
SREPPLine: Towards a Security Requirements
Engineering Process for Software Product Lines
Daniel Mellado
1
, Eduardo Fernández-Medina
2
and Mario Piattini
2
1
Ministry of Work and Social Affairs
Management Organism of Information Technologies of the Social Security
Software Development Centre of the National Social Security Institute, Madrid, Spain
2
ALARCOS Research Group, Information Systems and Technologies Department
University of Castilla-La Mancha
Paseo de la Universidad 4, 13071 Ciudad Real, Spain
Abstract. Security related requirements are increasingly becoming a significant
portion of the total set of requirements for many software systems. At the same
time, nowadays many systems are developed based on the product line engi-
neering paradigm. Within product lines, security requirements issues are ex-
tremely important because weakness in security can cause problems throughout
the lifecycle of a line. The main contribution of this work is that of providing a
standard-based process, which is an add-in of activities in the domain engineer-
ing as well as in application engineering processes. These processes deal with
the security requirements from the early stages of product line lifecycle in a
systematic and intuitive way especially adapted for product line based devel-
opment. It is based on the use of the latest security requirements techniques, to-
gether with the integration of the Common Criteria (ISO/IEC 15408) into the
product line lifecycle. Additionally, it deals with security artefacts reuse, by
providing us with a Security Resources Repository. Moreover, it facilitates the
conformance to the most relevant security standards with regard to the man-
agement of security requirements.
1 Introduction
Our society has become increasingly IT-based [31], depending as it does on a huge
number of software systems which have a critical role and which manage critical and
sensitive information, it is absolutely vital that Information Systems (IS) are properly
assured from the very beginning [1, 22], due to the potential losses faced by organiza-
tions that put their trust in all these IS. Moreover, it is widely-accepted the principle
which establishes that the building of security at the early stages of the development
process is cost-effective and also brings about more robust designs [17].
Furthermore, nowadays, there is an increase in the demand as well in the com-
plexity of the software needed. Thus, in order to obtain high-quality IS along with
higher productivity, software product line (SPL) based development has become the
Mellado D., Fernández-Medina E. and Piattini M. (2007).
SREPPLine: Towards a Security Requirements Engineering Process for Software Product Lines.
In Proceedings of the 5th International Workshop on Security in Information Systems, pages 220-232
DOI: 10.5220/0002424702200232
Copyright
c
SciTePress

most successful approach in the reuse field, because it can help us significantly re-
duce time-to-market as well as development costs [3, 4], by increasing the reuse of all
types of artefacts, thanks to the combination of coarse-grained components with a
top-down systematic approach where the software components are integrated into a
high-level structure.
Due to the complexity and extensive nature of product line development, security
and requirements engineering are much more important for a product line practice.
Security is a cross-cutting concern in software intensive systems and should conse-
quently be subject to careful requirements analysis and decision making, in addition
the requirements for cost-effective product line development complicate this task.
Therefore, the discipline known as Security Requirements Engineering is a very im-
portant part of the SPL development process for the achievement of secure SPL and
applications, because it provides techniques, methods and standards for tackling this
task in the development lifecycle. It also implies the use of repeatable and systematic
procedures to ensure that the set of requirements obtained is complete, consistent,
easy to understand and analysable by the different actors involved in the development
of the system [18].
In the last few years, it has been a spectacular growing of security standards and
security related proposals which have been developed to try to help develop security
critical IS. Moreover, it has recently been developed SPL reference architectures for
security and SPL requirements management approaches and tools, such as [14, 29].
Nevertheless, after analysing the previously performed comparative analyseses of
several relevant proposals of IS security requirements, as those of [6, 23, 28, 30,
32],etc. in [24, 25], we conclude that those standards and proposals are neither spe-
cific enough for a systematic and intuitive treatment of SPL security requirements,
nor make it easy the task of integrating security requirements engineering activities
into the SPL based development. In addition, they did not provide intuitive, system-
atic and methodological support for the management of security requirements, with
the aim of developing secure SPL and products that conform to the most relevant
security standards with regard to the management of security requirements (such as
mainly ISO/IEC 15408 [10] as well as ISO/IEC 27001 [12], ISO/IEC 17799 [11] or
ISO/IEC 21827 [8]).
