
ECG SIGNAL DENOISING
Using Wavelet in Besov Spaces
Shi Zhao, Yiding Wang
Graduate University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Zhongguancun East Road, Beijing, China
Hong Yang
Graduate University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Zhongguancun East Road, Beijing, China
Keywords: ECG, noise reduction, wavelet, Besov, nonlinear shrinkage function.
Abstract: This paper proposes a novel technique to eliminate the noise in practical electrocardiogram (ECG) signals.
Two state-of-the-art denoising techniques, which both based on wavelet bases, are combined together. The
first one is discussing wavelet bases in Besov spaces. Compared to traditional algorithms, which discuss
wavelets in
2
()
L
R spaces, the proposed technique projects ECG signals onto Besov spaces for the first time.
Besov space is a more sophisticated smoothness space. Determining the threshold of shrinkage function in
Besov space could eliminate Gibbs phenomenon. In addition, instead of using linear shrinkage function, the
proposed algorithm uses nonlinear hyper shrinkage function, which is proposed by Poornachandra. The
function tends to keep a few larger coefficients representing the function while the noise coefficients tend to
be reduced to zero. Combining the two techniques, we obtain a significant improvement over conventional
ECG denoising algorithm.
1 INTRODUCTION
Removing noise is an pertinent problem in ECG
signals processing. Usually, there are two kinds of
noises in ECG, power line frequency noise and
white noise. Power line frequency noise can be
regarded as the result of an electromagnetic
compatibility issues: background electromagnetic
field interference from surrounding equipments and
from buldings and power conductors. White noise is
usually considered from the measure equipment.
Previously, different filters based on Fourier
bases are used to eliminate the noises, such as notch
filter. The problem of these methods is that they
could not reduce the two kinds of noises at the same
time. In addition, because the notch has a relatively
large bandwidth, which means that the other
frequency components around the desired null are
severely attenuated, this method brings in signal
distortions. In 1995, Donoho (David L Donoho,
1995) proposed a novel denoising algorithm based
on wavelet shrinkage. It provides excellent
performance and since then, wavelets became a
state-of-the-art denoising method. Before long, P. M
Agante (P M Agante, 1995) applied soft-threshold
method in ECG and achieve good results. However,
traditional wavelet method has its drawbacks. They
are not shift invariant; therefore, for the signals not
smooth enough, it will appear Gibbs Oscillation
phenomenon at the location where the signal is sharp
changed. In ECG signals, there are R waves, which
change sharply. As a result, Traditional wavelet
denoising algorithm brings in Gibbs oscillation after
R waves.
In this paper, we apply two techniques to
eliminate the noise and restrain the Gibbs
phenomenon at the same time. First, we determine
the threshold of wavelet shrinkage function in Besov
spaces. Besov space
()
P
q
B
L
α
is a smoothness space
with
0
σ
> ,
2
(,) [1, )pq
∈
+∞ , it is defined by
()
(){ ()| }
P
q
Pp
q
BL
BL f LR f
α
α
=
∈<∞
(1)
Where the Besov seminorm
()
P
q
BL
α
is linked to the
smoothness modulus of the considered function.
Besides that, in stead of linear shrinkage function,
we use nonlinear shrinkage model (S.
Poornachandra, 2007). Combining the two novel
250
Zhao S., Wang Y. and Yang H. (2008).
ECG SIGNAL DENOISING - Using Wavelet in Besov Spaces.
In Proceedings of the First International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing, pages 250-254
DOI: 10.5220/0001058302500254
Copyright
c
SciTePress

techniques, we obtain a significant improvement
over conventional wavelet denoising algorithm. In
order to certify our idea, the noises in ECG signals
in our experiment are not added by hand. They are
from actual interfering. We collect the ECG signals
with noises by our own devices.
