
MOUSE CONTROL THROUGH ELECTROMYOGRAPHY
Using Biosignals Towards New User Interface Paradigms
Vasco Vinhas
Faculdade de Engenharia da Universidade do Porto, Rua Dr. Roberto Frias s/n, Porto, Portugal
LIACC - Artificial Intelligence and Computer Science Laboratory, Rua Campo Alegre 823, Porto, Portugal
Antonio Gomes
Faculdade de Engenharia da Universidade do Porto, Rua Dr. Roberto Frias s/n, Porto, Portugal
Keywords:
Medical Signal Acquisition, Analysis and Processing, Real-time Systems, User Interfaces.
Abstract:
Recent technologic breakthroughs have enabled the usage of minimal invasive biometric hardware devices
that no longer interfere with the audience immersion feeling. The usage of EMG to extend traditional mouse-
oriented user interfaces is a proof-of-concept prototype integrated in a wider horizon project. A subset of
the main project’s architecture was reused, specially the communication middleware, as a stable development
platform. An originally intended EEG hardware was adapted to perform EMG and therefore detect muscular
activity. It was chosen, as a practical proof-of-concept, that it was desired to detect winking as a triggering
device to perform a given traditional user interface action. The described application achieved extremely
positive records with hit rates of around 90%. The volume of false positives and undetected desired actions
are considered negligible due to both system development stage and application contextualization - non critical
systems. The success and acceptance levels of the project are really encouraging not only to the enhancement
of the proposed application but also to the global system continuous development.
1 INTRODUCTION
In this global scenario, the authors have defined and
already started a research project precisely with the
intention of using biosignals to assess user emotions
and use this information to enable subconscious in-
teraction. The contextualization of this work has nu-
merous points of interest both in the academic com-
munity and in commercial applications. The usage
of new hardware solutions and biosignals to enhance
traditional user interface paradigms or even to enable
new ones has managed to bring together multidisci-
plinary private organizations and research communi-
ties. In spite of the main project being still in an initial
stage, several high-level decisions have already been
taken and a high percentage of them have been either
implemented or designed.
Perfectly integrated in this scope, it was decided
to produce a spin-off application capable of testing
the global architecture and, simultaneously, generate
experimental results capable of test initial hypothesis
and therefore confirm them or generate new discus-
sion paths. The mouse control tool enabled trough
EMG is a proof-of-concept project with two distinct
sets of objectives.
The first encloses the goals directly related to
the experimentation and test of new interaction
paradigms by using innovative hardware solutions.
More specifically, it is intended to trigger regular
mouse interaction like right click or drag operations
by detecting user winking. Once again, these defined
actions have merely conceptualization purposes and
can be easily altered.
The second group of objectives regards the reuse
and consequent validation of the main project archi-
tecture, namely communication protocol and multiple
sensors data integration. With this option, the authors
are able to validate the defined approach by early pro-
ducing research results.
This document is organized as follows: in the next
section the current state of the art is presented, in sec-
tion 3 the mouse control project is described, specially
the most significant decisions are detailed and justi-
fied. In section 4, experimental results are presented
and related conclusions are extracted in section 5 as
well as future work areas are identified.
371
Vinhas V. and Gomes A. (2008).
MOUSE CONTROL THROUGH ELECTROMYOGRAPHY - Using Biosignals Towards New User Interface Paradigms.
In Proceedings of the First International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing, pages 371-376
DOI: 10.5220/0001061403710376
Copyright
c
SciTePress

2 STATE OF THE ART
Regarding the main project nature, this section is
structured in three wide components, namely, hard-
ware solutions for emotion classification, biologi-
cal data format standards and dynamic interaction
paradigms.
2.1 Hardware Solutions
Since the beginning of the last century that there have
been efforts to correlate biological signals to emo-
tional states (Marston, 1917). The most traditional ap-
proaches are based on the standard polygraph where
physiological variables such as blood pressure, pulse,
respiration and skin conductivity are recorded in or-
der to detect different levels of anxiety. Although the
polygraph lie detection accuracy is arguable, the fact
that it is an efficient tool to detect basic emotional
states, especially individual related, anxiety levels, is
not.
