
An Ontology for the Expression of Intellectual Property
Entities and Relations
Víctor Rodríguez
1
, Marc Gauvin
2
and Jaime Delgado
1
1
DMAG (Distributed Multimedia Applications Group)
Universitat Pompeu Fabra, Passeig de Circumval•lació, 8, 08003 Barcelona, Spain
Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya, Jordi Girona, 1-3, 08034 Barcelona, Spain
2
NetPortedItems, S.L.
Abstract. Ontologies represent knowledge in a particular area. Intellectual
Property (IP) Entities lifecycle lacks any explicit standard representation, and a
semantic expression of its processes and rules would report a series of benefits.
To formalise the expression of IP Entities and their relations, an Ontology Web
Language (OWL) ontology is proposed to establish a common framework
where the different interested parties can interact. As a demonstration, a sample
application based on the ontology is described, where a central reasoning server
receives qualified statements and queries over the ontology, giving the perti-
nent logical results.
1 Introduction
The word “ontology” comes from an ancient Greek word related to “being”. But be-
ing itself is an imprecise term. Webster’s dictionary defines two different meanings
for the verb “to be”. The first use is to give a name a predicate and the second is to
express existence. Thus, in one sense we can use the verb “to be” to attribute a prop-
erty to include a subject in a category or to express equivalence between two subjects;
in another sense, we can use it to assert the existence of a certain subject. Ontologies,
in the context of computer science, are also related to these two concepts and allow us
to represent both abstract models and their existing exemplars.
A model in an ontology is the explicit expression of the knowledge of a particular
domain. It represents a set of concepts as classes, their attributes, the relationships
between the classes and their restrictions. And although having a logical representa-
tion of a data model is by itself useful regardless the existence of individuals, ontolo-
gies exhibit fully their potential when they also express real beings as class instances
of the ontology.
In this paper, we present an ontology for representing the domain of Intellectual
Property (IP) Entities defined as the set of unique artistic and/or intellectual creations
and their manifestations, adaptations and subsequent stylistic instantiations.
Within this domain, a minimum set of actors (roles) are required to generate inde-
pendent (i.e. original works) or dependent IP Entities such that the relationship be-
Rodríguez V., Gauvin M. and Delgado J. (2007).
An Ontology for the Expression of Intellectual Property Entities and Relations.
In Proceedings of the 5th International Workshop on Security in Information Systems, pages 196-203
DOI: 10.5220/0002430101960203
Copyright
c
SciTePress

tween the different classes of actors are direct corollaries of the interdependence be-
tween the IP Entities created by them. A set of rights over actions that may be per-
formed on or with IP Entities may be attributed to other roles by the original rights
owner. These actions may create new dependant IP Entities whose rights transfer can
be performed along the value chain by virtue of provenance alone. Thus, the formal-
ised semantic expression of the relationships based on natural dependencies for using
and generating IP Entities provides a solid and common basis for computer based
inferring and reasoning about individuals of the different classes (IP Entities, roles
and rights).
In this sense, the model intends to be universal by focussing first on the notion of
an origin IP Entity called the original work and then the fundamental relationships
required for generating IP Entities dependent on the original work. For example, the
issue of how Intellectual Property is remunerated can vary substantially from country
to country but any system that supports IP, will necessarily support these fundamental
relationships if for nothing else to accurately attribute IP Entities to the appropriate
individuals (irrespective of economic or moral compensation). Precisely in this way,
the model herein is extendable to and interoperable with different specialisations of
IP Entity systems in the Semantic Web world based on ownership of original works
determined by provenance of their manifestations. This represents the key result and
benefit of expressing such knowledge in a standard machine readable way.
To show the benefits of using a semantic expression of the IP model, a small ap-
plication is also described, where IP Entities and actors are represented as individuals
of the Ontology.
After reviewing previous work in the field, this paper will first provide a descrip-
tion of an Intellectual Property model, then its expression as an Ontology and finally
a demonstrator application will be described.
2 State of the art
Digital Rights Management (DRM) systems were intended for managing IPR (Intel-
lectual Property Rights) in the digital world. The corresponding standards provide
means to represent actions related to rights, but only at a syntactic level. The most
extended DRM standards usually formalise XML schemas that define rights expres-
sion languages (REL), like MPEG-21 REL [1] or ODRL [2]. Some REL terms are
sometimes defined in a separate dictionary such as in the Rights Data Dictionary
(RDD) [3], but in this case the definition is a short description only for the human
comprehension. What this paper promotes is another approach where both the seman-
tics and the syntax are modelled in an Ontology so that computers may understand
and make use of the meanings that are expressed within the model..
