology.
2.1.1 Knowledge Focused Process Modelling
There exists many PMLs designed for very different
purposes (Curtis et al., 1992). Frequently, PMLs for
business process in general are used to model
knowledge flows (Hansen & Kautz, 2004;
Strohmaier & Tochtermann, 2005; Woitsch &
Karagiannis, 2002). Traditional PMLs can be used to
identify some issues related to knowledge flows
implicitly, such as the information sources required,
generated, or modified by an activity (Abdullah et
al., 2002; Davenport & Prusak, 2000). It is,
however, important that a PML used to analyze
knowledge flow provides explicit representation of
issues such as the knowledge consumed or generated
in activities, the knowledge required by the roles
participating in those activities, the sources of that
knowledge, or knowledge dependencies (Bera et al.,
2005; Papavassiliou & Mentzas, 2003).
Unfortunately, there is a lack of PMLs which focus
on the identification of knowledge involved in the
processes (Bera et al., 2005). One way to address
this situation is to adapt existing PMLs so as to
integrate the representation of knowledge.
It is recommended that the process be modelled
at different levels of abstraction (Checkland &
Scholes, 1999). First, a general view of the process
can be defined with a general and flexible process
modelling technique. To perform a detailed analysis,
a more formally constrained language should be
used (Conradi & Jaccheri, 1999). It can be also
helpful to use a PML designed for the type of
process that will be analyzed, since such a language
provides primitives to represent specific elements
involved in that type of processes; and the explicit
representation of those elements facilitate their
analysis. In our case, we have used Rich Picture
(Monk & Howard, 1998), and the Software Process
Engineering Metamodel (SPEM) (OMG, 2002).
Since the focus of this paper is not on the
modelling languages, just some examples will be
presented in the third section; more detailed
examples can be found in (Rodríguez-Elias et al.,
KNOWLEDGE FLOW ANALYSIS TO IDENTIFY KNOWLEDGE NEEDS FOR THE DESIGN OF KNOWLEDGE
MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS AND STRATEGIES - A Methodological Approach
493

2007). In this section we will limit our-self to just
present the main activities that are carried out in
each stage of KoFI.
2.1.2 To Identify Knowledge Sources
The first step, after modelled the first version of the
process, is identifying the main documents and
people involved in the process. It is important that
the sources identified be organized and classified.
To this end, a taxonomy can be defined. In fact,
defining taxonomies is one of the first steps in the
development of KMSs (Rao, 2005). An ontology can
be also developed to help defining the relationships
between the sources and the other elements of the
process. This ontology can be used to structure the
knowledge base of the process (O'Leary, 1998).
2.1.3 To Identify Knowledge Types
This stage starts by analysing the knowledge sources
identified in the first step; then, the types of
knowledge that can be obtained from the sources
found is defined together with the knowledge that
the people involved in the process may have or
require. In this step, a taxonomy and an ontology can
also help to classify the types of knowledge and
define their relationships with other elements of the
process. The ontology must define means for
relating the knowledge sources with the knowledge
areas or topics that can be found in them.
2.1.4 To Identify Knowledge Flows
In the third step, the process model is used to
identify how the knowledge and sources are
involved in the activities performed in the process.
The main activities of the processes must be
identified, also the decisions that people performing
those activities must make. The process models are
used to analyse how the knowledge flows through
the process while people involved perform their
activities; for example, what sources they consult, or
what documents are generated from doing the
activities. It is important to identify either flows of
knowledge between activities or between sources.
For instance, knowledge generated in one activity
that is used in others; or knowledge that is
transferred from one source to another. An example
of the last can be the transfer of knowledge of a
person to a document.
2.1.5 To Identify Knowledge Flow Problems
In the fourth step the knowledge flows identified are
analysed to find the problems that could be affecting
them. For example, if the information generated
from the activities is not captured, or if there are
sources that could help to perform some activities,
but are not consulted by the people in charge. To do
this, we propose to use problem scenarios. A
problem scenario is a story that describes how a
problem is happening (Rodríguez-Elias et al.,
2005b). Particularly, this story must show how the
problems detected affect the knowledge flow. Once
described the problem scenario, one or more
alternative scenarios must be defined to illustrate
possible solutions, and the manner in which those
alternative solutions may improve the flow of
knowledge. Problem and scenario definition are
useful means to obtain design requirements to
develop tools to address the problems found (Carroll
& Rosson, 1992; Cox et al., 2005).
