
A DRM Architecture for
Securing User Privacy by Design
?
Daniel Kadenbach, Carsten Kleiner and Lukas Grittner
Department of Computer Science, University of Applied Sciences and Arts Hannover, Germany
Abstract. Privacy considerations are one serious point against current DRM sys-
tems, because they would allow the License-Issuers to collect large amounts of
user data, up to the the time a user listens to a song or which users are read-
ing which kind of books. This sort of data could be used for marketing purposes
but also for malicious deeds. This paper addresses this threat and establishes a
DRM architecture which protects user privacy by the core of its design by adding
a third trusted party and an appropriate communication protocol. The work was
influenced by a project in mobile DRM b ased on the OMA specification [1].
1 Introduction
Privacy is a fundamental right in a free society, therefore its protection should be an
integral part of every new technology which could be used to harm it.
Digital Rights Management (DRM), or Digital Restrictions Management as referred
to by its critics [2], covers technologies for enforcing access and usage rules on digi-
tal content by encrypting the content objects and the use of licenses which contain the
decryption-key and usage-rules. In times of global connectivity even with mobile de-
vices DRM systems implemented without an eye upon protecting user privacy by fun-
damental design aspects can easily harm personal information rights of the customer or
even be used to facilitate user surveillance.
A typical DRM architecture can be seen in Figure 1. The content provider pack-
ages content objects from its databases and encrypts them before offering them to the
customer through a specified interface. The customer can download the content and
acquire a license from the License-Issuer with the help of the local DRM client. The
license includes the necessary key to decrypt the content along with usage rules which
are enforced by the DRM client.
Because the content has to be decrypted on the client-side one can actually see that
this sort of system can in the end only seriously be secured against local attacks if the
DRM software is secured by means of hardware, which could be solved by the use
of trusted computing (see [3] and [4] for more information about trusted computing
concerning DRM).
?
This project has been funded by the Lower Saxony Ministry for Science and Culture under
grant no AGIP FA 2005.692.
Kadenbach D., Kleiner C. and Grittner L. (2007).
A DRM Architecture for Securing User Privacy by Design.
In Proceedings of the 5th International Workshop on Security in Information Systems, pages 188-195
DOI: 10.5220/0002422301880195
Copyright
c
SciTePress
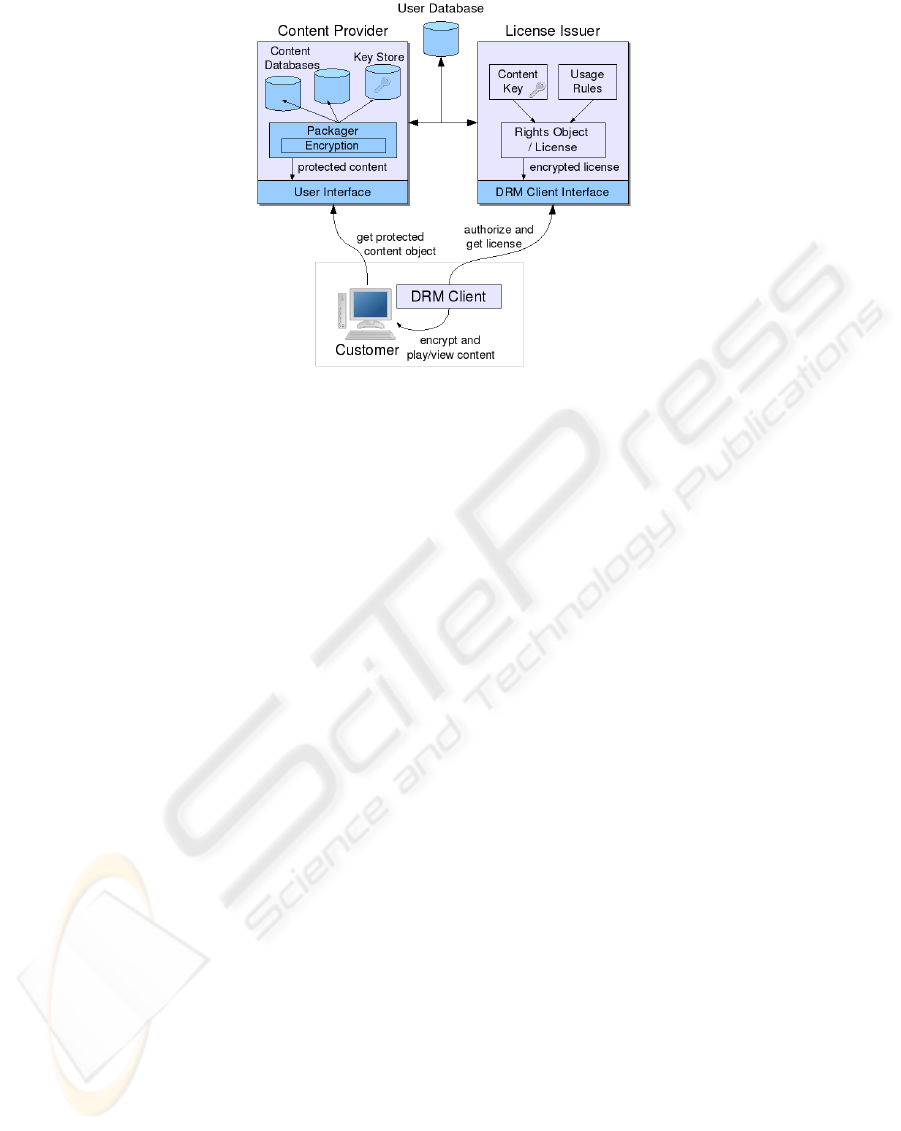
Fig. 1. Typical DRM Scenario.
