
WEIGHTS CONVERGENCE AND SPIKES CORRELATION IN AN
ADAPTIVE NEURAL NETWORK IMPLEMENTED ON VLSI
A. Daouzli, S. Sa¨ıghi, L. Buhry, Y. Bornat and S. Renaud
IMS-Bordeaux Labs, University of Bordeaux 1
351 cours de la Lib
´
eration, F-33405 Talence Cedex, France
Keywords:
Neuromorphic engineering, STDP, Hodgkin-Huxley model, analog VLSI.
Abstract:
This paper presents simulations of a conductance-based neural network implemented on a mixed hardware-
software simulation system. Synaptic connections follow a bio-realistic STDP rule. Neurons receive correlated
input noise patterns, resulting in a weights convergence in a confined range of conductance values. The
correlation of the output spike trains depends on the correlation degree of the input patterns.
1 INTRODUCTION
The first neurophysiology experiments on synaptic
plasticity were largely inspired by Hebb’s postu-
late (Hebb, 1949). Today, this postulate is often
rephrased in the sense that modifications in the synap-
tic transmission efficacy are driven by correlations in
the firing activity of pre- and postsynaptic neurons.
Spike-timing-dependent plasticity (STDP) describes
the adaptation temporal mechanisms (depression, po-
tentiation, saturation, ...) at the level of individual
spikes (Markram et al., 1997; Bi and Poo, 1998; Ab-
bott and Nelson, 2000; Feldman, 2000; Roberts and
Bell, 2002; Kepecs et al., 2002). Synapses with that
kind of plasticity were found in the cortex (Markram
et al., 1997), in hippocampus cells (Magee and John-
ston, 1997) and in cultured cells (Bi and Poo, 1998).
First studies showed the existence of Long Term Po-
tentiation (LTP) and Long Term Depression (LTD)
dependence, as functions of the synaptic weights to
the time difference between the pre- and postsynaptic
spikes.
More complex models were developed considering
phenomenons such as previous spikes effect for the
same neuron (Froemke and Dan, 2002), or the ef-
fect of synapse location (Rumsey and Abbott, 2003;
Froemke et al., 2005). STDP models can also have
different rules depending on the synaptic strength (Bi
and Poo, 1998; van Rossum et al., 2000). These
models are inspired by biophysical features. Con-
cerning functional aspects, STDP is known to en-
hance the connections strength for synchronized neu-
rons (van Rossum and Turrigiano, 2001; Song and
Abbott, 2001) and is supposed to play a role in neural
assembly synchronization (Singer and Gray, 1995).
Depending on the shape of the STDP model, the net-
work behavior can change, as the ratio between LTP
and LTD influences the weights convergence (Song
and Abbott, 2001).
Noise is considered as an interesting input in bio-
realistic neural networks as it helps modeling the
irregularity of real neuronal activity. Simulations
showed also the impact of noise inputs on the synap-
tic strength evolution when driven by STDP. In (Song
and Abbott, 2001), synaptic weights convergence is
bimodal. STDP is applied on synapses connecting
input noise spike patterns to a single spiking neuron.
These input spike trains can be cross-correlated and
have a Poisson distribution. With a different STDP
rule, where the potentiation (LTP) depends on the
synaptic strength, synaptic weights convergenceis not
bimodal but confined in a limited range (van Rossum
et al., 2000).
Here we propose to explore, in a small neural net-
work, the effect of correlated input noise patterns
(one pattern per neuron) when a STDP rule is ap-
plied on synapses. The effect is evaluated on synap-
tic (between neurons) conductance distribution and
on correlation in neurons’ spike trains. Every neu-
ron is attacked by an input noise pattern. These noise
patterns have different levels of correlation. We use
conductance-based model of cortical neurons.
STDP features are usually explored in large scale
spiking neural networks, or in only one single spiking
neuron. In this work, we use a 6 neurons network
with a complex neuron model based on the Hodgkin
and Huxley formalism (Hodgkin and Huxley, 1952).