3 A CASE STUDY
This section presents examples of the application of
the methodology in a real case. The examples are
extracted from the study of a software maintenance
process performed by the information systems
development department of a research center.
The study started by identifying the maintenance
process. This was done based on interviews to the
personnel of the department, observation, and
analysis of documents. This information was used to
model the process. First, we used Rich Picture to
obtain a general view of the process. Examples can
be found in (Rodríguez-Elias et al., 2005b).
Frequently, Rich Pictures are used to illustrate
the main activities of a process, the information
elements generated, modified or used in these
activities, the roles participating, and the main fears,
concerns, etc. of the people carrying out those roles
(Checkland & Scholes, 1999; Monk & Howard,
1998). In our case, we adapted Rich Pictures to
illustrate also the main knowledge or skills required
in each activity, and the knowledge and skills that
each role should have to perform the activity. The
models developed in this stage were useful to start
identifying sources of knowledge involved (people,
documents, etc.), the knowledge required in the
activities, and the one each role of the process have.
To develop a more formal and detailed model of
the process, we used SPEM (OMG, 2002) and an
extension of it that we have proposed in (Rodríguez-
Elias et al., 2007). The diagrams developed
ICEIS 2007 - International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
494
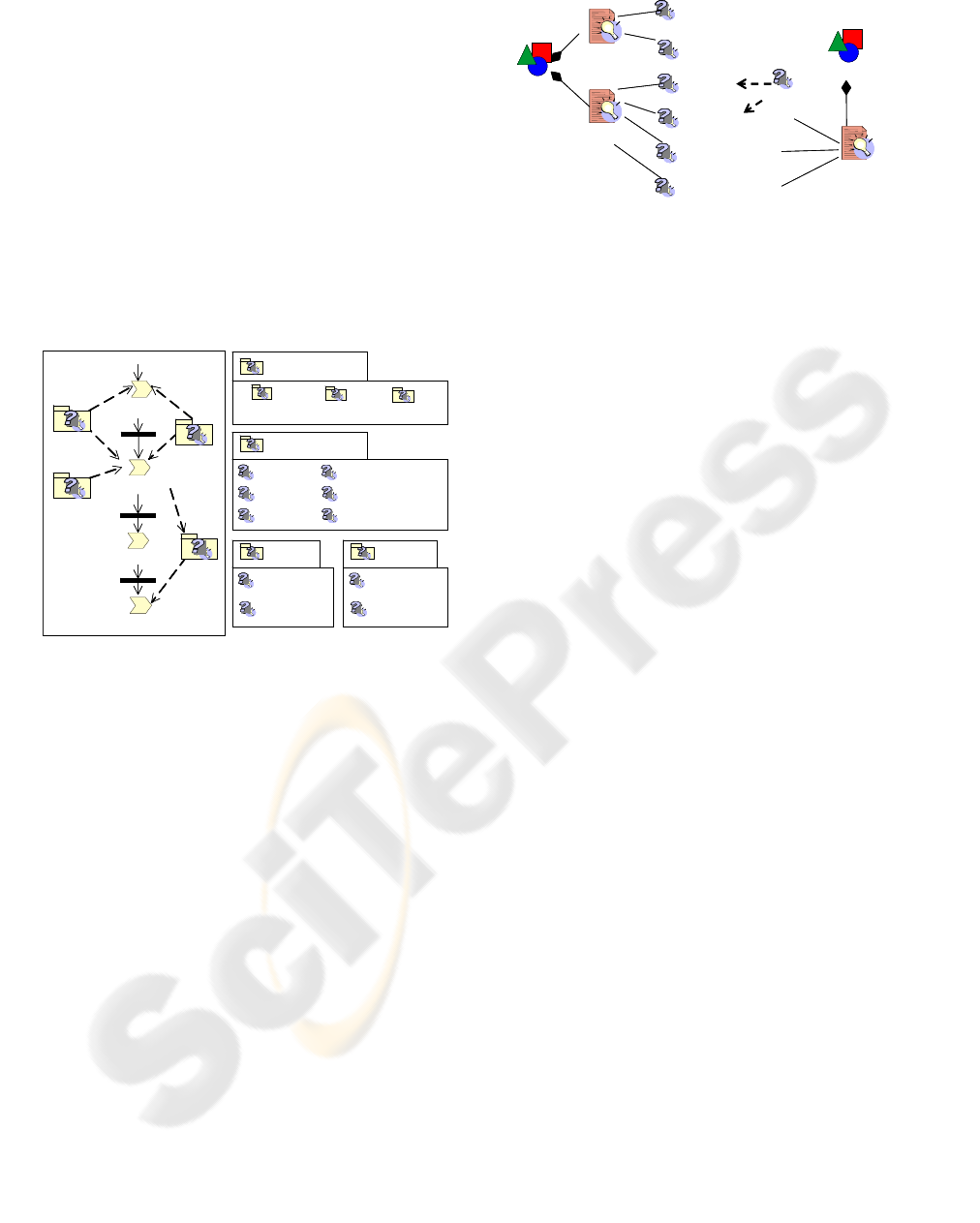
following this extension to SPEM, helped us for
different purposes; first, they were helpful to start
classifying the knowledge involved in the process by
grouping it in packages. Figure 2 shows an example,
where it is illustrated the sequence of some of the
activities performed by a software engineer, and the
main groups of knowledge involved; for instance,
the experience of the engineer and the information
contained in the documents used in these activities.
