
A HYBRID SEGMENTATION FRAMEWORK USING LEVEL
SET METHOD FOR CONFOCAL MICROSCOPY IMAGES
Quan Xue
1
, Severine Degrelle
2
, JuhuiWang
1
, Isabelle Hue
2
and Michel Guillomot
2
1
INRA, MIA-jouy, Lab. of Applied Mathematics and Informatics, Jouy en Josas F-78350, France
2
INRA, UMR 1198; ENVA; CNRS, FRE 2857, Biologie du Développement et Reproduction, Jouy en Josas F-78350, France
Keywords: Confocal microscopy, image segmentation, Level-Set, Fast Marching, Geodesic Active Contour.
Abstract: Based on variational and level set approaches, we present a hybrid framework with quality control for
confocal microscopy image segmentation. First, nuclei are modelled as blobs with additive noise and a filter
derived from the Laplacian of a Gaussian kernel is applied for blob detection. Second, nuclei segmentation
is reformulated as a front propagation problem and the energy minimization is obtained near the boundaries
of the nuclei with the Fast-Marching algorithm. For each blob, multiple locally optimized points are selected
as the initial condition of the front propagation to avoid image under-segmentation. In order to achieve
higher accuracy, a graphical interface is provided for users to manually correct the errors. Finally, the
estimated nuclei centres are used to mesh the image with a Voronoi network. Each mesh is considered as a
Geodesic Active Contour and evolves to fit the boundaries of the nuclei. Additional post-processing tools
are provided to eliminate potential residual errors. The method is tested on confocal microscopy images
obtained during trophoblast elongation in ruminants. Experimental results show that cell nuclei can be
segmented with controlled accuracy and difficulties such as inhomogeneous background or cell coalescence
can be overcome.
1 INTRODUCTION
Confocal microscopy imaging is one of the most
important technologies used to observe the cellular
developmental process. Image segmentation is a
major step to interpret the obtained images.
Correctly explored, it will provide important
information about cellular shape and tissue
organisation. Appropriate and automatic image
segmentation tools are usually necessary to assist the
analysis. However, segmenting confocal images is a
complex and laborious task. Several factors might
raise difficulties: (1) uneven background: Most of
the tissues are fluctuating during the image
acquisition and background is rarely uniform; (2)
local intensity variation inside a nucleus. Due to
imperfect staining during the experiment or intrinsic
cellular structure, one nucleus may be split into two
or more parts; (3) cell coalescence: Cell over-
clustering makes it hard to tell the exact nuclei
boundaries.
Many segmentation approaches relating to
biological images have been proposed in the
literature. Research shows that traditional image
segmentation methods such as thresholding, region
growing and edge-based approaches (Pitas, 2000)
can not be successfully applied to microscopy
images. Reported successful methods usually
focused on a specific type of images without
generality (Wu et al., 2005). Watershed
segmentation has been popular and considered as
one effective method. Thomas (Thomas and
Graham, 2007) modified watershed method to give
more accuracy for identifying intracellular structures
even in the presence of inhomogeneous background.
Wahlby (Wahlby et al., 2004) and Long (Long et al.,
2007) used both the intensity and geometry
information to appropriately detect nuclei. Those
methods are robust but the system is complicated
and need more time to adjust and analyse the
parameters to give the accurate result according to
the characteristics of images. All modified
watershed algorithms face over-segmentation
phenomena and have to provide post processes to
adjust the result, especially on cellular microscopy
images with high noise and cell coalescence. Based
on partial differential equations and variation models,
Solorzano (Solorzano et al., 2001), Chang (Chang et
277
Xue Q., Degrelle S., Wang J., Hue I. and Guillomot M. (2008).
A HYBRID SEGMENTATION FRAMEWORK USING LEVEL SET METHOD FOR CONFOCAL MICROSCOPY IMAGES.
In Proceedings of the First International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing, pages 277-282
DOI: 10.5220/0001065602770282
Copyright
c
SciTePress

al., 2007) and Dirk (Dirk et al., 2006) provide
another direction by using level set segmentation.
The solution is derived by minimizing a global
energy function. This method benefits from well
founded mathematical theories which allow
developers to analyze, understand, improve the
existing methods and work in a continuous setting in
higher dimensional space.
The paper is organized as follows: Section 2
introduces a hybrid structure supporting quality
control. Section 3 illustrates segmentation
approaches. The system is evaluated in Section 4.
Finally, Section 5 draws a conclusion.
