
CORRELATION ICP ALGORITHM FOR POSE ESTIMATION
BASED ON LOCAL AND GLOBAL FEATURES
Marco A. Chavarria and Gerald Sommer
Cognitive Systems Group. Christian-Albrechts-University of Kiel, D-24098 Kiel, Germany
Keywords:
Pose estimation, ICP algorithm, monogenic signal, pre-alignment, global and local features.
Abstract:
In this paper we present a new variant of ICP (iterative closest point) algorithm based on local feature correla-
tion. Our approach combines global and local feature information to find better correspondence sets and to use
them to compute the 3D pose of the object model even for the case of large displacements between model and
image data. For such cases, we propose a 2D alignment in the image plane (rotation plus translation) before
the feature extraction process. This has some advantages over the classical methods like better convergence
and robustness. Furthermore, it avoids the need of a normal pre-alignment step in 3D. Our approach was
tested on synthetical and real-world data to compare the convergence behavior and performance against other
versions of the ICP algorithm combined with a classical pre-alignment approach.
1 INTRODUCTION
The estimation of the object position is crucial for an
efficient robot-object interaction in research and in-
dustrial applications. In this context, geometric alge-
bra has been introduced in computer vision as a prob-
lem adaptive algebraic language for modeling geo-
metric related problems, see (Sommer, 2001). This
mathematical framework was used by (Rosenhahn
and Sommer, 2005) to formulate the monocular pose
estimation problem and the model representation.
For every model-based pose estimation or 3D reg-
istration algorithm, correspondences must be found
between model and acquired data. This is one of
the most challenging problems for this kind of ap-
proaches. The most common and simple solution is
the ICP algorithm introduced by (Besl and McKay,
1992), where the minimal Euclidean distance con-
straint is used to find correspondences. A comparison
of several variants of the ICP algorithms is presented
by (Rusinkiewicz and Levoy, 2001), where the origi-
nal ICP is combined with different distance metrics
and strategies to find correspondences and to align
artificially generated 3D meshes. A tracking algo-
rithm based on template and features data was pre-
sented by (Ladkos et al., 2007), where the systems
changes adaptively between templates and features
to deal with complex tracking scenarios. The above
cited methods assume tracking assumption condi-
tions. It means that the displacement between model
and scene is small enough to avoid convergence to a
local minimum. The approach proposed by (Shang
et al., 2007) uses known information about the limits
of the object velocity and the image frame rate to re-
duce the space transformation between every frame.
Then, the tracking is transformed into a classifica-
tion problem. In the work of (Sharp et al., 2002) the
ICP algorithm is combined with additional invariant
features like curvature, moment invariants and spher-
ical harmonics for registration of range images. In
(Chavarria and Sommer, 2007), structural informa-
tion from image and model (convexity, concavity and
straightness of segments) is used as extra correspon-
dence search constraints for monocular pose estima-
tion. The combination of ICP with such structural
features reduces the probability of being trapped in
a local minima. That means the algorithm is robust
against the tracking assumption up to certain limits.
For larger displacements between model and
scene, a pre-alignment step is needed to get an ini-
tial rough estimation of the pose. Then, the ICP algo-
rithm can be applied to obtain the final pose. In the
work of (Brujic and Ristic, 1996), a pre-alignment
based on the principal component analysis (PCA) is
used. Once that the principal components of the sets
of points are computed, the rough pose is obtained
by finding the 3D pose that aligns these main com-
ponents. Instead of extracting the main components
by PCA, (Murino et al., 2001) align the extracted 3D
skeletons of the model. A genetic algorithm is used
528
A. Chavarria M. and Sommer G. (2008).
CORRELATION ICP ALGORITHM FOR POSE ESTIMATION BASED ON LOCAL AND GLOBAL FEATURES.
In Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications, pages 528-534
DOI: 10.5220/0001079305280534
Copyright
c
SciTePress

in the work of (Lomonosov et al., 2006) to compute
the pre-alignment step. All these methods are based
on the alignment of the main components or skele-
tons extracted from sets of 3D points. That means,
the model points and the acquired data are defined in
3D. This is not the case for the monocular pose es-
timation, where the model is defined in 3D, but the
acquired data (contour data) is defined in the 2D im-
age plane. In order to perform a pre-alignment for
the monocular pose estimation, the components of the
data extracted from the image must be reconstructed
in 3D. Another option is to project the 3D model com-
ponents onto the image plane and apply a 2D version
of the above cited methods.
