
AN ARTICULATED MODEL WITH A KALMAN FILTER FOR REAL
TIME VISUAL TRACKING
Application to the Tracking of Pedestrians with a Monocular Camera
Youssef Rouchdy
CEREMADE, Univerist´e Paris Dauphine, Place du Mar´echal De Lattre De Tassigny, 75775 Paris Cedex 16, France
Keywords:
Visual tracking, Pedestrian tracking, Articulated models, Kalman filter, Sequential filtering.
Abstract:
This work presents a method for the visual tracking of articulated targets in image sequences in real time.
Each part of the target object is considered as a region of interest and tracked by a parametric transformation.
Prior geometric and dynamic informations about the target are introduced with a Kalman filter to guide the
evolution of the tracking process of regions. An articulated model with two areas is proposed and applied to
track pedestrians in the urban image sequences.
1 INTRODUCTION
The tracking approaches can be distinguished by sev-
eral criteria, for example:
1. • 2D approach without an explicit shape model,
• 2D approach with an explicit shape model,
• 3D approaches.
2. • tracking of primitives
• tracking of a region of interest (ROI)
3. • deterministic approach
• probabilistic approach
• classification approach
The choice of the tracking approach depends on the
application:
• the target objects are rigid or not,
• the camera used is monocular, stereo, fixed, mo-
bile,
• the precision and the computing time required for
the application.
The aim of this work is to develop a real-time al-
gorithm that allows the tracking of a deformable and
articulated target in an image sequence acquired by a
mobile mono-camera. The principal application is the
tracking of pedestrians in an urban environment and
to warn the driver should a pedestrian move into the
security area (see figure 1) around the vehicle.
This application is difficult to achieve for several
reasons: the camera is mounted on the vehicle (so a
Figure 1: The security area is defined by the red (dark) re-
gion, where Vp is the pedestrian velocity and Vh is the ve-
hicle velocity.
simple background subtraction does not apply), oc-
clusions are frequent and real time computing is re-
quired. Also, the appearence and resolution of the
target object -e.g. the pedestrian- change due to de-
formation of clothes, changes in the posture and the
motion of the camera. Figure 2 gives an idea of the
variation of the resolution. In the diagrams the width
and height (in pixels) of the window that contains the
pedestrian in the image are plotted against the dis-
tance of the camera.
The most popular techniques for the estimation of
motion are based on the parametric model (Bergen
et al., 1992), which is adapted to real time tracking.
These techniques model the motion of a ROI in an
image for example by the affine (6 DOF) or the
homographic (8 DOF) transformation. Problems
occur when the motion model that is used does
686
Rouchdy Y. (2008).
AN ARTICULATED MODEL WITH A KALMAN FILTER FOR REAL TIME VISUAL TRACKING - Application to the Tracking of Pedestrians with a
Monocular Camera.
In Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications, pages 686-693
DOI: 10.5220/0001089706860693
Copyright
c
SciTePress

0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40
0
500
1000
1500
Height
Distance camera/pedestrian (meters)
Projection of the bounding window (pixels)
First pedestrian
Second pedestrian
0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40
0
50
100
150
200
250
300
350
400
450
500
Width
Distance camera/pedestrian (meters)
Projection of the bounding window width (pixels)
First pedestrian
Second pedestrian
Figure 2: Dimensions of pedestrian in the image (in pix-
els) according to the variation of the distance between the
camera and a pedestrian.
not describe well the motion of the ROI. In (Weiss
and Adelson, 1996), the motion is segmented into
independent multiple motion areas. This method is
problematic when some of the areas do not contain a
high enough number of pixels or when they contain
noise. Others have introduced a constraint. The target
segments are connected to each other by joints. In
(Murray et al., 1994; Bregler et al., 2004), the twist
and product exponential map are used to introduce
constraints. In (Gavrila and Davis, 1995; Kakadiaris
and Metaxas, 1996), the human body is modeled by
rigid segments which are connected by joints. See
(Gavrila, 1999) for a comprehensive bibliography of
approaches used to analyse human motion, and see
(Zhang et al., 2006) for an analysis of motion with an
articulated model.
