
PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF WIRELESS SYSTEMS IN
TELEMEDICINE
Hybrid Network for Telemedicine with Satellite and Terrestrial Wireless Links
M. Luglio and F. Zampognaro
University of Rome Tor Vergata, Via del Politecnico 1, 00156 Rome, Italy
Keywords: Telemedicine, hybrid networks, DVB-RCS, wireless communications.
Abstract: Telemedicine services represent a valuable opportunity to provide medical assistance ensuring high
flexibility and prompt set up and to significantly reduce costs. The use of hybrid networks based on
satellites and terrestrial wireless systems can be extremely advantageous in terms of flexibility, capillarity
and integration with modern medical equipment, in particular representing a suitable solution in case of
disasters. In the paper such an architecture is described and key performance for some reference
applications, evaluated through simulation, are shown and discussed.
1 INTRODUCTION
Nowadays telemedicine is gaining increasing
interest, in particular in remote and disaster-struck
areas where telecommunication infrastructure can be
respectively missing or compromised.
The aim of this paper is to show feasibility and
effectiveness of an hybrid network architecture for
telemedicine, through performance evaluation
carried out by simulations. The proposed hybrid
network, selected also for the Telesal project
(Arenaccio, Aversa and Luglio, 2006), is composed
of a satellite core network, interconnected with
terrestrial wireless tails using commonly available
and consolidated wireless technologies.
Satellite systems are extremely suitable to
represent the core infrastructure of the network for
their capability to provide data access ubiquitously
and in mobility over very large areas, including
remote or impervious locations where typically
terrestrial telecommunication infrastructures are not
present or economically not viable. To complement
such characteristics, terrestrial wireless systems can
be fruitfully utilized realizing the terrestrial tails to
ensure capillarity and to improve efficiency and
flexibility (Luglio and Vatalaro, 2002).
Performances of some reference telemedicine
applications will be evaluated using NS2 as
simulation tool (Fall and Varadhan, 2007).
In section 2 an overview of the involved
technologies is introduced, in section 3 the network
architecture is described along with some
telemedicine applications. In section 4 the
simulations setup is presented offering some the
simulation outputs summaries. Finally in section 5
conclusions are drawn.
2 TECHNOLOGY REVIEW
Different kinds of satellite configuration
(geostationary and low orbit) can be utilized in the
proposed hybrid architecture. As concerns terrestrial
systems in particular WiMax, WiFi and Bluetooth
looks the most suitable technologies for our scope.
2.1 Satellite Networks
Two kinds of satellite systems are considered:
a) wide band VSAT systems using a
geostationary (GEO) satellite and
b) narrow band global communication
system using a low orbit (LEO)
satellite constellation.
VSAT systems (Very Small Antenna aperture
Terminal) are characterized by the use of directional
fixed or steerable (to allow mobility) dish antennas
with a size of around 80-120 cm. They usually adopt
star or mesh topology, using GEO satellites, which
200
Luglio M. and Zampognaro F. (2008).
PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF WIRELESS SYSTEMS IN TELEMEDICINE - Hybrid Network for Telemedicine with Satellite and Terrestrial Wireless
Links.
In Proceedings of the First International Conference on Health Informatics, pages 200-204
Copyright
c
SciTePress

are suitable for multi-nation coverage area (usually
at continental level). They can offer uplinks of up to
2 Mbit/s, with downlink up to 40 Mbit/s.
Communications suffer of a physical delay of about
550 ms round trip, since the GEO satellite is placed
in a 36000 km orbit. Star systems need a double hop
to allow two terminals to directly communicate,
from the terminal to the star-centre (called HUB)
and from it to the other terminal, resulting in
physical delay of four times 125-130 ms. Mesh
systems, instead, allow direct communication
between two terminals without crossing the HUB
(physical delay of two times 125-130 ms).
For the specific scenario that have been
simulated, DVB-RCS standard (ETSI EN 301 790,
2003), developed for VSAT systems, has been
selected. The architecture referred to the standard
usually applies to star topology, with a central HUB
called NCC (Network Control Centre). Downlink
channel is broadcasted to all users using DVB-S
standards (ETSI EN 300 421, 1997), while return
channel is shared with a MF-TDMA technique.
DVB-RCS allows each terminal to negotiate
capacity requests on demand for transmission on the
shared return link according to pre-defined service
level agreement:
• volume based dynamic capacity (VBDC), to
issue bandwidth requests based on the actual
volume of traffic needed;
• rate based dynamic capacity (RBDC), to issue
bandwidth request based on the estimation of
transmission rate;
• constant rate assignment (CRA), to obtain
guaranteed bandwidth assignment.