In this paper we present a new correlation-based
ICP algorithm for the monocular pose estimation of
3D free-form surfaces. It combines global and local
orientation features in an approach that performs bet-
ter even for cases where the classical versions of the
ICP algorithm fail (e.g. when the tracking assump-
tion is not met). Local orientation information in the
image computed from the monogenic signal response
(Felsberg and Sommer, 2004) and from the projected
models are used to describe the orientation of con-
tour segments for image and model points. Instead
of the minimal distance criteria used by the normal
variants of the ICP algorithm, correlation is used to
measure the similarity (in terms of the local orienta-
tion) of the contour segments. Furthermore, global
orientation is used to align the projected model data
with the detected contour features in the image plane.
That means, a simple 2D feature alignment is per-
formed. This allows to find better conditioned cor-
respondence sets even for larger displacements (rota-
tions and translations) without the need of an extra
pre-alignment step in 3D.
This paper is organized as follows, the image
feature extraction based on the monogenic signal is
briefly introduced in section 2. Section 3 describes
the global feature extraction for image and projected
model contours. The silhouette based pose estima-
tion and the correlation based ICP algorithms are pre-
sented in section 4. The 2D feature alignment proce-
dure follows in section 5. Finally, the result of several
experiments made on artificial and real-world data to
validate the efficiency and robustness of our algorithm
are presented in section 6.
2 LOCAL IMAGE FEATURES
The monogenic scale-space representation and phase-
based image processing techniques were introduced
by (Felsberg and Sommer,2004). If p(x;s) and q(x;s)
are the filter responses of an image convolved with the
Poisson and conjugate Poisson kernels respectively,
local amplitude a(x;s) and local phase r(x;s) are ob-
tained for a scale s according to
a(x;s) =
p
|q(x;s)|
2
+ |p(x;s)|
2
r(x;s) =
q(x;s)
|q(x;s)|
arctan
|q(x;s)|
p(x;s)
.
(1)
The amplitude is related to the local energy of the sig-
nal (presence of structure). The orientation and phase
are combined in the phase vector. The phase gives
information about the local symmetry of the signal
(type of structure) and the orientation gives the direc-
tion of the highest signal variance. Once that the am-
plitude and phase are obtained for a scale factor s, a
contour search algorithm based on the local phase and
orientation is applied to extract the contour segments.
By changing the scale factor, low contrast edges can
also be detected. Thus, for every contour point we get
as features its coordinates in the image and the local
orientation F
im
i
= {x
im
, y
im
, α
im
i
}.
3 GLOBAL FEATURE
EXTRACTION
The Fourier transform of a closed contour delivers a
set of complex coefficients that can be used to obtain
low pass approximations of it. If only the first coef-
ficient is used, the contour is approximated by a cir-
cle. As the number of the coefficients increases, a bet-
ter approximation of the contour is obtained. We use
a 2D real valued variant of this approach introduced
by (Lin and Hwang, 1987). Then, a closed contour
c(t) = f
1
(t)e
1
+ f
2
(t)e
2
in the image plane is approxi-
mated by
f
1
(t)
f
2
(t)
=
a
0
d
0
+
N−1
∑
k=0
a
k
b
k
c
k
d
k
sin(
2kπt
N
)
cos(
2kπt
N
)
,
(2)
with
a
0
=
1
N
∑
N−1
k=0
f
1
(t)
d
0
=
1
N
∑
N−1
k=0
f
2
(t)
a
k
=
1
N
∑
N−1
k=0
f
1
(t)cos(
2kπt
N
)
b
k
=
1
N
∑
N−1
k=0
f
1
(t)sin(
2kπt
T
)
c
k
=
1
N
∑
N−1
k=0
f
2
(t)cos(
2kπt
T
)
d
k
=
1
N
∑
N−1
k=0
f
2
(t)sin(
2kπt
T
).