Neurons are implemented on analog VLSI circuits,
and the whole simulation system is a mixed hardware-
software instrumentation tool (see section 2). These
286
Daouzli A., Saïghi S., Buhry L., Bornat Y. and Renaud S. (2008).
WEIGHTS CONVERGENCE AND SPIKES CORRELATION IN AN ADAPTIVE NEURAL NETWORK IMPLEMENTED ON VLSI.
In Proceedings of the First International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing, pages 286-291
DOI: 10.5220/0001069102860291
Copyright
c
SciTePress
same neural chips have already been successfully
used to simulate neural networks with STDP (Zou
et al., 2006b). The advantage of analog VLSI for
neural simulation is the speed of execution, it ensures
simulations in a biological real time. Furthermore,
hardware environment provides an electronic noise as
in biology living cells are in a noisy environment and
emulates in a way biological dispersion. In subsec-
tion 2.3, we present the STDP model we use and in
subsection 2.4 the method for correlating input noise
patterns. Then, in section 3, we show how hardware
parameters are related to biophysiological values. In
section 4, we present the simulation configuration,
tools to observe the distribution of synaptic weights
and the correlation of spikes, and we show results and
analysis of experiments. Finally, we discuss the spec-
ifications and the results of these experiments.
2 THE SIMULATION PLATFORM
We used for the simulation a hardware implementa-
tion of a conductance-based neuron model following
a Hodgkin and Huxley formalism. The implementa-
tion is done on analog VLSI circuits; the neural net-
work connectivity is driven by a custom hardware-
software system named PAX (Renaud et al., 2007).
This system is embedded on a computer through a
PCI interface board.
2.1 The Neurons Models
Analog VLSI circuits, model the neurons ionic cur-
rents, as described in the Hodgkin and Huxley for-
malism. An external capacitor connected to the cir-
cuits provides a voltage that is equivalent to the mem-
brane potential and ionic currents channels modulate
this potential. Four voltage-dependent ionic currents
are implemented: I
Na
+ ,I
K
+ ,I
LEAK
and a modulating
slow voltage-dependent potassium current I
M
. The
modeled neuron is the glutamate excitatory regular
spiking neuron (Connors and Gutnick, 1990). Hard-
ware neurons are characterized by their static pa-
rameters as time kinetics, potential offsets, conduc-
tance values (table 1), and by their functional fea-
tures as f(I) curves and spike-frequency adaptation
(see section 2.2). The neurons model parameter are
listed in table 1. m, n, mm in case of activation
and h in case of inactivation are state variables (s),
describing the state of ionic channels, defined by:
τ(V
MEM
)
ds(t)
dt
= s
∞
(V
MEM
) − s(t) with s
∞
(V
MEM
) =
1
1+exp(±
V
MEM
−V
OFFSET
V
SLOPE
)
.
The synapses conductance-based model is the kinetic
synapse model presented in (Destexhe et al., 1994).
It describes the synaptic strength as the duration of
postsynaptic receptors opening (AMPA receptors for
excitatory synapses). A pulse length represents the
conductance increase due to the release of transmit-
ters (Zou et al., 2006a).
Table 1: Ionic channels parameters for the implemented
model, relative to a membrane area of 0.00022cm
2
.
