ROBUST FACE ALIGNMENT USING CONVOLUTIONAL NEURAL
NETWORKS
Stefan Duffner and Christophe Garcia
Orange Labs, 4, Rue du Clos Courtel, 35512 Cesson-S´evign´e, France
Keywords:
Face alignment, Face registration, Convolutional Neural Networks.
Abstract:
Face recognition in real-world images mostly relies on three successive steps: face detection, alignment and
identification. The second step of face alignment is crucial as the bounding boxes produced by robust face de-
tection algorithms are still too imprecise for most face recognition techniques, i.e. they show slight variations
in position, orientation and scale. We present a novel technique based on a specific neural architecture which,
without localizing any facial feature points, precisely aligns face images extracted from bounding boxes com-
ing from a face detector. The neural network processes face images cropped using misaligned bounding boxes
and is trained to simultaneously produce several geometric parameters characterizing the global misalign-
ment. After having been trained, the neural network is able to robustly and precisely correct translations of
up to ±13% of the bounding box width, in-plane rotations of up to ±30
◦
and variations in scale from 90% to
110%. Experimental results show that 94% of the face images of the BioID database and 80% of the images of
a complex test set extracted from the internet are aligned with an error of less than 10% of the face bounding
box width.
1 INTRODUCTION
In the last decades, much work has been conducted
in the field of automatic face recognition in images.
The problem is however far from being solved as the
variability of the appearance of a face image is very
large under real-world conditions because of non-
constrained illumination conditions, variable poses
and facial expressions. To cope with this large vari-
ability, face recognition systems require the input face
images to be well-aligned in such a way that char-
acteristic facial features (e.g. the eye centers) are ap-
proximatelylocated at pre-defined positions in the im-
age. As pointed out by Shan et al. (Shan et al., 2004)
and Rentzeperis et al. (Rentzeperis et al., 2006), slight
misalignments, i.e. x and y translation, rotation or
scale changes, cause a considerable performance drop
for most of the current face recognition methods.
Shan et al. (Shan et al., 2004) addressed this prob-
lem by adding virtual examples with small transfor-
mations to the training set of the face recognition sys-
tem and, thus, making it more robust. Martinez (Mar-
tinez, 2002) additionally modeled the distribution in
the feature space under varying translation by a mix-
ture of Gaussians. However, these approaches can
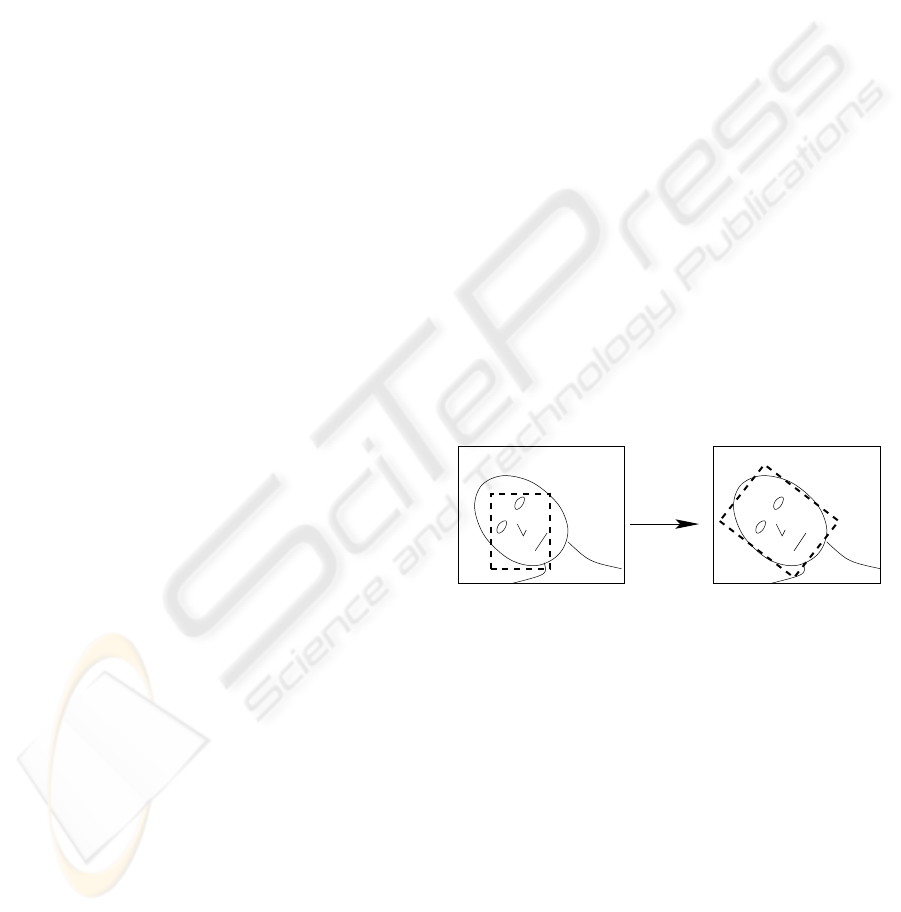
translation
scale
rotation
Figure 1: The principle of face alignment. Left: bound-
ing rectangle of face detector, right: rectangle aligned with
face.
