
Does the “Local Universe” Impact on Representations,
Levels of Utilisation of an HR Intranet by the Middle
Management User
Karine Guiderdoni – Jourdain
The Institute of Labour Economics and Industrial Sociology (LEST)
35 Avenue Jules Ferry - 13626 Aix en Provence cedex, France
Abstract. The e-HR dynamic implies the development and the integration of an
HR intranet in order to achieve a better distribution of messages and to optimise
the HR services delivered to HR clients, especially to the middle management.
This kind of ICT investment is very expensive. The question about its benefits
is quickly asked by the Board Management. That is why the assessment of the
HR intranet through middle management’s positions and uses is necessary. We
present in this paper the case of a HR department of a major Aeronautical and
Space company, which has developped an HR intranet. From 53 interviews of
middle managers, a typology of actors emerges : the “super technician”, the
“assembly line boss”, the “industrial artisan”, the “free electron” and the
“hybrid”. Each of them got specific position and use of this tool. This confirms
our hypothesis on the effect of what we call the local universe on practices of
the HR intranet tool.
1 Introduction
In response to a more competitive environment and stronger requirements from the
customers and the shareholders in terms of profitability, reduction of the structural
costs, the Human Resources Department has to convince the Board of Management of
its capacities of innovation, adaptability and flexibility. According to literature the e-
HR, is a global functioning mode of a company around a significant number of HR
processes which leads to the sharing of HR information and its treatment by direct
and free access of the employees, the Management and the HR function and to the
setting-up of a new HR organisation in order to optimise the customer relationship.
Achieving a better distribution of messages and optimising the HR service are the first
objectives. The middle management is one of the privileged customers to satisfy,
because its own role within the company also changes. The improvement of HR
communication is generally accompanied by the development and the integration of
an HR intranet, considered as a technical support with which the required
performances can be obtained.
This kind of HR strategy involves strong investments. So, the question of relevance
and the efficacy of this on-line service according to the expected goals is quickly
asked by the Board of Management.
Guiderdoni – Jourdain K. (2007).
Does the “Local Universe” Impact on Representations, Levels of Utilisation of an HR Intranet by the Middle Management User.
In Proceedings of the 1st International Workshop on Human Resource Information Systems, pages 120-129
DOI: 10.5220/0002415001200129
Copyright
c
SciTePress

Enrolling in these preoccupations, the Human Resources direction of a major
Aeronautical and Space company, which we shall name Aero, asks us to realize a first
survey about the perception and the use of the HR intranet, in order to evaluate
perceptions and uses of the middle management.
Our communication will articulate in two parts. Firstly, we will briefly present
literature about the link between e-HR concept and the development of HR intranet
tools. After explaining our research question and our model of analysis, we will
present and describe results of our investigation.
2 A Research in Progress
The evolution of the HR function has been announced in specialised magazines since
the end of the 1990s. Some researchers have made aware HR professionals of their
difficult position in the company and of the necessity to transform the function [14].
Thus, the HR department must show its added business value. To do so, certain
guidelines must be followed: become more service-oriented, more focused on its
clients, being aware of HR commitment and contribution towards the company
performance [8,14,15]. In this context, the support of Information Communication
Technology (ICT) is considered to be essential – which leads us to the e-HR dynamic.
2.1 The e-HR Dynamic Supported by the Development and the Integration of
a HR Intranet as a Basic Element of a New Model of Functioning
Regarding the definition of e-HR, we have been influenced by the thinking of Huub
Rüel and his colleagues. According to them, the e-component is not only the symbol
of a technical advance, but the imprint of a deeper transformation of the HR position
within the company: a new “way of thinking about interaction, service-provision, and
communication” in order to “redefine HR profession” [13].
The use of ICT would have an impact on the management of the HR process and
would transform the relation between the HR department and its environment. A
model of functioning based on e-HR stands for the access to and a treatment of the
HR information by all actors of the company, not only the HR staff. That is the
difference between the definition of ISHR and e-HRM [13]. Thus, this system would
provide employees with the responsibility to manage their own personal data and their
own professional development, whereas the manager, without an intermediary, would
completely intervene in the HR process. [3,4,7,13]. That is the aggregation of new
actors in the HR area.
In the literature, the HR intranet is presented at the same time as a tool for supporting
the middle management and for improving HR performance [10]. The main question
is to know why these two actors would accept to change or not in connection with the
development of an HR intranet.
