
MYHEART
Fighting Cardio-vascular Diseases by Prevention and Early Diagnosis
Ralf Schmidt, Jörg Habetha and Matthew Harris
Philips Research Europe, Weisshausstrasse 2, 52062 Aachen, Germany
Keywords: Personal Healthcare, cardio-vascular, prevention, vital body signs, wearables.
Abstract: MyHeart is an Integrated Project of the European Union aimed at developing intelligent systems for the
prevention and monitoring of cardiovascular diseases. The approach of the MyHeart project is to monitor
Vital Body Signs (VBS), to process the measured data and to give the user (therapy) recommendations.
Using its broad base of technical and business expertise, four concepts addressing cardiac health have been
developed and tested on a technical, business, realisability and usability level.
1 INTRODUCTION
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is the leading cause
of death in developed countries. Roughly 45% of all
deaths in the EU, and 37% in the U.S. are due to
CVD (Thom, 2006). Hundreds of billions of Euros
are spent worldwide each year on the treatment of
CVD. In order to maintain and improve the quality
of heath care without exploding costs, heath care
systems are undergoing a paradigm shift from
patient care in the hospital to care at home.
A healthy and preventive lifestyle as well as
early diagnosis of heart disease could save millions
of life years annually, simultaneously reducing the
morbidity and improving patient quality of life.
Prevention offers the opportunity to systematically
fight the origin of cardio-vascular diseases as well as
to improve the medical outcome after an event. To
enable a preventative health care system, a move is
required from the current, event driven treatment to
continuous and ubiquitous access to medical
excellence. Innovative methods are needed that
provide access to medical excellence in a cost-
effective way.
The MyHeart consortium (MyHeart, 2004)
involves 33 partners from 10 different countries. It is
a balanced multidisciplinary consortium of industry
(including Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs)),
research institutes, academia and medical hospitals.
Prominent industrial partners are Philips, with its
medical and technological expertise, Vodafone
(Foundation) as a leading service provider, and
Medtronic, a world-leader in cardiac technology.
The project started in January 2004 and has a
total duration of 45 months (until September 2007).
It is one of the largest biomedical and healthcare
research projects in the European Union with a
budget of about 35 million Euros.
The project brings technical capabilities in
functional clothing, on-body electronics, user
interaction, professional interaction, and algorithmic
development together with the business assessment
and development capabilities necessary to bring new
health technologies to the health care system.
The technological needs for MyHeart
applications span a wide range covering: monitoring
of vital signs (ECG, respiration, activity, etc.); body-
worn, low-power, mixed-signal hardware which runs
algorithms for detection of health status and
prediction of acute cardiac events; user interfaces for
citizens and medical professionals; low-power
wireless links and server architectures for data
handling at professional sites.
2 THE MYHEART APPROACH
It is the aim of the MyHeart project to fight CVD by
prevention and early diagnosis. This is done by
monitoring Vital Body Signs (VBS) with wearable
technology, processing the measured data and giving
(therapy) recommendations to the user of the
system. Using the measured data to give user
296
Schmidt R., Habetha J. and Harris M. (2008).
MYHEART - Fighting Cardio-vascular Diseases by Prevention and Early Diagnosis.
In Proceedings of the First International Conference on Health Informatics, pages 296-300
Copyright
c
SciTePress

feedback ‘closes the loop’ of measurement and
therapy. As illustrated in figure 1, this closed loop
can either consist of direct local feedback to the user
or of professional help by a physician or nurse. The
latter will typically be provided remotely, which
implies that the MyHeart system also comprises a
telemedical element. Data are transmitted to a
remote server, where a professional can access the
data and contact the patient subsequently.
VBS
Acquisition
Care Provider
Patient
Management
VBS
Processing +
Visualization
Patient
Self-management
Patient
Status
VBS
Acquisition
Care Provider
Patient
Management
VBS
Processing +
Visualization
Patient
Self-management
Patient
Status
Figure 1: MyHeart disease management and prevention
approach.
The system can be used for helping people to
lead a healthier life as well as for the improved
management of chronic diseases
.
3 THE MYHEART CONCEPTS
MyHeart has taken a very innovative approach in
ensuring the applicability of the project results in the
real world. The consortium has started with a set of
application ideas and only afterwards investigated
the necessary technologies in order to serve these
applications.
A concept is a concrete CVD application tailored
to a specific user group or customer segment. The
MyHeart project began with 16 concepts.
In the first one and a half years of the project, the
16 application concepts worked on answering the
following questions in detail:
• What is the application/value proposition?
• Who are the customers and how to address
them?