In this paper, as an evolution of our previous proposal SREP [25], we will present
a Security Requirements Engineering Process for software Product Lines (SREP-
PLine), which is a standard-based process that describes how to integrate security
requirements into the software engineering process in a systematic and intuitive way,
as well as a simple integration with the rest of requirements and the different
phases/processes of the SPL development lifecycle. Additionally, this process will
facilitate the fulfilment of the IEEE 830:1998 standard [7], and it will help develop IS
which conform to the aforementioned security standards with regard to the manage-
ment of security requirements, and without being necessary to perfectly know those
standards; hence, reducing the participation of security experts to achieve it. In order
to reach these goals, our approach is based on the reuse of security artefacts which are
integrated in the variability model of the SPL, by providing a Security Resources
Repository (SRR), together with the integration of the Common Criteria (CC)
(ISO/IEC 15408) into the SPL lifecycle.
221

The rest of the paper is organized as follows: in section 2, we will summarize the
main concepts of requirements engineering in software product lines. Then, in section
3, we will present an outline of our proposed security requirements engineering proc-
ess for software product lines (SREPPLine). Later, in section 4, we will explain the
security resources repository. Finally, in section 5, we will state our conclusions and
future work.
2 A Summary of Product Line Requirements Engineering
A software product line is a set of software-intensive systems sharing a common,
managed set of features
1
[15] that satisfy the specific needs of a particular market
segment or mission and that are developed from a common set of core assets in a
prescribed way [4].
The software product line engineering paradigm separates two processes: domain
engineering and application engineering [27]. Domain engineering is the process of
SPL engineering in which commonality and variability of the product line are defined
and realised, and it is composed of five key sub-processes: product management,
domain requirements engineering, domain design, domain realisation and domain
testing. According to [27],the domain requirements engineering sub-process encom-
passes all activities for eliciting and documenting the common and variable require-
ments of the product line. Hence, domain requirements engineering differs from re-
quirements engineering for single systems in the following subjects: commonality
analysis; variability analysis and modelling; and it tries to anticipate prospective
changes in requirements, such as laws, standards, technology changes and market
needs for future applications. Application engineering is the process of SPL engineer-
ing in which the applications of the product line are built by reusing domain artefacts
and exploiting the product line variability, and it is composed of the following sub-
processes: application requirements engineering, application design, application reali-
sation and application testing.
Product line requirements define the products and common and variable features
of the products in the product line. Requirements common across the entire family,
which constitute the product line requirements and an important core asset, should be
managed separately from requirements that are particular to a subset of the products
(or to a single product), which must be managed as well. Product line requirements
engineering incorporates different requirements sources, such as stakeholders (do-
main experts, etc.), existing products or competitors’ products, existing model do-
mains or the SPL scope. The product line scope bounds the products included in the
product line: product line requirements refine the scope by more precisely defining
the characteristics of the products in the product line. The scope and product line
requirements are tightly coupled and evolve together [4].
Finally, after analysing several relevant proposals of SPL requirements and some
SPL requirement management tool, as those of [4, 14, 16, 27, 29], we argue that those
proposals are neither specific enough for a systematic and intuitive treatment of SPL
1
A feature is an end-user visible characteristic of a system.
222
security requirements, nor make it easy the task of integrating security requirements
engineering activities into the SPL based development.
3 SREPPLine: a Security Requirements Engineering Process for
Software Product Lines
The Security Requirements Engineering Process for software Product Lines (SREP-
PLine) is an add-in of activities (that are decomposed into tasks which receive input
artefacts and which generate output artefacts, with the participation of different roles)
that are integrated into a SPL development process model of any organization provid-
ing it with a security requirements approach. The order in which they are performed
depends on the particular process that is established in the organization. Hence the
sub-process and its activities described in this paper can be combined with existing
development methods such as the Unified Process or other development processes. In
this paper we will describe the integration of our process into the SPL engineering
framework proposed in [27].