Later, we used knowledge package diagrams to
illustrate specifically the knowledge areas or
subjects involved in that sequence of activities.
Knowledge areas were defined as sub-packages that
were later detailed defining the specific knowledge
subjects grouped in that area.
Software Engineer
To download files to
be modified
To perform changes
To upload
modified files
To store the problem
solution into the PR
PR’s information
PR’s solution
SE’s experience
User knowledge
Knowledge of the
system
Structure of
the system
Structure of
the module
How the module
should work
Knowledge of the
domain of the system
Dependencies between
modules of the system
Dependencies of the
system with others systems
SE’s experience
Knowledge of
the system
Technical
knowledge
Technical
knowledge
Programming
language
Software
development
environment
Knowledge of
the process
Knowledge of
the process
Activities to be
done
Documents
involved
Software Engineer
To download files to
be modified
To perform changes
To upload
modified files
To store the problem
solution into the PR
PR’s information
PR’s solution
SE’s experience
User knowledge
Knowledge of the
system
Structure of
the system
Structure of
the module
How the module
should work
Knowledge of the
domain of the system
Dependencies between
modules of the system
Dependencies of the
system with others systems
SE’s experience
Knowledge of
the system
Technical
knowledge
Technical
knowledge
Programming
language
Software
development
environment
Knowledge of
the process
Knowledge of
the process
Activities to be
done
Documents
involved
Figure 2: Example of knowledge package diagrams.
We first defined general knowledge areas or
subjects in order to define a general model of the
process. Based on this general model, we latter
defined specific knowledge subjects, such as those
related to a specific application. For instance, when
we were analyzing the knowledge related to the
finances system, we changed the reference to the
system in the model of figure 2, to the finances
system, or the programming language area, to the
specific programming language used to develop the
finances system. Based on this we identified the
main sources where knowledge about the finances
system can be obtained, perhaps documents
describing its structure, people with knowledge of
the application domain, etc.
The knowledge packages were used as a basis for
developing a knowledge taxonomy to classify
knowledge into types, areas, and subjects. Then, the
next step was to identify the relationships between
the knowledge sources, and the knowledge that can
be obtained from them. For this, we used diagrams
as the shown in figure 3. These diagrams help
illustrate the knowledge areas or subjects that can be
consulted in knowledge sources; perhaps documents.
Requirements
specification
System’s design
documentation
Similar requests
Logbook
System
documentation
Structure of
the system
Structure of
the module
How the module
should work
Knowledge of the
domain of the system
Dependencies between
modules of the system
Dependencies of the
system with others systems
Files to be
modified
Requirements
specification
System’s design
documentation
Similar requests
Logbook
System
documentation
Structure of
the system
Structure of
the module
How the module
should work
Knowledge of the
domain of the system
Dependencies between
modules of the system
Dependencies of the
system with others systems
Files to be
modified
Figure 3: Example of a class diagram showing
relationships between sources and knowledge areas.