only cope with relatively little variations and, in prac-
tice, cannot effectively deal with imprecisely local-
ized face images like those coming from a robust face
detection systems.
For this reason, most of the face recognition meth-
ods require an intermediate step, called face align-
ment or face registration, where the face transformed
in order to be well-aligned with the respective bound-
ing rectangle, or vice versa. Figure 1 illustrated this.
Existing approaches can be divided into two main
groups: approaches based on facial feature detection
and global matching approaches, most of the pub-
lished methods belonging to the first group. Berg et
30
Duffner S. and Garcia C. (2008).
ROBUST FACE ALIGNMENT USING CONVOLUTIONAL NEURAL NETWORKS.
In Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications, pages 30-37
DOI: 10.5220/0001073200300037
Copyright
c
SciTePress

al. (Berg et al., 2004), for example, used a SVM-
based feature detector to detect eye and mouth cor-
ners and the nose and then applied an affine trans-
formation to align the face images such that eye and
mouth centers are at pre-defined positions. Wiskott
et al. (Wiskott et al., 1997) used a technique called
Elastic Bunch Graph Matching where they mapped a
deformable grid onto a face image by using local sets
of Gabor filtered features. Numerous other methods
(Baker and Matthews, 2001; Edwards et al., 1998;
Hu et al., 2003; Li et al., 2002) align faces by ap-
proaches derived from the Active Appearance Models
introduced by Cootes et al. (Cootes et al., 2001).
Approaches belonging to the second group are
less common. Moghaddam and Pentland (Moghad-
dam and Pentland, 1997), for example, used a max-
imum likelihood-based template matching method to
eliminate translation and scale variations. In a sec-
ond step, however, they detect four facial features to
correct rotation as well. Jia et al. (Jia et al., 2006) em-
ployed a tensor-based model to super-resolve face im-
ages of low resolution and at the same time found the
best alignment by minimizing the correlation between
the low-resolution image and the super-resolved one.
Rowley et al. (Rowley et al., 1998) proposed a face
detection method including a Multi-Layer Perceptron
(MLP) to estimate in-plane face rotation of arbitrary
angle. They performed the alignment on each candi-
date face location and then decided if the respective
image region represents a face.
The method proposed in this paper is similar to the
one of Rowley et al. (Rowley et al., 1998) but it not
only corrects in-plane rotation but also x/y translation
and scale variations. It is further capable of treating
non-frontal face images and employs an iterative es-
timation approach. The system makes use of a Con-
volutional Neural Network (CNN) (LeCun, 1989; Le-
Cun et al., 1990) that, after being trained, receives a
mis-aligned face image and directly and simultane-
ously responds with the respective parameters of the
transformation that the input image has undergone.
The remainder of this article is organized as fol-
lows. In sections 2 and 3, we describe the neural
network architecture and training process. Section 4
gives details about the overall alignment procedure
and in section 5 we experimentally assess the preci-
sion and the robustness of the proposed approach. Fi-
nally, conclusions are drawn in section 6.
2 THE PROPOSED SYSTEM
ARCHITECTURE
The proposed neural architecture is a specific type of
neural network consisting of seven layers, where the
first layer is the input layer, the four following lay-
ers are convolutional and sub-sampling layers and the
last two layers are standard feed-forward neuron lay-
ers. The aim of the system is to learn a function that
transformsan input pattern representing a mis-aligned
face image into the four transformation parameters
corresponding to the misalignment, i.e. x/y transla-
tion, rotation angle and scale factor. Figure 2 gives an
overview of the architecture.