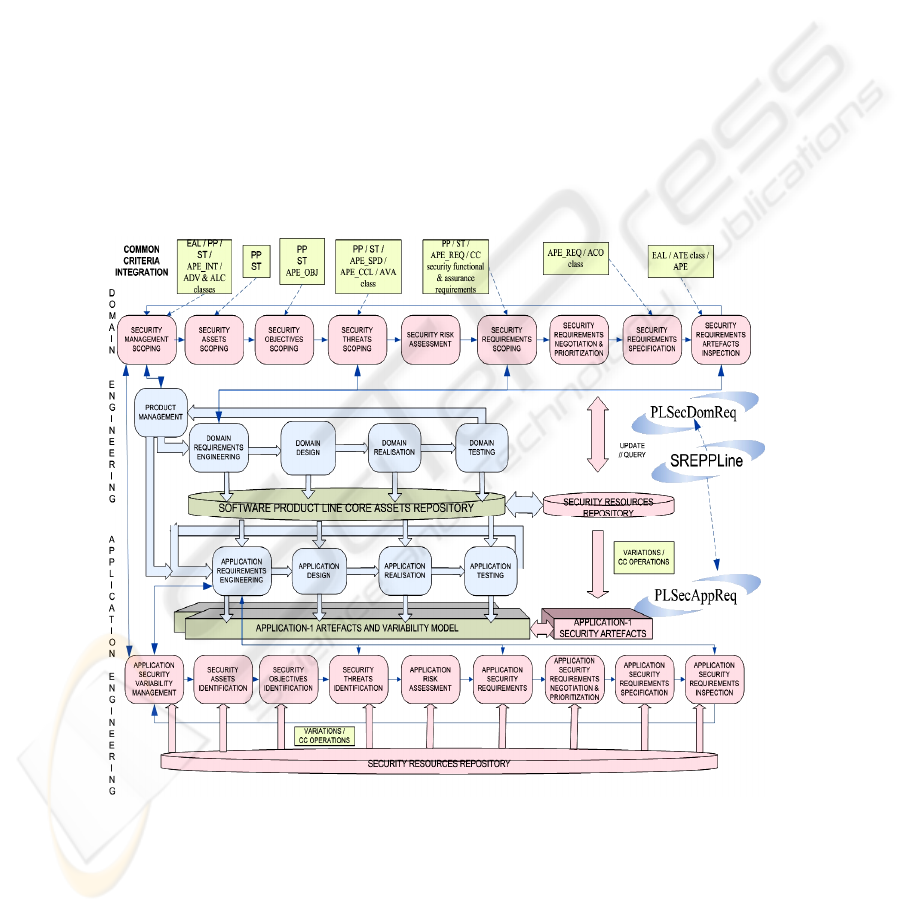
Fig. 1 The Software Product Line Security Requirements Engineering Framework.
As it is shown in Fig. 1, SREPPLine is composed of two sub-processes with their
respective activities: PLSecDomReq (Product Line Security Domain Requirements
223

Engineering sub-process) and PLSecAppReq (Product Line Security Application
Requirements Engineering sub-process). These sub-processes cover the four basic
phases of the requirements engineering according to [19]: requirements elicitation;
requirements analysis and negotiation; requirements documentation; and requirements
validation and verification. Therefore, at least, they have to be performed for each
iteration of the Domain or Application Requirements Engineering Process of the SPL,
respectively. However, in this paper due to space restrictions, we will outline the key
activities and tasks that have to be part of PLSecDomReq and we will present a brief
overview of PLSecAppReq (as an evolution of SREP [25]).
3.1 Product Line Security Domain Requirements Engineering Sub-process
The main goals of this sub-process (SP1) are the development of common and vari-
able security requirements which conform to IEEE 830:1998 as well as their precise
documentation in a Protection Profile
2
(PP) similar document and the development of
their common and variable related security artefacts following a CC similar format.
The process model of this sub-process is shown in Fig. 2.
SP1 - Activity A1.1: Security Management Scoping. This activity comprises the
following tasks: security resources repository improvement (up-to-date artefacts and
links); identification of specific stakeholders; security definitions agreement; security
environment identification (security policy, security standards, laws, constraints,
security needs and security acceptance criteria as well as the evaluation assurance
level (EAL) of the CC); identification of the relevant type of assets and security ob-
jectives; security cost impact and risk superficial estimations; and security features
identification (commonalities and variability).
SP1 - Activity A1.2: Security Assets Scoping. This activity comprises the following
tasks: security assets identification for each asset (or group of them) and for the envi-
ronment; security assumptions; security asset scoping, which aims at identifying par-
ticular components to be developed for reuse, common and variable assets; identifica-
tion of dependences between security assets; and valuation of security assets.
SP1 - Activity A1.3: Security Objectives Scoping. This activity comprises the fol-
lowing tasks: security objectives identification (commonality and variability analy-
sis); security objectives modelling and specification (APE_OBJ CC class); security
objectives valuation.