In the case of DRM privacy may be harmed because the License-Issuer in recent im-
plementations is e.g. able to obtain detailed personalized usage profiles. But privacy is
not incompatible with this new technology [5]. In this paper we want to draft a possible
architectural solution which protects user privacy in a DRM system by design, so that
buying a song on the internet would be like buying a CD in a shop by cash again as far
as privacy protection is concerned. After all the shopkeeper should only be interested in
being paid, and no customer would want to leave his/her address and bank data at every
shop or even inform the shopkeeper every time before consuming the product. Also it
should not be possible for the vendor to create named purchase statistics without the
explicit affirmation of the consumer.
In the following we want to draft an architecture which not only secures user privacy
and thus enhances the chance of user acceptance for DRM but which also has additional
benefits for the other involved participants. In particular we will shortly investigate
current DRM systems and their handling of user privacy in section 2. After that we will
establish concrete requirements for a DRM architecture which protects user privacy in
section 3 and discuss our solution to it in section 4. Closing we will discuss the pros
and cons of the drafted architecture.
2 Current DRM Systems and User Privacy
In one of the leading DRM specifications for mobile devices used currently, the OMA
DRM v2.0 specification, it is exclusively stated that privacy aspects are not covered and
had to be investigated and integrated further by its implementers [1]. This seems to be
a serious shortfall, because especially in the privacy field an open specification which
protects user rights could do a lot to let users feel more comfortable.
In a survey on behalf of the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research
different DRM systems were examined concerning their privacy protection and user
friendliness [6] among them were iTunes, Musicload with Microsoft Windows Media
Rights Manager, Sony DRM and Adobe Digital Media Store.
189

The survey revealed that nearly none of the systems offered an anonymous rights
acquisition, that most of the time customers had to reveal personal information which
was not necessary for the transaction, and that the systems stealthy gathered additional
information without notifying the user. In purchased iTunes-files there were even un-
encrypted personal details of the customer; the other systems encrypted additional data
in the files, so it could not be analysed further if they compromise user privacy. The
conclusion of the survey is that the examined DRM systems are unhandy, intransparent,
even threateningly and isolate users because they are not interoperable.
In [7] it is exclusively stated that transparency for personal data is recommended for
a better practice and thus for a greater user acceptance.
For other work in this field see Michiels et al [8] for a view into the design of DRM
architectures, Arnab and Hutchison [9] which examine how to improve the fairness to
the end user of DRM systems, Cohen [5] which examines aspects concerning the law
and user privacy in DRM systems or [10] for a position paper of the W3C on privacy
and DRM.
3 Requirements for a Privacy-Protected DRM System
From the preceding considerations the following requirements can be deduced for a
privacy protected DRM environment:
o The user should only enter as little information as is absolutely necessary to conduct
the requested services.
o Information shall only be given to parties which can be trusted by the user. Ideally
user information should only be kept at one central place entrusted in the care of a
respectable institution.
o It should be well-known to the user which data is send over the network.
o The decision if the vendors can survey purchase statistics per user should be in the
control of the user.
o Data should always be send encrypted in a way so that only the designated recipient
can decrypt it.
o The system should be designed and implemented in an open manner, so that its
privacy protection can be proven and trusted.
4 Architectural Draft
To secure user privacy we have to introduce a third trusted party in the content and rights
acquisition scheme of the DRM scenario. This party is some sort of financial institution
which offers services for the user and the DRM provider and is trusted by both of them.
The new architecture can be seen in Figure 2 and is described in detail below.
4.1 Communication between Customer and License-issuer
The first message which is sent in the whole scenario is issued by the Customer and
directed at the License-Issuer to get the possibly different licenses related to a speci-
fied content object (as seen in Figure 3). The content acquisition itself is not part of
190

Fig. 2. Overview of the Architectural Draft.
the process because it can be done in arbitrary ways like direct download from the
Content-Provider or super-distribution through a peer-to-peer network, which is possi-
ble because the content objects are encrypted.