The human brain always performance an al-
most hypnotic attraction to several research fields,
so in 1912, the Russian physiologist, Vladimir
Vladimirovich Pravdich-Neminsky published the first
EEG (Pravdich-Neminsky, 1913) and the evoked po-
tential of the mammalian. This discover was only pos-
sible due to previous studies of Richard Caton that
thirty years earlier presented his findings about elec-
trical phenomena of the exposed cerebral hemispheres
of rabbits and monkeys. In the 1950s, the English
physician William Grey Walter developed an adjunct
to EEG called EEG topography which allowed for the
mapping of electrical activity across the surface of the
brain. This enjoyed a brief period of popularity in the
1980s and seemed especially promising for psychia-
try. It was never accepted by neurologists and remains
primarily a research tool.
Due to the medical community skepticism, EEG,
in clinical use, it is considered a gross correlate of
brain activity (Ebersole, 2002). In spite of this reality,
recent medical research studies (Pascalis, 1998)(Af-
tanas, 1997) have been trying to revert this scenario
by suggesting that increased cortical dynamics, up to
a certain level, are probably necessary for emotion
functioning and by relating EEG activity and heart
rate during recall of emotional events. Similar efforts,
but using invasive technology like ECoG
1
, have en-
able complex BCI
2
like playing a videogame or oper-
1
Electrocorticography (ECoG) is the practice of using
an electrode placed directly on the brain to record electrical
activity directly from the cerebral cortex
2
Brain-computer interface (BCI), also called direct neu-
ral interface, is a direct communication between a brain (or
ating a robot (Leuthardt, 2004).
Some more recent studies have successfully
used just EEG information for emotion assessment
(K. Ishino, 2003). These approaches have the great
advantage of being based on non-invasive solutions,
enabling its usage in general population in a non-
medical environment. Encouraged by these results,
the current research direction seems to be the addi-
tion of other inexpensive, non-invasive hardware to
the equation. Practical examples of this are the intro-
duction of GSR
3
and oximeters by Takahashi (Taka-
hashi, 2004) and Chanel et al(G. Chanel, 2005). The
sensorial fusion, enabled by the conjugation of differ-
ent equipments, have made possible to achieve a 40%
accuracy in detecting six distinct emotional states and
levels of about 90% in distinguishing positive from
negative feelings. These results indicate that using
multi-modal bio-potential signals is feasible in emo-
tion recognition (Takahashi, 2004).
There also have been recorded serious commer-
cial initiatives regarding automatic minimal-invasive
emotion assessment. One of the most promising
ones is being developed by NeuroSky, a startup com-
pany headquarted in Silicon Valley, which has already
granted five million dollars, from diverse business an-
gels, to perform research activities (Rachel Konrad,
2007). There are two cornerstone modules, still in the
prototyping phase, yet already in the market. The first
is the ThinkGear module with Dry-Active sensor, that
basically is the product hardware component. Its main
particularity resides in the usage of dry active sen-
sors that do not use contact gels. Despite the intrinsic
value of this module, the most innovative distinct fac-
tor is the eSense Algorithm Library that is a powerful
signal processing unit that runs proprietary interpreta-
tion software to translate biosignals into useful logic
commands.
As previously referred it is still a cutting edge
technology, still in a development stage, nevertheless
it has proven its fundamental worth through participa-
tion in several game conferences(Authors, 2007c).
2.2 Data Formats
As an intermediate project subject, one must refer to
biological data format definition. This topic is partic-
ularly important to this project due to the absolute ne-
cessity of accessing, recording and processing, even-
tually in a distributed system, data which origin may
vary from multiple hardware solutions. The European
Data Format – EDF – is a simple digital format sup-
cell culture) and an external device.
3
Galvanic skin response (GSR) is a method of measur-
ing the electrical resistance of the skin.
BIOSIGNALS 2008 - International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing
372
porting the technical aspects of exchange and stor-
age of polygraphic signals. This format dates from
1992 and, nowadays, is a widely accepted standard for
exchange of electroencephalogram and polysomno-
gram data between different equipment and laborato-
ries (Kemp, 1992). This data format’s implementation
is simple and independent of hardware or software en-
vironments and has the peculiarity of enabling both
XML and raw text definition. This duality is espe-
cially important if there is any computing power limi-
tation and/or interoperability is a project requirement.
Although the unquestionable positive points of
EDF, hardly accommodates other investigations top-
ics. In order to overcome this critical hurdle, EDF+
is presented in 2003 as a more flexible but still sim-
ple format which is compatible to EDF that can not
only store annotations but also electromyography,
evoked potentials, electroneurography, electrocardio-
graphy and many more types of investigations. Its au-
thors believe that EDF+ offers a format for a wide
range of neurophysiological investigations which can
become a standard within a few years (Kemp, 2003).