Such an assignment scheme is called DAMA
(Demand Assignment Multiple Access) and it is
used to share the same upload channel dynamically
and efficiently among several terminals. According
to the request policy, different cost may by charged
by the satellite operator.
On the other hand LEO constellations are
composed of several satellites at low orbit (between
700 and 1500 km), which are in continuous
movement with respect to terrestrial Earth surface.
The system is designed to maximize the probability
of user-satellite line of sight even at high latitudes
and handover functionalities must be implemented
in order to keep connection when changing serving
satellite. LEO terminals use omnidirectional
antennas and offer limited bit rate, usually
dimensioned for voice communications (similar to
GSM). Latency is limited to a few ms, but variable
in time and affected to big spikes due to the
handover execution.
Globalstar has been selected for the simulation
campaign (http://www.globalstar.com/en/), due to its
common availability in Europe.
2.2 Terrestrial Wireless Networks
To realize the terrestrial component PANs (Personal
area networks), LANs (local area networks) or
WANs (wide area networks) concepts can be
adopted. The first two are usually associated to
license free bands (IMS), with data throughput
ranging from 1 up to tens of Mbit/s (with a coverage
from few meters to some tens of meters). In
particular Bluetooth (IEEE Std 802.15.1) and Wi-Fi
(IEEE Std. 802.11) are representative technologies
of PAN and LAN, respectively. A WAN is instead
capable of long range coverage with higher
throughput and it usually works either in licensed or
free bands. WiMAX (IEEE Std. 802.16e-2005) is an
example of WAN with allocation of commercial
frequency bands around 3.5 GHz. HIPERLAN
(ETSI EN 300 652, 1998) represents another
example of WAN system working in the unlicensed
band of 5.4 GHz.
For the purpose of our hybrid network proposal,
only the license-free LAN and PAN technologies
will be included, leaving to a future study a more
comprehensive integration of WAN, LAN and PAN
networks together with the satellite segment.
Wi-Fi is a widespread wireless technology that
provides wired-LAN-like connection service to
mobile devices in the range of around 100 m.
Maximal bandwidth available on Wi-Fi variants
ranges from 11 Mbit/s (standard 802.11b) to 54
Mbit/s (standard 802.11a or 802.11g). So far the
infrastructure mode, with a central base station
(called Access Point), has been widely deployed in
most cases, although Wi-Fi foresees an ad-hoc direct
connectivity. A set of base stations can serve up to
128 user terminal each, guaranteeing local mobility.
Newer standard 802.11i and 802.11e are defining
respectively stronger algorithms for security
(WPA2) and QoS at MAC layer.
Bluetooth is a PAN ad-hoc wireless system
which allows terminals to flexibly and
autonomously configure themselves to communicate
without a pre-existing infrastructure in a peer-to-
peer fashion. Bluetooth Standard version 1.1 is the
actual reference implemented in commercial
products such as headsets, GPS devices, etc. It is
designed to offer a total 1 Mbit/s data rate with a
coverage of 10 meters maximum. When Bluetooth
terminals get close enough, they can cluster into a
piconet and temporarily designate one master unit to
PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF WIRELESS SYSTEMS IN TELEMEDICINE - Hybrid Network for Telemedicine with
Satellite and Terrestrial Wireless Links
201

coordinate transmissions with up to seven slave
units. The time needed to join a piconet and start
service is in the order of some seconds.
Bluetooth is based on packet transmission and
frequency hopping (FH) technologies to provide
channelization among different piconets within the
same area, to form the so called scatternets. Each
Bluetooth service has a pre-defined QoS profile to
announce during setup, and it is accepted in the
piconet only if there are enough resources.
3 TELEMEDICINE NETWORK
The set up of a telecommunications network as
support to telemedicine can be extremely difficult in
remote or in disaster-struck areas. For instance, the
installation of a single dedicated point to point radio
link to restore or deliver GSM communication
channels can take several hours. In this context, the
use of satellite terminals can shorten this time to a
few minutes, thanks to the intrinsic broad coverage
of a satellite service. The core satellite network can
be complemented by terrestrial wireless tails
composed of Bluetooth piconets and Wi-Fi links.
3.1 Architecture
The proposed architecture is shown in Figure 1.