The ContentID and the URL of the License-Issuer which is needed to address this
message correctly can be read out from the content object. The ContentID in this mes-
sage specifies a content object in a unique way for which the License-Issuer offers
corresponding licenses.
Fig. 3. Consumer Message to Acquire a License-List.
As a response to this request, the License-Issuer sends its certificate to authenticate
itself and an asymmetrically encrypted list of the available licenses seen in Figure 4.
The contained descriptions should be human readable.
Fig. 4. License-List Response from License-Issuer.
The concrete implementation of this message exchange can be chosen conforming
with given requirements. Preferably it shall be implemented with Web Services, because
of their standardized security extensions and because their design fits very well into this
191

kind of service oriented architecture, but it could also be implemented using standard
HTTP(S)-technology to ease operating system integration.
4.2 Communication between Customer and Bank
To ensure the anonymity of the customer to other persons who might intercept the com-
munication there is a need to encrypt the data which is sent. Furthermore the customer
has to authenticate herself to the bank and the other way round. This is essential because
the bank must determine the identity of the customer for choosing the right account
which should be charged. Moreover the customer wants to know if she really commu-
nicates to the real bank-server. If she was not doing so she could expose private data. A
widely accepted solution for such needs is a PKI (Public Key Infrastructure). For more
information on PKIs see [11].
The bank has to administrate its own Certification Authority and give out a certifi-
cate for each of its online users. The certificate could be used both for authentication
and for encryption. The key-pair for a customer should be generated on the customers
computer and her private key must not be known by the bank. Otherwise the user would
not be secured against being spoofed by the bank.
However, even if every part of the certificate would be generated from the bank this
would still not be worse than the current situation where customers are trusting their
financial institutions. But it would not make use of the full potential of the described
architecture.
Customer and Bank have to exchange two messages. The first one, the License-
Request Initiation message (seen in Figure 5) is sent from the customer to the bank
as an order to start a license acquisition process. The message contains an encrypted
session key, which is encrypted with the public key of the License-Issuer so that it can
only be decrypted with the corresponding private key by the Issuer. With this session
key the Issuer afterwards encrypts the license object which is returned, so that only
the customer is able to decrypt it. Additionally the License-Request Initiation message
contains one license option from an afore acquired list, which the customer wants to
buy. To this license option a current time stamp is attached and then signed by the
customer.
Fig. 5. License-Request Initiation Message.
This signed license option can be regarded as a contract between the DRM vendor
and the customer, it contains the validity of the product, its price and description, the
time of the customer request and is signed by both the customer and the DRM vendor,
so none of them could reject it.
192

The last information in this message is the Issuer’s URL or other identification, so
the bank knows how to communicate with the Issuer.
After receiving and processing this message the bank contacts the License-Issuer
and tries to acquire the specified license for the customer which is shown in section 4.3
which describes the bank to License-Issuer communication. The second message then
is the response from the bank to the customer seen in Figure 6. If the status contains
“success” the request has been successful and a license has been provided which is then
forwarded to the customer. Otherwise the status contains a failure description.
Fig. 6. License-Delivery Message.
4.3 Communication between Bank and License-issuer
This communication has to be secured, too, but in this case in two ways. In this case
it is impossible to use a specific Certification Authority on either the bank’s or the
Issuer’s side (e.g. the bank could not be demanded to manage certificates for all possi-
ble Issuers). Both bank and Issuer have to acquire a certificate from one of the public
certification authorities. Even though this is coupled with spending money the effort
is negligible in comparison to the possible benefits. They will most probably already
have such certificates nowadays. The certificates could then be used as in the previous
scenario to authenticate and encrypt data.
The first message in this context is sent by the bank after it has received a License-
Request Initiation from the customer (see Figure 7). This message contains the license
selection, which the bank received from the customer and the certificate of the bank.
Before forwarding the license selection the bank removes the signature of the customer
to preserve the customer’s privacy. The bank then signs the license request to ensure its
authenticity.
Fig. 7. Trusted-Bank Requesting a License from the Issuer.
As a reply to the license-acquisition message the Issuer sends the message shown
in Figure 8 to the bank. The account data is needed for the bank to transfer money
for the license. By sending this message the contract is closed and after forwarding
the license to the customer (as described in section 4.2) the bank should carry out the
193

cash remittance to the License-Issuer. At this point it can also be seen clearly, that the
concrete implementation of this protocol has to ensure that no message could become
lost. In a Web Service scenario this can be accomplished by the use of WS-Reliable
Messaging [12].
Fig. 8. License-Response from Issuer.
