
IMPROVING AN AUTOMATIC ARRHYTHMIAS RECOGNISER
BASED IN ECG SIGNALS
Jorge Corsino, Carlos M. Travieso, Jesús B. Alonso and Miguel A. Ferrer
Technological Centre for Innovation in Communications (CeTIC), University of Las Palmas de Gran Canaria
Campus de Tafira, s/n, 35017, Las Palmas de Gran Canaria, Spain
Keywords: Automatic recognition of arrhythmias, electrocardiography, neural network, principal component analysis,
wavelet transform.
Abstract: In the present work, we have developed and improved a tool for the automatic arrhythmias detection, based
on neural network with the “more-voted” algorithm. Arrhythmia Database MIT has been used in the work in
order to detect eight different states, seven are pathologies and one is normal. The unions of different blocks
and its optimization have found an improvement of success rates. In particular, we have used wavelet
transform in order to characterize the patron wave of electrocardiogram (ECG), and principal components
analysis in order to improve the discrimination of the coefficients. Finally, a neural network with more-
voted method has been applied.
1 INTRODUCTION
In Europe, cardiovascular diseases are one of most
important causes of death, with a great repercussion
in health assistance budget. For instance, to obtain
an early exact cardiovascular diagnosis is one of the
most important missions for the physicians. The
electrocardiogram is the graphic description of the
heart electric activity registered from the body
surface and is a basic element in the diagnosis of
different heart diseases.
The objective of this study is to make deeper in
the extraction of characteristics and the later
automatic classification of heart pathologies,
analyzing every aspect that takes parting.
To carry on with this objective, we have
developed Matlab software (Matlab, 2006), clear
and easy, where users have three options to practise
with all tools at their hands: making a pre-processing
with wavelet transform and in order to play with the
developed filing.
Wavelet transform (Romero-Legarreta, 2005) is
a mathematics technique that has gained importance
in the last years in all kind of applications related
with non-stationary signal process.
Although the decomposition in well defined
blocks in time and frequency, wavelet transform can
characterise the local sign regularities. This skill
allows distinguishing electrocardiogram waves
(ECG) from noise and other artefacts.
In this paper, we establish the use of
approximated wavelet coefficients taken out from
the ECG signal in order to classify eight types of
beat: normal pulse (N), extra-systole (L), premature
ventricular contraction (R), premature auricular
contraction (/), blockade left branch (A), blockade
right branch paced beat (V), fusion of normal and
paced beat (f) and fusion of normal and premature
ventricular contraction (F).
The use of principal component analysis (PCA)
(Bianchi, 2006) on the wavelet coefficients has
improved their discrimination. Finally, we have used
an automatic classification based on artificial neural
networks (NN) (Bishop, 1995), (Juang, 1992). An
improvement have been applied to NN, we have
implemented the “more voted” method, obtaining
better success rates.
2 WAVELET TRANSFORM:
FEATURE EXTRACTION
The ECG features are extracted through a pre-
processing stage in which the Wavelet transform is
applied to original ECG signal.
The Discrete Wavelet Transform (DWT) is
defined as follows:
453
Corsino J., M. Travieso C., B. Alonso J. and A. Ferrer M. (2008).
IMPROVING AN AUTOMATIC ARRHYTHMIAS RECOGNISER BASED IN ECG SIGNALS.
In Proceedings of the First International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing, pages 453-457
DOI: 10.5220/0001066604530457
Copyright
c
SciTePress
[
]
[
]
[
]
,
,
jk
n
Cjk fn n
ψ
∈
=
∑
Z
(1)
where
kj,
ψ
is the transform function:
The application of different mother families on
pre-processing (artefacts elimination) and on the
feature extraction has got a set of good and
discriminate parameters.
3 PRINCIPAL COMPONENT
ANALYSIS
Principal components analysis (PCA) is a technique
used to reduce multidimensional data sets to lower
dimensions for analysis. The applications include
exploratory data analysis data and for generating
predictive models. PCA involves the computation of
the eigenvalue decomposition or Singular value
decomposition of a data set, usually after mean
centering the data for each attribute. The results of a
PCA are usually discussed in terms of scores and
loadings. This process applied to ECG arrhythmias
is named blind source separation, where there are
fewer sources than input channels.