2 INTRODUCTION TO WAVELET
SHRINKAGE FUNCTION IN
BESOV SPACE
Wavelet is defined as orthonormal basis functions
for the expansion of functions belonging to various
function spaces. Usually, it is the space of squared
integrable real functions
2
()
L
R (functions with finite
energy). Recently, it has been shown that more
sophisticated smoothness spaces, such as Besov
spaces, provide a suitable and more refined
characterization of real-life signals (Kathrin
Berkner, 2000). The wavelet series representation of
a function
2
() ( )
f
tLR∈ could be express as
00
0
0
21 21
() () ()
jj
jk k jk jk
kZ j j kZ
d
f
tct t
ϕψ
−∞−
∈=∈
=+
∑∑∑
(2)
ϕ
is called farther wavelet and
ψ
is called mother
wavelet.
,
()
jk
t
ϕ
and
,
()
jk
t
ψ
are the dilation and
translation of the wavelet function.
/2
,
() 2 (2 )
jj
jk
tk
ϕϕ
=−
(3)
/2
,
() 2 (2 )
jj
jk
tk
ψψ
=−
(4)
j
, k are the scaling and translation parameters
respectively,
,jk Z∈
,
/2
2
j
could maintain the unity
norm of the basis function at various scales. The
coefficients
00
,
j
kjk
cg
ϕ
= and ,
j
kjk
dg
ψ
= . Often
we set
0
0j =
, and in that case there is only one
scaling coefficient. The wavelet series are usually
discussed in
2
()
L
R spaces, but in our research, we
use a more sophisticated set of functions, Besov
spaces
()
P
q
B
L
α
( 0
α
<<∞, 0 p<≤∞, 0 q<≤∞). In
Besov spaces, for a function
()
P
q
f
BL
α
∈ , its norm
could be defined using its wavelet coefficients as (5)
(Kathrin Berkner , 2000)
0
0
1
1
/
(/21)
()
|| || | | 2 | |
P
q
qp
q
p
pjppp
jk jk
BL
kjjk
fc d
α
α
+−
>
⎛⎞
⎛⎞⎛ ⎞
⎜⎟
=+
⎜⎟⎜ ⎟
⎜⎟
⎝⎠⎝ ⎠
⎝⎠
∑∑∑
(5)
The three Besov parameters have natural
interpretations: a
p
-norm of the wavelet
coefficients is taken within each scale
j
, a weighted
q -norm is taken across scale, and the smoothness
parameter
α
controls the rate of decay of the
j
k
d ,
increasing
α
corresponds to increasing smoothness.
Based on reference (Antonin Chambolle, 1998),
the denoising problem could be described as follow.
Given a positive parameter
λ
and a signal
f
, find a
function
f
%
that minimize over all possible function
the functional
2
2
0
()
|| || || ||
2
P
q
q
B
LL
fff
α
λ
+−
(6)
Choose a proper
λ
, the
f
%
could be the denoising
signal of
f
. For simpleness, we set Besov
parameters
1pq
=
= . Then the problem could be
expressed as follow:
()
2
(1/2) 0
,,,
,,
min 2 | |
2
j
jk jk jk
jk jk
ddd
α
λ
−
+−
∑∑
(7)
That means for each
j
, k , we estimate the d
)
use follow expression:
2(1/2)
0
(1/2)
00
()2 ||
2
()max(| |2 /)
arg min
j
d
j
dd
sign d d
d
α
α
λ
λ
λ
−
−
−+
=⋅ −
=
)
(8)
That means the ECG signal has small Besov
norm if the wavelet coefficient in each scale have
small
1
l norms and those
1
l norms decay rapidly
across scale.
Note that any wavelet basis having
r
α
>
vanishing moments can be used to measure a Besov
norm (Hyeokho Choi, 2004).
3 INTRODUCTION TO
NONLINEAR SHRINKAGE
MODEL
Donoho and Johnstone were first to formalize the
wavelet coefficient thresholding for removal of
additive noise from deterministic signals (David L
Donoho, 1995). Wavelet thresholding is based on
the property that typical real-world signals have
sparse representations in the wavelet domain. The
small coefficients are usually correlated to noise.