2.3 User Interaction Paradigms
On the pure interactive multimedia systems domain,
one must refer to the growing immersion sensation
provided to the audience by several factors in di-
verse fields. As examples of this statement one must
consider the success of new generation videogame
consoles that have boosted audiovisual quality and
brought new interaction paradigms. Also worldwide
multimedia players, like Microsoft with table com-
puter and Apple with iPhone have invested hard in
the so-called ”multi-touch” interfaces, which allow
the user to move several fingers on a screen to manip-
ulate data, rather than relying on a mouse and menus.
In spite of these advances, the mainstream enter-
tainment industry has not changed the storyline lin-
earity yet, but some promising research projects are
trying to alter this reality. In this domain, one must
refer to Glorianna Davenport’s MIT Interactive Cin-
ema Group (Authors, 2007b) that have been focusing
its efforts on formal structures, construction methods,
and social impact of highly distributed motion video
stories.
Another recent interesting project is the apart-
ment drama, 15-minute interactive story called Faade
(Authors, 2007a), where two virtual characters pow-
ered by artificial intelligence techniques, allow them
to change their emotional state in fairly complicated
ways in response to the conversational english being
typed in by the human player.
3 PROJECT DESCRIPTION
In this section both global and specific projects are
described. With this intention, three subsections were
designed: in the first global IT architecture is pre-
sented and depicted; afterwards the main decisions
regarding the mouse control project are listed and de-
tailed; and finally the key features of the action clas-
sifier are explained.
3.1 Global Architecture
In order to best understand the mouse control project,
the main project IT design shall be considered and
described as it is used and tested. The architecture’s
key concept regards the possibility to access biosig-
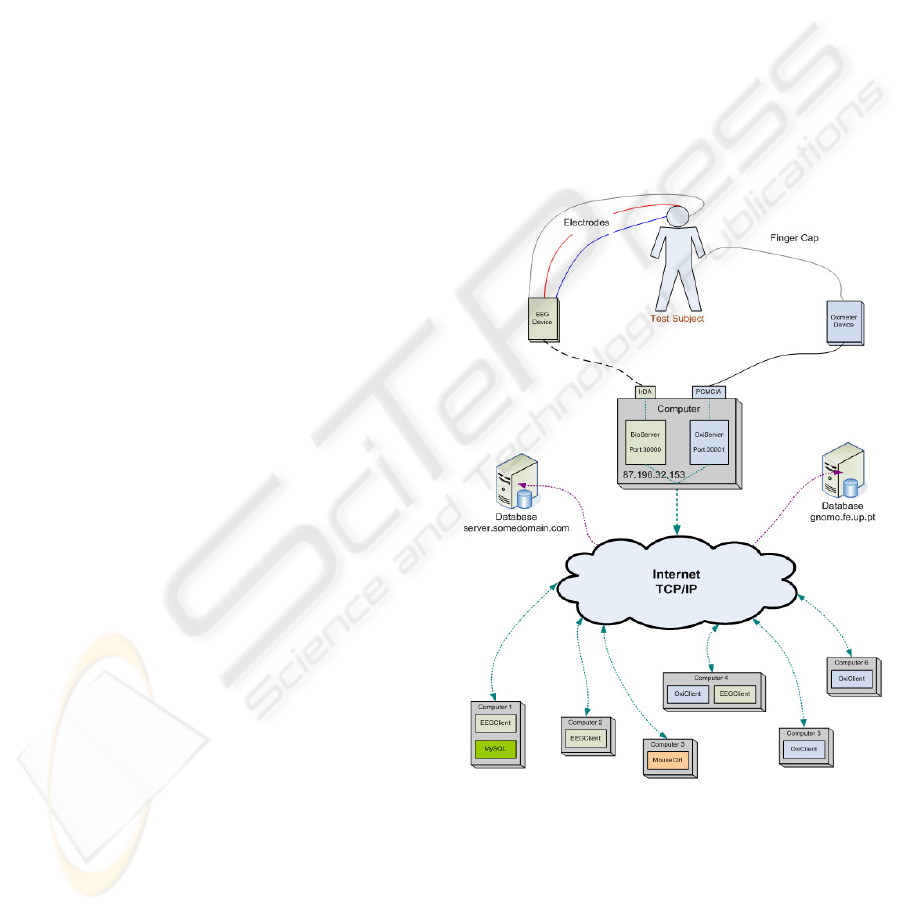
Figure 1: System Global Architecture.
nals independently of the resources physical location
and nature. In other words, one must be able to read
biosignals from a variety of equipments that might be
connected to an arbitrary subject in a remote location
without perceiving that other entities might be per-
forming similar accesses, processing and actions.