Connection between satellite terminal and HUB is
assumed to be alternatively realized with either
DVB-RCS or Globalstar.
An application client on the disaster-struck area
is assumed to be reached directly by the satellite
terminal, or being part of a Bluetooth piconet. In
both cases the connection with the Satellite Terminal
can be wired or realized via a Wi-Fi wireless link
(dashed line). Nodes of different segments are
connected with Ethernet cables or with internal bus
if integrated in the same hardware. In all cases
connectivity is implemented at IP layer to leverage
on IP built-in routing functionalities and address
resolution.
Security and QoS must also be carefully
considered in hybrid networks offering telemedicine
services. QoS is a key issue for real time services,
and must be offered end-to-end along the whole data
path. This means that each segment must be
coordinated centrally for its specific QoS
management setup. Security and encryption, usually
available for each technology independently, must
be ensured also end-to-end, due to the sensitivity of
data transmitted. End-to-end QoS and security could
be handled at IP layer, since it can be considered too
complex an adaptation of different QoS and security
procedures offered by the different technologies at
layer 2. Solutions like DiffServ and secure tunneling
(VPNs) could be adopted.
Figure 1: Network Architecture.
3.2 Reference Applications
Two kinds of applications, both real time and non
real time, will be tested over the proposed network.
Table 1 shows a list of these applications with the
most significant characteristics. The last two rows
show dimensions of representative files which can
be transferred by non real time telemedicine
applications.
Table 1: Telemedicine applications.
Real time
Application Protocol Codec Bitrate
Voice call RTP G729 8÷12 kbit/s
Video call RTP MPEG4 >384 kbit/s
Non Real time
Application
Data
Protocol Size Raw Size
compressed
Radiography FTP 5.7
Mbytes
380 kbytes
ECG trace FTP 90 kbytes 45 kbytes
4 SIMULATIONS
Simulations have been performed using NS2
platform. The architecture introduced in section 3.1
has been set up and verified with the help of NAM
(NS2’s visual output), as shown in Figure 2.
Application clients 4-6 have Bluetooth connectivity
to the Home Gateway. The Home Gateway and the
Application clients 7-8 have a Wi-Fi and wired
Ethernet connectivity to the satellite terminal,
respectively.
HEALTHINF 2008 - International Conference on Health Informatics
202
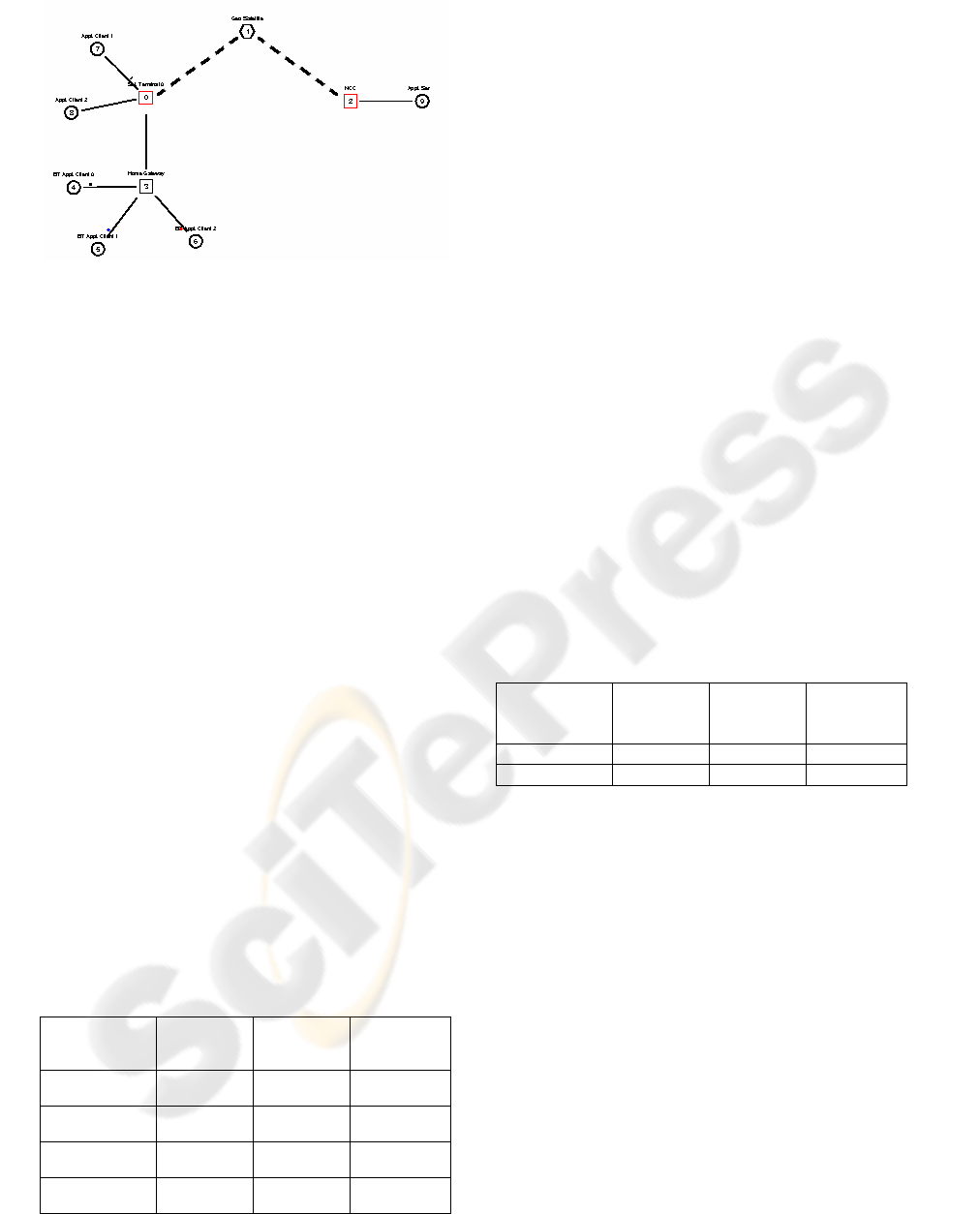
Figure 2: NAM output of NS2 simulation.
Traffic sources originated from Application
Clients are compatible with the applications listed in
Table 1. All the traffic is delivered from the
