
MULTI-LANE VISUAL PERCEPTION FOR LANE DEPARTURE
WARNING SYSTEMS
Juan M. Collado, Cristina Hilario, Arturo de la Escalera and Jose M. Armingol
Intelligent Systems Lab., Systems Engineering and Automation Dept., Universidad Carlos III de Madrid, Spain
Keywords:
Driver assistance systems, Intelligent transportation systems, Lane Departure Warning, Particle filter, Model-
based object tracking, Image analysis, Road vehicles.
Abstract:
This paper presents a Road Detection and Tracking algorithm for Lane Departure Warning Systems. An
inverse perspective transformation gives a bird-eye view of the road, where longitudinal road markings are
detected by exploration of horizontal gradient, looking for a road marking model. Next, a parabolic lane
model is fitted to road markings and tracked through a particle filter. The right and left lane boundaries are
classified in three types (solid, broken or merge lane boundaries), through a Fourier analysis, and adjacent lanes
are searched when broken or merge lines are detected. This gives the system the ability to automatically detect
the number and type of road lanes. This ability allows to tell the difference between allowed and forbidden
manoeuvres, such as crossing a solid line, and it is used by the lane departure warning system. Despite of its
importance, lane boundary classification has been seldom considered in previous works. A Lane Departure
Warning System launches an acoustic signal when a lane departure is detected. Warnings are suppressed when
the blinkers are enabled, or when the vehicle is crossing a solid line regardless of the state of the blinkers.
1 INTRODUCTION
The development of Driver Assistance Systems able
to identify dangerous situations involves deep anal-
ysis of the environment, including elements such as
road, vehicles, pedestrians, traffic signs, etc. and the
relationships among them. For instance, detecting a
vehicle in the scene represents a risky situation, but
the risk is higher when the vehicle is in an adjacent
lane in a two-way road – i.e. it is oncoming – than
when it is in a freeway. Likewise, there are differ-
ences between crossing a broken line in a freeway
and crossing a solid line in a two-way road. How-
ever, most current Driver Assistance Systems cannot
differentiate between these situations.
Most of the current research effort moves towards
accurate fitting of high order models to the lane shape.
Many models and approaches have been proposed.
Some proposals model the horizontal curvature of the
lane boundaries as parabolas (Zhou et al., 2006; Park
et al., 2003; McCall and Trivedi, 2006), third or-
der polynomials (Southall and Taylor, 2001), splines
(Wang et al., 2000) or snakes (Yuille and Coughlan,
2000; Wang et al., 2004; Kim, 2006). Other propos-
als include vertical curvature in their models. In (Cha-
puis et al., 2002) and (Nedevschi et al., 2005) vertical
curvature is modelled as a parabola, and horizontal
curvature as a third-order polynomial.
However, there are few works on longitudinal road
markings classification (solid, broken, merge, etc.),
variable multi-lane detection, or road type recogni-
tion, although this information is essential. Few
works consider the existence of other lanes, which is
directly related to the road type (highway, two-way,
etc.). The direction of vehicles on other lanes, the pos-
sible manoeuvres and the speed limit, are just some
examples of facts that depend on the road type.
In (Campbell and Thomas, 1993) a six parame-
ter model that merges shape and structure is used.
The shape is modelled as a second order polynomial,
and the structural model considers the road line as a
square waveline, with its period, duty cycle and phase.
The parameters can be tracked from frame to frame,
but the algorithm requires an initialization step that
is very time consuming, and only one lane boundary
mark is fitted to each frame. In (Risack et al., 1998)
road lines are roughly classified in solid or broken, by
analyzing the gaps between the measurement points.
If the gap overcomes a threshold the road marking
is classified as broken. Thus, the algorithm can eas-
360
M. Collado J., Hilario C., de la Escalera A. and M. Armingol J. (2008).
MULTI-LANE VISUAL PERCEPTION FOR LANE DEPARTURE WARNING SYSTEMS.
In Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications, pages 360-367
DOI: 10.5220/0001077903600367
Copyright
c
SciTePress
ily be mistaken with any obstacle or structured noise
that occludes the marking line, such as shadows or
other vehicles. This work also tries to estimate the left
and right adjacent lanes assuming that some of their
parameters are identical to those of the central lane.