Leak I
LEAK
= g
LEAK
(V
MEM
−V
EQUI
)
g
LEAK
= 33nS, V
EQUI
= −80mV
Na I
Na
= g
Na
m
3
h(V
MEM
−V
EQUI
)
g
Na
= 11µS , V
EQUI
= 50mV
m :V
OFFSET
= −37mV , V
SLOPE
= 7.2mV
h :V
OFFSET
= −42mV , V
SLOPE
= −4.6mV
τ(m) = 0.03ms, τ(h) =
n
3.00ms if V
MEM
>0
0.25ms if V
MEM
<0
K I
K
= g
K
n
4
(V
MEM
−V
EQUI
)
g
K
= 1.1µS, V
EQUI
= −100mV
n :V
OFFSET
= −37mV , V
SLOPE
= 11.38mV
τ(n) = 3ms
Mod. I
M
= g
M
m(V
MEM
−V
EQUI
)
g
M
= 10nS, V
EQUI
= −100mV
mm :V
OFFSET
= −35mV , V
SLOPE
= 11.4mV
τ(mm) =
n
300ms if V
MEM
<0
8ms if V
MEM
>0
2.2 Neurons Functional Features
In the PAX system, values of stimulation currents
are electronic values that can differ from one neuron
to the other to trigger a same frequency. This phe-
nomenon is due to the mismatch and variations in the
VLSI circuits fabrication process. We use the f(I)
curves to benchmark the circuits and tune the simu-
lation parameters. The measured f(I) curves match
the software simulations of the corresponding model.
Differences exists concerning origin and scale val-
ues for the current range of the f(I) curves. Spike-
frequency adaptation shape observed on raster-plots
is consistent with biological data. These results are
detailed in (Lewis et al., 2006).
2.3 The Neural Network Connectivity
The STDP algorithm used is based on (Badoual et al.,
2006) biophysical model equation:
+(ω
ji
− ω
LTD
)
∑
l
Q[t −
˜
t
i
(t)]δ(t − t
j,l
)
i
(1)
where ω
ji
is the synaptic weight from neuron j (presy-
naptic) to i (postsynaptic). t
i,k
and t
j,l
are respec-
tively the sets of post- and presynaptic spikes times.
WEIGHTS CONVERGENCE AND SPIKES CORRELATION IN AN ADAPTIVE NEURAL NETWORK
IMPLEMENTED ON VLSI
287

P and Q are respectively the amount of LTP (potenti-
ation) and LTD (depression) change and are given by:
P(t) = A
+
exp(−t/τ
P
) and Q(t) = A
−
exp(−t/τ
Q
). ε
k
are functions taking into account spikes history of a
neuron and are given by ε
j
= 1−exp[−(t−
˜
t
j
(t))/τ
εj
]
and ε
i
= 1− exp[−(t −
˜
t
i
(t))/τ
εi
]. ω
LTP
is the maxi-
mal soft bound while ω
LTD
is the minimal soft bound.
˜
t
j
(t) is the neuron j last spike time and
˜
t
i
(t) is the neu-
ron i last spike time.
The STDP equation (1) is based on a precise biophys-
ical model. Parameters for exponential constants are
A
+
= 0.1 concerning potentiation and A
−
= 0.005 for
depression. Time constants are τ
P
= 14.8ms for po-
tentiation exponential of P and τ
Q
= 33.8ms for de-
pression exponentialfor Q. The eligibility ε (influence
of previous spikes of a same neuron), has an expo-
nential time constant for the presynaptic neuron τ
εj
=
28ms and for the postsynaptic neuron τ
εi
= 88ms
(Froemke and Dan, 2002). This takes into account
features as frequency dependence and spike triplets.
The STDP algorithmic implementation and parame-
ters are detailed in (Zou, 2006).
2.4 Correlated Input Noise Patterns
The noise inputs applied to neurons are coded as pat-
terns generated from a Poisson distribution and cor-
related with a defined degree. The Poisson distribu-
tion X is obtained as follows: X = {x
1
,..x
n
}/x
i
=
N(0,1).
p
m− 1/2+ m where N(0,1) is a normal dis-
tribution, m the average. X is converted in an absolute
time pattern Y: X = {x
1
,..x
n
} → Y = {y
1
,..y
n
}:
Y : y
i
=
i
∑
j=1
x
j
(2)
Noise input patterns are generated with one event
around each Y event. The time-lap between the event
Y and the pattern event is given by ε:
ε = N(0,1).(α − 1).
T
6
(3)
where N(0,1) is a normal distribution, T is the average
period and α ∈ [0,1] is the correlation coefficient.