The retina l
1
receives a cropped face image of
46× 56 pixels, containing gray values normalized be-
tween −1 and +1. No further pre-processing like
contrast enhancement, noise reduction or any other
kind of filtering is performed.
The second layer l
2
consists of four so-called fea-
ture maps. Each unit of a feature map receives its
input from a set of neighboring units of the retina
as shown in Fig. 3. This set of neighboring units is
often referred to as local receptive field, a concept
which is inspired by Hubel and Wiesel’s discovery of
locally-sensitive, orientation-selective neurons in the
cat visual system (Hubel and Wiesel, 1962). Such lo-
cal connections have been used many times in neural
models of visual learning (Fukushima, 1975; LeCun,
1989; LeCun et al., 1990; Mozer, 1991). They allow
extracting elementary visual features such as oriented
edges or corners which are then combined by subse-
quent layers in order to detect higher-order features.
Clearly, the position of particular visual features can
vary considerably in the input image because of dis-
tortions or shifts. Additionally, an elementary feature
detector can be useful in several parts of the image.
For this reason, each unit shares its weights with all
other units of the same feature map so that each map
has a fixed feature detector. Thus, each feature map
y
2i
of layer l
2
is obtained by convolving the input map
y
1
with a trainable kernel w
2i
:
y
2i
(x,y) =
∑
(u,v)∈K
w
2i
(u,v)y
1
(x+ u,y+ v) + b
2i
, (1)
where K = {(u,v) | 0 < u < s
x
; 0 < v < s
y
} and
b
2i
∈ R is a trainable bias which compensates for
lighting variations in the input. The four feature maps
of the second layer perform each a different 7×7 con-
volution (s
x
= s
y
= 7). Note that the size of the ob-
tained convolutional maps in l
2
is smaller than their
input map in l
1
in order to avoid border effects in the
convolution.
Layer l
3
sub-samples its input feature maps into
maps of reduced size by locally summing up the out-
ROBUST FACE ALIGNMENT USING CONVOLUTIONAL NEURAL NETWORKS
31

Translation Y
Scale factor
Translation X
Rotation angle
convolution 7x7
convolution 5x5
subsampling
subsampling
l
1
: 1x46x56
l
2
: 4x40x50
l
3
: 4x20x25
l
4
: 3x16x21
l
5
: 3x8x10
l
6
: 40
l
7
: 4
Figure 2: Architecture of the neural network.
convolution 5x5
subsampling
Figure 3: Example of a 5× 5 convolution map followed by
a 2× 2 sub-sampling map.
put of neighboring units (see Fig. 3). Further, this sum
is multiplied by a trainable weight w
3j
, and a trainable
bias b
3j
is added before applying a sigmoid activation
function Φ(x) = arctan(x):
y
3j
(x,y) = Φ
w
3j
∑
u,v∈{0,1}
y
2j
(2x+ u,2y+ v) + b
3j
.
(2)
Thus, sub-sampling layers perform some kind of aver-
aging operation with trainable parameters. Their goal
is to make the system less sensitive to small shifts,
distortions and variations in scale and rotation of the
input at the cost of some precision.
Layer l
4
is another convolutional layer and con-
sists of three feature maps, each connected to two
maps of the preceding layer l
3
. In this layer, 5 × 5
convolutionkernels are used and each feature map has
two different convolution kernels, one for each input
map. The results of the two convolutions as well as
the bias are simply added up. The goal of layer l
4
is
to extract higher-level features by combining lower-
level information from the preceding layer.
Layer l
5
is again a sub-sampling layer that works
in the same way as l
3
and again reduces the dimension
of the respective feature maps by a factor two.
Whereas the previous layers act principally as fea-
ture extraction layers, layers l
6
and l
7
combine the
extracted local features from layer l
4
into a global
model. They are neuron layers that are fully con-
nected to their respective preceding layers and use
a sigmoid activation function. l
7
is the output layer
containing exactly four neurons, representing x and
y translation, rotation angle and scale factor, normal-
ized between −1 and +1. After activation of the net-
work, these neurons contain the estimated normalized
transformation parameters y
7i
of the mis-aligned face
image presented at l
1
. Each final transformation pa-
rameter p
i
is then calculated by linearly rescaling the
corresponding value y
7i
from [-1,+1] to the interval of
VISAPP 2008 - International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
32

Figure 4: Examples of training images created by manually
misaligning the face (top left: well-aligned face image).
the respective minimal and maximal allowed values
pmin
i
and pmax
i
:
p
i
=
pmax
i
− pmin
i
2
(y
7i
+ 1) + pmin
i
, i = 1..4 .