Likewise, in (Aufrére et al., 2001) lateral lanes are
search for, and an array of probabilities which defines
its presence is kept based on the score of detection.
This paper presents the Road Tracking and Clas-
sification module of the IvvI project (Intelligent Ve-
hicle based on Visual Information). Its goal is to au-
tomatically detect the position, type, and number of
the road lanes with a monocular on-board camera,
and can guess the presence of lateral lanes even if
they are not visible. In this work, three type of lane
boundaries are considered, namely: solid, broken and
merge. This perceptual skill pretends to be the basis
of a better evaluation of the potential danger of a sit-
uation.
2 ROAD LANES DETECTION
AND TRACKING
2.1 Road Model
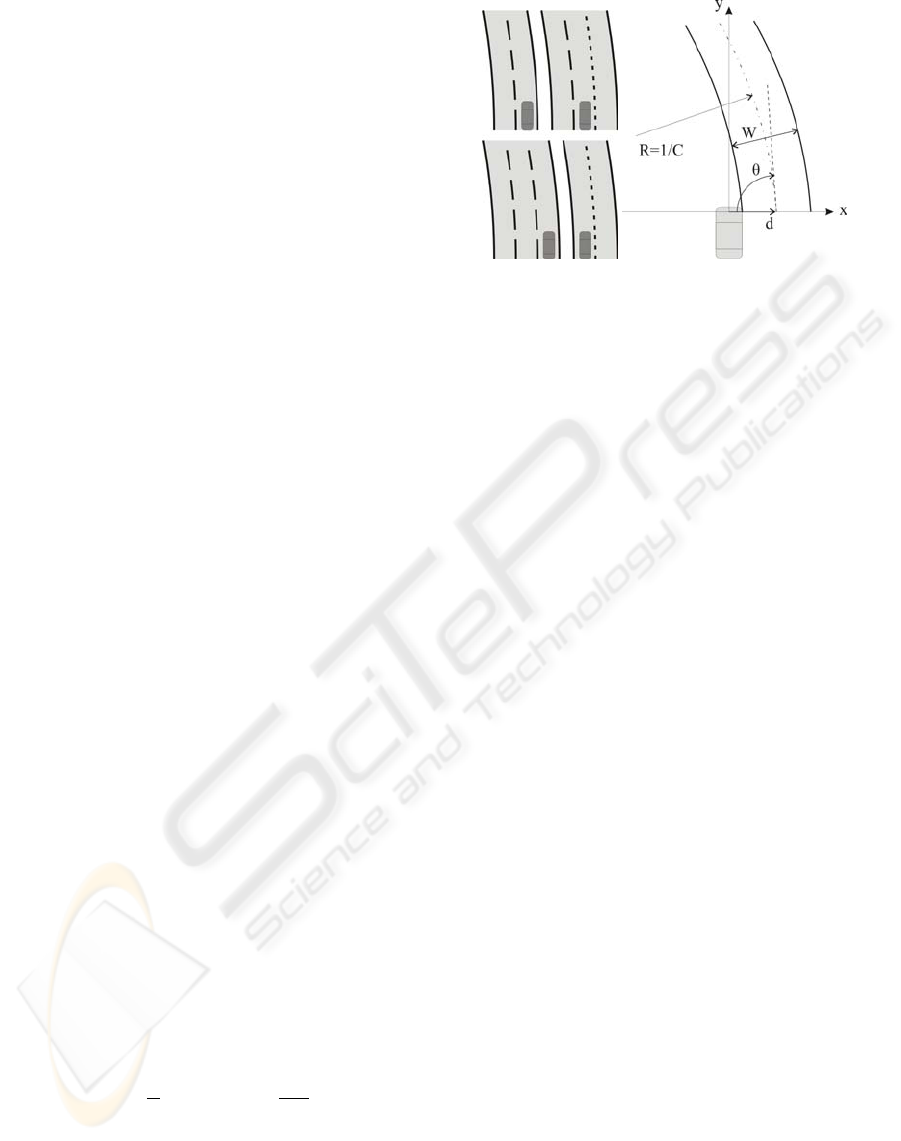
In this work road model and lane model are not con-
sidered to be the same. The road model is composed
of a variable number of lanes which are separated by
lane boundaries (figure 1(a)). These boundaries can
belong to one of three different types:
• Continuous for standard lane separation (further
on referred as solid lines).