3 FIXING HARDWARE/BIOLOGY
EQUIVALENCES
The stimulation currents applied to neurons are not
directly linked to the biophysical values. The possi-
ble values are in the range 0 to 4095. We have the
same inconvenience with synaptic conductances. In
the hardware, the values are coded as integers that
can vary from 0 to 255. To find for each VLSI neu-
ron the correspondence with biophysical values, we
developed a neuron model using the software NEU-
RON (Hines and Carnevale, 1997) corresponding to
the VLSI neuron model. The morphology of the neu-
ron is a cylinder of 1 section, diameter 96 nm and
length 73 nm. Having equivalent models, we devel-
oped a protocol to define the biophysical equivalent
to the digital parameters values used in PAX.
3.1 Determining Synaptic
Conductances in the Pax System
We extracted from the measurements on the PAX sys-
tem a rule for converting a PAX synaptic strength
value in a biophysical corresponding conductance
value and conversely. We created a two neurons net-
work (figure 1). Neuron A was stimulated by a cur-
rent I
A
that implies oscillations at about 8.5 Hz. Neu-
ron B is stimulated by a current I
B
that implies os-
cillations at about 3 Hz. Then an excitatory synapse
ω
AB
is created connecting A to B with A presy-
naptic to B. The synaptic strength increases from 0
to 255 for PAX, 0.02 µS for NEURON. For each
weight, neurons frequencies f
A
and f
B
are measured
(f
A
doesn’t change for NEURON and is near con-
stant for PAX with standard deviation equal to 0.4
and mean value 8.7 Hz). Equations (f(ω) = a.ω +
b) of the straight line fitting the experiments points
are calculated for both measurements on PAX and
on NEURON. The rules (ω
PAX
= a.ω
NEURON
+ b ;
ω
NEURON
= a
′
.ω
PAX
+ b
′
) give the correspondence
between the biological model and the hardware pa-
rameter. Results are: ω
NEURON
= (0.0943ω
PAX
+
3.0562)/1070.33 and ω
PAX
= (1070.33ω
NEURON
−
3.0499)/0.0943 .
Figure 1: Network of two neurons A and B stimulated by
constant currents, respectively I
A
and I
B
. ω
AB
is the synaptic
strength of the excitatory synapse connecting A to B.
3.2 Determining Stimulation Currents
in the Pax System
The aim here is to extract from measurements a cor-
respondencebetween a PAX stimulation current value
and its biophysical equivalent. The principle is to ex-
cite a neuron B by a presynaptic neuron A. A is stim-
ulated as in previous section with a static current. The
weight of synapse connecting A to B is also constant.
BIOSIGNALS 2008 - International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing
288

The B stimulation current varies in a range such that:
the lowest value doesn’t make B oscillating and the
highest value synchronizes B to A firing. Data col-
lected for each neuron B’s stimulation current I
B
are
frequency of B f
B
and A’s frequency f
A
(constant).
I
A
was chosen to have a frequency f
A
= 8.5Hz. Us-
ing PAX this frequency is approximate (for 10 trials:
m=8.7, SD=0.4) due to electronic noise. The simu-
lations duration is 30 s. Frequencies are calculated
between 2 s and 29 s. The equivalent synaptic weight
is calculated using the rule defined in subsection 3.1.
The correspondence is not exactly linear between fre-
quency and current, but the rule that we establish pro-
vides a good approximation of the biophysical val-
ues corresponding to PAX parameters. This process
has to be repeated for every neuron because of their
intrinsic variability. We obtain for every PAX neu-
ron, a correspondence rule: I
PAX
= a.I
NEURON
+b and
I
NEURON
= a
′
.I
PAX
+ b
′
. For instance, the rule giving
the PAX neuron number 2’s biophysical current value
is: I
NEURON
= −0.01625I
PAX
+ 36.363.