5 Conclusion
To further investigate our drafted architecture and to proof our concepts we imple-
mented a prototypical scenario with the described components and the proposed proto-
col. Technically our implementation uses Web Services for the communication and the
security related requirements are solved by the use of Web Service Security functional-
ity like encryption, signing and certificates.
Summing up we found the following benefits of the drafted architecture:
+ Privacy-protection of the customer. Only the Trusted Bank needs to know the cus-
tomers data (and the banks already have the necessary data of their customers).
Vendors do not need and have no chance to know who is buying their goods. Just if
the customer chooses to use the same session key for one or more vendors repeat-
edly, it would be possible for the vendors to collect anonymous purchase-statistics.
Additionally there is just one point where customer data is stored, so it is easier to
protect user privacy at this point through an independent party and by sophisticated
technical and organisational means.
+ Digitally signed contracts. They provide an evidence for both customer and seller
and thus ensure the non-repudiation of the transaction.
+ Trust in being paid. License-Issuers can be sure they are actually paid, because they
only have to trust a few banks, in contrast to thousands different users and the bank
is able to check the accounts of its users before the acquisition.
+ Unique way for money transfers. The billing for all transactions is handled in the
same way. The customer and the vendors are not burdened anymore to handle dif-
ferent money transfer schemes. The Issuers do not have to build their own account-
ing interface as today.
+ Bank advantage. As central service provider in online trade with digital goods.
+ Usability. Better usability for the customer, because it is not necessary anymore to
create different accounts (for each vendor) or give away personal information more
than one time.
One can see that there are certain benefits not only for the customer, but also for
banks and Content-Owners/License-Issuers. On the other hand this solution would im-
pose the following burdens, which however should be far more than compensated by
the afore mentioned points:
194

– Additional infrastructure. The banks have to set up a highly accessible service in-
terface, but they already have similar services e.g. for online-banking.
– Single point of failure. The trusted-bank is the bottleneck of the architecture. Even
if data-throughput should be low because of the simple protocol and the small mes-
sages which are exchanged, the servers have to be secured against denial of ser-
vice, but the same issues are already addressed in recent classical online banking
systems.
– Effort to establish PKIs. Additional effort has to be considered to establish the
Public-Key-Infrastructure for the trust relationships.
6 Future Work
We need to further proceed with our prototypical implementation of this architecture
and therefore exactly define the needed Web Service interfaces and setup the PKI-
infrastructure to examine the benefits and challenges of this architecture in a greater
detail and to perform a detailed security assessment. We also want to investigate possi-
ble ways to improve user experience and acceptance of DRM systems even further.
References
1. Open Mobile Alliance: OMA Digital Rights Management V2.0 Specifications (2006)
http://www.openmobilealliance.org/release program/drm v2 0.html.
2. Free Software Foundation: Digital restrictions management and treacherous computing
(2006) http://www.fsf.org/campaigns/drm.html.
3. Erickson, J.S.: Fair use, drm, and trusted computing. Commun. ACM 46 (2003) 34–39
4. Cooper, A., Martin, A.: Towards an open, trusted digital rights management platform. In:
DRM ’06: Proceedings of the ACM workshop on Digital rights management, New York, NY,
USA, ACM Press (2006) 79–88
5. Cohen, J.E.: DRM and privacy. Commun. ACM 46 (2003) 46–49
6. Grimm, R., Puchta, S., M
¨
uller, M.: privacy4drm (2005)
https://www.datenschutzzentrum.de/drm/privacy4drm.pdf.
7. Grimm, R.: Privacy for digital rights management products and their business cases (2005)
http://www.uni-koblenz.de/ grimm/texte/Privacy4DRM Tech-Axmedis-Grimm-final.pdf.
8. Michiels, S., Verslype, K., Joosen, W., Decker, B.D.: Towards a software architecture for
drm. In: DRM ’05: Proceedings of the 5th ACM workshop on Digital rights management,
New York, NY, USA, ACM Press (2005) 65–74
9. Arnab, A., Hutchison, A.: Fairer usage contracts for drm. In: DRM ’05: Proceedings of the
5th ACM workshop on Digital rights management, ACM Press (2005) 1–7
10. Vora, P., Reynolds, D., Dickinson, I., Erickson, J., Banks, D.: Privacy and digital rights
management. In: In Proceedings of the W3C Workshop on Digital Rights Management
(Sophia-Antipolis, France, Jan. 22–23, 2001). (2001)
11. Choudhury, S.: Public Key Infrastructure Implementation and Design. Wiley & Sons (2002)
12. Iwasa, K., Durand, J., Rutt, T., Peel, M., Kunisetty, S., Bunting, D.: Web ser-
vices reliable messaging tc, ws-reliability 1.1 (2004) http://docs.oasis-open.org/wsrm/ws-
reliability/v1.1/wsrm-ws reliability-1.1-spec-os.pdf.
195