For an HR actor, anxious to show his added value to the business, the intranet tool can
become a material support on which a number of new HR applications can be found.
These services would provide the HR function with the opportunity to change.
121

For the middle management, things are different because it is considered a key actor
of the company’s transformations. Its position is between the Board of Management
and the staff, and it is this position, which makes it to manage concretely evolutions
of identities, of professions and larger work transformations. It means that the middle
management "becomes the initiator and the founder" of ICT [6]. This is why HR
consider him as their first customer to satisfy.
According to this vision, the accessibility of new HR services would give the
opportunity to the middle management to explore new forms of organisation and to
become more independent [3,6].
To explain the link between the e-HR dynamic and the development of HR intranet ,
we refer to the two work. In their article, French researchers, Laval, Guilloux and [6]
explain the Intranet potentialities as the main instrument for the HR department to
improve its performance. They present six applications
1
in relation with three stages
of HR intranet development. The first stage corresponds to the “Intranet
Corporate”, which is mainly focused on internal communications, with a special site
for HR information (HR processes, legal elements). It is dedicated to all employees of
the company. The second stage is called “Intranet RH Généraliste”
2
, of which the
originality is e-administration. Using the workflow technology, HR offers to
employees some on-line automated administrative services (leaves, bills, certificates
…). Others sections are: more information about mobility management; an access to
training services; specific applications to support new forms of network organisation.
This intranet is currently managed by the HR function. Such on-line administrative
services lead the HR intranet manager to create specific interfaces for each actor
(employees, managers, HR staff, and the Board of Management). It corresponds to an
HR Self-Service approach. The “Intranet Spécialisé”
3
is the most accomplished
stage. Containing the previous level, it has been further enriched by new applications:
e-learning, e-competence and knowledge management. We are in a transversal
dynamics, of which one of the main objectives is to capitalise the company’s
knowledge.
Usually, the main authors who try to give a definition of e-HR concept conclude to
three important impacts of ICT on HR Management [8,7,13,15,6]. The first one is an
operational impact with the development of ISHR. It concerns the basic HR activities
in the administrative area (new data base ; payroll ; personnel data administration…).
The second impact is relational. It concerns more advanced HRM activities. It is on
line HR tools, that support basic business processes (recruiting, training, performance,
management and appraisal, rewards). The last impact is transformational with the
concept of virtual HR function. It concerns activities with strategic character such as
organisational change processes, strategic re-orientation, strategic competence
management and strategic knowledge management [13].
Beyond the abstract and normative models, the concrete example of these HR
transformations is scarce in the academic literature. That leads us to take into account
three approachs at the same time : technical approach (evolution of the tool) ;
1
Six applications : HR information, e-administrative ; e-mobilité ; e-recruitment ; e-learning ;
e-competence and applications for knowledge management
2
Non-specialised HR Intranet.
3
Specialised Intranet.
122
strategical and organizational approach (Board Management’ s expectations;
evolution of means and structure…) and individual approach (the stakes perceived by
of the different actors in using the on line tools).
2.2 Research Question
One of fundamental research questions that our Phd work aims at answering is to
understand why in a specific population as the middle management of a big company,
differencies of representations, utilisations and expectations of a general HR intranet
can be noticed. The question of the relevance of a HR strategy based on e-HR
dynamics is implicitly asked. Our main assumption on this point is that the
differencies of representations, utilisations and expectations of a HR intranet can be
explained by the concept of “local universe”.
We are located in a theoretical framework where the limited rationality of agents [9]
implies the taking into account of the universe that characterizes them, notably from
the professional and organizational measurements [1].
To summarize this idea, we use the local universe concept, associating professional
dimension and organizational structure.
The professional dimension notion sends back to the individual professional
capacities, but also to policies of the actor’s department. According to the nature of
his activity, his objectives…the individual is not going to use the technological tool in
the same way.
The organizational structure notion sends back to reports between the different
agents, to the hierarchical relations. We will use here categories proposed by [11].