• Discontinuous for standard lane separation (fur-
ther on referred as broken lines).
• Discontinuous for merge lane separation (further
on referred as merge lines).
The lane model is represented in figure 1(b). It
follows a parabolic curve, and comprises four param-
eters: C (curvature), θ (vehicle orientation respect to
the lane axis), d (distance to the axis of the lane), and
W (lane width).
The lane boundaries follow (1), and are horizontal
displacements of the lane axis:
x(y) =
C
2
y
2
− θy − d −
kW
2
(1)
where k is an index that identifies which lane bound-
ary the equation refers to. This algorithm con-
siders up to three possible lanes, i.e., four lane
boundaries which are represented by the values k =
{
3,1,−1,−3
}
. The value k = 0 represents the lane
axis.
(a) Lane Types (b) Lane Model
Figure 1: Road Model.
2.2 Preprocessing
2.2.1 Perspective Transformation
Every Lane Departure Warning System based on vi-
sion has to transform between camera coordinates and
world coordinates, although this relation is not always
explicit, as in (Lee, 2002). Many works start with
an inverse perspective transformation (Broggi et al.,
1999; McCall and Trivedi, 2006) to obtain an image
of the road in world coordinates (see figure 2(a)). This
technique has the following advantages:
• Process an image with size and resolution inde-
pendent of the CCD sensor.
• Direct conversion to world coordinates.
• Facilitates the extraction of the road markings
profile, which is needed for the road markings
classification step detailed in section 2.4.
The inverse perspective transformation assumes
that the road is flat. The flat road assumption is a
reasonable approximation, as the effects of the devia-
tion from this hypothesis are small (Guiducci, 1999)
when it is performed with precise extrinsic calibration
parameters.
2.2.2 Road Markings Detection
This step extracts from the original image the pix-
els that are candidates to belong to longitudinal road
markings. Longitudinal road markings can be consid-
ered as bright bands over a darker background. As
the lane curvature is small in the nearby region of the
road, these lines are mainly vertical in the bird-eye
view image of the road. Therefore, the search for pix-
els that belong to road markings consists of looking
for dark-bright-dark transitions in the horizontal di-
rection.
MULTI-LANE VISUAL PERCEPTION FOR LANE DEPARTURE WARNING SYSTEMS
361

(a) (b) (c) (d) (e)
Figure 2: (a) Inverse perspective image; (b) Road markings
detected by exploring horizontal gradient; (c) Hit or Miss
transformation; (d) Removal of small objects; (e) Distance
Transform.
To make the algorithm somehow independent of
illumination variations, the image is equalized to
make the width of the histogram cover the whole
range. The equalization is performed after the per-
spective transformation, otherwise undesired parts of
the image would be equalized, such as the sky, which
in a sunny day can be saturated, thus reducing the con-
trast of the road markings instead of enhancing it.
The borders of the image are extracted with a spa-
tial filter that applies the first step of the Canny filter
to estimate the orientation of the border, and is used to
obtain a horizontal gradient image. The borders that
are not essentially vertical are discarded. The algo-
rithm scans the horizontal gradient image row by row,
searching for a pattern composed of a pair of peaks of
opposite sign (the first, positive, and the second, neg-
ative) which are spaced a distance equal to the road
marking width. The road marking width is consid-
ered to be between ten and sixty centimetres in world
coordinates. When this pattern is found, the middle
point is labelled as a road marking. Figure 2(b) is the
result of processing figure 2(a) in this way.
Two additional steps have been implemented in
order to filter noise. First, a Hit or Miss transforma-
tion fills the gaps when some pixels have not been
detected (figure 2(c)), by filtering the resultant image
with the following kernels:
X 1 X
0 1 0
0 0 0
1 0 0
0 1 0
0 0 0
0 0 1
0 1 0
0 0 0
0 0 0
0 1 0
X 1 X
0 0 0
0 1 0
1 0 0
0 0 0
0 1 0
0 0 1
where the bold zero indicates the kernel centre.
There still there may be some false detections.
These would not be important unless for the distant
transform that will be performed further on (see sec-
tion 2.3.1 and figure 2(e)). Spurious pixels distort
quite a lot this transformation, so objects with area
less than 2 pixels are eliminated (figure 2(d)).