(3)
3 TRAINING PROCESS
We constructed a training set of about 30,000 face im-
ages extracted from several public face databases with
annotated eye, nose and mouth positions. Using the
annotated facial features, we were able to crop well-
aligned face images where the eyes and the mouth are
roughly at pre-defined positions in the image while
keeping a constant aspect ratio. By applying trans-
formations on the well-aligned face images, we pro-
duced a set of artificially mis-aligned face images that
we cropped from the original image and resized to
have the dimensions of the retina (i.e. 46× 56). The
transformations were applied by varying the transla-
tion between −6 and +6 pixels, the rotation angle
between −30 and +30 degrees and the scale factor
between 0.9 and 1.1. Figure 4 shows some train-
ing examples for one given face image. The respec-
tive transformationparameters p
i
were stored for each
training example and used to form the corresponding
desired outputs of the neural network by normalizing
them between −1 and +1:
d
i
=
2(p
i
− pmin
i
)
pmax
i
− pmin
i
− 1 . (4)
Training was performed using the well-known
Backpropagation algorithm which has been adapted
in order to account for weight sharing in the convo-
lutional layers (l
2
and l
4
). The objective function is
simply the Mean Squared Error (MSE) between the
computed outputs and the desired outputs of the four
neurons in l
7
. At each iteration, a set of 1,000 face
images is selected at random. Then, each face im-
age example of this set and its known transformation
Face Detection
Alignment estimation
by CNN
Translation Y = +4
Rotation angle = −14
Scale factor = 0.95
Translation X = − 2
Adjust by 10% using
the inverse parameters
30 iterations ?
Face extraction
and rescaling
Save final
parameters
no
yes
Figure 5: Overall alignment procedure.
parameters are presented, one at a time, to the neu-
ral network and the weights are updated accordingly
(stochastic training). Classically, in order to avoid
overfitting, after each training iteration, a validation
phase is performed using a separate validation set. A
minimal error on the validation set is supposed to give
the best generalization, and the corresponding weight
configuration is stored.
4 ALIGNMENT PROCESS
We now explain how the neural network is used to
align face images with bounding boxes obtained from
a face detector. The overall procedure is illustrated in
Figure 5. Face detection is performed using the Con-
volutional Face Finder by Garcia and Delakis (Garcia
and Delakis, 2004) which produces upright bounding
boxes. The detected faces are then extracted accord-
ing to the bounding box and resized to 46 × 56 pix-
els. For each detected face, the alignment process
is performed by presenting the mis-aligned cropped
face image to the trained neural network which in turn
gives an estimation of the underlying transformation.
ROBUST FACE ALIGNMENT USING CONVOLUTIONAL NEURAL NETWORKS
33

A correction of the bounding box can then simply be
achieved by applying the inverse transformation pa-
rameters (−p
i
for translation and rotation, and 1/p
i
for scale). However, in order to improve the correc-
tion, this step is performed several (e.g. 30) times in
an iterative manner, where at each iteration, only a
certain proportion (e.g. 10%) of the correction is ap-
plied to the bounding box. Then, the face image is
re-cropped using the new bounding box and a new
estimation of the parameters is calculated with this
modified image. The transformation with respect to
the initial bounding box is obtained by simply accu-
mulating the respective parameter values at each it-
eration. Using this iterative approach, the system fi-
nally converges to a more precise solution than when
using a full one-step correction. Moreover, oscilla-
tions can occur during the alignment cycles. Hence,
the solution can further be improved by reverting to
that iteration where the neural network estimates the
minimal transformation, i.e. where the outputs y
7i
are
the closest to zero.
The alignment can be further enhanced by succes-
sively executing the procedure described above two
times with two different neural networks: the first one
trained as presented above for coarse alignment and
the second one with a modified training set for fine
alignment. For training the fine alignment neural net-
work, we built a set of face images with less variation,
i.e. [−2,+2] for x and y translations, [−10, +10] for
rotation angles and [0.95,1.05] for scale variation. As
with the neural network for coarse alignment, the val-
ues of the output neurons and the desired output val-
ues are normalized between −1 and +1 using reduced
extrema pmin
′
i
and pmax
′
i
(cf. equation 4).