We add that this “power of user” [12] could be different according to the local
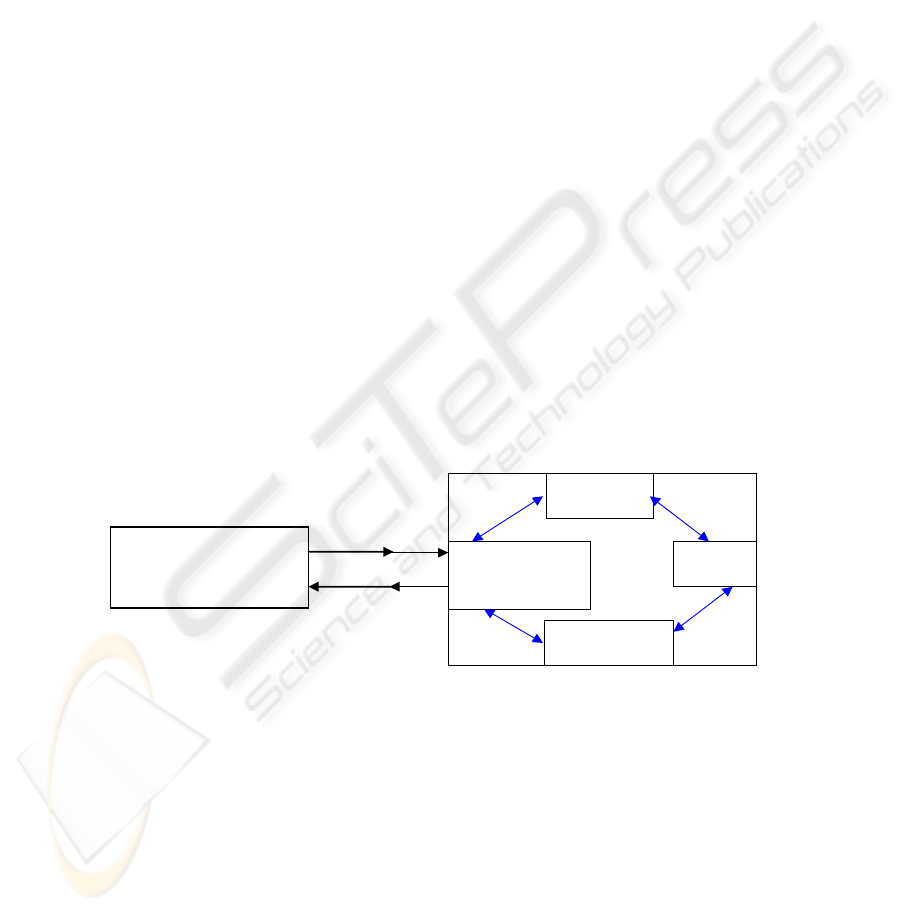
universe in which the user is. In the diagram below, we try to summarize our ideas.
Fig 1. Dynamics between Users and Conceptors.
We start our research by leading a survey in order to a better understanding of the
users of the HR intranet. In order to define a typology of users, we have been
influenced by the work of Iribarne &Tchobanian in a big french company France [2].
Authors propose a typology of users : the reticent; the utilitarian; the innovator; the
strategist. We have added to this typology the neutral user.
Local universe of the user
-activity
-organisation of his sector
- hierarchy influence…
Level of demand vis à vis
technology’evolution
Position and
level of use
Representations
of the technology
Dynamics of HR intranet
development
HR Intranet
123
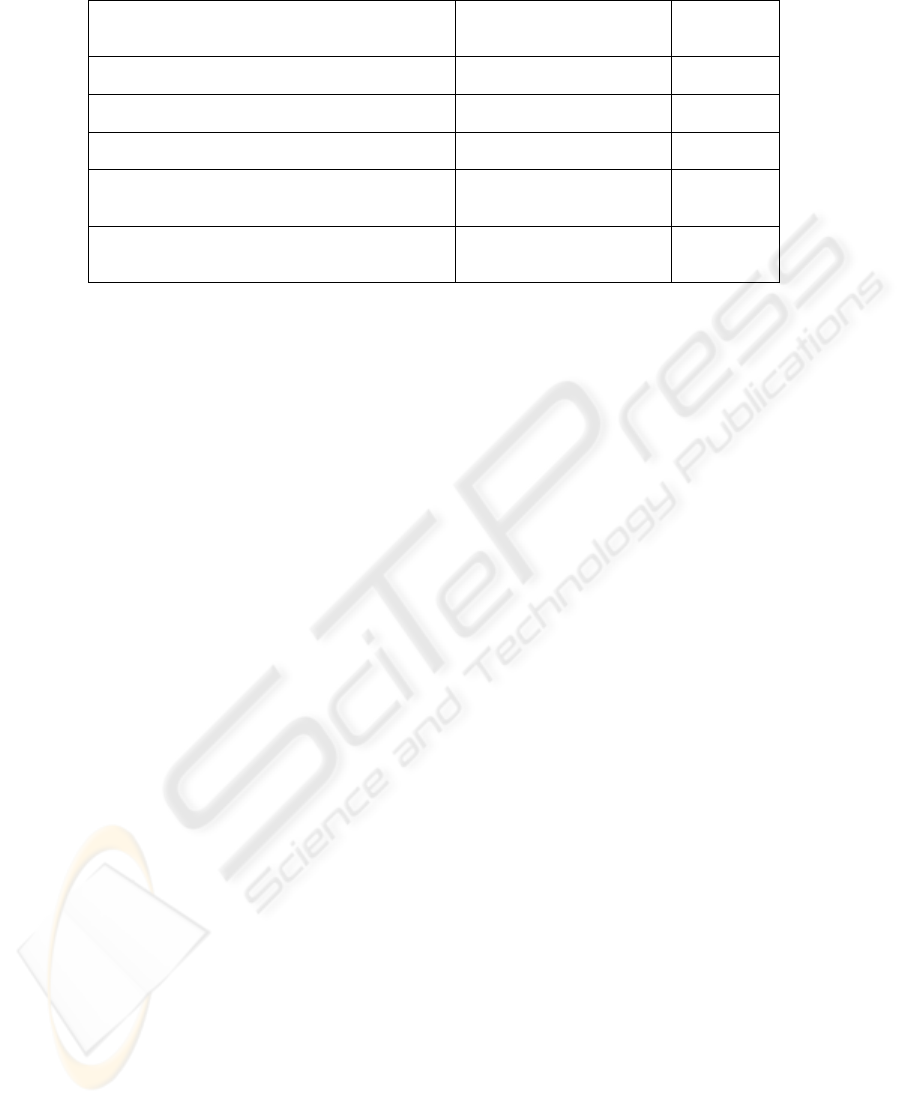
Type of middle management speech in relation to
HR tools
Level of use of HR tools Type of
manager
position
“I’m afraid of losing some part of my work and a
dehumanization of social relations”.
Rare or no use Reticent
“the tool seems interesting. But it doesn’t take really
part of my working environment”.
Punctual use Neutral
“the tool is functional and useful. However, I’m not
satisfied, I expect something better from the system”
Regular use Utilitarian
“the tool contributes to ameliorate my work and makes
me find new solutions and feel more committed and
self-sufficient”.
Daily use Innovator
“the tool contributes to give me the opportunity to
work differently in a more efficient way and in the
same time to serve my own interests”.
Permanent use Strategist
Fig 2. Adaptation of the typology of ICT user of [2].
3 Survey Results