2 HYBRID FRAMEWORK
Drawing outlines of cells with a mouse, the result
can be regarded as absolutely accurate and objective,
but it is a hard work and difficult to repeated.
Automatic methods are fast and convenient, but
some errors occur. Therefore, the solution for image
segmentation is a trade-off between precision and
speed. When high accuracy is needed, the system
needs interactivity with the analyzer or provides an
automatic result with limited errors. To deal with a
wide variety of biological microscopy images, a
hybrid framework with quality control will be
preferable.
We constructed such a hybrid framework
combining PED-based level set approaches with
selectable interaction which supports automatic and
semi-automatic segmentation with a robust error-
checking stage, as shown in Figure 1. The nuclei are
firstly modelled into blobs with some additive noise
and Laplacian of Gaussian (LoG) filter is regarded
as a blob-detector. Using gradient information, a
front propagation fast marching is applied to
segment cellular nuclei. The result can be directly
outputted after morphology filter or used to enhance
the last result. An interactive module is provided to
prevent error propagation and Voronoi meshing is
created from those appropriate centres. From cellular
shape information, geodesic active contour (GAC) is
introduced to refine nuclei boundaries. Post
processing methods are added as supplementary
module to correct for potential errors.
Figure 1: Diagram of hybrid framework.
3 METHOD DESCRIPTION
3.1 Blob Detection
On confocal images from ruminant trophoblast cells
e.g. Figure. 2 (A), one sees that most nuclei are
nearly round. Laplacian of Gaussian filter has been
proved to be an effective blob-detector (Byun et al.
2006) since LoG filter is able to detect particular
edges by determining the peak point of the ridge.
Therefore, we aimed at detecting regions which are
brighter than the surrounding to overcome
inhomogeneous background.
Although the nuclei of trophoblast cells are not
exactly round, our objective is focused on rotation
invariance of objects, so that it is fitful to over-fit a
circle model into the whole image. From the
experimental results, we found that the diameter of
LoG filter is proportional to nuclei average diameter
and this initial value can be set in advance since the
kind of cells are known, e.g. bovine or ovine
trophoblast. LoG filter will get a smooth image local
maximal values of which nearly correspond to the
nuclei centres shown in Figure 2. (B).
After blob-detector, an H-convex filter is added
for enhancing the local maximum. H-convex
belongs to a kind of morphological method and has
the effect of extracting objects that are brighter than
background by at least H-intensity units. It is
relatively straightforward and does not require
homogeneity in the background. The enhanced local
maximal result can be gotten in Figure 2. (C).
BIOSIGNALS 2008 - International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing
278

Figure 2: Results in each module.
3.2 Fast Marching
Fast marching method (Sethian, 1996) has
monotonically advancing front with positive speed
to build solutions outward from the boundary
condition by choosing the smallest time in its
evolution, until it adopts the form of the enclosing
nuclei delineated by the staining. The segmentation
result from fast marching is gotten in Figure 2 (D).
Our speed function is provided by sigmoid
function:
Min
e
MinMaxIS
I
+
⎟
⎟
⎠
⎞
⎜
⎜
⎝
⎛
+
⋅−=
⎟
⎠
⎞
⎜
⎝
⎛
−
−
α
β
1
1
)()(
'
(1)
where I is intensity of input pixel,
'
I
is the intensity
of output pixel,
Min
and
Max
are the minimum and
maximum values of output image,
α
defines the
width of input intensity range and
β
defines
intensity around which the range is centred.
Since some cell nuclei are connected closely,
segmentation results depend on initial seed
positions, so that multiple seeds will have more
chances not to miss objects. However, having seeds
distributed inside the nuclei is not helpful for
contour expansion. Therefore, instead of randomly
selecting multiple points as initial condition, we
searched the best seeds for each candidate by finding
its local minimum through comparison with
neighbours as shown in Figure 3.
Figure 3: Seeds optimization by local searching.
The selection of optimal seeds gives a better
result in detecting nuclei, and that this result is stable
shown Table 1. The more seeds can be assigned
nearby the edge of nuclei, the more precise the fast
marching segmentation can be. Table 1 also shows
that the number of initial seeds is important. If too
many seeds are put in one image, many single nuclei
will be divided into multiple parts due to local
intensity variations. Normally the distances we have
selected are 16 pixels in row, 16 pixels in column
and a searching radius of 3 pixels. For some special
trophoblast images we had to adjust these
parameters carefully.