(3)
The coefficients a
k
, b
k
, c
k
, d
k
are called elliptic co-
efficients . If only the fist coefficient is used, the con-
tour will be approximated by an ellipse. If the coeffi-
cients are arranged in a matrix, the parameters of such
ellipse, which approximates the contour, are extracted
CORRELATION ICP ALGORITHM FOR POSE ESTIMATION BASED ON LOCAL AND GLOBAL FEATURES
529

Figure 1: Examples of the extracted global orientation. Up-
per figures: projected surface models onto the image plane
(triangle, motor part and power socket) and example of real-
world images. Bottom figures: extracted contours and the
corresponding major and minor axes.
by single value decomposition according to:
svd
a
k
b
k
c
k
d
k
=
cosθ
k
−sinθ
k
sinθ
k
cosθ
k
A
k
0
0 B
k
R(ψ).
(4)
The indexes A
k
and B
k
are the lengths of the major
and minor axes of the ellipse and θ
k
is the angle of
the major axis with respect to the image axis x. The
phase matrix R(ψ), defines the angular distance from
the main axis to the first point of the contour. Thus,
for a projected model or a detected image contour, we
obtain as global features F
img
= {p
img
= [a
0
, d
0
], θ
k
},
which defines the global position and orientation of
the contour in the image plane. Some examples for
projected models and real images can be seen in fig-
ure 1. In the practice, this method of computing the
mayor and minor axis is very similar than perform-
ing a PCA analysis on the point covariances. Despite
of that, we apply the elliptical descriptors because of
the ability to compute low pass approximations of the
contours. This will eventually allows to avoid the lo-
cal minima problem in some specific scenarios, see
(Rosenhahn et al., 2003).
4 CORRELATION BASED ICP
ALGORITHM
An algorithm for pose estimation of 3D surfaces mod-
els was proposed by (Rosenhahn et al., 2003), where
the 3D silhouette of the model is extracted for every
iteration of the minimization process. Originally, the
classical ICP algorithm was applied to find the pose
of the silhouette. The position of the complete sur-
face model is updated and the process is repeated for
a given number of iterations. We use a similar idea,
but in our approach the 3D silhouette is projected onto
the image plane and its global and local features are
Figure 2: Algorithm for the silhouette based pose estima-
tion.
computed in 2D. The algorithm is summarized in fig-
ure 2.
4.1 Correlation as Similarity Criteria
Instead of the Euclidean metric used by the origi-
nal ICP algorithm, we use the correlation as a sim-
ilarity measure to find correspondences. For a con-
tour segment or range n around a projected model
point x
i
, {x
i−n
, ·· · , x
i+n
}, we define a vector con-
taining the local orientation values of this segment as
o
mod
i
= {α
mod
i−n
, ·· · , α
mod
i+n
}. We call it orientation pro-
file vector and the local orientation is directly com-
puted from the projected model points. Similarly, an
orientation profile vector of an image contour seg-
ment (computed from the monogenic signal response)
is defined as: o
img
i
= {α
img
i−n
, ·· · , α
img
i+n
}. The similarity
of these profile vectors can be computed by the corre-
lation matrix as
corr(o
img
i
, o
mod
j
) =
cov(o
img
i
, o
mod
j
)
p
V
img
V
mod
, (5)
where cov(o
mod
i
, o
img
j
) is the covariance matrix and
V
mod
, V
img
are the variances of image and model data.
The correlation may vary in a range between -1 and 1,
where -1 indicates perfect negative correspondence, 0
indicates no correspondence and 1 indicates perfect
correspondence. For an image point with orientation
profile o
img
i
, the corresponding model point (with ori-
entation profile o
mod
j
∈ MOD) will be the one with
maximal correlation,
corr(o
img
i
, MOD) = max
j=1,···,n
{corr(o
img
i
, o
mod
j
)}. (6)
4.2 Outlier Elimination
Noise in the image and the presence of partial oc-
clusions may cause not well conditioned correspon-
dences that must be eliminated. To achieve that, the
angular positions of image contour θ
img
i
and model
points θ
mod
j
with respect to the major axis are used as
an extra feature, see figure 3. Once that a candidate
VISAPP 2008 - International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
530

Figure 3: Left: 2D feature alignment based on the differ-
ence of global orientation angles and position in the image
plane. Angular position of a contour point with respect to
the major axis (middle). Interval within the pair is consid-
ered to be a good conditioned correspondence (right).
correspondence pair has been found, it is rejected if
the following criterion is fulfilled
k θ
img
i
− θ
mod
j
k> t, (7)
where t is a given threshold value that defines the in-
terval within which the correct correspondence must
be. The introduction of this criterion in the algorithm
reduces considerably the number of correspondence
pairs as it can be seen in the examples of figure 7.