We spent four years within the Human Resources direction of a major Aeronautical
and Space company, which we shall name Aero. We made a longitudinal and
qualitative research [5]. In order to provide the data necessary to measure perceptions
and uses of the HR tools, formal interviews were conducted with middle managers.
We conducted two waves of interviews (in 2002 and 2005). This population
represents more than 1,000 persons. We distinguish three groups : managers of a
department or similar position (level 1), managers of sub-department (level 2), and
team’s managers (level 3). The results of the first wave of interviews will be
presented in the next session. In 2002, a total of 53 semi-structured interviews were
conducted in 13 departments, grouped into four areas of activity: research/design,
production, sales/ marketing and managerial/administrative.
3.1 Individuals Engaged in Research/design Activities : The “Super
Technicians”
A Fairly Limited Representation of the Tool and its Usefulness: Information
Content not Related to Their Needs. Firstly, all these individuals are engaged in
research or design activities. The very nature of their work means they work either
alone on projects or in teams on joint projects. Most of the individuals interviewed are
graduates of engineering schools and pursue their specialities within the engineering
and design department. They are accustomed to using a number of technological tools
in the course of their work, the complexity of which is far greater than that of an HR
intranet (e.g. 3D design software). Thus it might be thought at first blush that this
highly technically qualified population, which obviously attaches great importance to
technology, would find no difficulty in using a tool like the HR intranet.