With this concept in mind, Figure 1 is more under-
standable, as it shows the several project dimensions.
MOUSE CONTROL THROUGH ELECTROMYOGRAPHY - Using Biosignals Towards New User Interface Paradigms
373
First, an arbitrary number and diversity of devices are
connected to one or more subjects. Each device driver
is encapsulated in a particular server software tool,
responsible for signal diffusion, securing third-party
code in a given logical compartment. These devices,
as illustrated, might have distinct communication pro-
tocols but their are normalized to standard TCP/IP
socket communication with a in-house developed log-
ical protocol. Having this communication base estab-
lished biosignal diffusion is possible to a wide kind
of receivers that must explicitly connect to the broad-
cast server(s). These clients might have distinct ob-
jectives, namely signal visualization and/or process-
ing; data storage; semantic extraction; etcetera.
3.2 Specific Decisions
Having the global system design being described in
the previous subsection, the authors believed that a
natural spin-off tool for proof of concept and test pur-
poses would be materialized in a simple, yet effective,
efficient and significant client application, capable of
receiving realtime biosignals, process them and ex-
tract semantic information.
Two main specific decisions were taken. The first
one resided in the choice of the base interaction mech-
anism. The decision fell to a traditional mouse hard-
ware piece due to its simplicity and global usage. Two
mouse functions/modes were selected for extension
with the developed tool: right click and drag. Once
the first is an operation less used than the left-click
and some interaction paradigms do not contemplate it
– original Macintosh machines – the second is a alter-
native mouse action with visual repercussions.
Regarding action classification, the authors chose
wink detection, mainly, for three reasons: it is an ac-
tion that most people are able to perform – at least
with the non-dominant eye; it has a clear signal sig-
nature; and it stills remains as an unused potential in-
teraction mechanism.
3.3 Action Classifier
The action classifier module resides its success in the
correct detection of user winking. In order to achieve
realtime high classification hit rates – and once again
having in mind the concept decisions referred in the
previous subsection – this module had to keep low
levels of complexity without loosing its efficiency.
A signal study showed that muscular activity re-
garding quick winks had a very recognizable pattern
with two consecutive signal peeks, having the second
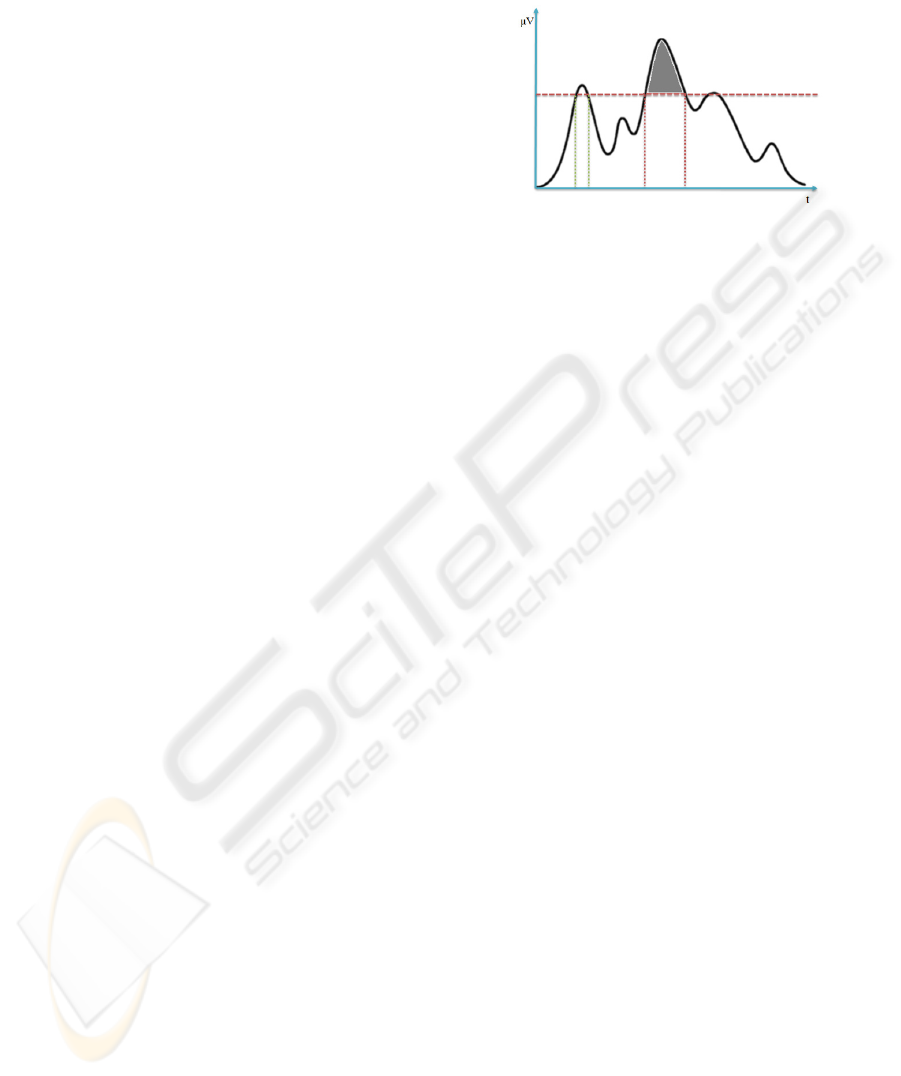
a lower strength. Figure 2 illustrates the shape of two
possible consecutive winks delimited by the two ver-
tical segments.