In this work, we model the target by rigid seg-
ments which are connected by a priori informations
representing the joints. The constraints are intro-
duced as a priori informations using a Kalman filter.
This permits a higher reach connection between the
multiple areas without increasing the DOF of the
system. The contribution of each segment and of
each joint is regulated by the covariance matrices of
the Kalman Filter. So the Kalman filter proposed
introduces a priori geometric (e.g. the connection
between the multiple areas) and dynamic (constant
velocity) informations about the target. Furthermore,
the Kalman filter smooths the trajectory of the target.
In the next section, a different approach to model the
dynamic evolution in the context of visual tracking
with sequential filtering is presented. Subsequently,
we will focus on the Kalman filtering. In section
3, an articulated model based on a Kalman filtering
is proposed. In section 4, an articulated model is
proposed to track a pedestrian in image sequences
and experimental results are given.
2 SEQUENTIAL FILTERING AND
TRACKING IN IMAGE
SEQUENCES
In this section, an introduction of the use of the se-
quential filtering in the context of the visual tracking
is given. The measurements acquired up to framet are
denoted Y
t
and X
t
represents the configuration of the
target objects at the time t. The process {X
t
; t ∈ N}
is modeled as a Markov process of initial distribu-
tion p(X
0
) and transition equation p(X
t
|X
t−1
). The
observations {Y
t
; t ∈ N} are assumed to be condition-
ally independent given the process {X
t
; t ∈ N} and
of marginal distribution p(Y
t
|X
t
). The principle of se-
quential filtering is to apply Bayes’s theorem at each
time-step, obtaining a posteriori p(X
t
|Y
t
) based on all
available information:
p(X
t
|Y
t
) =
p(Y
t
|X
t
)p(X
t
|X
t−1
)
p(Y
t
)
(1)
where we can write p(Y
t
|X
t
) instead of p(Y
t
|X
t
,Y
t−1
)
due to the conditional independence assumption. Ac-
cording to custom in filtering theory, a model for the
expected motion between time-steps is adopted. This
takes the form of a conditional probability distribution
p(X
t
|X
t−1
) termed the dynamics. Using the dynamics
equation, (1) becomes
p(X
t
|Y
t
) =
p(Y
t
|X
t
)
R
p(X
t
|X
t−1
)p(X
t−1
|Y
t−1
)dX
t−1
p(Y
t
)
(2)
It is assumed that the predicted values of the states
and the observations, X
t
and Y
t
, respectively, evolve in
time according to:
X
t
= f
t
(X
t−1
,V
t
), (3)
Y
t
= g
t
(X
t
,W
t
). (4)
where f
t
and g
t
are the state and the observation func-
tions, respectively, which are supposed to be known.
The state noise V
t
and the measurement noise W
t
have
known distributions.
In visual tracking the choice of the dynamical
model p(X
t
|X
t−1
) depends on the type of the images,
the a priori information available and the applica-
tion. Typically, the elasticity model is used to track
the elastic structure (Rouchdy et al., 2007) and the
Navier-Stockes model is used to track a fluid struc-
ture (Cuzol et al., 2007). When a good a priori infor-
mation is available the prediction can be introduced
by learning (Blake et al., 1999). The most popular
dynamical model used is autoregressive (Black and
Fleet, 1999; Perez et al., 2002) and corresponds in the
AN ARTICULATED MODEL WITH A KALMAN FILTER FOR REAL TIME VISUAL TRACKING - Application to the
Tracking of Pedestrians with a Monocular Camera
687

first order to the model of constant velocity, which is
the model adopted in this work.
The choice of the observations depends on the ap-
plication and the image and can be subjective in some
cases. The cues usually used are edge information
(Blake and Isard, 1998) and color distributions (Perez
et al., 2002). There exists also a model based on mo-
tion and appearance (Sidenbladh and Black, 2003). In
(Sidenbladh and Black, 2003), several cues are com-
bined to make the model robust to a change of appear-
ance.