2
The Common Criteria define a Protection Profile as an implementation independent statement
of security requirements that is shown to address threats that exist in a specified environment
224
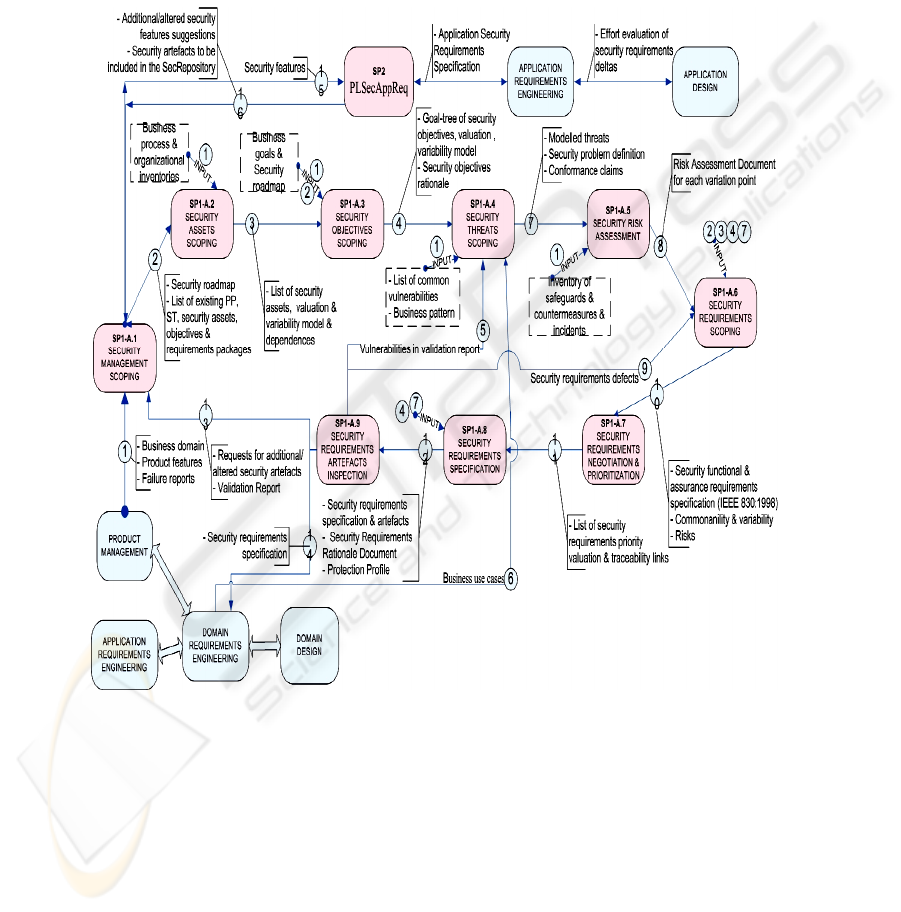
SP1 - Activity A1.4: Security Threats Scoping. This activity comprises the follow-
ing tasks: identification of potential vulnerabilities in public domain sources; identifi-
cation of the attack tree associated with the business pattern or SPL domain; identifi-
cation of the misuse cases and threats for each security objective and asset (common-
ality and variability analysis), because each asset is targeted by threat/s that can pre-
vent the security objective from being achieved; threats modelling and specification;
validation of security objectives against threats and assets and their variability mod-
els.
Fig. 2. Activity model of PLSecDomReq.
SP1 - Activity A1.5: Security Risks Assessment. This activity comprises the follow-
ing tasks in order to achieve 100% risk acceptance: assessing whether the threats are
relevant according to the security level specified by the security objectives; estimating
the security risks based on the relevant threats, their likelihood and their potential
negative impacts, depending on the variation points. To do so, the ISO/IEC 13335
225

(GMITS) [9], provides guidance on the use of the risk management process. In Spain
it could be used MAGERIT [21], which conforms to ISO/IEC 13335.
SP1 - Activity A1.6: Security Requirements Scoping. This activity comprises the
following tasks: security requirements elicitation, the suitable security requirements
or the suitable package of security requirements that mitigate the threats at the neces-
sary levels with regard to the risk assessment must be selected; identification of
common security requirements according to the elicited requirements and through the
previously performed risk analysis; defining variable requirements and variability
dependencies; security requirements modelling; definition of CC operations (itera-
tion, assignment, selection or refinement); definition of security test/metric and coun-
termeasure for each security requirement. Thus, at the end of this activity and accord-
ing to ISO/IEC 17799:2005 it must have been specified the functional, assurance, and
organizational security requirements, along with the security requirements for the IT
development and operational environment.