However, it would seem that, contrary to this received idea, they actually make
limited use of this tool. Over and above simple use of the HR intranet, we found that
they were sufficiently familiar with the ‘Employees’ Space’ to visit it regularly (once
124

a month). They were acquainted with its broad outlines but not with the details of the
various menu items. This explains why the majority position vis-à-vis the tool is
utilitarian, with a ‘reluctant’ minority.
The Type of Organisation Induces these Managers to Seek Out Specific HR
Information. We are dealing here with an organisation of the ‘professional
bureaucracy’ type, in [11]. Much of the coordination is handled by those engaged in
research and design. The hierarchical relationship remains strong (mechanistic). The
decentralised organisational structures mean individual workers have greater
autonomy, which in some cases is experienced as relative isolation within the R&D
department and, more widely, within the company as a whole (they criticise the lack
of general information on the company’s major projects and orders and on its strategic
focus…).
This structural isolation is compounded by the vagaries of top-down information
flows. Most of the managers interviewed took the view that the flow of information
was generally haphazard and dependent on the goodwill of superiors. This general
feeling was reinforced by the specific case of HR information: at the time of the
survey at least, the HR department’s image could be summarised in a single word –
opacity. So much so, indeed, that most of the managers said they found themselves in
an awkward position when their juniors raised questions after receiving information
from their trade unions. At the time of the survey, none of the information to be found
in the ‘Employees’ Space’ was sufficiently detailed to provide answers to topical HR
questions on salaries, careers, the award of bonuses or promotions.
These managers felt they were not in a priority position when it came to the
distribution of HR information. The ‘Employees’ Space’ did not provide them with
targeted management information that might help them to carry out their duties. All
this merely served to reduce the perceived usefulness of this ‘Employees’ Space’ and
explains why this population made limited use of it. Most of the individuals using this
intranet site did so in their capacity as employees and not as managers.
Conditions of Access and Initial Strategy for Introducing the Tool. These
explanations linked to the tool’s informational content can be supplemented by
strictly technical considerations, such as the conditions of access and initial
introduction strategy. In order to access the ‘Employees’ Space’, at least two
conditions must be met.
The first is to have a network account (login and password). All employees whose
work involves the use of a computer have such an account. All the managers in this
population meet this condition. Having their own or even a shared computer gives
individuals an opportunity to access the company’s general intranet. They also have to
be able to navigate the intranet from the start page and access the ‘Employees’
Space’. Once on this site, they still have to be able to find what they are looking for.
Consequently, the second condition for access lies in the ability of individuals to use
these internet/intranet tools. The designers of the intranet talk of a simplified
architecture that allows intuitive navigation. However, the survey results seem to
contradict them.
This last point raises the question of the type of training provided by the company
when the general intranet was being set up. It is clear that there was no systematic
125

training programme providing instruction in the use of this new tool. Managers said
they had learnt on the job or from informal contacts within the company.
The “Super Technicians” and their Strategy Vis à Vis the HR Intranet. This
particular population of managers engaged in research and design activities can be
described as ‘super technicians’. With just a few exceptions, these managers all
follow the same career trajectory: whether they end up as heads of department or
directors of research, they all enter the company as graduate engineers. After five to
ten years’ service, having proved their technical competence and displayed some
aptitude for management, they are entrusted with a management function. However,
management forms no part of their basic training. The time they devote to their jobs
as technical experts is gradually eroded by their new functions as coordinators, which
require them to operate in both the bureaucratic and social spheres. In this context,
managers receive information from a multiplicity of different sources (e-mails,
newspapers, intranet sites etc.). This proliferation of information, which they have to
sift and diffuse themselves, gradually leads them to become weary of and lose interest
in these tools, which ultimately they regard as useless and a waste of time. When
these ‘super technicians’ are asked what they expect of the HR intranet, it is hardly
surprising that they demand HR information targeted specifically at management that
would enable them to answer frequently asked questions both about HR procedures
(how to proceed in such and such a case) and about more general and strategic issues
within the company. What they want is information that would enable them to
develop a discourse shared by all managers and create an aid for all managerial staff
within the company.
3.2 Production Managers: “Assembly Line Bosses or Industrial Artisans”
We now enter the world of production, and more specifically that of the industrial
workshop and assembly line.