5 FEATURE ALIGNMENT IN 2D
The principle of the 2D feature alignment is illus-
trated in figure 3. The dotted object represents the
projected model and the solid object the detected ob-
ject in the image with their corresponding main axes
with global features F
mod
= {p
mod
, θ
mod
} and F
img
=
{p
img
, θ
img
} respectively. First, the projected model
points x
i
are aligned (rotated and translated in 2D) by
the matrix T(φ, t
r
). As can be seen in the figure, the
angle φ is the orientation difference of the major axes
and t
r
the translation vector between the respective
centers of mass. Once that the projected model points
have been aligned to the detected image points, the
local features (orientation profiles) are computed and
the correlation-based ICP algorithm is applied.
The effect of aligning the features is visualized
in figure 4. The graphics show the orientation pro-
files of two corresponding points obtained with the
simple correlation and with the aligned features.
With aligned features the profiles are more similar
and therefore better conditioned correspondences are
found.
Let us notice that in contrast with the classical pre-
alignment approaches where the rough pose is com-
puted in 3D by a minimization approach, the rotation
and translation in our approach are computed directly
from the global orientation and position differences.
0 20 40 60 80
−0.2
−0.1
0
0.1
0.2
0.3
Points
Orientation (degree)
Simple orientation profiles
Model orientation
Contour orientation
0 20 40 60 80
−0.2
−0.1
0
0.1
0.2
0.3
Points
Orientation (degree)
Aligned orientation profiles
Model orientation
Contour orientation
Figure 4: Orientation profiles of two corresponding points
with simple correlation (upper graphics) and with additional
feature alignment (lower graphics), and examples of corre-
spondences between an object model and image contour.
6 EXPERIMENTS
The robustness against the tracking assumption (large
rotations and translations) was tested and com-
pared with the normal variant of ICP algorithm (see
(Rusinkiewicz and Levoy, 2001)) and with the struc-
tural ICP algorithm (Chavarria and Sommer, 2007).
In a second experiment, our ICP variant was com-
pared with an approach based on the PCA pre-
alignment used in (Brujic and Ristic, 1996) and
(Murino et al., 2001). In both cases the initial position
of the model is known, then it is translated to a certain
position (ground truth) and projected onto the image
plane to generate an artificial image. On this artificial
image the local and global features are extracted. The
pose is calculated with the projective pose estimation
algorithm of (Araujo et al., 1998) and compared with
the ground truth. Several object models were used for
our experiments (see figure 1). Finally, some exam-
ples for a real data scenario are presented.
6.1 Robustness Against Rotations
From the initial position of the model, its main ori-
entation axes were extracted in 3D. Each axis defines
a rotation axis α, β and γ, as it can be seen in figure
5. The model was rotated around these axes and in its
new position the pose was computed and compared
with the ground truth. The left graphics of figure 5,
show a comparison of the convergence behavior for
the motor and power socket models. In this case the
model was rotated -30 degrees around the γ axis. The
normal ICP algorithm does not convergeto the ground
truth pose as it can be seen in the graphics. In contrast
to the structural ICP variant, the number of iterations
needed to converge is significatively reduced with the
correlation based ICP.