SP1 - Activity A1.7: Security Requirements Negotiation and Prioritization. This
activity comprises the following tasks: interdependences with other functional and
non-functional requirements and trade-offs in the security variability model and there-
fore in the orthogonal variability model; balancing the risk with the economical im-
pact of implementing countermeasures.
SP1 - Activity A1.8: Security Requirements Specification. This activity comprises
the following tasks: security requirements modelling and security requirements
specification.
SP1 - Activity A1.9: Security Requirements Artefacts Inspection. This activity
comprises the following tasks: i) it is verified whether the security requirements con-
form to CC (ISO/IEC 15408) and to IEEE 830-1998 standard, because according to
this standard, a quality requirement has to be correct, unambiguous, complete, consis-
tent, ranked for importance and/or stability, verifiable, modifiable, and traceable. ii)
Furthermore, SREP proposes the use of the SSE-CMM (ISO/IEC 21827) in order to
help in the evaluation of the product line security engineering process in the Domain
Testing sub-process, with the help of the CC_SSE-CMM [20] approach. Thereby, we
propose to evaluate the security of the SPL along with the product line security engi-
neering process by using the CC assurance requirements and the SSE-CMM at the
same time with the help of CC_SSE-CMM. iii) It will verify in the Domain Testing
sub-process the fulfilment of the previously approved EAL and the CC evaluation.
3.2 Product Line Security Application Requirements Engineering Sub-process
PLSecAppReq (Product Line Security Application Requirements Engineering sub-
process) activities in this sub-process (SP2) are similar to SREP [25] activities, except
for some specific tasks and activities that are unique to security requirements engi-
226

neering in SPL. The main goals of this sub-process are: elicitation and documentation
of the security requirements and their related security artefacts; to make them conform
to IEEE 830:1998, as well as to gather them in a Security Targets
3
(ST) similar docu-
ment; at the same time to reuse, as much as possible, the security domain artefacts and
requirements.
Due to space restrictions, we have enumerated in Fig. 1 the key activities of
PLSecAppReq sub-process and below we will only describe the key differences be-
tween this sub-process and security requirements engineering for single systems (such
as SREP):
- Requirements elicitation is based on the communication of the available com-
monality and variability of the SPL. Most of the requirements are not elicited
anew, but are derived from the domain requirements.
- During security requirements elicitation, the differences between security appli-
cation artefacts and security domain artefacts (sec-deltas) must be detected,
evaluated with regard to the required adaptation effort, and suitably documented.
If the required adaptation effort is early known, trade-off decisions concerning
application security artefacts are possible not only to reduce the effort but also to
increase the amount of domain artefacts.
4 The Security Resources Repository
SREPPLine proposes a Security Resources Repository (SRR), which facilitates the
product line security requirements engineering by making it easier the development
with security requirements reuse, which is an important concept in SPL because it
helps us increase the security requirements quality for an improved use in subsequent
projects [32]. Moreover, it helps manage in an easier way one of the most important
factors of success in the development of a secure SPL: the management of commonal-
ities and variability of the security requirements and their traceability links.
The security requirements can be obtained from security objectives or threats
starting from the assets for a new SPL or for a new product of a SPL. Furthermore,
the SRR uses the concept of package, understood as a homogeneous set of require-
ments that can be applied to different products of the SPL, and that are put together to
satisfy the same security objectives as well as to mitigate the same threats, being a
bigger and more effective reuse unit. The security domain requirements engineering
as well as the security application requirements engineering sub-processes are sup-
ported by this repository.
Next, we will outline the most important and/or complex aspects of the meta-
model shown in Fig. 3:
- ‘Domain Threat’ and ‘Domain Security Requirement’ (or CC Component) are
described independently of particular products. They can be represented as dif-
ferent specifications, thanks to the elements ‘Threat Specification’ and ‘Security
3
The Common Criteria define a Security Target as an implementation dependent statement of
security needs for a specific identified product.
227

Requirement Specification’. They are included in the core assets of the SPL, to-
gether with the ‘Security Objective’, which are documented through a goal tree
specified in XML in order to enable the explicit documentation of variability.
Besides all of them support traceability links.
- ‘Security Requirement Package’ is a set of requirements that work together to
satisfy the same security objectives and mitigate the same threats.
- The ‘Security Requirement – Security Requirement’ relationship allows an in-
clusive or exclusive trace between requirements, that is variability constraints.
An exclusive trace between requirements means that they are mutually alterna-
tive, for example that they are in conflict or overlapping, whereas, an inclusive
trace between requirements means that to satisfy one, other/other/s is/are needed
to be satisfied. In addition, it is used to model the dependencies with other func-
tional and non-functional requirements. Traces among requirements in the SPL
infrastructure do automatically also exist in the products.