Figures 2(b-d) show the three steps of the Road
Markings Detection.
2.3 Tracking
Lane boundaries are tracked with the ConDensation
filter (Isard and Blake, 1998). The filter is used due to
its capacity to recover from losses of the lane track.
The dynamics of the lane boundaries are modelled
as a second order autoregressive process (ARP), ac-
cording to (2):
x
t
= A
2
x
t−2
+ A
1
x
t−1
+ D
0
+ B
0
w
t
(2)
where x
t
is the state vector composed of the four pa-
rameters of the lane model, and w
t
is a vector of gaus-
sian noise.
2.3.1 Probability Density Estimation
The fit of a lane hypotheses x
t
to the observations is
evaluated by two terms.
The first term F
1
is a weighted sum of the number
of road markings the lane has:
F
1
=
N
∑
i=0
w
i
· I
RM
(x(y
i
),y
i
) (3)
where I
RM
is the M×N image of road markings (fig-
ure 2(d)), y
i
and x
i
are the coordinates of the image
expressed in the reference system of figure 1(b), and
w
i
= w(y
i
) is a weight which depends on the height of
the image as explained below.
The coordinates y
i
and x(y
i
) represent all the pix-
els of a hypothesized lane x
t
in the inverse perspective
image. They are expressed in world coordinates, and
follow (4) and (1), respectively, where ∆y is the pixel
height, and y
min
is the y value corresponding to the top
bottom pixel (figure 3(a)).
y
i
= y
min
+ i∆y (4)
The weights w
i
are used to give more importance
to the pixels at the bottom of the image than the pix-
els at the top. The relation between pixel size in the
inverse perspective image and in the original image
depends on the position of the pixel, as shown in fig-
ure 3(a). Pixels at the bottom of the inverse perspec-
tive image take up a bigger part of the CCD image
than pixels at the top, therefore they are more reliable.
The weights w
i
express this relation by calculating the
ratio ∆v/∆y. From figure 3(b) the following equation
system can be deduced:
v
f
= tan ∆ϑ
H
y
= tan (ϑ − ∆ϑ)
(5)
Solving (5) for v, by equalizing ∆ϑ, we obtain (6):
VISAPP 2008 - International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
362

(a)
(b)
Figure 3: Calculus of weights w
i
.
Figure 4: Weights for ∆y = 0.1 m/pixel, ϑ = 0.05 rad, and
H = 1.18 m.
v(y) = f tan
ϑ − arg tan
H
y
(6)
Finally, the weights are defined as:
w(y
i
) = k
v(y
i+1
) − v(y
i
)
∆y
(7)
where k is a proportionality constant.
The experiments have shown that the use of weights
w
i
gives a significant improve of efficacy, as it
achieves a better fit of the lane in the bottom part of
the image, reducing the oscillations in the output pa-
rameters. Figure 4 shows the weights for the values
used in the IvvI.
The second term F
2
measures how close the lane
is to road markings:
F
2
=
N
∑
i=0
w
i
· I
DRM
(x(y
i
),y
i
) (8)
where y
i
, x(y
i
) and w
i
are the same as for F
1
in (3), and
I
DRM
is a Distance Transform with exponential decay,
of the image of road markings I
RM
. Figure 2(e) shows
the distance transform for figure 2(d).
The posterior density function is estimated
through (9):
F = k
1
· F
1
+ k
2
· F
2
(9)
where k
1
and k
2
are constants used to give the same
importance to both terms.
The output of the tracker is the particle x
t
with the
highest value for F.
2.3.2 Learning of the Model Dynamics
The parameters A
2
, A
1
, D
0
and B
0
from (2), are
learned from observations with the recursive algo-
rithm proposed by (Isard, 1998).
First a hand-made model is used to track an easy
sequence, with a straight section followed by a left
turn and a right turn after that. This sequence had no
traffic. The observations of this sequence were used
to minimize the model, and the new parameters were
used now to track two more difficult sequences, with
lane changes and traffic, in order to refine the param-
eters.
2.4 Road Markings Classification
The extracted lines are classified in the different types
of lines that are found on roads. The main difficulty of
this task is the lack of international standardization of
the length and frequency of the white stripes in broken
lines. However, most roads have the three basic line
types already mentioned: solid, broken and merge.