A Limited Representation of the Tool and Its Usefulness: Tool Itself Far
Removed from their Daily Concerns. Like the previous category of managers,
attachment to the product is very strong, since they are involved in its physical
production. The employees they supervise are primarily skilled manual workers, and
their hierarchies often have their roots in the world of the craft worker. Simply by
virtue of carrying on their trades, these workers have an esprit de corps and a sense of
solidarity that does not exist elsewhere. To return to the use of the HR intranet, the
survey results are very revealing: the level of use is very low, non-existent even.
Views as to the intranet’s usefulness are not very positive (“Waste of time, I can get
the information elsewhere/no instinct for the intranet, paper culture”). The dominant
position vis-à-vis the tool is ‘neutral’, with a ‘reluctant’ minority. The first
explanation for these results is that the HR intranet tool, like the company’s intranet
as a whole, is a virtually alien tool in this world. Some are reluctant users, but the
majority are indifferent.
Quite a number of individuals in this population use these technologies in their private
lives, which means they are not immediately repulsed by the tool.
126

Organisational Type and Working Conditions Encourage Contact with Local
HR Units. Pressure and the pace of work mean that managers needing to find answers
to HR questions prefer to contact the local HR units in workshops and assembly lines,
either in person or by telephone. This quick and easy method of contact meets their
needs. Since the trade unions have greater influence in this world, these shop floor
managers also maintain regular contacts with trade union representatives, who
generally receive HR information before them. This state of affairs is deplored by
these managers who, like the previous group, feel it places them in an awkward
position, but they simply have to put up with it.
In addition, there is the question of the conditions of access to the tool. Without going
back over what has already been said above, there is one feature unique to these
production activities. We interviewed managers on three levels of the management
hierarchy. Those on the bottom level (3) have the title ‘team leader’ (or foreman);
most of them are not classified as managers but they do have managerial functions.
Some share an office and a computer, others do not. This constitutes a de facto
constraint on access to the tool. In order to overcome this difficulty, interactive
terminals are currently being installed in the workshops.
Two Types of Actor: The “Assembly Line Boss” and the “Industrial Artisan”.
The first type of actor is the ‘assembly line boss’. Managers in this category are on
level 1 or 2 of the hierarchy and are responsible for more than 200 people on average.
They generally reach their position as a result of internal promotion. They are above
all men of action, with considerable charisma, who are more at ease on the shop floor
than behind a computer. Moreover, computers (the bureaucratic aspect) are associated
with secretarial occupations. This type of actor tends to be reluctant to use the tool,
since they perceive it as an additional tool that will take up a considerable amount of
their time and will offer little in the way of value added.
We use the term ‘industrial artisan’ to denote the second type of actor. Most of this
group are managers on level 2 and, particularly level 3 of the hierarchy. These
individuals are also leaders. Those on level 2 are responsible for 100 people on
average, including 5 to 6 team leaders (or foremen). These latter are in charge of
smaller teams (30 skilled workers). The type of organisation favoured in the work
shops and on the assembly lines is the ‘divisional structure’. Further down the
hierarchy, however, the type of organisation fluctuates between ‘mechanical
bureaucracy’ and the ‘simple structure’. In formal terms, team leaders (level 3) are
part of a large division, but in their daily work they enjoy some room for manoeuvre
(provided they meet their targets). In fact, some behave like small company directors,
hence the designation ‘industrial artisan’.
When these managers were asked about their expectations of the HR intranet, they all
found it difficult to formulate a response. This was because they did not use it. What
they wanted, rather, was direct communication between individuals, with a summary
of the discussions being made available on the HR intranet.
127

3.3 Individuals Engaged in Sales/Marketing Activities: The “Free Electron”
We will not linger long over this type of actor, since the survey results place this
category in the leading position when it comes to use of and position vis-à-vis the HR
intranet tool (mostly ‘utilitarian’, with an ‘innovative’ minority).
With this population, we enter a new reference world, that of the salesman. The very
nature of their activity gives these level 1 and 2 managers a high degree of autonomy.
The are in charge of small teams. Of course they have targets to meet, but this is not
done on the same terms as in the production department. They have permanent access
to the tool, since they use their computers more or less continuously. Many use the
Internet to keep up to date with the activities of competitors or of customers, which is
why we use the term ‘Free Electron’ to describe them. As far as the ‘Employees’
Space’ is concerned, they use it regularly but expect much more of the HR department
(more concrete HR information on salaries and management tools enabling them to
save time). The notion of targeted management information articulated by the ‘super
technicians’ is also echoed by this group.