Table 1: Comparison between random and optimal seeds.
radius
(pixels)
Number
of nuclei
4×4 8×8
16×
16
32×
32
64×
64
Optimal 398 360 337 339 310
3
Random 419 364 332 319 307
Optimal 319 312 303 304 302
5
Random 337 312 299 288 275
3.3 Interactivity
The centre of each nucleus can be estimated from
the above results. Despite accuracy rate is averagely
high, there is still a possibility of a few failures to
occur as indicated by white arrows on Figure 2 (E).
On our images, the error rate varies from 1% to
10%. If more than one seed is located inside a
nucleus, this will cause over-segmentation,
conversely when no seed is found within a nucleus,
the object is lost. Therefore, the centres of nuclei are
very important for the final result. In order to
prevent error propagation, human interactivity is
necessary to view and adjust results in this stage.
Through an interface, the user can make decision
based on visual examination of the nuclei, so that an
immediate feedback enables the user to produce
reliable results e.g. Figure 2 (F).
A HYBRID SEGMENTATION FRAMEWORK USING LEVEL SET METHOD FOR CONFOCAL MICROSCOPY
IMAGES
279
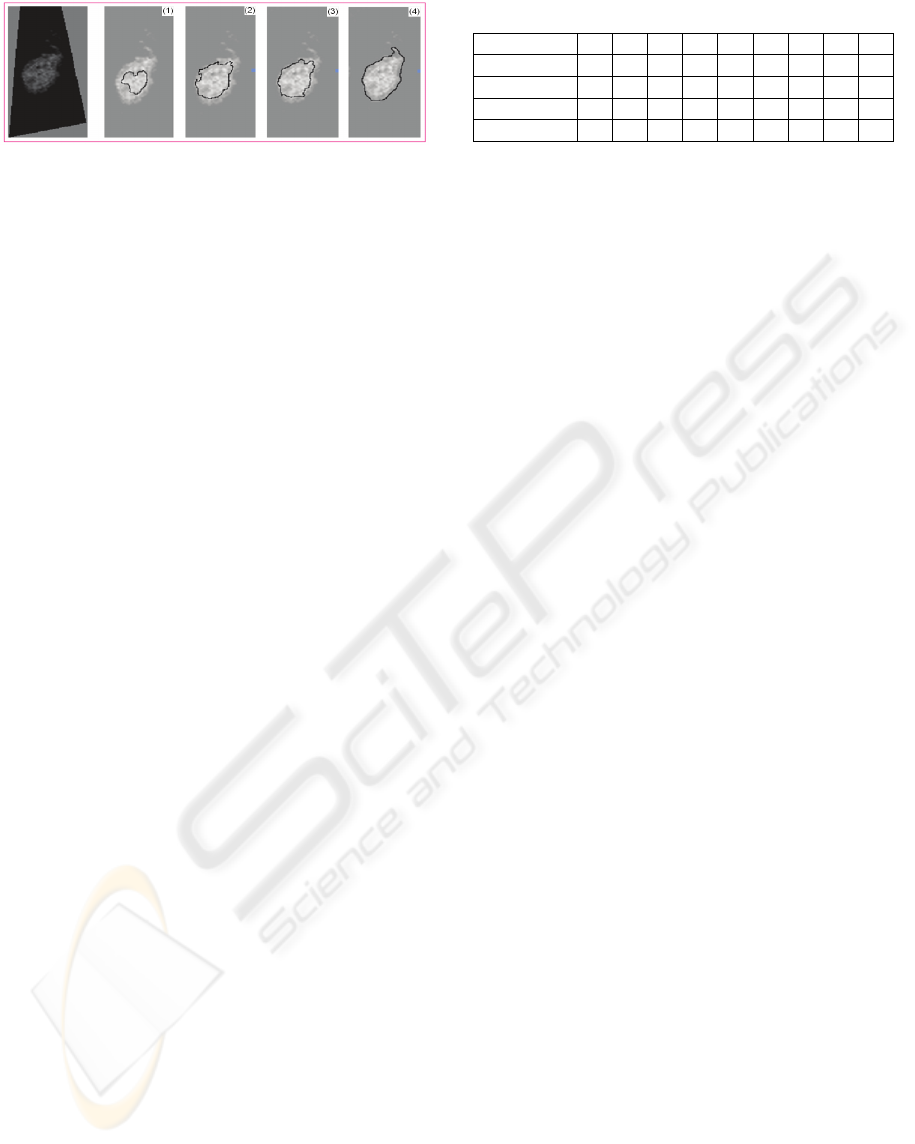
Figure 4: Refinement by GAC in one Voronoi mesh.