The lane boundaries classification is based on the
Fourier transform of its profile. Fourier transform is
applied to the profile obtained from the binary image
of detected road markings (figure 2(d)), instead of the
original greyscale image (figure 2(a)). There are two
reasons for this. On one hand, the greyscale image
has both temporal and spatial differences in illumi-
nation, which distorts the Fourier transform. On the
other hand, if the fit of the estimated lane to the road
markings is not exact, the profile does not correspond
to the lane boundary but to the tarmac, because the
lane boundaries are scarcely two pixels wide. Thus,
line profile is obtained from the road markings image,
and a pixel is considered to belong to a lane bound-
ary if it is closer than three pixels to the line, in the
horizontal direction.
Lane boundaries are classified by analyzing the 30
first frequencies of the power spectrum, with the fol-
lowing rules:
MULTI-LANE VISUAL PERCEPTION FOR LANE DEPARTURE WARNING SYSTEMS
363

(a) Detected
lane bound-
aries
(b) Top left (c) Left (d) Right (e) Top right
Figure 5: Power spectrum of the Fourier transform of the four detected lane boundaries, in logarithmic scale.
1. If there is a local maximum within the frequen-
cies 20 and 29, of which value exceeds a thresh-
old (0.60 in logarithmic scale), it is a merge lane
boundary.
2. If the value for frequency 0 is very large (over
4.5), it is a solid lane boundary.
3. If there is a local maximum within frequencies 3
and 5, of which value is over a threshold (1.5), it
is a broken lane boundary.
4. If none of the above conditions is met, it is as-
sumed that the line is solid by default, with a noisy
road markings profile due to weak paint or oc-
clusions, so that the value for frequency 0 is too
small.
These thresholds have been deduced heuristically,
by inspection of three road sequences of 3508, 2919
and 5351 frames, respectively.
It has been noticed that, occasionally, weak paint,
stains or occlusions introduce in the power spectrum
frequencies in the range of broken lane boundaries,
but, when this happens, the value for frequency 0 is
still high. This is the reason why the condition for
solid lane boundaries is checked before the condition
for broken.
Figure 5 shows the power spectrum of the Fourier
Transform of the four lane boundaries detected in fig-
ure 5(a). Figures 5(b-e) represent the power spectrum
for lane boundaries from left to right. In these fig-
ures, the top left column depicts the line profile ob-
tained from the image of road markings, and the re-
mainder columns are the power spectrum, where, fre-
quencies for broken and merge lane boundaries are
represented in dark grey and pale grey, respectively.
The two horizontal lines are the thresholds for broken
lane boundary (upper line), and merge lane boundary
(lower line).
2.5 Detection of Additional Lanes
The classification of road lines is used to build a more
complete model of the road. The algorithm considers
the presence of additional lanes when a not solid line
is detected. At present, up to three lanes are consid-
ered, the own lane and one more to each side. When a
lane boundary is classified as broken or merge, a new
lane is supposed to be adjacent to that lane bound-
ary. In figure 7 there are examples of roads with one,
two and three lanes, where it can be seen that adjacent
lanes are guessed even if they are occluded.
3 LANE DEPARTURE WARNING
A Lane Departure Warning System that uses lane
recognition has been developed. Let d
left
= d −W/2
and d
right
= W /2 − d be the distance of the vehicle
centre to the left and right lane boundaries, respec-
tively. When d
left
or d
right
is below a threshold, em-
pirically set to 1.0 m, it is considered that the driver
is performing a lane change manoeuvre. The state of
the blinkers is monitored so that the system warns the
driver if one of these situations occurs:
• The vehicle is crossing a not solid lane boundary
with the blinkers off.
• The vehicle is crossing a solid lane boundary, re-
gardless of the state of the blinkers.
VISAPP 2008 - International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
364

(a) Vehicle (b) Processing system
(c) Stereo camera (d) Colour camera
Figure 6: IvvI.
4 RESULTS
4.1 Experimental Platform: The IvvI
Experiments were carried out in the IvvI platform
(figure 6) which is an experimentation platform for
researching and developing Advance Driver Assistant
Systems based on Image Analysis and Computer Vi-
sion. It makes possible to work with video sequences
instead of static images, thus a great number of differ-
ent situations can be analyzed, and the algorithms are
tested under real conditions.