3.4 Individuals Engaged in Managerial and Administrative Activities : The
“Hybrid”, The Difficulty of Identifying a Typical Actor
We had difficulty in finding a common designation for these individuals. This is in
fact more of a hybrid category, in the sense that these individuals are close to the ‘free
electron’ in some respects, such as their use of the HR intranet (except that, when it
comes to their views on the HR department and their type of expectations, a minority
of them adopted the ‘neutral position). Their working conditions and access to the HR
tools are similar in many regards to those of the previous category (cf. table). In sum,
there are within the middle management population a number of different approaches
to use of the HR intranet, even though most of the expectations that were expressed
were homogeneous and the majority positioning was utilitarian. Nevertheless, there
are sectors and types of actors that are below what, in our view, is the minimum
threshold for use of the tool. Consequently, what types of recommendations should
we make to the parties commissioning the survey? Should we recommend a universal
response or should a number of different responses be formulated depending on the
actors identified?
4 Conclusion
The first results of our survey drive us to think that the profit expected by HR
conceptors around the performance of the HR Intranet on middle managers's practices
are not so obvious. That means that the rationalizing logical of the tool meets different
local universes, driving to practices and uses of the intranet in an unexpected way.
Middle management was making moderate use of the HR intranet at the time of the
survey in 2002. Our main result is the emergence of five typical actors : « super
technicians » ; « assembly line bosses » ; « industrial artisans » ; « free electron » ;
« hybrid ». Which of them has specific links with the HR intranet.
128

In general terms, those survey results confirm the hypotheses that the nature of
managers’ activities and organisational structure had an effect on representations,
levels of utilisations and expectations of an HR intranet. Our next question that we
need to answer is : could the local universe concept be a strong element to re-
interrogate the Orlikowky Structurationist Theory through a new way of
understanding links between ICT and Work ?
References
1. Beret, P. : Coordination et engagement des agents dans une démarche qualité : la
construction des apprentissages. Travail et Emploi 90, (2002) 99-112.
2. Iribarne, A. (d’) & Tchobanian, R. : ‘Technologies multimédia en réseaux et dynamiques
des activités professionnelles : le cas de France Télécom (Multimedia technology in
networks and the dynamics of professional activities : a case study). Formation-emploi, 82,
(2003) 91-105.
3. Kalika, M. : e-RH : réalités managériales, Editions Vuilbert Collection Recherche (2005)
4. Karakanian, M (2000), Are Human Resources departments ready for e-HR ? Information
Systems Management, 17 (4), (2000) 35-39.
5. King, G. & Keohane, R. & Verba, S.: Designing Social Inquiry. Princeton, Princeton
University Press (1994)
6. Laval, F. & Guilloux, V. & Kalika, M. : Les Intranets RH : pratiques des entreprises et
problématiques. In e-GRH : Révolution ou Evolution ? Relever le défi de l’intégration des
TIC dans la fonction Ressources Humaines, Kalika, M. Editions Liaisons (2002) 63-90.
7. Lengnick-Hall, M.L & Moritz, S. The impact of e-HR on the human Resource Management
Function. The Journal of labor research, 24 (3), (2003) 365-379.
8. Lepark, D.P & Snell S.A : Virtual HR : strategic human resource management in the 21
st
century. Human Resource Management Review, 8 (3), (1998) 215-234.
9. March, J. G & Simon Herbert : Organizations, New york, John Wiley &Sons (1958)
10. Messeghem, K. & Pierson, F. : Intranet et rôle de l’encadrement intermédiaire.
Proceedings of the second Journée d’étude “ GRH et TIC ”, Université Paris-Dauphine,
(2003)
11. Mintzberg, H : Structure in five, Prentice Hall (1983)
12. Orlikowsky, W. J. Using technology and Constituting Structures : A Practice Lens for
Studying Technology in Organizations. Organization Science, 11 (4), (2000) 404-428
13. Rüel, H. & Bondarouk T. & Looise J.K : E-HRM : innovation or irritation ? An exploration
of web-based human resource management in large companies, Lemma Publishers, Utrecht
(2004)
14. Ulrich D : Human Resource Champions, Harvard Business School Press, Boston (1997)
15. Wright, P. : Introduction : strategic human resource management research in the 21
st
century. Human Resource Management Review, 8 (3), (1998) 187-191
129