For a nonlinear system (e.g. the function f
t
or g
t
in equations (3) is nonlinear) the probability p(X
t
|Y
t
)
is approximated by a Monte Carlo (MC) method. Un-
fortunately, the classical sampling for the MC method
is guaranteed to fail as time increases. To deal with
this problem a step of selection is added -(Gordon,
1993) gives the first operationally effective method.
Theoritical convergence results of this algorithm are
given in (Del Moral, 1997). A good reference and co-
herent treatement of these techniques including con-
vergence results and applications to visual tracking
are presented in (Doucet et al., 2002).
When the observation density p(Y
t
|X
t
) is assumed
to be Gaussian and the dynamics are assumed lin-
ear with additive Gaussian noise the solution is ob-
tained analytically and this method corresponds to the
Kalman filter. In this case the dynamical system is
written as:
X
t
= A
t
X
t−1
+ B
t
V
t
, (5)
Y
t
= C
t
X
t
+ D
t
W
t
, (6)
where A
t
, B
t
, C
t
and D
t
are matrices and V
t−1
, W
t−1
are vectors of i.i.d standard normal variants. The
state noise V
t
and the measurement noise W
t
are sup-
posed to be Gaussian and independent with the matri-
ces covariances Q
t
and R
t
, respectively. In this case,
p(X
t
|X
t−1
), p(Y
t
|X
t
) and p(X
t
|Y
t
) have a Gaussian dis-
tribution with the covariance matrices Q
t
, R
t
and Γ
t
,
respectively. Where the covariance matrix Γ
t
and the
estimation of the vector state X
t
are computed recur-
sively with the Kalman filter, the Kalman recursion is
given in section 3.5 and documented in (Kalman and
Bucy, 1961).
3 ARTICULATED MODEL BASED
ON KALMAN FILTER
3.1 Motion Estimation
The image is a projection of 3D points of the space on
an image plane. Let a rectangle that moves in the 3D
space be such that the deformationsin the image plane
are described by a rigid transformation. Let I
1
be the
image of this object at the time t
1
and let I
t
n
be the
image at t
n
. In (Faugeras et al., 2001), it is shown that
the points on the rectangle of the two frames are re-
lated by a homographic transformation and that they
are defined by eight parameters. Subsequently, it is
supposed that the deformation of a target is obtained
by a homographic transformation. Otherwise, the ob-
ject is approximated by a set of rigid links. We re-
strict ourselves to this type of motion to reduce the
complexity.
3.2 Modelisation and Predictions
Let {R
l
r
}
N
l=1
be a set of supposed rigid areas of an
articulated target, let c
l
be the coordinates of the
barycenter of the region R
l
r
, and let s
l
be the surface
of R
l
r
. The elements of the set {R
l
r
}
1
l=N
are correlated
by their barycenters with the relations
ψ
1
(c
1
, ··· , c
N
, s
1
, ··· , s
N
) = d
1
; . . . ;
ψ
N
(c
1
, ··· , c
N
, s
1
, ··· , s
N
) = d
m
(7)
where m is the number of the constraint functions ψ.
These constraints are introduced as a priori informa-
tions with the Kalman filter. An example of the track-
ing of a pedestrian in an image sequence using two
correlated areas is given in section 4.
The constraintes (7) are supposed to be linear. If
this is not the case, they can be linearized. The con-
straints are introduced into the dynamic system of the
Kalman filter. The constraints (7) are introduced in
the filter with a function g
t
= (g
1
t
, ··· , g
m
t
). At the time
t, the state vector X
t
is defined by
X
t
=
c
1
t
, ··· , c
n
t
, v
t
1
, ··· , v
N
t
, s
1
t
, ··· , s
N
t
, g
1
t
, ··· , g
m
t
,
and follows the state equations:
X
t
= AX
t−1
+ BV
t−1
, (8)
Y
t
= CX
t
+ DW
t−1
, (9)
where A, B,C and D are fixed matrices and V
t−1
, W
t−1
are vectors of i.i.d standard normal variants. The ma-
trix A introduces dynamic, e.g. constant velocity, and
geometric, e.g. the correlation between the areas, a
priori informations about the target.