Figure 2: Classifier Parameters Appliance.
Once again keeping the approach simple enough
to be enable realtime computation even in mobile
devices, two distinct parameters where defined to,
through signal monitoring, enable reliable action clas-
sification. These parameters were designated peek
value and time span and are also visible in the re-
ferred illustration. The peek value can be understood
as a threshold and is illustrated as the dotted horizon-
tal line. Only signal values above this threshold are
considered for further analysis. Again in Figure 2 it
is visible that only to signal intervals respect this pri-
mary condition. The time span parameter is designed
to prevent extemporary phenomenons like jitters and
represent the minimum temporal interval that the sig-
nal must consistently be above the peek value. If a
closer look is given to the reference illustration, one
is able to perceive that the first wink candidate is dis-
carded because its signal is too brief and only the sec-
ond is valid. One important note is that either of these
parameters is configurable to best fit the user natural
abilities. More on this feature is elaborated in sections
4 and 5.
4 RESULTS
In this section experimental results are objectively
presented. In the first subsection, experimental con-
ditions are detailed and in the second, collected data
is depicted and treated for analysis purposes.
4.1 Experimental Conditions
In order to perceive the accuracy and adequacy of the
developed software tool, there were conducted sev-
eral experiments. There were formed two distinct
groups of subjects: one where users attended a fif-
teen minute theoretical formation, where the authors
explained the tool’s basics and how actions were de-
tected. After these sessions, subjects had another ten
BIOSIGNALS 2008 - International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing
374
minutes to free practice and to get in touch with the
application. The second group of users did not have
any kind of training specific regarding the presented
software. Experimental subjects were randomly se-
lected among laboratory researchers and college stu-
dents, constituting two groups os user with fifteen el-
ements.
Test sessions were similar both to trained and un-
trained user groups. Each session was supervised by
one of the authors and each subject was asked to close
his non-dominant eye ten times, as winking, when-
ever the subjected wanted to perform a mouse action
– either it was a right-click or activate drag mode op-
eration. Environment conditions were similar to both
groups either in terms of noise, illumination and time
of day.
As sessions were defined in performing a given
action ten times, or equal number of actions were de-
tected – false positives – accuracy rates have been
fractioned in steps of five percent.