As the model rotates around the 3D axes, its ap-
pearance changes with respect of the image plane
and therefore its local structure. Because of that, it
is interesting to analyze the rotation ranges within
which the algorithm is capable to converge to the
CORRELATION ICP ALGORITHM FOR POSE ESTIMATION BASED ON LOCAL AND GLOBAL FEATURES
531
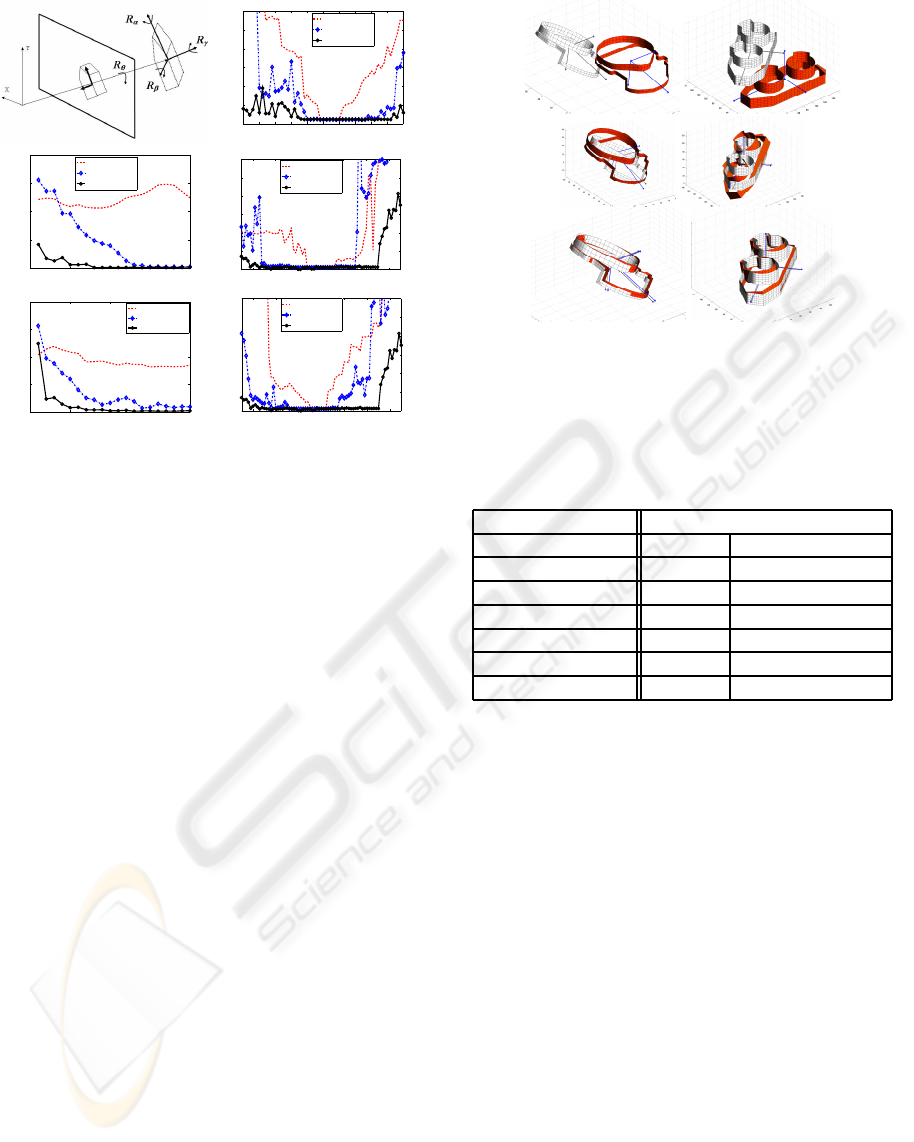
−50 −40 −30 −20 −10 0 10 20 30 40 50
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
Angle alfa
Absolute error (mm)
Pose error for rotations
Normal ICP
Structural ICP
Correlation
0 5 10 15 20
0
5
10
15
20
Iteration
Absolute error (mm)
Convergence for the power socket
NormalICP
Structural ICP
Correlation
−60 −40 −20 0 20 40 60
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
Angle beta
Absolute error (mm)
Pose error for rotations
Normal ICP
Structural ICP
Correlation
0 5 10 15 20
0
5
10
15
20
Iteration
Absolute error (mm)
Convergence for the motor part
NormalICP
Structural ICP
Correlation
−60 −40 −20 0 20 40 60
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
Angle gamma
Absolute error (mm)
Pose error for rotations
Normal ICP
Structural ICP
Correlation
Figure 5: Left: Setup for the experiment for the rotation
case (upper figure) and convergence behavior comparison
for the power socket (middle figure) and motor part (bot-
tom figure). Right: convergence ranges for rotations around
the axes α (upper figure), β (middle figure) and γ (bottom
figure).
ground truth pose. The figure 5 also shows a compar-
ison of the convergence ranges for the power socket
model. The normal variant of the ICP algorithm con-
verges for relatively small rotations around all axes.
Whereas the structural and correlation based ICP vari-
ants allow larger rotations. In the case of the rotation
axes α and γ the extracted silhouette changes dras-
tically with respect of the image plane as the angle
increases, therefore the region where the algorithm
converges is smaller. Despite of that, the correlation-
based ICP variant shows larger convergence ranges
than the structural and classical variants.