IvvI is equipped with:
• A DC/AC power converter connected to the vehi-
cle’s battery, that feeds the computers and cam-
eras.
• Two PCs in the vehicle’s boot, used for process-
ing of the images grabbed by the cameras (fig-
ure 6(b)).
• An electronic multiplexer for the video, mouse
and keyboard signals, that allows a human oper-
ator to work with two systems simultaneously.
• A stereo-vision system (figure 6(c)) with two
CCD progressive scan cameras used for vehicle,
road, and pedestrian detection.
• A colour CCD camera for the detection of traffic
signs and another vertical signs (figure 6(d)).
4.2 Discussion
The algorithm has been tested with several road se-
quences. The Particle filter works with 1000 particles,
and the whole algorithm runs at 12fps in a 2.2GHz
Pentium IV processor, including image capture and
(a) frame 954 (b) frame 1037
(c) frame 1928 (d) frame 2072
(e) frame 2234 (f) frame 3161
Figure 7: Some examples.
rectification of stereo-images. Stereo-image rectifica-
tion is required by other algorithms of the IvvI, thus
it is always performed. Preprocessing, tracking, and
line classification takes about 30ms.
Figure 8 shows the output of the lane tracking
through a sequence of 2500 frames that includes
left and right turns, two roundabouts, and two lane
changes. The sequence belongs to a road that con-
nects a city to a highway. Although this algorithm
is not intended for urban scenarios, this sequence is
much noisier than a well conserved highway, thus it
is a good test for this Driver Assistance System. The
figure shows the four lane parameters and the score of
the best fit, measured as explained in section 2.3.1.
The high dispersion of the angle parameter is due
to camera vibrations. The stereo cameras are attached
to the vehicle through a flexible arm and a suction pad
adhered to the windshield, as in figure 6(c). The way
the flexible arm is disposed causes the transmission of
horizontal vibrations to the cameras.
The main failure case of the algorithm are round-
abouts, which correspond to the two shaded zones of
figure 8. As the algorithm is not intended to work
in roundabouts but in main and secondary roads, the
high curvature of the roundabouts exceeds the limits
imposed to the lane parameters, so that the lane model
cannot fit to road markings. Hence, the score of the
MULTI-LANE VISUAL PERCEPTION FOR LANE DEPARTURE WARNING SYSTEMS
365
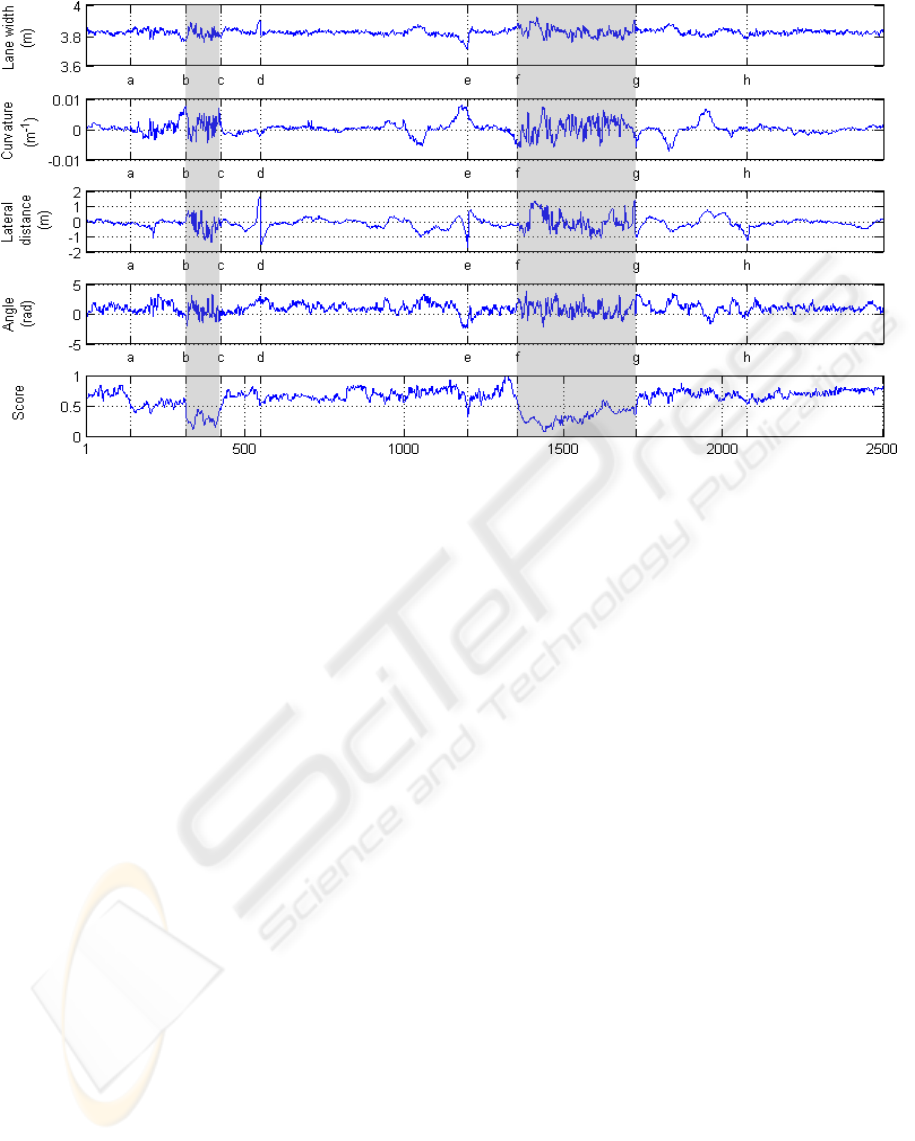
Figure 8: Sequence.
estimated lane lowers significantly, and it is used as a
indicator of tracking correctness. Accordingly, the al-
gorithm suppresses all warnings when score is below
0.4.
The stretch between points (a) and (b) of figure 8
presents a high variance in curvature because of a bus