• How to do it technically?
• Why to believe in the concept (How to
prove that it delivers what is claimed)?
• Where is the business?
In mid 2005, 4 of the 16 concepts were selected
for further development in the remaining two years
of the project. The criteria for selecting or
combining concepts were:
• Medical credibility and feasibility
• Technical credibility and feasibility
• Business credibility and feasibility
• Critical project success factors (like size
and excellence of the consortium)
The selected product concepts cover four major
user segments: the healthy (Activity Coach), those at
risk for developing CVD (Take Care), sufferers from
a cardiac event (Neurological Rehabilitation), and
chronically ill people (Heart Failure Management).
In the following sections, the four product concepts
are presented.
3.1 Activity Coach
The value proposition for the Activity Coach is to
empower and allow the end user get maximum
benefit from regular exercise sessions, both in terms
of pleasure and health impact, anywhere, anytime
through giving professional, easy to understand
coaching which is tailored to the user’s profile, goals
(Dunn, 1999) and personal performance.
The target group is people exercising for fitness
and fun. The activity coach will help guide and
motivate this group, both in the fitness studio and
outdoors to give them optimal exercise result for the
effort given.
As shown in figure 2, the system consists of four
main components:
The Body Signal Sensor (BSS), integrated into
a textile garment, is responsible for monitoring the
required vital signals. A one lead ECG is used to
derive the heart rate. A stretch sensor is used to
measure respiration rate. Furthermore, an
accelerometer is used to measure the step rate while
running.
The Fitness Coach Bike (FCB) is an indoor bike
with integrated sensors measuring the pedaling rate,
a processing and communication unit, and a user
interaction device.
The Personal Mobile Coach (PMC) is a device
for the outdoor scenario. It receives data from BSS
via Bluetooth and generates appropriate feedback
and interacts with the user and the service centre.
The Fitness Coach Service Centre (FCSC) is
the professional platform that provides online
services to the user. It receives all the data from the
session, processes it using algorithms for fitness
status assessment and performance analysis, and
stores all the results. It also provides a web-based
interface through which professional users are able
to access different functionalities such as session
results visualisation, messaging services, or the
training program schedule.
MYHEART - Fighting Cardio-vascular Diseases by Prevention and Early Diagnosis
297
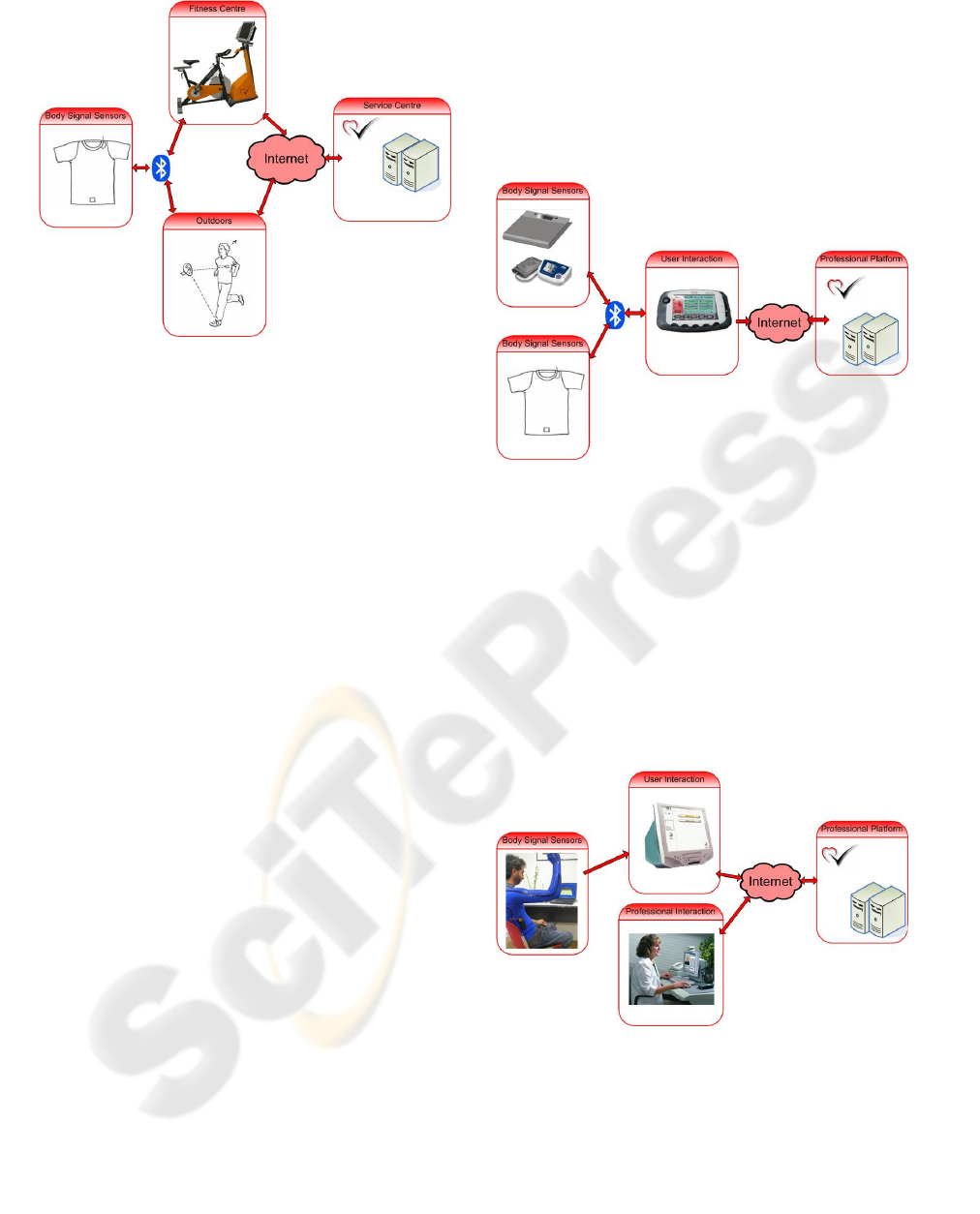
Figure 2: Architecture of the Activity Coach System.
During exercise, body and exercise equipment
sensors measure heart rate, respiration rate,
temperature and step or pedal rate. The data is
processed by personalised algorithms, and user
feedback is given on the FCB and the PMC. When
using the FCB, the level of exercise can also be
adapted automatically, guiding the user through the
exercise. The system coaches and motivates the user