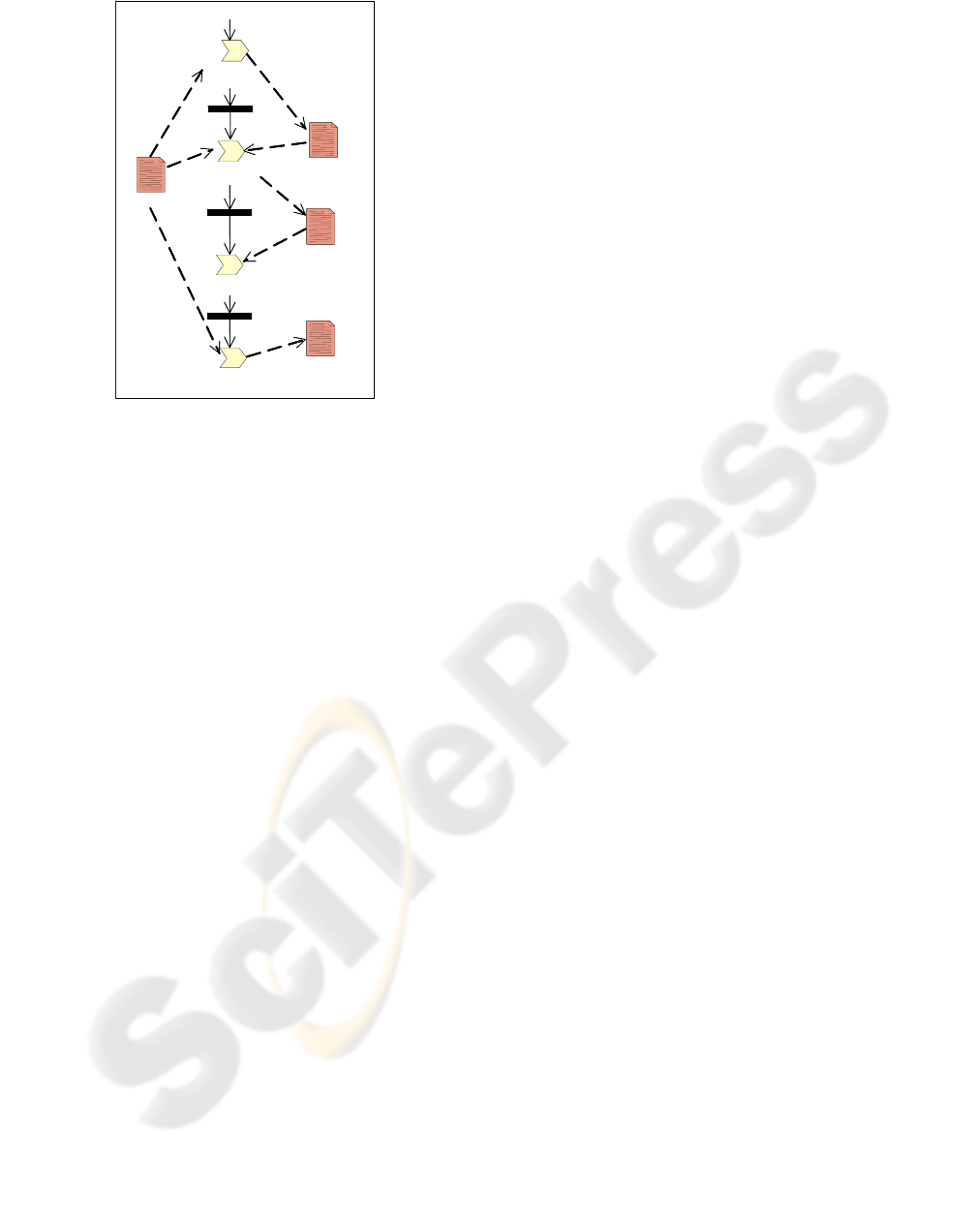
The third step was the identification of transfers
of knowledge between activities and sources. This
was done basically with two types of diagrams.
First, the transfers of knowledge between activities
were analyzed in activity diagrams as the one of
figure 4. These diagrams can illustrate the
documents generated or modified in one activity that
are used in others. This can help to get an idea about
the information that is translated in those documents.
To define explicitly the knowledge that those
documents have, we used the type of diagram that
was show in figure 2. For instance, in figure 4 can be
seen that the problem report contain information
used in different activities, as well, this project
report is used to capture the solution given to the
problem reported. Therefore, it is used as a
knowledge repository, which can transfer knowledge
between activities, between people, and in time,
since it will be possible to know in the future how a
specific problem was solved.
The transfers of knowledge between knowledge
sources were illustrated in diagrams where the
sources participating, the knowledge being
transferred, and the activity where the transfer is
taking place are showed. These diagrams are not
presented here for space limitations.
After the identification of the main knowledge
flows we started the definition of problem scenarios
to illustrate the main types of problems affecting the
knowledge flow. Particularly, the scenarios
identified illustrated problems related to two main
domains: experts finding and document
management. The main problem that these scenarios
highlighted was that, in many occasions people do
not consult sources that could be useful to them,
because they do not know about their existence, their
location or the knowledge they could have. After
analyzing the types of problems found, we started
the definition of alternative scenarios to illustrate
possible solutions to these problems. Based on these
types of alternative scenarios, a support system can
be designed, see (Rodríguez et al., 2004).