that joined the road just in front of the vehicle, thus
occluding road markings almost completely.
Points (d) and (e) are lane changes correctly de-
tected and tracked. The stretch between (d) and (e)
contains a left turn followed by a right turn as can be
seen in the curvature graph. The lane change took
place while turning right.
The stretch between (g) and (h) again contains two
curves. The point (h) represents another failure case.
It corresponds to figure 7(d), when the lane followed
the exit lane until the merge lane boundary appeared
in the image. The algorithm believed that the vehicle
was leaving the lane to the left, and a false alarm was
launched.
Figure 7 shows some examples of detected roads,
where the black dots display the estimated lanes.
Lane boundary classification is showed by chang-
ing point thickness and spacing between consecutive
points. Figure 7(a) contains the three boundary types.
The two outermost, with fine points and short spacing,
are solid lines. The left boundary of the centre lane,
with thick points and big spacing, is a merge line,
while the right boundary, with intermediate thickness
and intermediate spacing, is a broken line.
Figure 7(a) is a three-lane road, while figures 7(b)
and 7(c) are two-lane roads. Figure 7(f) is a two-
lane road, but as the lane boundaries are both solid,
no more lanes are looked for.
Figure 7(e) shows a road with two lanes in which
only one is detected. Due to the vertical curvature of
the road, the lane model cannot fit to both left and
right lane boundaries, and tends to fit the solid line
because it contains more pixels. Therefore, the left
line of the model deviates from the true lane bound-
ary, and the profile extracted does not correspond to
a road marking, but to the tarmac. Thus, the line is
classified as solid.
Figure 7(c) is an example of one of the advantages
of the algorithm. Although a vehicle occludes the left
lane, the two lanes are still detected, because the left
lane boundary is identified as broken.
5 CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE
WORK
In this paper, the Road Detection and Tracking mod-
ule of the Advanced Driver Assistance System for the
IvvI project, has been presented. It is able to track the
road and automatically identify lane boundary types
and detect adjacent lanes if present. It can process a
video sequence at 12fps. Lane departures are detected
and warned as explained above.
The main contribution of this work is the auto-
matic detection of adjacent lanes, and the ability to
warn a lane departure depending on the state of the
VISAPP 2008 - International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
366

blinkers and the type of the lane boundary that will be
crossed.