5 EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS
To evaluate the proposed approach, we
used two different annotated test sets, the
public face database BioID (available at
h t t p : / / www.humanscan.com/support/downloads
/facedb.php) containing 1,520 images and a private
set of about 200 images downloaded from the Inter-
net. The latter, referred to as Internet test set, contains
face images of varying size, with large variations in
illumination, pose, facial expressions and containing
noise and partial occlusions. As described in the
previous section, for each face localized by the face
detector (Garcia and Delakis, 2004), we perform
the alignment on the respective bounding box and
calculate the precision error e which is defined as the
mean of the distances between its corners a
i
∈ R
2
and the respective corners of the desired bounding
box b
i
∈ R
2
normalized with respect to the width W
of the desired bounding box:
e =
1
4W
4
∑
i=1
ka
i
− b
i
k . (5)
Figure 6 shows, for the two test sets, the propor-
tion of correctly aligned faces varying the allowed er-
ror e.
For example, if we allow an error of 10% of the
bounding box width, 80% and 94% of the faces of
the Internet and BioID test sets respectively are well-
aligned. Further, for about 70% of the aligned BioID
faces, e is below 5%.
We also compared our approach to a different
technique (Duffner and Garcia, 2005) that localizes
the eye centers, the nose tip and the mouth center. The
face images with localized facial features are aligned
using the same formula as used for creating the train-
ing set of the neural network presented in this paper.
Figure 7 shows the respective results for the Internet
test set.
To show the robustness of the proposed method,
we added Gaussian noise with varying standard de-
viation σ to the input images before performing face
alignment. Figure 8 shows the error e versus σ, aver-
aged over the whole set for both of the test sets. Note
that e remains below 14% for the Internet test set and
below 10% for the BioID test set while adding a large
amount of noise (i.e. σ up to 150 for pixel values be-
ing in [0,255]).
Another experiment demonstrates the robustness
of our approach against partial occlusions while
adding black filled rectangles of varying area to the
input images. Figure 9 shows, for two types of oc-
clusions (explained below), the error e averaged over
each test set with varying s, representing the occluded
proportion with respect to the whole face rectangle.
For a given detected face, let w be the width and
h be the height of the bounding box. The first type
of occlusion is a black strip (”scarf”) of width w and
varying height h at the bottom of the detected face
rectangle. The second type is a black box with as-
pect ratio w/h at a random position inside the detected
rectangle. We notice that while varying the occluded