6.2 Pre-alignment Comparison
The PCA based pre-alignment algorithms ((Brujic
and Ristic, 1996) and (Murino et al., 2001)) align
clouds of points in 3D by aligning its main axes. This
implies that correspondences between the axes must
be found. With these correspondences, the align-
ment is computed by a minimization process that
takes in general several iterations. In contrast to that,
the correlation algorithm combined with the 2D fea-
ture alignment needs only one iteration to compute
a rough pose. Thus, in the next experiments we com-
pare the first iteration of the correlation ICP algorithm
against the pre-alignment based on the principal com-
ponent analysis. Since we align model 3D data with
Figure 6: Pre-alignment comparison of PCA and 2D align-
ment. Initial position (upper row), PCA pre-alignment re-
sult (middle row) and computed pose after the first iteration
of the correlation-based ICP (lower row).
Table 1: Error comparison for the pre-alignment step(motor
part model).
Rotation (degree) Absolute error (mm)
PCA CORRELATION
0 14.9172 3.1682
10 15.8307 3.4555
20 17.0352 3.4002
30 18.6300 2.7695
40 20.5412 6.6615
50 22.6003 5.2424
image detected contours, we use a version of this ap-
proach which aligns the model in 3D by aligning the
principal components in the image plane.
The model was translated and rotated around the γ
axis from 0 to 50 degrees, see upper row of figure 6.
The middle row shows the result of the pre-alignment
with the PCA and the bottom row shows the result
after the first iteration with the correlation-based ICP.
Let us remember that the PCA alignment version used
for the monocular pose estimation aligns the axes of
the detected image contour and the projected model
silhouette. In contrast to the 3D case, only two prin-
cipal axes can be extracted and aligned in the image
plane. This loss of information has the effect that, al-
though the major and minor axes are roughly aligned,
the error in 3D is significantly larger. On the other
hand, the result of the correlation based ICP is con-
siderably better than that of the PCA based algorithm.
The table 1 shows the absolute error and the differ-
ence angle of the major orientation axis in 3D respec-
tively.
VISAPP 2008 - International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
532
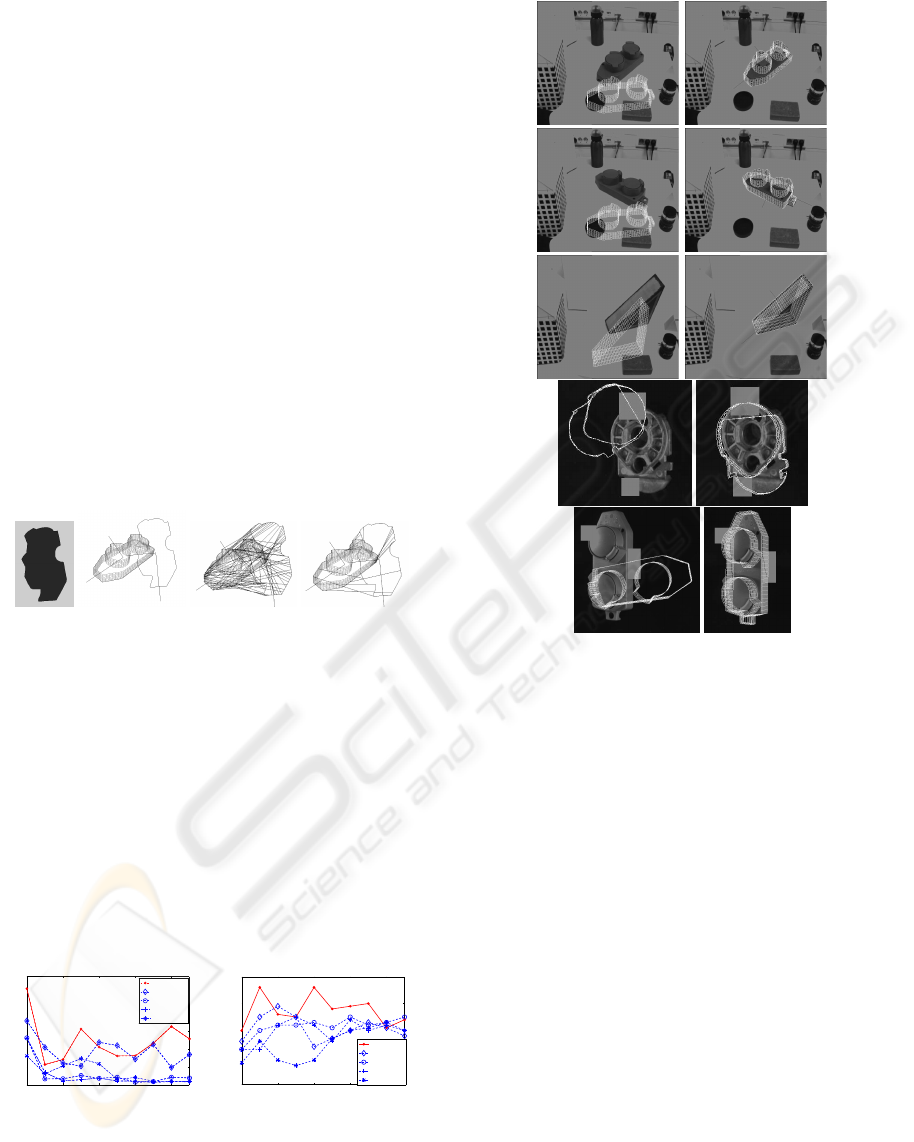
6.3 Pre-alignment with Partial
Occlusions
As described in the last experiments, an artificial
image was generated where some partial occlusions
where simulated. This can be seen in the figure 7.