The algorithm successfully tracked the road ex-
cept for three failure cases: when road is occluded by
a vehicle (as in traffic jams), in roundabouts, and in
stretches with high vertical curvature.
Therefore, future work considered at present in-
cludes the installation of inertial sensors for vehicle
trajectory prediction and pitch correction, monitor-
ing of curvature variance to detect road occlusions
by other vehicles, and the inclusion of lane boundary
classification in the tracking model.
REFERENCES
Aufrére, R., Chapuis, R., and Chausse, F. (2001). A model-
driven approach for real-time road recognition. Ma-
chine Vision and Applications, 13(2):95–107.
Broggi, A., Bertozzi, M., Fascioli, A., and Conte, G. (1999).
Automatic Vehicle Guidance: The Experience of the
ARGO Autonomous Vehicle. World Scientific.
Campbell, N. W. and Thomas, B. T. (1993). Navigation
of an autonomous road vehicle using lane bound-
ary markings. In Charnley, D., editor, Intelligent
Autonomous Vehicles. IFAC International Conference
on, pages 169–174. Pergamon Press.
Chapuis, R., Aufrere, R., and Chausse, F. (2002). Accurate
road following and reconstruction by computer vi-
sion. Intelligent Transportation Systems, IEEE Trans-
actions on, 3(4):261–270.
Guiducci, A. (1999). Parametric model of the perspective
projection of a road with applications to lane keeping
and 3d road reconstruction. Computer Vision and Im-
age Understanding, 73(3):414–427.
Isard, M. and Blake, A. (1998). Condensation – conditional
density propagation for visual tracking. International
Journal of Computer Vision, 29(1):5–28. Kluwer Aca-
demic Publishers.
Isard, M. A. (1998). Visual Motion Analysis by Probabilis-
tic Propagation of Conditional Density. PhD thesis,
Oxford University.
Kim, Z. (2006). Realtime lane tracking of curved local road.
In Intelligent Transportation Systems, IEEE Interna-
tional Conference on, pages 1149–1155.
Lee, J. W. (2002). A machine vision system for lane-
departure detection. Computer Vision and Image Un-
derstanding, 86(1):52–78.
McCall, J. and Trivedi, M. (2006). Video-based lane esti-
mation and tracking for driver assistance: survey, sys-
tem, and evaluation. Intelligent Transportation Sys-
tems, IEEE Transactions on, 7(1):20–37.
Nedevschi, S., Danescu, R., Marita, T., Oniga, F., Pocol, C.,
Sobel, S., Graf, T., and Schmidt, R. (2005). Driving
environment perception using stereovision. In Intel-
ligent Vehicles Symposium. Proceedings of the IEEE,
pages 331–336, Las Vegas, Nevada, U.S.A.
Park, J. W., Lee, J. W., and Jhang, K. Y. (2003). A lane-
curve detection based on an lcf. Pattern Recognition
Letters, 24(14):2301–2313.
Risack, R., Klausmann, P., Küger, W., and W.Enkelmann
(1998). Robust lane recognition embedded in a real-
time driver assistance system. In Intelligent Vehicles
Symposium. Proceedings of the IEEE, pages 35–40.
Southall, B. and Taylor, C. (2001). Stochastic road shape es-
timation. In Computer Vision (ICCV). Proceedings of
the 8th IEEE International Conference on, volume 1,
pages 205–212.
Wang, Y., Shen, D., and Teoh, E. K. (2000). Lane detec-
tion using spline model. Pattern Recognition Letters,
21(8):677–689. Pattern Recognition Letters, vol.21,
no.8, July 2000. p. 677-689.
Wang, Y., Teoh, E. K., and Shen, D. (2004). Lane detection
and tracking using b-snake. Image and Vision Com-
puting, 22:269–280.
Yuille, A. L. and Coughlan, J. M. (2000). Fundamental lim-
its of bayesian inference: order parameters and phase
transitions for road tracking. Intelligent Transporta-
tion Systems, IEEE Transactions on, 22(2):160–173.
Zhou, Y., Xu, R., Hu, X., and Ye, Q. (2006). A robust
lane detection and tracking method based on com-
puter vision. Measurement Science and Technology,
17(4):736–745.
MULTI-LANE VISUAL PERCEPTION FOR LANE DEPARTURE WARNING SYSTEMS
367