This is not the first initiative in this field. There are other semantic representations
that cover the terms we deal with, and there are general purpose ontologies of legal
terms [4], but they do not include all the subtle details of an integral IP model. A first
formal effort was IPROnto [5], specifically aimed at describing a general model for
IPR. Other efforts include the formalisation of the MPEG 21 RDD (called RDDOnto
[6]). Yet another, OREL [7], proposes an alternate Rights Expression Language based
197

also on an OWL Ontology aimed at replacing MPEG-21 REL licenses, and another
work [8] in a similar approach is based on making inferences over a MPEG-21 REL
model with CLIPS. Finally, the DMP Creation Model was specified with the intent to
express a minimum and sufficient set of uses and dependencies of and between IP
Entities common to any system where the ownership of original works are determined
by their provenance.
The work we present here, is less elaborate than IPROnto in that it does not intend
to express several related fields at once such as both genesis and legal treatment of IP
Entities. Also, it is not linked to any upper ontology such as SUMO [9]. Experience
has shown that overly complex Ontologies are difficult to manage in terms of main-
taining both consistency as per available machine based reasoners and corresponding
human understanding of the relationships between concepts. These relationships need
to be agreed to in order for the model to be trusted in its implementation. In this way,
a basic set of easily agreed principles can be extended to include any number of sce-
narios that adhere to the same core set of underlying precepts.
3 The Intellectual Property Entity Model
The scope of the model includes any setting where individuals generate original IP
and subsequent derived IP and that can be represented digitally. The basic chain of
actions in the IP value chain whereby different related IP Entities are generated is
similar to the one proposed by the Digital Media Project (DMP) [10], as follows:
original concept or idea, material manifestation, adaptation, reproduction and distri-
bution to others interested in enjoying it. In each of the steps new unique IP Entities
are made and can be classified as follows:
− Work: An original abstract idea that can be uniquely attributable.
− Adaptation. A work that is based on another work.
− Manifestation. The tangible physical expression of a work such as a musical score,
manuscript or event that can be recorded.
− Instance. A particular execution or rendition of a manifestation.
− Copy. A copy of an instance or a manifestation, equal to other copies.
− Product. A collection of one or more copies ready to be distributed.
The individuals that act on these basic IP Entities can be classified according to a
set of generic roles that can be adopted by an agent i.e. a person or group thereof who
incarnates one or more roles. The list of roles are:
− Creator. The author of the work, who translates his idea into a material realization.
− Adaptor: The creator of an adaptation from a work.
− Instantiator. An agent who executes a performance or rendition of the work.
− Producer. An agent who compiles commercial distributable products.
− Distributor. An agent who distributes the product.
− End User. The last agent to use the content.
198

Work Manifestation Instance Product
Creator
Instantiator
Makes manifestation
Makes instance
Producer
Makes product
Distributor
Distibutes
End User
Create work
Fig. 1. Value IP Entity Value Chain and roles.
The creator has full rights over the work, and can trade with these rights. Each role
represents a set of actions that can be attributed to any agent capable of performing
those actions (i.e. a distributor can distribute products), but in order to have the right
to execute actions associated with roles, agents need the required authorisation (i.e.
the distributor can distribute a particular product if and only if he is authorised to do
so). Furthermore, the actions that can be performed on or with the IP Entities can be
grouped into:
− Actions that generate new independent and dependent IP Entities: create, adapt,
make manifestation, make instance, make product..
− Actions required to use IP Entities , like the act of “playing” a song etc.
Rights may be transferred with exclusivity or not, and some may be resold or not.
The Creator may retain rights, and the execution of certain actions require his ap-
proval through transfer of the corresponding rights. In many cases not all of the roles
intervene, and the requirements for the transfer of rights may differ, but these differ-
ences should be capable of being expressed as particular specialization of the model
implemented as extensions. Although this present design of the ontology does not
consider the representation of conditions imposed on the execution of the rights (as
RELs usually do), conditions could be the basis for possible future extensions.