In addition, there could have been links further on to design level specifications,
security test cases, countermeasures, etc., as well as traceability links with other arte-
facts (“artefacts dependencies”), through the relationship between a variant of the
orthogonal variability model and the associated development artefact, because our
proposed model process is based on the concept of the orthogonal variability model
of Pohl et al. [27]. Thus, the SRR must be integrated into the SPL core assets reposi-
tory to facilitate these traceability links between the variability model of the SPL and
the different types of security artefacts and the other development artefacts.
Finally, we would like to point out the fact that using the CC, a large number of
security requirements on the SPL itself and on the products development can be de-
fined. Nevertheless, the CC neither provide us with methodological support, nor con-
tain security evaluation criteria pertaining to administrative security measures not
directly related to IS security measures. However, it is known that an important part
of the security of an IS can be often achieved through administrative measures.
Therefore, according to ISO/IEC 17799:2005, we propose to include legal, statutory,
regulatory, and contractual requirements that the organization, its trading partners,
contractors, and service providers have to satisfy, and their socio-cultural environ-
ment. After converting these requirements into software and system requirements
format, these requirements along with the CC security requirements would be the
initial subset of security requirements of a SPL, acting like horizontal security re-
quirements patterns for the software product lines of the organization.
228
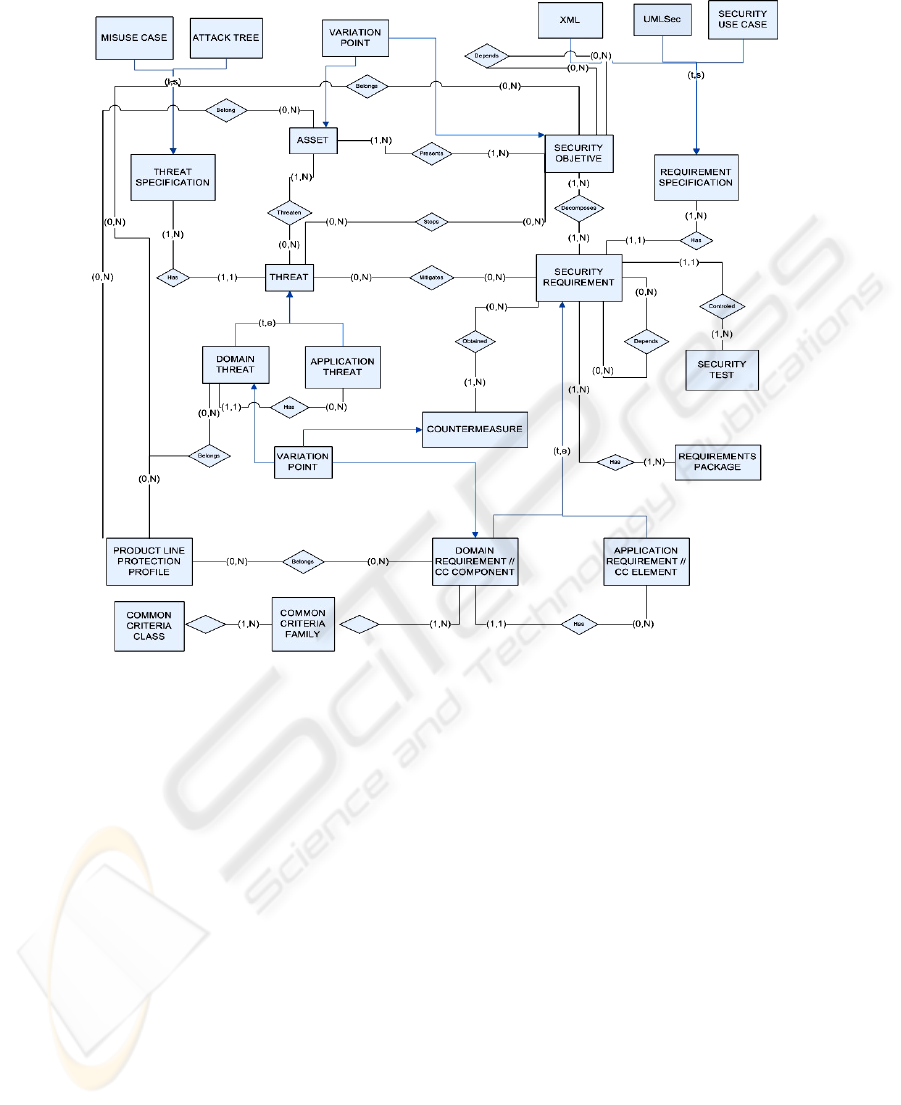
Fig. 3. Product Line Security Resources Meta-model.