4 EXPERIMENTS AND RESULTS
4.1 Experiment: STDP Simulation with
Correlation
The PAX system, including the VLSI neurons’ was
used for the experiments. The system is embedded
in a computer, through a PCI interface, that computes
plasticity algorithms. The computer features are: pro-
cessor Intel Pentium 4
R
, dual core, 2.6GHz, cache:
512 Ko, SDRAM: 1Go. The operating system is the
Ubuntu
R
Linux system. We ran a series of simula-
tions with STDP as described in section 2.3 and noise
input patterns as described in subsection 2.4. The sim-
ulated neural network comprises six excitatory neu-
rons with all-to-all connectivity. All connections fol-
low a STDP rule. ω
LTP
is fixed in order to have all
neurons presenting a non-bursting activity bursts. The
experiment will help evaluating the STDP effects in
this small excitatory network when correlated noise
patterns are stimulating the neurons.
Network and Neurons Features. The neurons are
stimulated by constant currents chosen from f(I)
curves to maintain the membrane potential under the
firing threshold. Each neuron receive additional stim-
ulation: an input noise pattern (rate 5Hz) tuned in or-
der to trigger an oscillating frequency lower than 5Hz
(mean value 3Hz). All currents are in the biological
range [0.4nA-0.5nA].
Initial synaptic weights are either null or randomized
using an uniform law. Corresponding randomized
conductances values, using the correspondence rules
determined in section 3.1, are in the range [0nS-20nS]
which corresponds to numerical values in the range
[0-180]. Furthermore, a neuron receives synaptic in-
puts from all other neurons and projects its output to
all synapses of the other neurons. The simulation lasts
360 seconds. When a neuron spikes, all the related
synaptic weights are recalculated using the STDP al-
gorithm. For data analysis, each weight change is
recorded together with the timing. For each neuron,
all the timing of its spikes are also recorded for further
analysis.
4.2 Analysis Tools
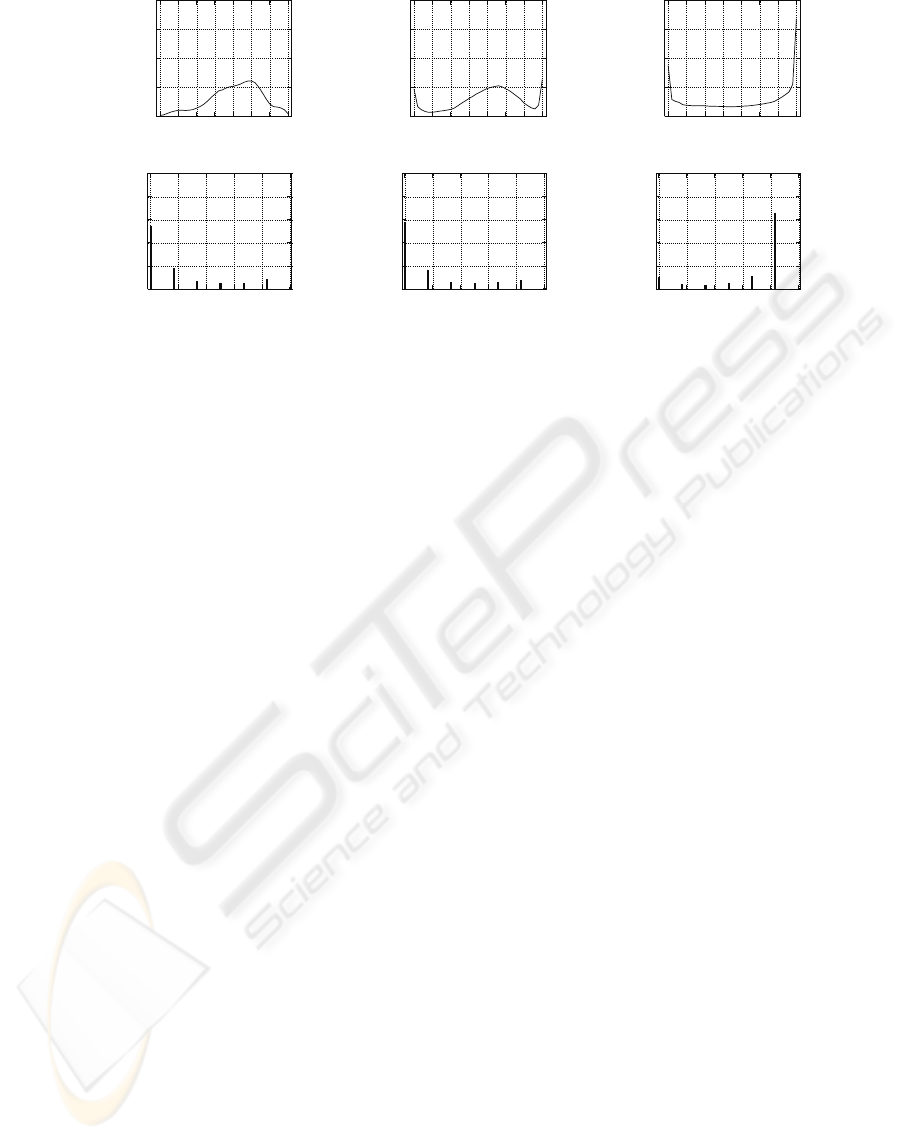
Weight Histogram. The method used to assess
weight convergence is the building of a histogram of
weights distribution (see top line of figure 2). For this
experiment, the encoded maximum weight value is
180. We divide the weight axis into 36 bins, thus each
section corresponds to an interval of 5. The weights
distribution is then calculated at the end of the simu-
lation and normalized.
Spike Correlation Histogram. To evaluate the cor-
relation between the neurons output firing patterns, a
correlation histogram is defined (see bottom line of
figure 2). The method is to divide the time axis into