4 Intellectual Property Entity Ontology
The mere fact of expressing a model with a set of logical statements requires a precise
analysis that is by itself beneficial for the understanding of the problem. The result of
the analysis is a set of ontology classes, their attributes and the relations between
them; a description of an ontology is described therefore as a hierarchical list of
classes and relations.
OWL (Ontology Web Language) has been chosen as the particular Ontology lan-
guage as it is becoming the standard in the Semantic Web. OWL is built on top of
RDF [11] which in turn is XML based and its simplicity is kept containing only a set
of sentences expressed as triples with the form “subject – predicate - object”.
Mapping a class for each of the concepts in the previous sections, we have the fol-
lowing classes:
199
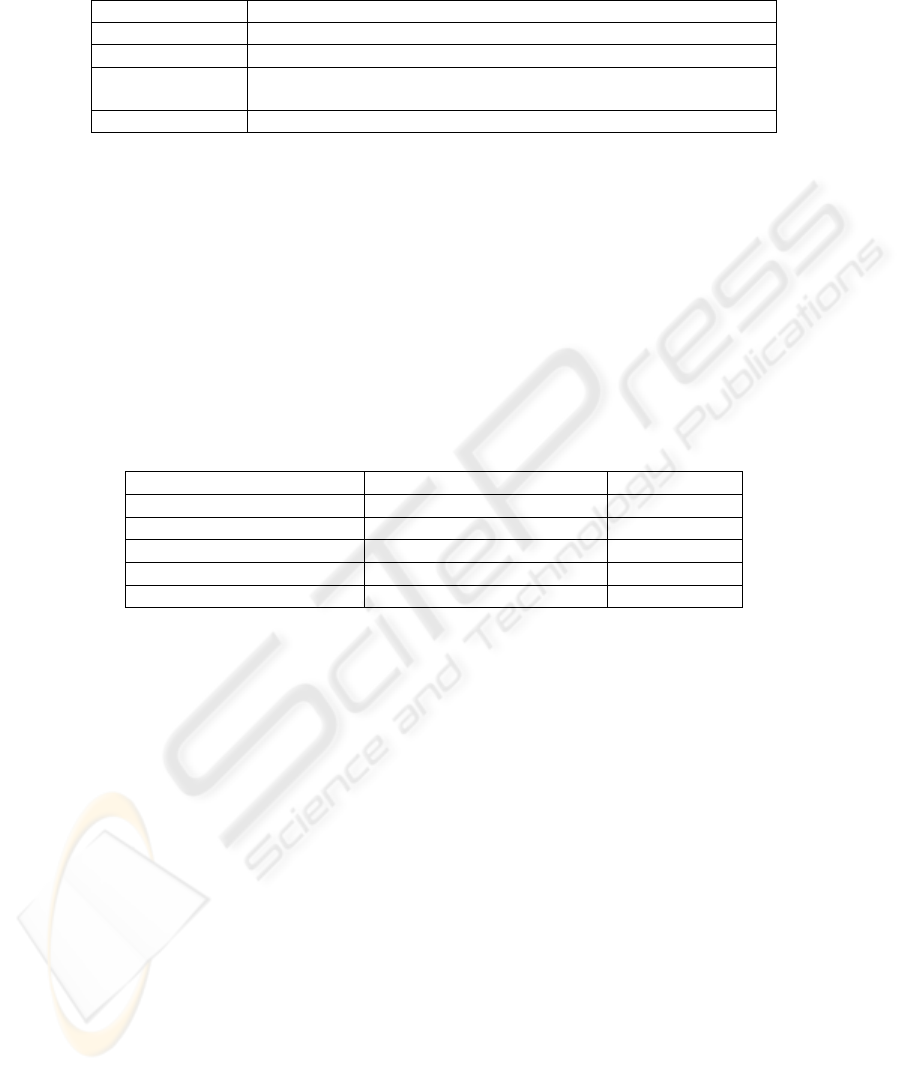
Table 1. Main classes of the ontology.
Root classes Subclasses
IP Entities Work, Adaptation, Manifestation, Instance, Copy, Product
Roles Creator, Adaptor, Instantiator, Producer, Distributor, EndUser
Actions TransformingActions (adapt, perform, etc.), ConsumeRights (play
etc)
Auxiliary classes
Each of the above classes have a set of attributes describing the concept. For ex-
ample, each role has a creation date and time attribute, a reference code attribute so
they can be associated with external databases etc. Several auxiliary classes are also
defined. They are aimed at facilitating the expression of complex sentences, for ex-
ample, the class Authorisation is defined, which contains the proper relations of an
authorisation: who gives the permission, to whom, over which item and to do what.