application clients to the satellite terminal via a
wired or wireless link, through the satellite (in
alternative DVB-RCS or Globalstar) up to the
application server at the other end of the network.
The application server is representing the operative
centre for emergency handling. TCP New Reno has
been used as transport protocol for file transfer and
standard UDP for real time traffic.
For simulations using DVB-RCS as satellite
technology, a return link capacity of 512 kbit/s with
the correct physical delay has been considered. For
DAMA capacity requests, RBDC has been simulated
according to (Roseti and Kristiansen, 2006) while
CRA consists in a granted capacity, similar to a
SCPC service (Single Channel Per Carrier, unshared
uplink channel). For all the other technologies
involved (Bluetooth, WiFi, Globalstar), common
operational values as seen in section 2 have been
used in NS2 simulated links.
Non real time application performances are
summarized in Table 2. For this class of applications
the performance index considered is the average
time needed by the application on a Bluetooth node
to send one data file (including reception and
acknowledgement) to the application server at the
other end of the network.
Table 2: Non Real Time Average Data Transfer Time.
Data Globalstar DVB-RCS
w/ RBDC
requests
DVB-RCS
w/ CRA
requests
Radiography
RAW
Not
performed
140s 115.6s
Radiography
Compressed
333.5s 16s 12.5s
ECG trace
RAW
79.6s 6.9s 4.9s
ECG trace
Compressed
45.9s 4.8s 3.4s
Figures clearly show the differences in
performances between GEO and LEO satellite
system, and also between the two different request
policies for DVB-RCS. The use of satellite to
transfer medical data of limited size is acceptable
under all conditions, while bigger size data transfer
is not practical for narrow band Globalstar satellite
system.
For real time applications, two different setup
have been considered for the two alternative GEO
and LEO satellite systems:
• When using DVB-RCS, a video call with five
simultaneous voice calls with higher quality
profile (12 kbit/s each) have been initiated from
the Bluetooth nodes 4-6. Other two voice calls
have been initiated from Application clients 7
and 8
• Over the Globalstar system, only one voice call
originated by a Bluetooth node could be
performed at the minimum codec rate (8 kbit/s)
In both cases the packet error rate has been
verified to remain under 1%.
The one way average delay of RTP packets
delivery from source to destination, measured at the
two ends of the network, has been used as
performance index for the real time applications.
The averaged delay values are shown in Table 3.
Table 3: Real Time average packets delay (one way).