sections, each section corresponding to 10 ms. Spikes
occurring in each time section are accumulated. As
we have 6 neurons, the maximum count per section
is 6 if every neuron spikes in that 10 ms window, ex-
cept if a neuron spikes 2 times in the same window.
We don’t consider that exception here. For every pos-
sible spikes count (here from 1 to 6), the number of
sections having this value is calculated. Both axis are
then normalized. This provides a graph showing the
spikes distribution relative to a minimal time window.
If the spikes of different neurons are well correlated
in that time window, distribution tend to 1, whereas
distribution will be closer to 0 for uncorrelated activ-
ity.
4.3 Results Analysis
As we can see on the bin histogram of figure 2A,
the weights after STDP are distributed in a limited
range when the correlation of input patterns is weak
(α < 0.5, α from equation 3). When the input cor-
relation grows, extrema values of the weights appear
(e.g. with α = 0.6 figure 2C). When the input correla-
tion is maximum (α = 1) then the weights distribution
WEIGHTS CONVERGENCE AND SPIKES CORRELATION IN AN ADAPTIVE NEURAL NETWORK
IMPLEMENTED ON VLSI
289
0
0.05
0.1
0.15
0.2
0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35
Normalizeddistribution
ofweights
Binnumber
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1
Normalizednumber
oftimewindows
Normalizedspikescounts
0
0.05
0.1
0.15
0.2
0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35
Normalizeddistribution
ofweights
Binnumber
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1
Normalizednumber
oftimewindows
Normalizedspikescounts
0
0.05
0.1
0.15
0.2
0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35
Normalizeddistribution
ofweights
Binnumber
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1
Normalizednumber
oftimewindows
Normalizedspikescounts
E
A
B
C
D
F
Figure 2: Simulation of input correlation’s effect on the synaptic weights convergence and the spikes correlation. Time
simulation lasts 360 s with initial weights randomized and a frequency of input noise around 5Hz. Top line: Weight histograms
for a simulation with input correlation of 0.35 (A), 0.6 (C) and 1 (E). Bottom line: Correlation histograms for a simulation
with a time window of 10 ms. The input correlations are 0.35 (B), 0.6 (D) and 1 (F).
is bimodal (figure 2E). At the same time, the correla-
tion histogram shows that correlation of output spikes
in a window time of 10 ms is weak when correlation
input has α < 0.8 (figure 2B and D), grows when α
is higher. Up to a high correlation when α = 1 (fig-
ure 2F).