area up to 40% the alignment error does not substan-
tially increase, especially for the scarf type. It is, how-
ever, more sensitive to random occlusions. Neverthe-
less, for s < 30% the error stays below 15% for the
Internet test set and below 12% for the BioID test set.
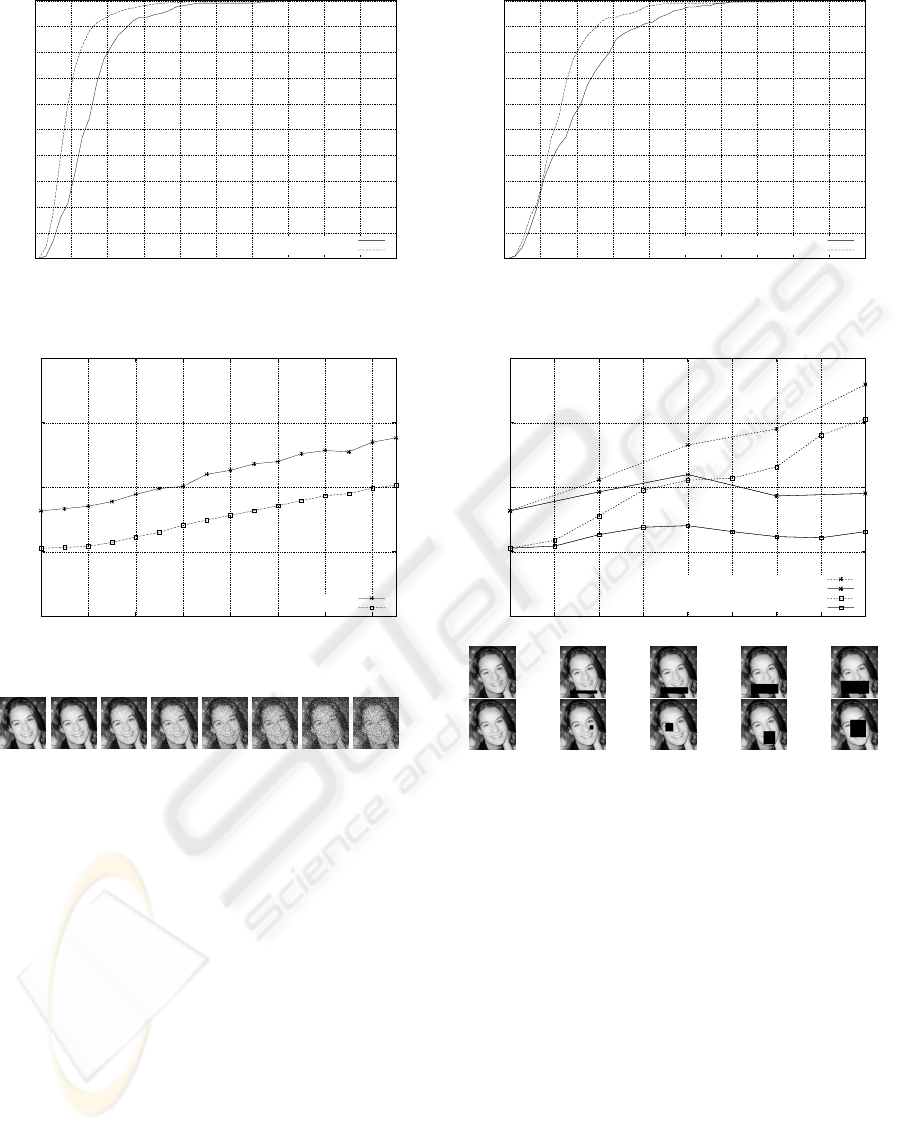
Figure 10 shows some results on the Internet test
set. For each example, the black box represents the
desired box, while the white box on the respective left
image represents the face detector output and the one
VISAPP 2008 - International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
34
0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.8
0.9
1
0 0.05 0.1 0.15 0.2 0.25 0.3 0.35 0.4 0.45 0.5
Rate of correct alignment
Mean corner distance: e
Internet test set
BioID test set
Figure 6: Correct alignment rate vs. allowed mean corner
distance.
0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.8
0.9
1
0 0.05 0.1 0.15 0.2 0.25 0.3 0.35 0.4 0.45 0.5
Rate of correct alignment
Mean corner distance: e
Feature detection approach
Our approach
Figure 7: Precision of our approach and an approach based
on facial feature detection (Duffner and Garcia, 2005).
0
0.05
0.1
0.15
0.2
0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140
mean e
standard deviation
Internet
BioID
Figure 8: Sensitivity analysis: Gaussian noise.
0
0.05
0.1
0.15
0.2
0 0.05 0.1 0.15 0.2 0.25 0.3 0.35 0.4
mean e
occluded porportion s
Internet: random rectangle
Internet: scarf
BioID: random rectangle
BioID: scarf
0
0.05
0.1
0.15
0.2
0 0.05 0.1 0.15 0.2 0.25 0.3 0.35 0.4
mean e
occluded porportion s
Internet: random rectangle
Internet: scarf
BioID: random rectangle
BioID: scarf
Figure 9: Sensitivity analysis: partial occlusion.
on the respective right image represents the aligned
rectangle as estimated by the proposed system.
The method is also very efficient in terms of com-
putation time. It runs at 67 fps on a Pentium IV
3.2GHz and can easily be implemented on embedded
platforms.
6 CONCLUSIONS
We have presented a novel technique that aligns faces
using their respective bounding boxes coming from a
face detector. The method is based on a convolutional
neural network that is trained to simultaneously out-
put the transformation parameters corresponding to a
given mis-aligned face image. In an iterative and hier-
archical approach this parameter estimation is gradu-
ally refined. The system is able to correct translations
of up to ±13% of the face bounding box width, in-
plane rotations of up to ±30 degrees and variations in
scale from 90% to 110%. In our experiments, 94%
of the face images of the BioID database and 80%
of a test set with very complex images were aligned
with an error of less than 10% of the bounding box
width. Finally, we experimentally show that the pre-
cision of the proposed method is superior to a feature
detection-basedapproach and very robustto noise and
partial occlusions.