Correspondences were found with the correlation ICP
algorithm with the outlier elimination criteria of equa-
tion (7). Additionally, the threshold value t was var-
ied to see how it affects in the convergence behav-
ior of the algorithm. The results of this experiment
are shown in figure 8. The graphic of the left shows
the convergence behavior for different threshold val-
ues (from 10 to 50 degrees). A better convergence is
achieved for threshold values between 20 and 30 de-
grees. The right graphic shows the number of corre-
spondences for every iteration of the algorithm after
applying the outlier elimination criteria of equation
(7). From initially 96 pairs, the number of correspon-
dences is considerably reduced during the iterations.
Figure 7: From left to right: Artificial generated image with
simulated occlusions. Initial position for the experiment.
Correspondences with only the correlation ICP algorithm.
Correspondences after eliminating the outliers.
The presence of partial occlusions affects the lo-
cal structure of the contour and therefore the orien-
tation profiles of each point. If only the correlation
correspondence search is applied, a big number of ill
conditioned correspondences are found (see figure 7).
Once they are eliminated, a reduced set of correspon-
dences is obtained. Despite of that, the remaining
pairs are the best conditioned correspondences and
the pose can be computed with them.
0 2 4 6 8
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
iteration
pose error (mm)
convergence of the pose for the occlusion case
t=50 degree
t=40 degree
t=30 degree
t=20 degree
t=10 degree
0 2 4 6 8
0
10
20
30
40
iteration
number of correspondences
number of correspondences with partial occlusions
t=50 degree
t=40 degree
t=30 degree
t=20 degree
t=10 degree
Figure 8: Left graphic: convergence behavior of the algo-
rithm for the occlusion case. Right graphics: number of
correspondences for each iteration.
Figure 9: Experiments in real images including the partial
occlusions case. Initial position of the model (left column)
and computed pose (right column).
6.4 Experiments on Real World Images
Finally, we applied our algorithm to real image data.
A single calibrated camera system providing gray
value images of 620 x 540 pixels is used. The al-
gorithm was tested on a Linux based system with a
3 GHz Intel Pentium 4 processor. Figure 9 shows
some examples taken from different test sequences
and examples with partial occlusions in the image.
The average computing time per frame for the image
processing module (contour extraction, global and lo-
cal feature extraction) was 224 milliseconds and the
complete pose calculation process (image processing
plus pose estimation) was 4.73 seconds. Addition-
ally to the outlier elimination criterion of equation
(7), the Euclidean distance criterion used by (Masuda
et al., 1996) was combined with the outlier elimina-
tion of equation (7). Correspondence pairs are re-
jected if their point-to-point distance is larger than 2.5
times the standard deviation of the complete corre-
spondence set.