The blind source separation consists in several
sources that are mixed in a system, these mixtures
are recorded and then they have to be separated to
obtain the estimations of the original sources. The
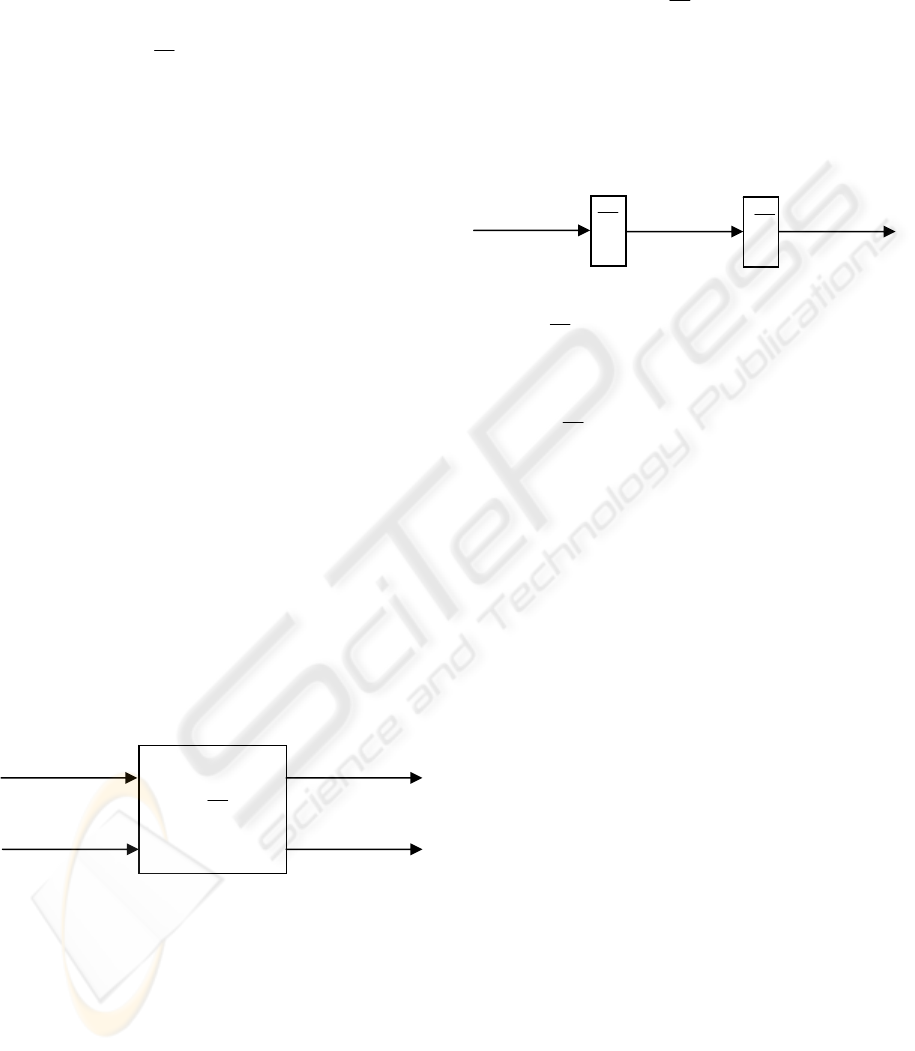
following figure shows the mixing system:
Figure 1: 2 Sources – 2 Mixtures system.
Generally, there are n source signals statistically
independent
)](),...,([)(
1
tststs
n
= , and m
observed mixtures that are linear and instantaneous
combinations of the previous
signals
)](),...,([)(
1
txtxtx
n
= . Beginning with the
linear case, the simplest case, we have that the
mixtures are:
(3)
Now, we need to recover s(t) from x(t). It is
necessary to estimate the inverse matrix of H, where
h
ij
are contained. Once we have this matrix:
(4)
Where y(t) contains the estimations of the original
source signals, and is the inverse mixing matrix.