ROBUST FACE ALIGNMENT USING CONVOLUTIONAL NEURAL NETWORKS
35

Figure 10: Some alignment results with the Internet test set.
VISAPP 2008 - International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
36

REFERENCES
Baker, S. and Matthews, I. (2001). Equivalence and ef-
ficiency of image alignment algorithms. In Com-
puter Vision and Pattern Recognition, volume 1, pages
1090–1097.
Berg, T., Berg, A., Edwards, J., Maire, M., White, R., Teh,
Y.-W., Learned-Miller, E., and Forsyth, D. (2004).
Names and faces in the news. In Computer Vision and
Pattern Recognition, volume 2, pages 848–854.
Cootes, T., Edwards, G., and Taylor, C. (2001). Active ap-
pearance models. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Anal-
ysis and Machine Intelligence, 23(6):681–685.
Duffner, S. and Garcia, C. (2005). A connexionist ap-
proach for robust and precise facial feature detection
in complex scenes. In Fourth International Sympo-
sium on Image and Signal Processing and Analysis
(ISPA), pages 316–321, Zagreb, Croatia.
Edwards, G., Taylor, C., and Cootes, T. (1998). Interpreting
face images using active appearance models. In Auto-
matic Face and Gesture Recognition, pages 300–305.
Fukushima, K. (1975). Cognitron: A self-organizing mul-
tilayered neural network. Biological Cybernetics,
20:121–136.
Garcia, C. and Delakis, M. (2004). Convolutional face
finder: A neural architecture for fast and robust face
detection. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and
Machine Intelligence, 26(11):1408 – 1423.
Hu, C., Feris, R., and Turk, M. (2003). Active wavelet net-
works for face alignment. In British Machine Vision
Conference, UK.
Hubel, D. and Wiesel, T. (1962). Receptive fields, binocu-
lar interaction and functional architecture in the cat’s
visual cortex. Journal of Physiology, 160:106–154.
Jia, K., Gong, S., and Leung, A. (2006). Coupling face
registration and super-resolution. In British Machine
Vision Conference, pages 449–458, Edinburg, UK.
LeCun, Y. (1989). Generalization and network design
strategies. In Pfeifer, R., Schreter, Z., Fogelman, F.,
and Steels, L., editors, Connectionism in Perspective,
Zurich.
LeCun, Y., Boser, B., Denker, J., Henderson, D., Howard,
R., Hubbard, W., and Jackel, L. (1990). Handwritten
digit recognition with a back-propagation network. In
Touretzky, D., editor, Advances in Neural Information
Processing Systems 2, pages 396–404. Morgan Kauf-
man, Denver, CO.
Li, S., ShuiCheng, Y., Zhang, H., and Cheng, Q. (2002).
Multi-view face alignment using direct appearance
models. In Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition,
pages 309–314.
Martinez, A. (2002). Recognizing imprecisely localized,
partially occluded, and expression variant faces from a
single sample per class. IEEE Transactions on Pattern
Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 24(6):748–763.
Moghaddam, B. and Pentland, A. (1997). Probabilistic vi-
sual learning for object representation. IEEE Trans-
actions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence,
19(7):696–710.
Mozer, M. C. (1991). The perception of multiple objects:
a connectionist approach. MIT Press, Cambridge,
USA.
Rentzeperis, E., Stergiou, A., Pnevmatikakis, A., and Poly-
menakos, L. (2006). Impact of face registration errors
on recognition. In Artificial Intelligence Applications
and Innovations, Peania, Greece.
Rowley, H. A., Baluja, S., and Kanade, T. (1998). Rota-
tion invariant neural network-based face detection. In
Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages 38–
44.
Shan, S., Chang, Y., Gao, W., Cao, B., and Yang, P. (2004).
Curse of mis-alignment in face recognition: problem
and a novel mis-alignment learning solution. In Auto-
matic Face and Gesture Recognition, pages 314–320.
Wiskott, L., Fellous, J., Krueger, N., and von der Malsburg,
C. (1997). Face recognition by elastic bunch graph
matching. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and
Machine Intelligence, 19(7):775–779.
ROBUST FACE ALIGNMENT USING CONVOLUTIONAL NEURAL NETWORKS
37