In (van Rossum et al., 2000), where the STDP rule
has no soft bound (ω
LTP
and ω
LTD
) and where LTP
depends on the synaptic strength (ω
ji
), the weights
always converge in a limited range. In (Song et al.,
2000), where the soft bound is introduced but with
no LTP depending on ω
ji
, the weights systematically
show a bimodal convergence.
Our STDP model was simulated in (Zou and Des-
texhe, 2007) in single neuron configuration. In that
case, all weights converge into a limited range.
The experiments we presented showed that this same
STDP rule applied to a 6-excitatory neurons network
lead to more complexe figures, mixing bimodal and
range limited weights convergence.
5 DISCUSSION AND
CONCLUSIONS
Using analog VLSI circuits for computational neuro-
science is a performant solution for running simula-
tions at biological real time. The system used can also
be interfaced with real biological neurons to create a
hybrid neural network (Le Masson et al., 2002). One
inconvenient, as seen in section 3, is that the tuning of
some parameters depends on the fabrication for pa-
rameters. The correspondence rules developed pro-
vides an estimation of biophysical values and only
in a short range because of non-linearities. However,
benchmarks showed us the network patterns were re-
spected by such a simulation tool (Zou et al., 2006a).
In our experiments, we showed that the weights dis-
tribution convergence depends on correlation of input
noise patterns. This convergence mixes bimodal con-
vergence and range confinement convergence. This
phenomenon is not covered by other STDP rules. We
also showed that the input correlation degree influ-
ences the correlation in neurons spikes. For the next
PAX system generation, STDP computation will be
embedded in the hardware system. A more important
number of neurons will be available with available in-
hibitory neurons. Experiments will be continued on
more complex neural networks.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work is supported by the European Community
Grant FACETS (IST-2005-15879).
REFERENCES
Abbott, L. F. and Nelson, S. B. (2000). Synaptic plastic-
ity: taming the beast. Natural Neuroscience, 3:1178–
1183.
Badoual, M., Zou, Q., Davison, A. P., Rudolph, M., Bal,
T., Fr´egnac, Y., and Destexhe, A. (2006). Biophys-
ical and phenomenological models of multiple spike
interactions in spike-timing dependent plasticity. Int.
J. Neural Syst., 16(2):79–98.
Bi, G. and Poo, M. (1998). Synaptic modifications in cul-
tured hippocampal neurons: dependence on spike tim-
BIOSIGNALS 2008 - International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing
290

ing, synaptic strength, and postsynaptic cell type. The
Journal of Neuroscience, 18(24):10464–10472.
Connors, B. and Gutnick, M. (1990). Intrinsic firing pat-
terns of diverse neocortical neurons. Trends in Neuro-
sciences, 13:99–104.
Destexhe, A., Mainen, Z., and Sejnowski, T. J. (1994). An
efficient method for computing synaptic conductances
based on a kinetic model of receptor binding. Neural
Computation, 6:10–14.
Feldman, D. E. (2000). Timing-based LTP and LTD at ver-
tical inputs to layer II/III pyramidal cells in rat barrel
cortex. Neuron, 27:45–56.
Froemke, R. C. and Dan, Y. (2002). Spike-timing-
dependent plasticity modification induced by natural
spike trains. Nature, 416:433–438.
Froemke, R. C., Poo, M., and Dan, Y. (2005). Spike-
timing-dependent plasticity depends on dendritic lo-
cation. Nature, 434:221–225.
Hebb, D. O. (1949). The Organization of Behaviour. John
Wiley & Sons.
Hines, M. L. and Carnevale, N. T. (1997). The neuron sim-
ulation environment. Neural Computation, 9:1179–
1209.