5 Conclusions and Further Work
Nowadays, software security is generating a growing interest mainly due to the in-
creasingly crucial nature of the IS with corresponding levels of new legal and gov-
ernmental requirements. At the same time, there is an increasing need to obtain high-
quality IS along with higher productivity. For this reason, software product line based
development has become the most successful approach for ensuring quality, eco-
nomic efficiency and manageability of software systems [2]. Nevertheless, require-
ments management and security of information are much more critical in SPL due to
the complexity and extensive nature of them. Therefore, we believe that it is vital to
deal with security at all stages of SPL development, especially in the management of
security requirements, since these form the basis for the achievement of a robust IS.
Hence, the contribution of this work is that of providing a standard-based process
that deals with security requirements from the early stages of SPL development in a
systematic and intuitive way specially adapted to SPL based development, which is
229

based on the use of the latest security requirements techniques, such as UMLSec [13],
security use cases [5] or misuse cases [30]; as well as on the reuse of security arte-
facts, by providing a Security Resources Repository (SRR), together with the integra-
tion of the Common Criteria (ISO/IEC 15408) into the SPL lifecycle. Furthermore, it
also conforms to the most relevant security standards with regard to the management
of security requirements such as the aforementioned ISO/IEC 15408 and ISO/IEC
17799:2005 (sections: 0.3, 0.4, 0.6 and 12.1) and ISO/IEC 27001:2005 standard (sec-
tions: 4.2.1, 4.2.3, 4.3, 6.a, 6.b and A.12.1.1). Furthermore, it facilitates that the prod-
ucts of the SPL conform to these former standards as well as the fulfilment of the
IEEE 830:1998 standard. In addition, SREPPLine suggests using a method to carry
out the risk assessment which conforms to ISO/IEC 13335 (GMITS).
As the application of any methodology or requirements engineering process will
normally fail because it has to be manually performed, further work is also needed to
develop a new version of our previously developed CARE (Computer-Aided Re-
quirements Engineering) tool (SREPTOOL [26]) in order to support and gather the
new characteristics of our proposed security requirements engineering process for
software product lines. Furthermore, we will carry out a refinement of the theoretical
approach by proving it with a real case study to complete and deeply detail SREP-
PLine. Finally, we will work to complement this process in order to provide a holistic
framework for security engineering in software product lines.
Acknowledgements
This paper is part of the ESFINGE (TIN2006-15175-C05-05) and RETISTRUST
(TIN2006-26885-E) projects of the Ministry of Education and Science (Spain), and
of the MISTICO (PBC-06-0082) and DIMENSIONS (PBC-05-012-2) projects of the
Consejería de Ciencia y Tecnología de la Junta de Comunidades de Castilla- La Man-
cha and the FEDER.
References
1. Baskeville, R., The development duality of information systems security. Journal of Man-
agement Systems, 1992. 4(1): p. 1-12.
2. Birk, A., Heller, G., John, I., MaBen, T.v.d., Müller, K., and Schmid, K., Product line
engineering industrial nuts and bolts. 2003, Fraunhofer IESE: Kaiserslautern.
3. Bosh, J., Design & Use of Software Architectures. 2000: Pearson Education Limited.
4. Clements, P. and Northrop, L., Software Product Lines: Practices and Patterns. SEI Series
in Software Engineering. 2002: Addison-Wesley.
5. Firesmith, D.G., Engineering Security Requirements. Journal of Object Technology, 2003.
2(1): p. 53-68.
6. Firesmith, D.G., Security Use Cases. Journal of Object Technology, 2003: p. 53-64.
7. IEEE, IEEE 830: 1998 Recommended Practice for Software Requirements Specifications.
1998.
8. ISO/IEC, ISO/IEC 21827:2002 Information technology -- Systems Security Engineering --
Capability Maturity Model (SSE-CMM). 2002.
230

9. ISO/IEC, ISO/IEC 13335 Information technology - Security techniques - Management of
information and comunications technology security - Part 1: Concepts and models for in-
formation and comunications technology security management. 2004.
10. ISO/IEC, ISO/IEC 15408:2005 Information technology - Security techniques - Evaluation
criteria for IT security, (Common Criteria v3.0). 2005.