3.4 Geodesic Active Contour
From nuclei centres, Voronoi mesh is directly
produced in Figure 2 (G), which can be regarded as
a reference map in refining nuclei by geodesic active
contours (Vicent et al. 1997). Since Voronoi mesh
gives a limited small region to minimize the GAC
energy function, it is sure that one nucleus is gotten
just in one Voronoi-mesh. The refining result is
shown in Figure 2 (H).
GAC consists of double forces which control the
last shape and it is important to balance inside and
outside forces. When the propagation term is set too
high, the contour will go too far inside as illustrated
in Figure 4. In our application to ruminant
trophoblast cells, all nuclei are nearly rounded so
that curvature term is responsible for smoothness.
3.5 Post Processing
When confocal images are very blurred or tightly
clustered, a few errors cannot be avoided with
automatic detection to correct these potential errors
by human visual system. We provide a
supplementary module. As an example (Figure 2: I),
one lost nucleus has been recovered with this
module.
4 EXPERIMENTS
This section describes how our hybrid framework is
used to segment the nuclei on 2D confocal images
from ruminant trophoblast. There are more than one
thousand of images with varying cellular
characteristics and varying background noise in
dataset. Selecting different modules, four types of
pipeline are designed shown in Table 2.
Table 2: Pipelines with different modules.
Module 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
Pipeline A × × × ×
Pipeline B × × × × × ×
Pipeline C × × × × × × ×
Pipeline D × × × × × × × ×
Figure 5 gives four typical images as examples
to show the results of our framework. Our approach
is compared with the existing methods in ITK and
ImageJ which are using fast marching and K-means
clustering individually. In row 1, when confocal
images have good quality, all methods can be used
successfully, with similar errors. However, when
nuclei are clustered together (see row 2), our method
keeps stable whereas the other methods lose the
ability to separate each nucleus in the clusters. For
example, ITK can only detect the whole cluster edge
and cannot divide it further while ImageJ produces
many connected regions. In row 3, when nuclei are
organised in a special structure, the exiting methods
(ITK and ImageJ) cannot identify the objects
whereas the nuclei are correctly detected by our
method and the contour is closer to the true shape.
When there are many small nuclei and their size
changes continuously (row 4), our result is also
stable and useful.
Our framework is a scalable system with quality
control through the selection of modules and the
setting of the initial parameters based on the
characteristics of the original image to balance terms
in the energy function of level set. Through
adjusting the parameters on propagation and smooth
term, the nuclear edges can be detected and refined
step by step by active contour as in Figure 6, from
(a) to (d).
It is often necessary to complete a confocal
image automatic segmentation with an acceptable
error rate. Successful results can be obtained with
our scalable procedure. Since the modules related to
the human interaction are selectable, we can use the
level set methods directly. Figure 7 gives an
example. The first column comes from the fast
marching following the blob-detector and we use
morphology filter to enhance the result. In the
second column, results from GAC without
interactivity are provided. Some error is propagated
from fast marching module because the gravity
centre of the nuclei is wrongly estimated from fast
marching segmentation. GAC can skip the false
nuclei but will produce good results with coherent
nuclei. So, the number of nuclei from GAC
decreases for factual objects.
BIOSIGNALS 2008 - International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing
280

Figure 5: Comparison of proposed algorithm with fast marching in ITK and K-mean clustering in ImageJ (high quality,
nuclei coalescence, special structure and low quality from left column to right column). The first row is the original
confocal images. The second, the third and the fourth row respectively correspond segmentation results from ITK, ImageJ
and proposed algorithm (Pipeline C).
Table 3: Segmentation results expressed as numbers of detected nuclei with each method.
Image
Actual
number
Fast marching
in ITK
K-means in
ImageJ
FM with blob-
detector
(Pipeline A)
GAC without
interactivity
(Pipeline B)
GAC with
interactivity
(Pipeline C)
With post
processing
(Pipeline D)
(a) 280 253(-27) 265 (-15) 298 (+18) 294 (+14) 280 (+0) 280
(b) 378 281(-97) 347 (-31) 402 (+24) 373 (-5) 374 (-4) 378
(c) 294 236(-58) 179 (-115) 328 (+34) 318 (+24) 292 (-2) 294
(d) 704 544(-160) 652 (-52) 737 (+33) 729 (+25) 711 (+7) 704
Number 1656 1314 (-342) 1443 (-213) 1765 (+109) 1714 (+63,-5) 1657 (+7,-6) 1656
Error rates 20.65% 12.86% 6.58% 4.11% 0.79% 0%
In Table 3, we conclude and compare the
error rates from all of the methods discussed
above. “+” means over-segmented nuclei and “-”
means under-segmented. Their sum is divided by
factual total numbers to compute the error rate.