to continue the trainings plan, and creates an
immersive environment.
3.2 Take Care
The value proposition of Take Care is to empower
the user to change her lifestyle by assessing CVD
risk factors and providing appropriate improvement
plans and personalised recommendations (Duchna,
2003; Euroaspire, 2001; Gordon, 2004).
By providing reliable and trustworthy education,
monitoring and coaching, the Take Care system
aims at supporting the user to learn and listen to
his/her own body, reducing the risk factors for CVD.
The Take Care system is aimed at healthy users that
have risk factors for CVD that are willing to spend
money out of their own pocket for help in adpoting a
healthier lifestyle.
As shown in Figure 3, the Take Care user
interaction (UI) device is at the centre of the Take
Care system. It is the platform for giving feedback
and receiving input from the user, receiving input
from sensors, and running personalised algorithms.
To initialise the system, initial user data from a
weight scale, a blood pressure meter and a
cholesterol meter are inputted into the UI device and
used to automatically generate a risk profile and
lifestyle plan. The UI device then controls and
communicates with the measurement devices,
following a daily routine. It receives vital body signs
(heart rate, respiration rate and activity level) from
the on-body electronics connected to textile sensors,
and sleep quality data from piezo and textile
electrodes integrated into the bed. The data is
processed on the UI device, which then gives
feedback and coaching to the user. The UI device
can also forward the data to a professional centre for
further examination.
Figure 3: Architecture of the Take Care System.
3.3 Neurological Rehabilitation
The value proposition of the Neural Rehabilitation
concept is to enable early intensive rehabilitation for
patients following a cerebrovascular event (Sulch,
2001; Micieli, 2002) by using a telemonitoring
system, using wearable technology, speech therapy
tools, learning tools and communication tools.
The main users are patients with stroke
symptoms, physicians, physiotherapists, and
occupational therapists.
Figure 4: Architecture of the Neurological Rehabilitation
System.
The patient station, connected to the therapist
station, the server site and the user sensors, is the
user interface with the patient, giving feedback on
the exercises carried out. Wearable electronics
integrated into an upper torso garment is used to
HEALTHINF 2008 - International Conference on Health Informatics
298

monitor the patient movement during rehabilitation
exercises. A speech therapy unit is used to carry out
and evaluate speech exercises.
The therapist site is used by the physician to
monitor the patient’s exercises and progress. At
present, the therapist can only monitor the patient
exercises offline. In the future, online monitoring
could be possible.
The server site is a central server that hosts a
database of configurations, exercises, session
recordings, demographic data, and the rehabilitation
protocol. The physician may access the server
through the therapist site to configure the treatment
for a particular patient, or to view the recorded data.