4.2 Collected Data
As described in the previous subsection, experiments
were conducted considering two sets of fifteen sub-
jects, one with trained elements and the other with
untrained ones. The thirty sessions have been com-
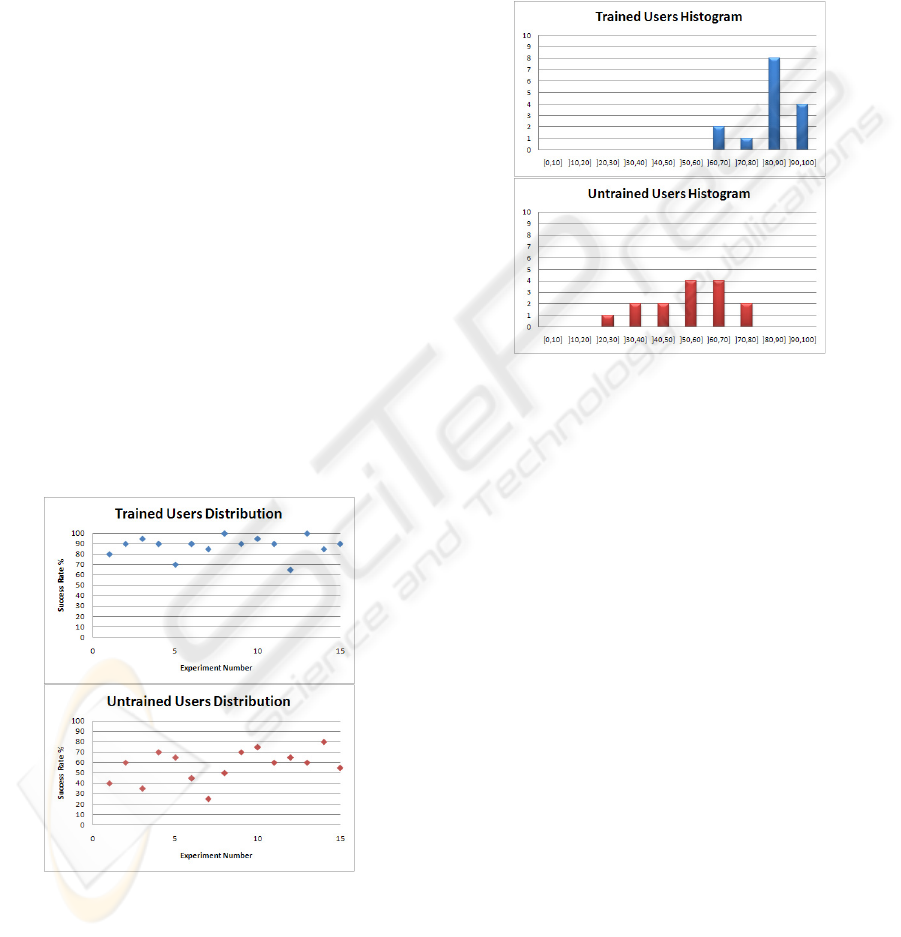
pleted in on week and the collected data distribution
is illustrated in Figure 3. One must clearly refer that
Figure 3: Experiment Result Distributions.
the trained users group has a greater performance with
an average success rate of around ninety percent, min-
imum values of sixty-five and registry error free ses-
sions. If we consider the untrained set, the average
rate drops to less than sixty percent with lower bounds
of twenty-five and maximum values of eighty percent.
These result distributions were translated into his-
tograms, for analysis purposes, as visible through Fig-
ure 4. If a deeper study is conducted, one must re-
fer that eighty percent of the trained subjects regis-
tered three or less errors. On the other hand, the
untrained user group results are more distributed, al-
though they are slightly concentrated in success rates
between fifty-five and seventy percent.
Figure 4: Experiment Result Histograms.
5 CONCLUSIONS
In this section, extracted conclusions are presented
and future work topics are identified. Regarding the
first theme, one must state that the objectives depicted
at the beginning were completed achieved. In what
concerns to the main project goals, the communica-
tion protocol was successfully tested, the IT archi-
tecture was used and validated and it was proved the
versatile equipment usage, once again, sustaining the
defined structural design. The specific project goals
were also accomplished as it was proved the concept
of utilizing biosignals to control interaction facets,
even when this case study is merely a proof of con-
cept.
Another important conclusion is the need of dis-
tinguish trained users from untrained ones, when con-
sidering the tool’s usability values. One ought to refer
that previous contact with the concept allied with a
few minutes of practice enhances the software utiliza-
tion success rates. However, even the untrained group
of users has registered fair results. These can be rated
as more than acceptable if one considers the whole
project’s intention.
Considering only the classification engine, a reg-
istered positive key point is the system ability to dis-
MOUSE CONTROL THROUGH ELECTROMYOGRAPHY - Using Biosignals Towards New User Interface Paradigms
375

tinguish user winking from user blinking, especially
if user specific parameterization is considered. How-
ever, even if this last feature is discarded, the default
parameter values are sufficient to discard weaker sig-
nals that, with high probability, refer to blinking.