Now we have defined the simplest case, it is time to
explain the general case that involves convolutive
mixtures. The process is defined as follows:
Figure 2: BSS General problem.
Where is the mixing system:
(5)
The h
ij
are FIR filters, each one represents an
acoustic transference multipath function from
source, i, to sensor, j. i and j represent the number of
sources and sensors.
4 NEURAL NETWORK
For this present work, we have implemented a
supervised classification system for the discrete
wavelet coefficients. Firstly, a neural network
classification system using time intervals obtained
from the previous extraction process is implemented.
This classifier has used a Feed-Forward Neural
Network (NN) with a Back-propagation algorithm
for training (Bishop, 1995), (Juang, 1992), where the
number of input units is given by the dimension of
the vector of features. And the number of output
units is given by the number of pathologies to
identify. Too, we have researched with different
number of neurons in the hidden layer, in order to
get the optimum recogniser.
Besides, the found success has been improved
using the method of the ‘more voted’, where we
have built a schedule with different neural networks
(see figure 1).
[]
2
,
22
j
j
jk
nnk
ψψ
−
−
⎡
⎤
=⋅ −
⎣
⎦
(2)
X
1
X
2
Y
1
Y
1
H
T
n
xxxx ]...[
21
=
T
m
yyyy ]...[
21
=
T
n
xxxx ]
ˆ
...
ˆˆ
[
ˆ
21
=
H
W
∑
=
⋅=
n
j
jiji
tshtx
1
)()(
)()( txWty ⋅=
H
⎥
⎥
⎥
⎦
⎤
⎢
⎢
⎢
⎣
⎡
=
nnn
n
hh
hh
H
...
.........
...
1
111
BIOSIGNALS 2008 - International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing
454
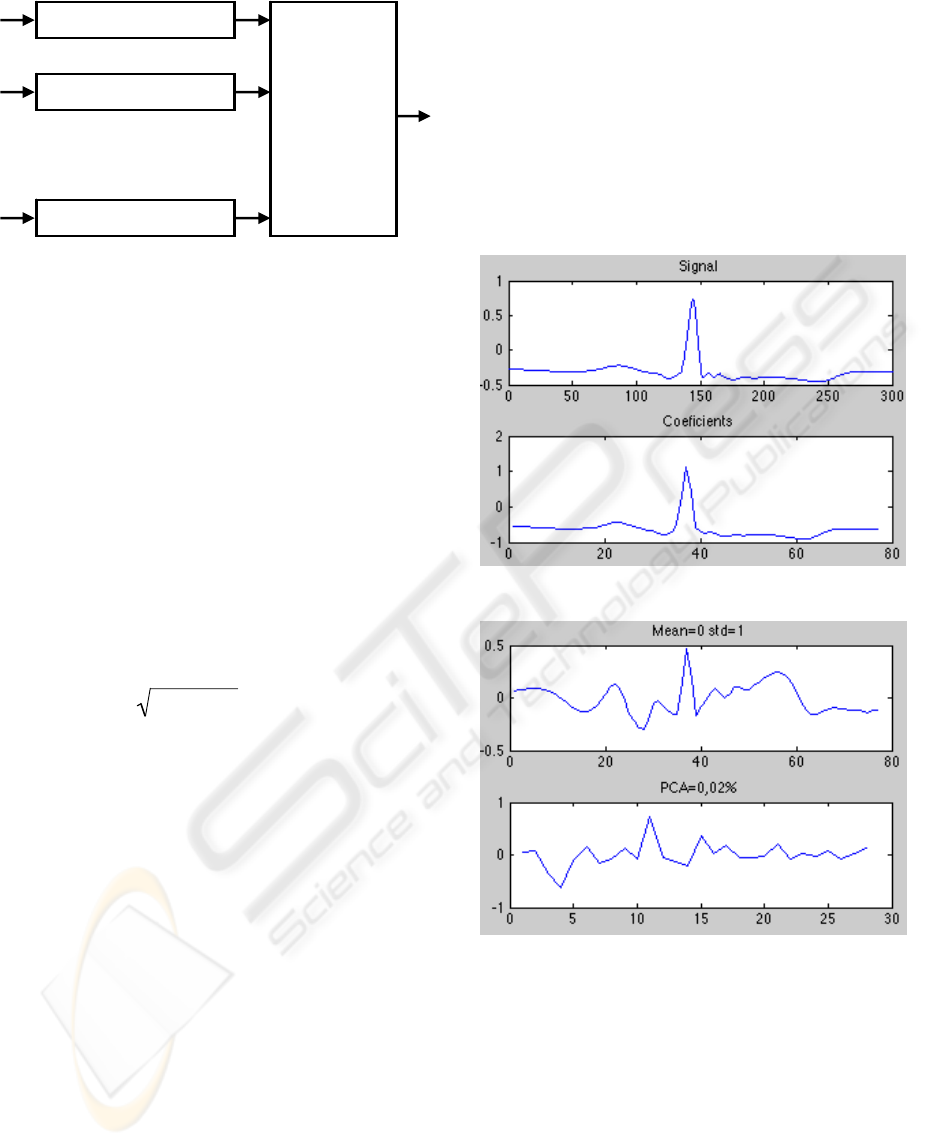
Figure 3: Classification System with ‘more voted’
algorithm, based on NN.
5 EXPERIMENTS
We have taken 24 signals from the MIT-BIH
ARRHYTHMIA database (MITDB)( MIT-BIH,
2007), choosing 750 samples from each class, 6000
beats to classify; some of them are recognized by the
MIT as difficult classifying signals. To remove noise
from signals, the net interferences and the base line
variations, we have use techniques proposed in (1).
It consists in obtaining detail coefficients for
different wavelet levels, to apply them a non-lineal
form threshold, using a soft-thresholding calculated
by the inverse transform to obtain the result signal.
The threshold follows this
expression:
∂
= 2log(N)
ˆ
σ
; where N is the