The system consists of three main stations (the
patient station, the therapist station, and the server
site), and the communication structure between
them.
3.4 Heart Failure Management
The main objective of the Heart Failure
Management concept is to improve the outcome of
heart failure patients with respect to mortality,
morbidity and quality of life (Swedberg, 2005;
Steward, 2001). This objective is achieved by
monitoring vital body signs that are relevant for
heart failure on a daily basis (currently these
parameters are only measured at infrequent visits to
the physician) using easy to use equipment in the
patient’s home. The data is automatically analysed
in order to detect changes in the patient’s health
status early enough to allow early therapy
intervention, thus avoiding severe deterioration and
hospitalisation.
The end users of the system are patients with
heart failure (NYHA classes II-IV), and the
physicians and nurses caring for the patient.
Typically, the system would be funded by disease
management organisations (DMO) and health care
insurances.
The user interface for the heart failure concept is
a PDA. Like in the Take Care concept, it is the
platform for giving feedback and receiving input
from the user, receiving input from sensors, and
running personalised algorithms. The PDA controls
and communicates with the measurement devices. A
textile vest with integrated textile sensors and
wearable electronics is used to measure vital body
signs relevant for heart failure management. ECG
sensors incorporated into the bed sheet and pillow,
and a piezo sensor under the sheet capture ECG,
breathing and movement data during the night. A
weight scale and blood pressure cuff send their
measured values to the PDA using Bluetooth. The
PDA uses personalised algorithms to process the
measured data, and to detect a possible deterioration
in the patient’s health status, triggering action by the
patient or medical professional.
The PDA also communicates with a professional
platform which receives preprocessed patient data
and gives health care professionals access to the
application configuration, and the patient’s data.
Figure 5: Architecture of the Heart Failure Management
System.
4 VA L I D AT I O N
Medical and technical validation and business
assessment are important aspects to be addressed by
each MyHeart concept. In each concept studies are
being carried out with prototype systems with end
users to assess usability and medical effectiveness.
For the Heart Failure concept an observational study
with 200 heart failure patients will be carried out in
Germany and Spain. In this one year study, the heart
failure system will be used to make daily
measurements of vital body parameters. At the end
of the study, medical incidents will be correlated
with the measured data to deduce which
(combination of) parameters can be used to give
warnings of a forthcoming decompensation.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was supported in part by the IST-2002-
507816 MyHeart Project.
REFERENCES
Thom, T. et al., 2006. AHA Statistical Update. Heart
Disease and Stroke Statistics - 2006 Update
Circulation. 113:e85-e151.
MyHeart IST-2002-507816 project, 2004. Information
available on http://www.cordis.lu/ist.
MYHEART - Fighting Cardio-vascular Diseases by Prevention and Early Diagnosis
299

Dunn A et al., 1999. Comparison of Lifestyle and
Structured Interventions to Increase Physical Activity
and Cardiorespiratory Fitness. JAMA 28:327.
Duchna HW et al., 2003. Sleep Disordered Breathing and
Cardio and Cerebrovascular Diseases: Update of
Clinical Significance and Future Prospectives. 2003
Somnologie 7: 101-121.
Lifestyle and Risk Factor Management and Use of Drug
Therapies in Coronary Patients from 15 Countries –
Principal Results from EUROASPIRE II, 2001.
European Heart Journal 22: 554-572.
Gordon NF et al., 2004. Getting Risk Factors to Goal:
Lifestyle Intervention is Worth the Effort in Patients
With Hypertension, Hyperlipidemia and/or
Hyperglycemia. 53rd Annual Scientific Sessions of
American College of Cardiology. New Orleans.
Sulch D et al., 2001. Randomized Controlled Trial of
Integrated (Managed) Care Pathway for Stroke
Rehailitation. Stroke 31:1929-34.
Micieli G et al., 2002. Guideline Application for Decision
Making in Ischemic Stroke (GLADIS) Study Group.
Guideline Compliance Improves Stroke Outcome: A
Preliminary Study in 4 Districts in the Italian Region
of Lombardia. Stroke: 33(5) 1341-7.
Swedberg K et al., 2005. Guidelines for the Diagnosis and
Treatment of Chronic Heart Failure: Executive
Summary (Update 2005): The Task Force for the
Diagnosis and Treatment of Chronic Heart Failure of
the European Society of Cardiology. Eur Heart J:26
1115-1140.
Stewart S and Blue L (Ed.), 2001. Improving Outcomes in
Chronic Heart Failure, BMJ Books.
HEALTHINF 2008 - International Conference on Health Informatics
300