Normally we do not use post processing module
and the average error ratio is limited into 0.8%.
The experimental results show that our hybrid
segmentation framework is satisfactorily accurate.
A HYBRID SEGMENTATION FRAMEWORK USING LEVEL SET METHOD FOR CONFOCAL MICROSCOPY
IMAGES
281

Figure 6: Refining boundary by GAC method with
quantity control.
Figure 7: Automatic segmentation results by Pipeline A
(first row) and Pipeline B (second row).
5 CONCLUSIONS
This paper demonstrates the effectiveness of a
hybrid framework for cellular segmentation. It
combines the efficiency of the automatic
segmentation procedures with the accuracy of the
human visual system. Based on confocal images of
ruminant trophoblast, our experiments showed that
the proposed approach provides reliable results and
presents numerous advantages regarding to manual
analysis or automatic methods in terms of objectivity
and applicability.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
QX and SD are respectively supported by an INRA
and an Ile–de-France post-doctoral fellowship.
Scientific financial support comes from an INRA
AgroBi grant to JW and IH. We thank A Trubuil P
Adenot* and G Lehmann* for helpful discussions
(*INRA MIMA2 platform) and INRA experimental
farms for embryo production.
REFERENCES
Byun. J.Y., Verardo. M.R., Sumengen. B., Lewis. G.P.,
Manjunath. B.S., Fisher. S.K., 2006. Automated tool
for the detection of cell nuclei in digital microscopic
images: Application to retinal images. Molecular
Vision, pp.949-960. August 2006.
Chang. H., Park. C., Parvin. B., 2007. Quantitative
representation of three-dimensinal cell culture models.
In ISBI’07, IEEE International Symposium on
Biomedical Imaging: From Nano to Macro, pp.536-
539. April 12-15, 2007. Washington DC, USA.
Dirk. P., Jens. R, Nick. T., Badrinath. R., 2006. Spatio-
Temporal Cell Cycle Phase Analysis Using Level Sets
and Fast Marching Methods. In MIAAB’06, 1st
international workshop on Microscopic Image
Analysis with Applications in Biology. On 5
th
of
October 2006. Copenhagen, Denmark, USA.
Long. F.L., Peng. H.C., Myers, E., 2007. Automatic
segmentation of nuclei in 3D microscopy images of
c.elegans. In ISBI’07, IEEE International Symposium
on Biomedical Imaging: From Nano to Macro,
pp.536-539. April 12-15, 2007. Washington DC, USA.
Pitas. I., 2000. Digital image processing algorithms and
applications. Wiley-Interscience publication. New
York, 1
st
edition
Sethian, J.A., 1996. Level set methods and fast marching
methods. CAMBRIDE UNIVERSITY Press.
Solorzano. C.O., Malladi. R., Lelievre.S.A., Lockett. S.J.,
2001. Segmentation of nuclei and cells using
membrane related protein markers. Journal of
Microscopy, Vol.201, Pt 3, pp.404-415, March 2001.
Thomas, J.G., Graham, W., 2007. WatershedCounting3D:
A new method of segmenting and counting punctuate
structures from confocal image data. Blackwell
Synergy - Traffic, Volume 8 Issue 4 pp. 339-346, April
2007.
Vicent. C., Ron. K, Guillermo. S., 1997. Geodesic Active
Contours. International Journal of Computer Vision,
Vol.22 (1), pp.61-79, 1997.
Wahlby. C., Sintorn. I.M., Erlandsson. F., Borgefors. G.,
Bengtson. E., 2004. Combining intensity, edge, and
shape information for 2D and 3D segmentation of cell
nuclei in tissue sections. Journal of Microscopy,
Vol.215, Pt 1, pp.67-76, July 2004.
Wu. H.S., Xu. R., Harpaz. N., Burstein. D., Gil. J., 2005.
Segmentation of intestinal gland images with iterative
region growing. Journal of Microscopy, Vol.220, Pt 3,
pp.190-204, December 2005.
BIOSIGNALS 2008 - International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing
282