KNOWLEDGE FLOW ANALYSIS TO IDENTIFY KNOWLEDGE NEEDS FOR THE DESIGN OF KNOWLEDGE
MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS AND STRATEGIES - A Methodological Approach
495
Software Engineer
To download files to
be modified
To perform changes
To upload
modified files
To store the problem
solution into the PR
Source files
Problem report
Problem report
(with solution)
Source files
(modified)
Software Engineer
To download files to
be modified
To perform changes
To upload
modified files
To store the problem
solution into the PR
Source files
Problem report
Problem report
(with solution)
Source files
(modified)
Figure 4: Example of an activity diagram showing flows
of documents between activities.
As can be seen from the case study presented
here, the application of the methodology was useful
in different ways, which include the identification
and classification of the main knowledge sources
and types involved in the process and the main
problems affecting the knowledge flow. The
following section presents a summary of the main
contributions of the application of the methodology
in this study, and the lessons learned from doing it.
4 LESSONS LEARNED
We shall describe the five main lessons learned from
this study: two from the researchers’ perspective,
and three from the practitioners’ perspective.
4.1 Researchers’ Perspective
• Structuring a knowledge base. The
identification of knowledge sources and types,
the relationships between them, and the way
they are related with the activities and other
elements of the process, helped us defining
schemas to classify knowledge types and
sources. The schemas were used to define
taxonomies, which were the basis of an
ontology of knowledge and sources. The
ontology was used for structuring a knowledge
map for managing the knowledge base of the
process, see (Rodríguez-Elias et al., 2005a).
• Obtaining design requirements for support
systems. The identification of the problems
affecting the knowledge flow, and the
alternative solutions through the problem
scenarios, were helpful to gather design
requirements for supporting tools focused on
solving those problems. For instance, a KM
system was designed from some scenarios
observed. A prototype of this system is
described in (Rodríguez et al., 2004).
4.2 Practitioners’ Perspective
• Becoming aware of the knowledge flow
problems. The members of the group studied
have become aware of some of the problems
they face in their maintenance process. As a
consequence, they are taking actions to address
some of those problems. For instance, they have
developed a web portal where all the documents
and information of the systems being
maintained will be easily accessible.
• Improving current tools usage. The
identification of the support tools used by the
workers of the process, and the manner those
tools are being used to obtain knowledge,
contributed to start seen those tools as
knowledge flow facilitators. This was helpful to
start defining strategies for better using those
tools as part of the KM support of the process.
• Improving knowledge sharing. Through the
analysis of the models, members of the
maintenance team had became aware of sources
of knowledge they did not know previously, and
that can be used to obtain important knowledge
for their activities. Now those sources are
shared with the rest of the team.
5 CONCLUSIONS
To define successful KM initiatives, it is important
that they be aligned to the work processes of the
organization where they will be applied. To do this,
a first step is to study those processes with focus on
the knowledge involved, in order to identify the real
knowledge needs of the workers in charge of those
processes. In this paper we have presented a
methodology defined to accomplish this. The
application of the methodology was illustrated with
a case study. The study helped us to show that the
methodology helps accomplish the three main
objectives for which it was defined: the
identification of the knowledge base of the process,
the support systems involved in the knowledge flow,
and design requirements for support systems
oriented to solve the problems affecting the flow of
ICEIS 2007 - International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
496

knowledge. However, the evaluation of the
effectiveness of the solutions proposed from the
application of the methodology is a long term work
that opens possibilities for our future work, which
also include the application of the methodology to
other cases in order to continue evaluating its
benefits and limitations.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work is partially supported by CONACYT
under grant C01-40799 and the scholarship 164739
provided to the first author, in Mexico; and by
MECENAS (PBI06-0024, Junta de Comunidades de
Castilla-La Mancha, Consejería de Educación y
Ciencia), and ESFINGE (TIN2006-15175-C05-05,
Ministerio de Educación y Ciencia (Dir. Gral. de
Investigación)/ Fondos Europeos de Desarrollo
Regional (FEDER)) projects, in Spain.
REFERENCES
Abdullah, M. S., Benest, I., Evans, A., & Kimble, C.,
2002. Knowledge modelling techniques for
developing knowledge management systems. Proc.
European C. on Knowledge Management, Dublin,
Ireland, 15-25.