Despite the enunciated positive features and con-
clusions, there were identified some issues, namely
the existence of false-positive results that refer to
other user muscular activity. These faults are included
in the numbers presented in section 4 and are, in most
cases, related to sudden and wide head movements.
On the other hand, some winks are not detected as
it is necessary some vigor. However, this issue, as
referred, can be suppressed by tuning classification
parameters. At last, some minor occasional, applica-
tion stability issues were detected, especially in what
concerns the mapping between wink detection and ac-
tion triggering, mainly due to the tool’s lack of matu-
rity. This last issue is development-oriented and does
not have a negative impact in what concerns the main
project’s concept.
5.1 Future Work
The main future work topics are not related to this
particular tool, once it is a proof of concept one, but
rather with the main global project. With this in mind,
there were identified the following areas:
• Reading Hardware Diversity Reinforcement: It is
intended to handle a greater number and diversity
of devices capable of acquiring biosignals so that
information fusion, conjugation and complemen-
tary is possible;
• Semantic Leap: It is intended to use syntactic in-
formation – biological signal – to extract more
complex information like emotions and simple
commands;
• Software Control: The accomplishment of the
previous item would enable both conscious and
subconscious control of several tools and/or mul-
timedia contents;
• IT Architecture and Network Reinforcement:
Full-duplex data transfer would enhance user
training and system adaptation levels.
Considering the main project’s intentions and the
future work topics referred, diverse practical appli-
cations come into sight. Some of them might be
the videogame and virtual entertainment industry,
multimedia contents adaptability, user interfaces en-
hancement, direct advertising, medical applications,
namely in phobia treatments and psychological eval-
uations.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors would like to thank Professor Eugenio
Oliveira for his guidance and support. A special men-
tion is also due to LIACC for hardware purchase and
excellent laboratory work conditions.
REFERENCES
Aftanas, L. (1997). Nonlinear forecasting measurements
of the human eeg during evoked emotions. In Brain
Topography, volume 10, pages 155–162.
Authors, V. (2007a). Faade a one-act interactive drama. In
Avaiable online at http://www.interactivestory.net/.
Authors, V. (2007b). Mit interactive cinema group. In Ava-
iable online at http://ic.media.mit.edu/.
Authors, V. (2007c). Neurosky, do you mind fact sheet. In
Technical Report.
Ebersole, J. (2002). Current Practice of Clinical Electroen-
cephalography. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.
G. Chanel, J. Kronegg, D. G. (2005). Emotion assessment:
Arousal evalutation using eeg’s and peripheral physi-
ological signals. In Technical Report.
K. Ishino, M. H. (2003). A feeling estimation system us-
ing a simple electroencephalograph. In Proceedings
of 2003 IEEE International Conference on Systems,
Man, and Cybernetics, pages 4204–4209.
Kemp, B. (1992). A simple format for exchange of digitized
polygraphic recordings. In Electroencephalography
and Clinical Neurophysiology, pages 391–393.
Kemp, B. (2003). European data format ’plus’ (edf+), an
edf alike standard format for the exchange of phys-
iological data. In Clinical Neurophysiology, pages
1755–1761.
Leuthardt, E. (2004). A braincomputer interface using elec-
trocorticographic signals in humans. In Journal of
Neural Engineering, pages 63–71.
Marston, W. (1917). Systolic blood pressure changes in
deception. In Journal of Experimental Psychology,
volume 2, pages 117–163.
Pascalis, V. D. (1998). Eeg activity and heart rate during
recall of emotional events in hypnosis: relationships
with hypnotizability and suggestibility. In Interna-
tional Journal of Psychophysiology, volume 29, pages
255–275.
Pravdich-Neminsky, V. V. (1913). Ein versuch der reg-
istrierung der elektrischen gehirnerscheinungen. In
Zbl Physiol, pages 951–960.
Rachel Konrad, A. P. (2007). Next-generation
toys read brain waves. In Avaiable online at
http://www.usatoday.com/tech/products/games/2007-
04-29-mindreadingtoys
N.htm.
Takahashi, K. (2004). Remarks on emotion recognition
from bio-potencial signals. In The second Interna-
tional Conference on Autonomous Robots and Agents.
BIOSIGNALS 2008 - International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing
376