Data Globalstar DVB-RCS
w/ RBDC
requests
DVB-RCS
w/ CRA
requests
Voice Call 0.27s 0.48s 0.36s
Video Call n.a. 0.61s 0.35s
Globalstar and DVB-RCS with CRA profiles
show similar performances for the voice call average
delay. In fact, in both cases there is no need for
explicit bandwidth requests which introduce an
additional access delay. RBDC request policy has a
bigger average delay compared to the other two
cases, because periodic requests based on estimated
rate must be issued by the terminal to the NCC, thus
increasing the perceived delay by an additional
factor. RBDC is usually associated to a cheaper
contract with satellite operator in comparison with
CRA.
Jitter has resulted limited when simulation
adopted the Globalstar network and the DVB-RCS
with CRA profile. In particular some significant
variations are present during LEO satellite handover,
which was not simulated in our NS set up and
usually occurs every 20 minutes in average.
PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF WIRELESS SYSTEMS IN TELEMEDICINE - Hybrid Network for Telemedicine with
Satellite and Terrestrial Wireless Links
203

Instead, when DVB-RCS system adopts RBDC
access scheme, significant jitter variations are
observed. Please note that RBDC allocation
mechanism is not standardized by DVB and the
reported effect might vary depending on the selected
implementation.
In particular the jitter is due to voice calls
packets pattern, a small packet each 10 ms,
according to the codec standards. Small packets can
trigger the request of a bigger capacity of the
simulated DVB-RCS system which remains
assigned to the terminal for a longer time (in this
simulation 100 ms), resulting in temporary extra
capacity. As consequence, the time needed for the
delivery of packets decreases, resulting in a lower
perceived rate needed. This vicious loop makes
RBDC requests oscillating, together with system
capacity assigned. This affects packet delivery delay
too, which is shown in Figure 3 for a voice call.
Figure 3: Packet delay oscillations on RBDC requests.
A proper de-jitter buffer (Ferrari and Verma,
1991) must be designed at receiver side in order to
compensate the packet arrival latency variations for
this case.
5 CONCLUSIONS
The paper describes a hybrid network for
telemedicine applications adopting satellite networks
and wireless technologies of different kinds. Both
sample real time and non real time applications has
been run in a simulated scenario including all the
described network links, to assess performances.
The results obtained has proven the feasibility of
such an hybrid network including satellite links. In
particular positive results has been obtained with
both GEO and LEO systems, taking into account
limitations of LEO narrow band capacity. The main
differences between different systems and the use of
different request policies for DVB-RCS has been
discussed.
REFERENCES
S. Arenaccio, F. Aversa and M. Luglio, 2006. A satellite
based wireless network for telemedicine: the Telesal
Project. In 12
th
Ka and Broadband Communications
Conference, Naples, Italy, pp.749-754.
M. Luglio, F. Vatalaro, 2002. The Use of Wireless
Technology for Telemedicine. In Symposium on
Telemedicine In Care Delivery, Technology and
Application, pp.353-359
K. Fall and K. Varadhan, 2007. The NS Manual,
http://www.isi.edu/nsnam/ns/doc/index.html
ETSI EN 301 790, 2003, Digital Video Broadcasting
(DVB); Interaction Channel for Satellite Distribution
System, V1.3.1.
ETSI EN 300 421, 1997, Digital Video Broadcasting
(DVB); Framing structure, channel coding and
modulation for 11/12 GHz satellite service, V1.1.2.
ETSI EN 300 652, 1998, Broadband Radio Access
Networks (BRAN) - HIgh PErformance Radio Local
Area Network (HIPERLAN) Type 1, v1.2.1
IEEE Std 802.15.1, 2002, Wireless MAC and PHY
Specifications for Wireless Personal Area Networks
(WPANs™)
IEEE Std 802.11, 1999, Wireless LAN Medium access
control (MAC) and Physical Layer (PHY)
Specifications.
IEEE Std 802.16e-2005, Air Interface for Fixed
Broadband Wireless Access Systems- Physical and
MAC Layers for Combined Fixed and Mobile
Operation in Licensed Bands.
C. Roseti and E. Kristiansen, 2006, TCP behaviour in a
DVB-RCS environment. In Proceedings of 24th AIAA
International Communications Satellite Systems
Conference (ICSSC), San Diego.
D. Ferrari and D. Verma, 1991. Buffer Space Allocation
for Real-Time Channels in a Packet Switching
Network. Technical report, Information Computer
Science Institute, Berkeley, California.
HEALTHINF 2008 - International Conference on Health Informatics
204