Therefore, by choosing an orthogonal basis, which
could efficiently approximates the signal with few
nonzero coefficients; we could choose a particular
threshold and set the coefficient bellow the threshold
to zero. Using these coefficients in an IDWT to
reconstruct the data, we could kill the noise.
ECG SIGNAL DENOISING - Using Wavelet in Besov Spaces
251

The shrinkage function proposed by Donoho and
Johnstone are the hard and the soft shrinkage
function. Hard thresholding simply sets the
coefficients below a threshold T to zero, as (9). Soft
thresholding first shrinks each coefficient by
T and
then hard thresholds, as (10).
0,
()
,
H
T
x
x
δ
=
||
||
x
T
x
T
≤
>
(9)
(
)
( ) sgn( ) | |
S
T
x
xxT
δ
+
=−
(10)
Both hard and soft shrinkages have their
disadvantages. Due to the discontinuities of the
shrinkage function, hard shrinkage estimate tends to
have bigger variance and can be unstable, that is,
sensitive to small changes in the data. The soft
shrinkage estimate tends to have bigger bias, due to
the shrinkage of large coefficients (S.
Poornachandra, 2007).
To overcome the drawbacks of hard and soft
shrinkage, we decide to use nonlinear shrinkage
function. There are two kinds nonlinear shrinkage
estimate in our experiment. The first is called
nonnegative garrote shrinkage function (M. Vetterli,
1995), which was first introduced by Breiman
(1995) as follow:
2
() 1 ( / )
G
xx x
λ
δλ
+
⎡⎤
=−
⎣⎦
(11)
The shrinkage function
()
G
x
λ
δ
is continuous and
it provides a good compromise between the hard and
the soft shrinkage functions. It is less sensitive than
hard shrinkage to small fluctuations and less biased
than soft shrinkage. The second shrinkage function
is called hyper shrinkage, which is proposed by S.
Poornachandra as follow:
(
)
( ) tanh( * ) | |
hyp
x
xxt
λ
δρ
+
=−
(12)
The major advantage of hyper shrinkage is its
nonlinearity, that is, the function in wavelet domain
tends to keep a few larger coefficients representing
the function while the noise coefficient tend to be
reduced to zero.
4 NOISE REDUCTION BY OUR
METHOD
The objective of this paper is to eliminate the noise
buried in practical ECG signals. In our research, we
combine the two techniques we mention above.
First, we determined the threshold of shrinkage
function for each level in Besov spaces. It is
obviously that for each subband, the parameter
α
should be different. We set
j
α
for each level
experimentally. Then we use the two kinds of
nonlinear shrinkage functions to obtain the estimated
coefficients. Finally, using these coefficients the
original ECG signal is thus recovered. The general
process is showed bellow. The decomposition level
is 6.
Step 1. Choose db3 wavelets, and do DWT.
Step 2. Choose
α
at each level. For the fist level
0
0.9
α
=
, and
0
0.25* (log( 2))
j
sqrt j
α
α
=
++
for each
level.
Step 3. Determine the threshold based on the
j
α
.
Step 4. Apply hyper shrinkage function and the
estimated coefficients obtained.
Step 5. IDWT use the estimated coefficients.
5 SIMULATIONS AND RESULTS
In our research, the ECG signals are obtained by our
own devices. Each piece of signal is about 1 min
long. The sampling rate is 1200Hz.
In our research, we use five different denoising
methods. We show original signal and the processed
4 signals and their spectrums in Fig.1 to Fig.6. In
order to see clearly, we show their details of the
sample points around R waves. The method in Fig.2
determines the threshold in
2
()
L
R spaces and use
hard thresholding shrinkage function, while in Fig.3
the thresholds is determined in
2
()
L
R spaces and use
soft thresholding method. The other three discuss the
thresholds in Besov spaces. Whereas Fig.4 uses soft
shrinkage function, Fig.5 use nonnegative garrote
shrinkage function and the last one uses hyper
shrinkage function.
Figure 1: The original signal and its spectrum.