More important are the relations that join the concepts. A relation binds two re-
sources (that can be classes), and for each relation a domain and a range can be de-
fined. A domain is the set of possible classes where the relation can be applied, and a
range is the set of possible values of a relation relator. The next table shows the main
relations in the ontology.
Table 2. Ontology relations.
Relation Domain Range
ResultsIn TransfomingAction IPEntity
ComesFrom IPEntity IPEntity
RequiresAuthorisationFrom Action Role
CanExercise Role Action
CanApply Action IPEntity
− ResultsIn. Maps TransformingActions into IPEntities, stating the resulting IP En-
tity after applying a certain transforming action. For example, there is a relation
“ResultsIn” that binds Adapt (subclass of TransformingAction) with Adaptation.
− RequiresAuthorisationFrom. This object property maps Actions to Roles, and says
for an action, which roles must authorise the execution of the right
− ComesFrom. Maps IPEntities to IPEntities, stating the IP Entity upon which an-
other depends for its genesis
− CanExercise. States regardless of authorizations, which Actions can be performed
by which roles. Not all roles can perform all actions, for example, an EndUser can
execute the right called play (providing t it has permissions), but cannot make an
adaptation as this is not a task proper of its role.
− CanApply. States which Actions can or cannot be applied over a given IP Entity.
For example, a Work cannot be Played.
Apart from the above, there are a number of relations that impose logical restric-
tions. There are some exclusivity relations (an individual of the ontology can not be
Action and Role at the same time, but can play different roles at the same time), and
200

cardinality relations i.e every Work has one and only one Creator etc. (an abstract
creator can be an individual or a group).
5 A Sample Application
What we have seen in the previous sections becomes interesting in the context of
practical applications. The ontology is the main asset we present, but as a complement
and to show its utility, the description of a practical system implementation follows.
The application is in the form of a logical validator which determines if a given
agent can exercise a particular right over a particular IP Entity. The application con-
sists of a central server which receives sentences expressing facts and queries over IP
Entities; and its answers will be the logical result of the received expressions.
Central Validator
Bob´s computer
Bob is a Creator
Bob creates
OntoSong.mp3
Bob gives Alice right
to Adapt OntoSong.mp3
Alice´s computer
Alice is an Adaptor
Query
-- May I Adapt OntoSong.mp3?
-- Authorised
Fig. 2. Schema of a simple application.
As can be seen in Figure 2, a Central Validator receives assertions like “Bob is a
Creator”, and “Bob Creates OntoSong.mp3”, and queries of the kind: “May Alice
adapt OntoSong.mp3?” which in turn are answered according to the logical result of
the previously introduced knowledge.
Externally it takes the form of a web application, where the central server offers a
site where users can log in once authenticated. Each of the remote clients (like Bob or
Alice) can issue assertions valid within their domain. That is to say, Bob cannot say
“Alice created a song”, but he can create a new composition.
The composition of these assertions is facilitated by an easy to use web interface,
but what is actually sent over the network is one or more OWL triples (RDF triples),
which the Central Validator stores. The queries are translated in turn into an
SPARQL [12] expressions, a specific query language for RDF.
The Central Validator contains the rules of the model as an OWL file, and addi-
tionally stores the incoming sentences in a database. The triples in an RDF model can
be easily kept in a single SQL table with 3 columns, therefore all RDF operations are
inherently implementable as SQL operations and thus the system retains simplicity.
Storage of data in the form of Ontology individuals does not compete with other ad-
201

hoc relational databases in efficiency or security but information structure is known
to everybody and reasoning can be directly performed over these expressions.
The Central Validator has a core module able to parse, read and store all the OWL
triples, and reason over them. Many middleware platforms facilitate these tasks, and
our particular choice points at a Java based system, which makes use of the Jena [13]
and Pellet [14] libraries. These libraries are intended for the former to read and parse
OWL triples and the later to perform the first order logical inferences. These are par-
ticular choices of minor interest, because the Ontology is given in XML, a platform
that is technologically neutral. On top of these libraries, an API with a set of functions
is defined. The API has already been programmed and submitted to the DMP.