number of decomposition levels and coefficients
represent the details coefficients for the level to
filter. In function of the wavelet family and the
decomposition level, the result will change. In this
work, we take Daubechies 3 of level 3 following our
studies. Also we take different types of parameters
as temporal as Fourier and Wavelet coefficients.
With temporal parameters took out from our
previous works and algorithms (the time of Pwave,
PR segment, QRS complex, QT segment and T
wave, and the area of P wave, QRS complex and the
T wave) we did not get to characterize any kind of
beats, the same result were taken with Cosen Fourier
Transform (DCT).
Hence we only select the approximation wavelet
parameters like “in-parameters”. The classification
is realised with a neural networks using back-
propagation. Once took out the wavelet coefficients
with sym4 family and the third decomposition level,
the neural networks has three layers. To obtain the
number of neurons of the hidden layer, we tried with
different numbers and with 45 we got the best result
with an error of 26%. How the error is too much, we
make principal components analysis, since with it,
the network size and the computational cost are
reduced. With this study the characteristic vector is
ortogonalised to avoid the correlations of his
components, is arranged and the components with
less information are deleted. The algorithm is
applied to the characteristic vector, the mean is
established in cero and the standard deviation in one,
after, the PCA is applied, in this case with 0,02%.
The variations are showed in the next figures:
Figure 4: Signal and its coefficients.
Figure 5: Modification of the coefficients.
With this technique, the network in trained again
with the same conditions and the result with 55
neurons in the least error: 2,27%. This shows us a
satisfactory study. Many trainings are realises where
characteristics are: 3.000 beats (375 per class) for
the training stage and the same quantity for the test
stage, different PCA values (0,02%, 0,2 % and 2 %)
the second, the third and the fourth decomposition
level and ten wavelet families (Bior2.4, Bior5.5,
Bior 6.8, Harr, Sym2, Sym4, Sym5, Sym8, rBio3.1,
rBio5.5). With the result obtained we noticed is
Neural Network
1
‘More Voted’
Algorithm
Neural Network
2
Neural Network
N
.