BIOSIGNALS 2008 - International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing
252
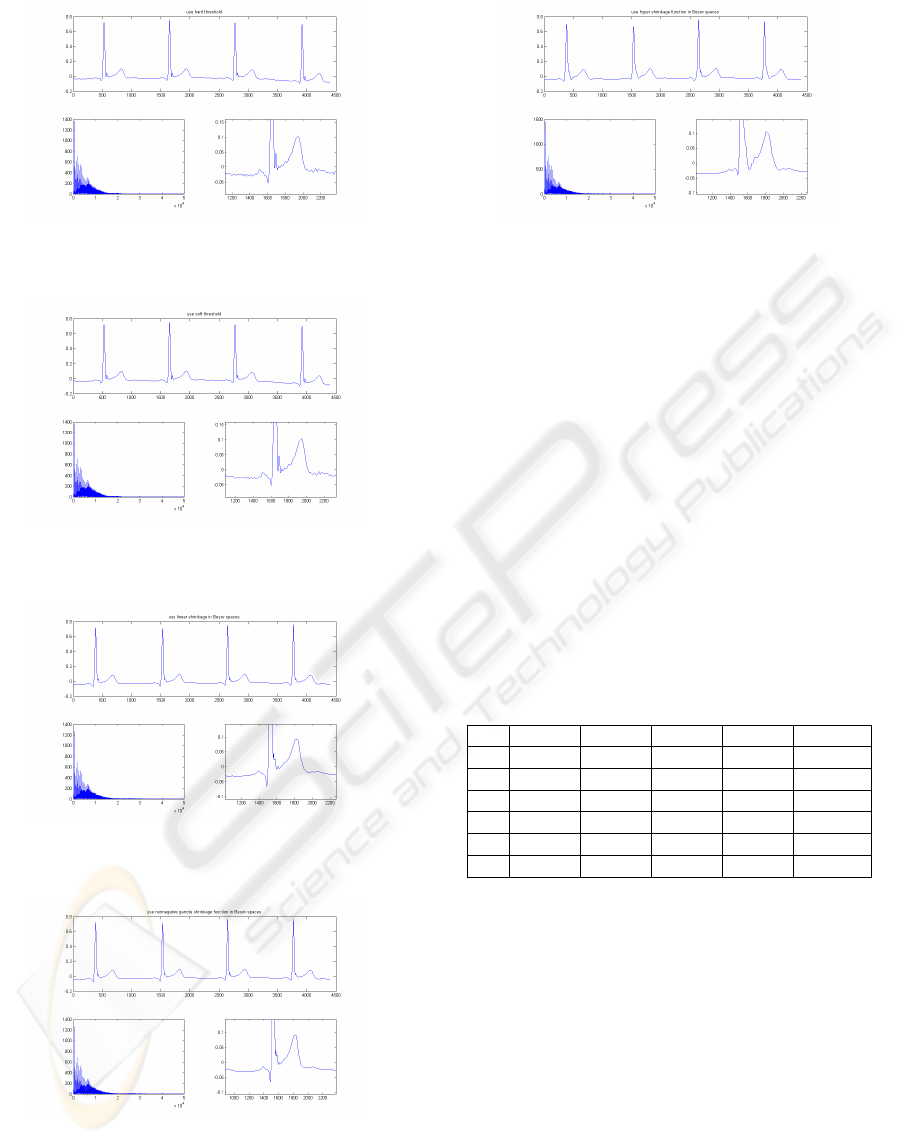
Figure 2: Determine the threshold in
2
()
L
R and use hard
thresholding.
Figure 3: Determine the threshold in
2
()
L
R and use soft
thresholding.
Figure 4: Determine the threshold in Besov spaces and use
soft thresholding.
Figure 5: Determine the threshold in Besov spaces and use
nonnegative garrote shrinkage function.
Figure 6: Determine the threshold in Besov spaces and use
hyper shrinkage function.