11. ISO/IEC, ISO/IEC 17799 Information technology - Security techniques - Code of practice
for information security management. 2005.
12. ISO/IEC, ISO/IEC 27001:2005 Information technology -- Security techniques -- Informa-
tion security management systems -- Requirements. 2005.
13. Jürjens, J., UMLsec: extending UML for secure systems development. UML 2002 - The
Unified Modeling Language. Model Engineering, Languages,Concepts, and Tools. 5th In-
ternational Conference., 2002. LNCS 2460: p. 412-425.
14. Käkölä, T. and Dueñas, J.C., Software Product Lines: Research Issues in Engineering and
Management. 2006: Springer.
15. Kang, K., Cohen, S., Hess, J.A., Novak, W.E., and Peterson, S.A., Feature-Oriented Do-
main Analysis (FODA) Feasibility Study. 1990, Software Engineering Institute, Carnegie-
Mellon University.
16. Kim, J., Kim, M., and Park, S., Goal and scenario bases domain requirements analysis
environment. The Journal of Systems and Software, 79(7) (2005). p. 926 - 938.
17. Kim., H.-K., Automatic Translation Form Requirements Model into Use Cases Modeling
on UML. ICCSA 2005, LNCS, 2005: p. 769-777.
18. Kotonya, G. and Sommerville, I., Requirements Engineering Process and Techniques.
Hardcover ed. 1998, UK: John Willey & Sons. 294.
19. Kotonya, G. and Sommerville, I., Requirements Engineering Process and Techniques.
2000: John Willey & Sons.
20. Lee, J., Lee, J., Lee, S., and Choi, B., A CC-based Security Engineering Process Evalua-
tion Model. 27th Annual International Computer Software and Applications Conference
(COMPSAC'03), 2003: p. 130-.
21. López, F., Amutio, M.A., Candau, J., and Mañas, J.A., Methodology for Information Sys-
tems Risk Analysis and Management. 2005: Ministry of Public Administration.
22. McDermott, J. and Fox, C. Using Abuse Case Models for Security Requirements Analysis.
in Annual Computer Security Applications Conference. 1999. Phoenix, Arizona.
23. Mead, N.R. and Stehney, T. Security Quality Requirements Engineering (SQUARE) Meth-
odology. in Software Engineering for Secure Systems (SESS05), ICSE 2005 International
Workshop on Requirements for High Assurance Systems. 2005. St. Louis.
24. Mellado, D., Fernández-Medina, E., and Piattini, M., A Comparative Study of Proposals for
Establishing Security Requirements for the Development of Secure Information Systems.
The 2006 International Conference on Computational Science and its Applications (ICCSA
2006), Springer LNCS 3982, 2006. 3: p. 1044-1053.
25. Mellado, D., Fernández-Medina, E., and Piattini, M., A Common Criteria Based Security
Requirements Engineering Process for the Development of Secure Information Systems.
Computer Standards and Interfaces, 29(2) (2007). p. 244 - 253.
26. Mellado, D., Rodríguez, M., Fernández-Medina, E., and Piattini, M., Soporte Automatizado
a la Ingeniería de Requisitos de Seguridad. X Workshop Iberoamericano de Ingeniería de
Requisitos y Ambientes de Software (IDEAS'07), 2007: p. (accepted).
27. Pohl, K., Böckle, G., and Linden, F.v.d., Software Product Line Engineering. Foundations,
Principles and Techniques. 2005, Berlin Heidelberg: Springer.
28. Popp, G., Jürjens, J., Wimmel, G., and Breu, R., Security-Critical System Development
with Extended Use Cases. 2003: 10th Asia-Pacific Software Engineering Conference. p.
478-487.
29. Schmid, K., Krennrich, K., and Eisenbarth, M., Requirements Management for Product
Lines: A Prototype. 2005, Fraunhofer IESE.
231

30. Sindre, G. and Opdahl, A.L., Eliciting security requirements with misuse cases. Require-
ments Engineering 10, 2005. 1: p. 34-44.
31. Siponen, M.T., Secure-System Design Methods: Evolution and Future Directions. IT Pro-
fessional, 8(3) (2006). p. 40-44.
32. Toval, A., Nicolás, J., Moros, B., and García, F., Requirements Reuse for Improving Infor-
mation Systems Security: A Practitioner's Approach. Requirements Engineering, 6(4)
(2002). p. 205-219.
232