.
.
IMPROVING AN AUTOMATIC ARRHYTHMIAS RECOGNISER BASED IN ECG SIGNALS
455
better have a lot of approximation coefficients and
alter make a PCA, instead of hace less quantity of
approximation coefficients, then in better a low level
and apply PCA. The best result were obtained with
the wavelet rBio 3.1 at level 2 and PCA= 0,02%
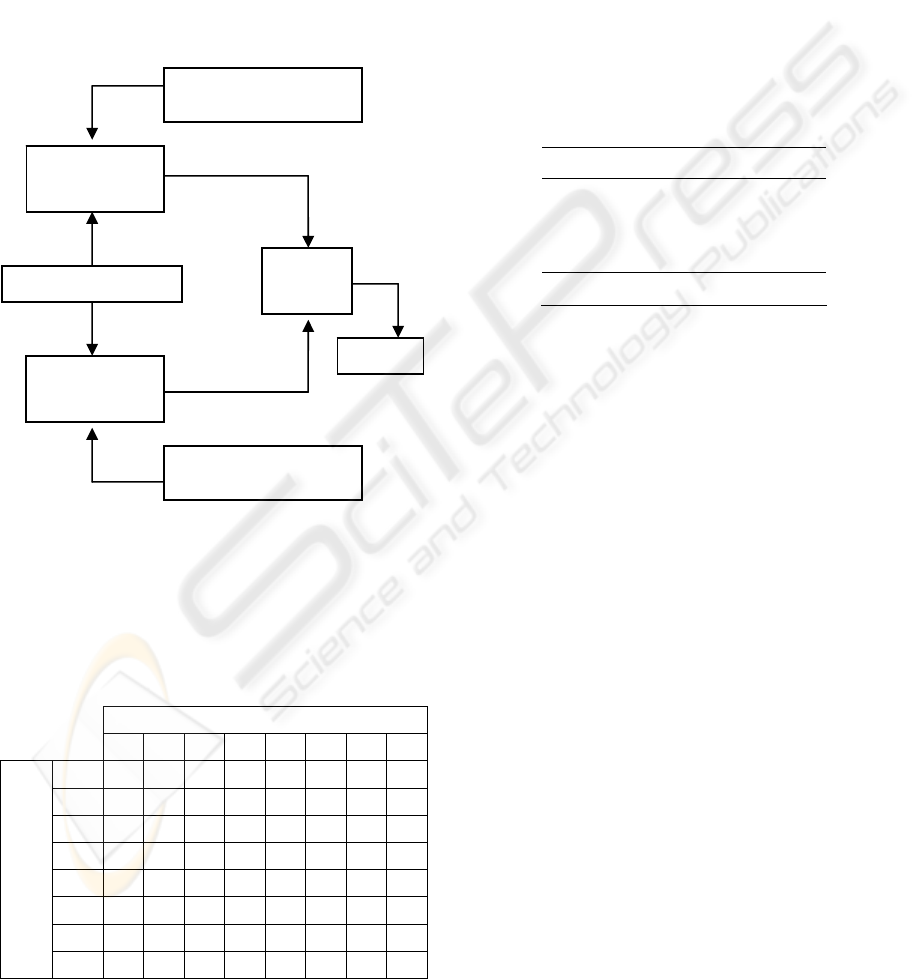
with 1,97% of error. “The most voted” technique is
applied to boot the result. This model consist of
select some networks an apply to all the same test in
parallel. Finally, the results are compared and the
result most voted is selected. In the figure 4 a double
network is represented with only two parallel
networks.
Figure 6: Parallel neural network.
With this new structure, the filing reduces error
to 1.8% in the simulation and 1.4 in the train
process. For the entire database, it has an error of
1.6%.
Table 1: Matrix confusion.