As we seen from the pictures above, combined
with threshold determined in Besov spaces and
hyper shrinkage function, the recovered signal is the
most visually pleasant. The proposed technique
almost eliminate Gibbs phenomenon. To describe
the oscillation of the recovered signal
quantificational, we calculate the total variation of
the six signals. Total variation for a uniform
sampling discrete signal
f
is defined as (S. Mallat,
1998).
|| || | [ ] [ 1]|
NV N N
n
ffnfn
=
−−
∑
(13)
Where
|| ||
NV
f is the Total Variation. In order to
certify the effectiveness of the proposed method, we
give 4 pieces of signals’ Total Variation. They are
show in Table 1.
Table 1: Total Variation of the signals.
1 2 3 4 average
T1 0.3914 0.3747 0.3801 0.3875 0.3834
T2 0.1789 0.1654 0.1388 0.1252 0.1521
T3 0.1789 0.1654 0.1388 0.1252 0.1521
T4 0.1721 0.1517 0.1006 0.1177 0.1355
T5 0.1758 0.1504 0.1030 0.1206 0.1374
T6 0.1431 0.1371 0.0803 0.0919 0.1131
In the above table, T1 means the original signals’
Total Variation. T2 to T6 correspond Fig.2 to Fig.5.
In the table, we could notice easily that discussing
threshold in Besov space and using nonlinear
shrinkage function could obtain good results. And
among those, hyper shrinkage is the most effective,
it has the least oscillation.
6 CONCLUSIONS
This paper proposes a novel approach to eliminate
the noises in practical ECG Signals. First, we use the
characterization of Besov space, which is a
smoothness spaces, through wavelet
ECG SIGNAL DENOISING - Using Wavelet in Besov Spaces
253

decompositions. Then we apply nonlinear shrinkage
function instead of linear shrinkage function. The
experiment results show that the proposed algorithm
is visually pleasant compared to traditional methods.
It could eliminate the noise successfully, and at the
same time, it suppresses Gibbs oscillation. The
proposed technique has potential application in data
acquisition systems, which are generally
encountered by noise.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This research is supported by High Technology
Research and Development Program of China (863
Program): 2006AA01Z133. The ECG signals
collection device is designed by Shen Yadong, who
is a graduate student in Tsinghua University, China.
REFERENCES
S. Poornachandra, N. Kumaravel, 2007. A novel method
for the elimination of power line frequency in ECG
signal using hyper shrinkage function. Digital Signal
Process, doi:10.1016/j.dsp.2007.03.011.
S. Mallat, 1998. A Wavelet Tour of Signal Processing.
Academic Press. San Diego, 2
nd
edition.
David L Donoho, 1995. De-noising by soft thresholding.
IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 41(3): 613-627.
P M Agante, J P Marques de Sa, 1995. ECG noise filtering
using wavelets with soft-threshold method. IEEE
Computers in Cardiology, 26:535-538.
M. Vetterli, J. Kovacevic, 1995. Wavelet and Subband
Coding. Prentice Hall International, Englewood Cliffs,
NJ.
Kathrin Berkner, Michael J. Gormish, Edward L.
Schwartz, and Martin Boliek, 2000. A new wavelet-
based approach to sharpening and smoothing of
images in Besov spaces with applications to
deblurring. Proceedings. 2000 International
Conference on Image Processing, Vol 3: 10-13
Hyeokho Choi, Richard G. Baraniuk, 2004. Multiple
wavelet basis image denoising using Besov ball
projections. IEEE signal processing letters, Vol. 11.
NO.9.
D. Leporini, J. C. Pesquet, 2000. Bayesian wavelet
denoising: Besov priors and non-Gaussian noises.
Elsevier Science Signal Processing,81: 55-67.
Alexandre Almeida, 2004. Wavelet bases in generalized
Besov spaces. Elsevier mathematical analysis and
applications, Appl.304: 198-211.
Antonin Chambolle, Ronald A. DeVore, Nam-yong Lee,
and Bradley J. Lucier, 1998. Nonlinear wavelet image
processing: variational problems, compression, and
noise removal through wavelet shrinkage. IEEE
Transactions on image processing, Vol. 7, NO.3.
BIOSIGNALS 2008 - International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing
254