Bera, P., Nevo, D., & Wand, Y., 2005. Unravelling
knowledge requirements through business process
analysis. CAIS, 16, 814-830.
Carroll, J. M., & Rosson, M. B., 1992. Getting around the
task-artifact cycle: How to make claims and design by
scenario. ACM Transactions on Information Systems,
10(2), 181-212.
Checkland, P., & Scholes, J., 1999. Soft system
methodology in action: John Wiley and Sons.
Conradi, R., & Jaccheri, L., 1999. Process modelling
languages. LNCS 1500, 27-52.
Cox, K., Phalp, K. T., Bleistein, S. J., & Verner, J. M.,
2005. Deriving requirements from process models via
the problem frames approach. Information and
Software Technology, 47(5), 319-337.
Curtis, B., Kellner, M. I., & Over, J., 1992. Process
modeling. CACM, 35(4), 75-90.
Davenport, T. H., & Prusak, L., 2000. Working
knowledge: How organizations manage what they
know. Boston, Massachusetts, USA: Harvard Business
School Press.
Hansen, B. H., & Kautz, K., 2004. Knowledge mapping:
A technique for identifying knowledge flows in
software organizations. LNCS, 3281, 126-137.
Jennex, M. E., & Olfman, L., 2005. Assessing knowledge
management success. Intl. J. of Knowledge
Management, 1(2), 33-49.
Maier, R., & Remus, U., 2002. Defining process-oriented
knowledge management strategies. Knowledge and
Process Management, 9(2), 103-118.
Monk, A., & Howard, S., 1998. The rich picture: A tool
for reasoning about work context. Interactions, 5(2),
21-30.
Nissen, M. E., 2002. An extended model of knowledge-
flow dynamics. Communications of the Association
for Information Systems, 8, 251-266.
O'Leary, D. E., 1998. Using ai in knowledge management:
Knowledge bases and ontologies. IEEE Intelligent
Systems, 13(3), 34-39.
OMG, 2002. Software process engineering metamodel
specification (SPEM), last access October 2004 from
http://www.omg.org/technology/documents/formal/sp
em.htm
Papavassiliou, G., & Mentzas, G., 2003. Knowledge
modelling in weakly-structured business processes.
Journal of Knowledge Management, 7(2), 18-33.
Rao, M. (Ed.)., 2005. Knowledge management tools and
techniques: Practitioners and experts evaluate km
solutions. Amsterdam: Elsevier.
Rodríguez, O. M., Martínez, A. I., Favela, J., Vizcaíno, A.,
& Piattini, M., 2004. Understanding and supporting
knowledge flows in a community of software
developers. LNCS, 3198, 52-66.
Rodríguez-Elias, O. M., Martínez-García, A. I., Vizcaíno,
A., Favela, J., & Piattini, M., 2005a. Constructing a
knowledge map for a software maintenance
organization. Proc. of Poster Session of the 21st
ICSM, Budapest, Hungary, 51-54.
Rodríguez-Elias, O. M., Martínez-García, A. I., Vizcaíno,
A., Favela, J., & Piattini, M., 2005b. Identifying
knowledge flows in communities of practice. In E.
Coakes & S. A. Clarke (Eds.), Encyclopedia of
communities of practice in information and knowledge
management. Hershey, PA, USA: Idea Group Inc., pp.
210-217.
Rodríguez-Elias, O. M., Martínez-García, A. I., Vizcaíno,
A., Favela, J., & Piattini, M., 2007. Organización de
conocimientos en procesos de ingeniería de software
por medio de modelado de procesos: Una adaptación
de SPEM. Proc. of the JIISIC'07, Lima, Perú, 257-265.
Stewart, T. A., 2002. The case against knowledge
management. Business 2.0, 3(February), 80.
Strohmaier, M., & Tochtermann, K., 2005. B-kide: A
framework and a tool for business process-oriented
knowledge infrastructure development. Journal of
Knowledge and Process Management, 12(3), 171-189.
Wiig, K., 2004. People-focused knowledge management:
How effective decision making leads to corporate
success. Amsterdam: Elsevier.
Woitsch, R., & Karagiannis, D., 2002. Process-oriented
knowledge management systems based on km-
services: The promote approach. Intl. J. of Intelligent
Systems in Accounting, Finance & Management, 11,
253-267
KNOWLEDGE FLOW ANALYSIS TO IDENTIFY KNOWLEDGE NEEDS FOR THE DESIGN OF KNOWLEDGE
MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS AND STRATEGIES - A Methodological Approach
497