OUTPUT CLASSES
N L R / A V f F
N 375 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
L 0 372 0 0 0 0 3 0
R 1 0 372 0 2 0 0 0
/ 0 0 0 375 0 0 0 0
A 16 0 3 2 351 1 1 1
V 0 0 0 0 2 369 3 1
f 0 0 0 4 0 0 371 0
INPUT CLASSES
F 0 1 0 2 4 0 7 361
In the confusion matrix we can see, that the class
that has more errors is the premature ventricular
contraction, classifying this as normal beat, this is
because the morphology of the auricular premature
contraction is similar to the normal. Respect to the
classification between normal and pathologic signals
the filing detect the healthy signals whit a 100% and
the pathologic signal with a 99,35 % being the total
classification between this two classes a 99.7%.
Respect to the computational time, we remember
that the filing has three parts: the extractions of
wavelet characteristics, the principal components
analysis and the test process. This time are detailed
in the table 2:
Table 2: Load times in seconds.
Process Computational Time
Wavelet 0,010623 s
PCA 0,002571 s
Test 0. 111877 s
TOTAL 0,1251 s
Having in mind that a full beat has an
approximated duration of 800 ms, the filing will
classify the beat only 125 ms later, without the time
of pre-processing and segmentation. These times are
Matlab time. The part of classification depends on a
well segmentation process, this is we propose to
make a robust segmentation for noise and cardiac
pathologies.
Finally, we have compared our results with other
authors (Song, 2005), (Zimmerman, 2004),
(Jankowski, 2003). The new blocks used for this
application and with the optimization of the
remainder of the blocks, we can observe as our
results are better than the previous references.
6 CONCLUSIONS
It has been implemented and improved an automatic
arrhythmias recogniser using a neural network with
more voted algorithm. We have found error rate of
1.8% with independent samples, only using for the
test (8 different classes); and an error rate of 0.3%
for pathology or normal class.
The ECG signal used is from MIT arrhythmias
database, and it has been parameterized with DWT
coefficients and selected with PCA.
Evaluation se
t
N
eural
Network
N
eural
Network
More
voted
Decision
Random weights
Random weights
BIOSIGNALS 2008 - International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing
456

REFERENCES
Matlab 2006, http://www.mathworks.com. The
Mathworks. Last Visit: 07-16-2006
Romero-Legarreta, I.,. Addison, P.S, Reed, M.J., Grubb,
N.R., Clegg, G.R., Robertson, C.E., Watson, J.N.,
2005. Continuous wavelet transform modulus maxima
analysis of the electrocardiogram: Beat-to-beat
characterization and beat-to-beat measurement, Int. J.
Wavelets, Multiresolution and Information
Processing, Vol.3, pp. 19-42.
Bianchi, M.F.de, Guido, R.C., Nogueira, A.L., Padovan,
P., 2006. “A wavelet-PCA approach for content-based
image retrieval” Proceeding of the Thrity-Eighth
Southeastern Symposium on System Theory, pp. 439 –
442.
Bishop, C.M., 1995. Neural Networks for Pattern
Recognition, Oxford University Press.
Juang, B.H., Rabiner, L.R., 1992. Spectral representations
for speech recognition by neural networks-a tutorial”
Proceedings of the Proceedings of the Workshop
Neural Networks for Signal Processing, 1992, pp. 214
– 222.
MIT-BIH, 2007,
http://www.physionet.org/physiobank/mitdb. MIT-
BIH Arrhythmia Database. Last Visit: 07-16-2007.
Song, M.H., Lee, J., Cho, S.P., Lee, K.J., Yoo S.K, 2005.
Support Vector Machine Based Arrhythmia
Classification Using Reduced Features. International
Journal of Control, Automation, and Systems. Vol. 3.
nº. 4. 571-579.
Zimmerman, M.W., Povinelli, R.J., 2004. On Improving
the Classification of Myocardial Ischemia Using
Holter ECG Data. Computers in Cardiology. Chicago.
Illinois, 377-380.
Jankowski, S., Oreziak, A., 2003. Learning System for
Computer-Aided ECG Analysis Based on Support
Vector Machines. International Journal of
Bioelectromagnetism. Vol. 5. nº 1. 175–176.
IMPROVING AN AUTOMATIC ARRHYTHMIAS RECOGNISER BASED IN ECG SIGNALS
457