Hodgkin, A. L. and Huxley, A. F. (1952). A quantitative
description of membrane current and its application to
conduction and excitation in nerve. Journal of Physi-
ology, 117:500–544.
Kepecs, A., van Rossum, M. C. W., Song, S., and Tegner,
J. (2002). Spike timing dependent plasticity: common
themes and divergent vistas. Biological Cybernetics,
87:446–458.
Le Masson, G., Renaud-Le Masson, S., Debay, D., and Bal,
T. (2002). Feedback inhibition controls spike transfer
in hybrid thalamic circuits. Nature, 417:854–858.
Lewis, N., Bornat, Y., Alvado, L., Lopez, C., Daouzli, A.,
Levi, T., Tomas, J., Saghi, S., and Renaud, S. (2006).
Pax : un outil logiciel / mat´eriel d’investigation pour
les neurosciences computationnelles. In NeuroComp,
pages 171–174.
Magee, J. C. and Johnston, D. (1997). A synaptically con-
trolled, associative signal for hebbian plasticity in hip-
pocampal neurons. Science, 275:209–213.
Markram, H., Lubke, J., Frotscher, M., and Sackmann,
B. (1997). Regulation of synaptic efficacy by co-
incidence of postsynaptic APs and EPSPs. Science,
275:213–215.
Renaud, S., Tomas, J., Bornat, Y., Daouzli, A., and Saighi,
S. (2007). Neuromimetic ICs with analog cores: an
alternative for simulating spiking neural networks. In
InternationaI Symposium on Circuits And Systems,
pages 3355–3358. IEEE.
Roberts, P. D. and Bell, C. C. (2002). Spike timing depen-
dent synaptic plasticity in biological systems. Biolog-
ical Cybernetics, 87:392–403.
Rumsey, C. C. and Abbott, L. F. (2003). Equalization of
synaptic efficacy by activity- and timing-dependent
synaptic plasticity. The Journal of Neurophysiology,
91:2273–2280.
Singer, W. and Gray, C. M. (1995). Visual feature integra-
tion and the temporal correlation hypothesis. Annual
Review of Neuroscience, 18:555–586.
Song, S. and Abbott, L. (2001). Cortical development and
remapping through spike timing-dependent plasticity.
Neuron, 32:339–350.
Song, S., Miller, K., and Abbott, L. (2000). Competi-
tive hebbian learning through spike-timing-dependent
synaptic plasticity. Nature Neuroscience, 3:919–926.
van Rossum, M. C. W., Bi, G.-Q., and Turrigiano., G.
(2000). Stable hebbian learning from spike timing-
dependent plasticity. The Journal of Neuroscience,
20:8812–8821.
van Rossum, M. C. W. and Turrigiano, G. (2001). Cor-
relation based learning from spike timing dependent
plasticity. Neurocomputing, 38-40:409–415.
Zou, Q. (2006). Computational models of spike timing
dependent plasticity: synapses, neurons and circuits.
PhD thesis, Universit´e Paris VI.
Zou, Q., Bornat, Y., Sa¨ıghi, S., Tomas, J., Renaud, S., and
Destexhe, A. (2006a). Analog-digital simulations of
full-conductance-based networks of spiking neurons
with spike timing dependent plasticity. Network: com-
putation in neural systems, 17:211–233.
Zou, Q., Bornat, Y., Tomas, J., Renaud, S., and Destexhe,
A. (2006b). Real-time simulations of networks of
hodgkin-huxley neurons using analog circuits. Neu-
rocomputing, 69:1137–1140.
Zou, Q. and Destexhe, A. (2007). Kinetic models of spike-
timing dependent plasticity and their functional con-
sequences in detecting correlations. Biol. Cybern.,
97(1):81–97.
WEIGHTS CONVERGENCE AND SPIKES CORRELATION IN AN ADAPTIVE NEURAL NETWORK
IMPLEMENTED ON VLSI
291