CORRELATION ICP ALGORITHM FOR POSE ESTIMATION BASED ON LOCAL AND GLOBAL FEATURES
533

7 CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE
WORK
An ICP algorithm based on feature correlation for
pose estimation of 3D surfaces was presented. The
experimental results show that our approach performs
more efficiently than the normal and structural ICP
variants. It also shows better convergence behavior,
which reduces the probability of being trapped in a
local minimum during the minimization process. An
important feature of our approach is that in the first
iteration of the process, the pose error is smaller than
that of the PCA based pre-alignment step. The ex-
periments show the convergence limits of the algo-
rithm when only one camera is available. The integra-
tion of an additional camera would increase the view
range over the object and therefore the convergence
ranges.The computation of local and global features
in every iteration and the 3D silhouette extraction step
increase the computation time of the algorithm. Real
time is not reached with our approach, but the re-
ported computation time is a good tradeoff consid-
ering the robustness of the algorithm. A natural ex-
tension for our approach is to adapt the correlation
ICP algorithm and combine it with the structural ICP
variant in a system which deals with more complex
scenarios like more general object occlusions, local
model deformations, illumination changes or similar.
REFERENCES
Araujo, H., Carceroni, R., and Brown, C. (1998). A
fully projective formulation to improve the accuracy
of Lowe’s pose-estimation algorithm. Comput. Vis.
Image Underst., 70(2):227–238.
Besl, P. and McKay, N. (1992). A method for registration
of 3-d shapes. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis
and Machine Intelligence, 14(2):239–256.
Brujic, D. and Ristic, M. (1996). Analysis of free form
surface registration. In International Conference of
Image Processing. Lausanne, Switzerland, pages 393–
396.
Chavarria, M. and Sommer, G. (2007). Structural icp algo-
rithm for pose estimation. In 2nd International Con-
ference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications,
VISAPP 2007, March 8-11, Barcelona, Spain, pages
341–346, Portugal. INSTICC.
Felsberg, M. and Sommer, G. (2004). The monogenic scale-
space: A unifying approach to phase-based image
processing in scale-space. Journal of Mathematical
Imaging and Vision, 21(1):5–26.
Ladkos, A., Behimane, S., and Navab, N. (2007). A real-
time tracking system combinig template-based and
feature-based approaches. In 2nd International Con-
ference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications,
VISAPP 2007, March 8-11, Barcelona, Spain, pages
325–332, Portugal. INSTICC.
Lin, C.-S. and Hwang, C.-L. (1987). New forms of shape
invariants from elliptic fourier descriptors. Pattern
Recognition., 20(5):535–545.
Lomonosov, E., Chetverikov, D., and Ek´art, A. (2006).
Pre-registration of arbitrarily oriented 3d surfaces us-
ing a genetic algorithm. Pattern Recognition Letters,
27(11):1201–1208.
Masuda, T., Sakaue, K., and Yokoya, N. (1996). Regis-
tration and integration of multiple range images for
3-d model construction. In ICPR ’96: Proceedings of
the 1996 International Conference on Pattern Recog-
nition (ICPR ’96) Volume I, page 879, Washington,
DC, USA. IEEE Computer Society.
Murino, V., Ronchetti, L., Castellani, U., and Fusiello, A.
(2001). Reconstruction of complex environments by
robust pre-aligned ICP. In Proc. Third Int. Conf. on
3-D Digital Imaging and Modeling, pages 187–194.
Rosenhahn, B., Perwass, C., and Sommer, G. (2003). Pose
estimation of free-form surface models. In Michaelis,
B. and Krell, G., editors, 25. Symposium f¨ur Muster-
erkennung, DAGM 2003, Magdeburg, volume 2781 of
LNCS, pages 574–581. Springer-Verlag, Berlin.
Rosenhahn, B. and Sommer, G. (2005). Pose estimation in
conformal geometric algebra, part II: Real-time pose
estimation using extended feature concepts. Journal
of Mathematical Imaging and Vision, 22:49–70.
Rusinkiewicz, S. and Levoy, M. (2001). Efficient variants
of the ICP algorithm. In Proceedings of the Third Intl.
Conf. on 3D Digital Imaging and Modeling, pages
145–152, Quebec City, Canada.
Shang, L., Jasiobedzki, P., and Greenspan, M. (2007).
Model-based tracking by classification in a tiny dis-
crete pose space. IEEE Transactions on Pattern
Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 29(6):976–989.
Sharp, G., Lee, S., and Wehe, D. (2002). ICP registra-
tion using invariant features. IEEE Transactions on
Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 24(1):90–
102.
Sommer, G., editor (2001). Geometric Computing with Clif-
ford Algebras. Springer-Verlag, Heidelberg.
VISAPP 2008 - International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
534