OWL IP Ontology
Pellet + Jena
API Functions Set
WebService server
Central Validator
WebService client
Web Interface
Client
IP Model
Individuals
database
Fig. 3. Architecture model of the application.
The communication between the Central Validator and the clients is carried out
with Web Services. The server parses the OWL triples that it receives and checks
their validity before adding them to the knowledge store, and accepts queries under
two forms: as functions belonging to a set of predefined calls in an API, and as free
SPARQL queries. The client thus makes no triple processing at all, keeping a light
client interface. Figure 3 shows the architecture structure of the application.
6 Conclusions
An Ontology was presented for describing an Intellectual Property model. Objects
referred to as IP Entities were represented along the value chain, as well as the actors
that play roles over them. The expression of the model was achieved using an Ontol-
ogy Web Language whose short description was also given. A practical application
was described in order to support the comprehension of the proposed model.
The authors believe that based on the natural inter-dependence between IP Entities,
roles and subsequent rights upon which both business and legal rules must depend on,
202

expression of a corresponding Ontology using the standard Semantic Web Language
is necessary to provide the required machine readable expressivity. Furthermore, a
world where digital communication of original works and subsequent IP Entities re-
quires trusted machine based management of the associated relationships between
roles, further attests to the importance of such an effort.
This work, in response to a call for technology, has been accepted by the Digital
Media Project, for its inclusion in the Interoperable DRM Platform (IDP) specifica-
tion as of v.2.1. [12].
Acknowledgements
This work has been partly supported by NetPortedItems S.L. (CMOnto Project), the
Spanish Administration (DRM-MM project, TSI 2005-05277) and the FP6 Network
of Excellence VISNET-II.
References
1. ISO/IEC. ISO/IEC IS 21000-5 – Rights Expression Language
2. Ianella, R. (ed.): Open Digital Rights Language v.1.1 http://www.w3.org/TR/odrl/
3. ISO/IEC. ISO/IEC IS21000-6 – Rights Data Dictionary
4. Visser, P.R.S., and T.J.M. Bench-Capon: The formal specification of a legal ontology. In:
Legal Knowledge Based Systems; foundations of legal knowledge systems. Proceedings
JURIX'96 (1996)
5. Delgado, J.; Gallego, I.; Llorente, S. and García, R.: IPROnto: An Ontology for Digital
Rights Management. 16th Annual Conference on Legal Knowledge and Information Sys-
tems, JURIX 2003 Frontiers in Artificial Intelligence and Applications, Vol. 106, IOS
Press. (2003)
6. Delgado, J., Gallego, I. and García, R.: Use of Semantic Tools for a Digital Rights Diction-
ary. E-Commerce and Web Technologies, (2004)
7. Yuzhong Qu, Xiang Zhang, Huiying Li: An Ontology-based Rights Expression Language,.
Proceedings of the 13th international World Wide Web. New York, NY, USA, (2004).
8. Chun Hui Suen: Efficient design of interpretation of REL license using Expert Systems, to
appear in Proceedings of the Workshop on Digital Rights Management Impact on Con-
sumer Communications, Las Vegas, Nevada, USA, January 2007
9. Suggested Upper Merged Ontology (SUMO), owned by IEEE at http://www
.ontologyportal.org/.
10. Gauvin, M, Delgado, J., Value Chain Ontologies for Intellectual Property Objects, Europe-
China Conference on Intellectual Property in Digital Media, Shangai, China, October 2006
11. Lassila, O. and Swick R.R. (eds.): “Resource Description Framework, Syntax Specifica-
tion”. W3C Recommendation, 2004, http://www.w3.org/TR/rdf-syntax-grammar.
12. Prud'hommeaux E. and Seaborne A., (eds.) SPARQL, SPARQL Protocol and RDF Query
Language, W3C Working Draft, Oct. 2006, http://www.w3.org/TR/ rdf-sparql-query/
13. Jena – A Semantic Web Framework for Java. http://jena.sourceforge.net/
14. Pellet: An OWL DL Reasoner. http http://pellet.owldl.com/
15.DMP Creation Model Ontology, Approved Document No. 3 – Technical Specification:
Interoperable DRM Platform, Version 2.1
203