VISAPP 2008 - International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
688

3.3 Measurement
For each set R
l
r
, the estimation of the parameters of the
transformation model is achieved by the minimization
problem:
λ
l
t
= arg min
λ∈R
α
∑
p∈R
l
r
I
t
(φ
l
t
(λ, p)) − I
r
(p)
2
(10)
where I
r
is the reference image, I
t
the current image,
φ
l
t
are the parametric transformations determined by
the parameters λ
l
t
for each l ∈ {1, ··· , N} and where
α is the parameters number. The measurement vector
is computed from the transformations φ
l
t
and defined
by
Y
mes
t
=
z
1
t
, ··· , z
n
t
, v
t
1
, ··· , v
N
t
, s
1
t
, ··· , s
N
t
, g
1
t
, ··· , g
m
t
,
where z
l
t
and s
l
t
are the barycenters and the surfaces,
respectively, of the areas φ
l
t
(λ
l
t
, R
l
r
). From z
l
t
and s
l
t
we
compute the quantity g
i
t
for each (i, l) ∈ {1, ··· ,m} ×
{1, ··· , N}. The image motion of the point z
i,l
t
from
time t − 1 to time t is :
v
l
t
=
z
l
t
− z
l
t−1
∆t
.
The minimization of the problem (10) is achieved by
the ESM algorithm, see (Malis, 2004; Benhimane and
Malis, 2004).
3.4 Initialization
Using the first reference image, the user segments the
target manually into a set of areas. The surface of the
areas, the distance between the barycenters of the ar-
eas and other geometric characteristics are computed
from the initial set of areas to initialize the Kalman
filter.
3.5 Filtering
This step allow us to introduce a goodness of fit crite-
rion between a reference template and possible candi-
dates in the current image. If the additional noise v
t
is
supposed to be Gaussian, then the observation density
p(Y
t
|X
t
), associated to the prediction and measure-
ment described in the previous section, has a Gaussian
distribution with a Covariance matrix error R. The
density p(X
t
|Y
t
) has also a Gaussian distribution with
a covariance matrix error Q. So the estimation of the
state is computed by a Kalman filter with the rela-
tions:
• initialization
– X
0
, P
0
, R and Q are given
• prediction
–
¯
X
t
= AX
t−1
–
¯
Y
t
= C
¯
X
t
–
¯
P
t
= AP
t−1
A
∗
+ Q
• filtering
– K
t
=
¯
P
t
C(C
¯
P
t
·C + R)
−1
,
– X
t
=
ˆ
X
t
+ K
t
(Y
mes
t
−
¯
Y
t
),
– P
t
= (1− K
t
C)
¯
P
t
.
K
t
is called the gain. The difference Y
mes
t
−
¯
Y
t
is
called the measurement innovation. The innovation
reflects the discrepancy between the predicted mea-
surement C
¯
X
t
and the actual measurement Z
mes
t
. Let
Q =
Q
1
0 0
0 Q
2
0
0 0 Q
3
, R =
R
1
0 0
0 R
2
0
0 0 R
3
The covariance matrix (Q
1
, R
1
), (Q
2
, R
2
) and
(Q
3
, R
3
) are associated to the barycenters, the surface
and the constraints, respectively.
4 APPLICATION TO TRACK A
PERSON
4.1 Measurements and Predictions
To track a pedestrian in an image sequencee, we track
the head and the torse which are supposed to be con-
nected: the head stays close to the torse. Two areas
F
1
and F
2
are used, one coresponding to the head and
other to the torse.
4.1.1 Method 1
The vector state X
t
is defined by the centers of the
windows F
1
and F
2
and by their velocity v
1
t
and v
2
t
,
respectively:
X
t
= (c
1
t
, v
1
t
, c
2
t
, v
2
t
)
The prediction matrices are defined by
A =
1 0 ∆t 0 0 0 0 0
0 1 0 ∆t 0 0 0 0
0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0
1 0 ∆t 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 1 0 ∆t
0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
,
AN ARTICULATED MODEL WITH A KALMAN FILTER FOR REAL TIME VISUAL TRACKING - Application to the
Tracking of Pedestrians with a Monocular Camera
689
C =
1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
These predicions introduce the a priori informa-
tion that the first component of the window center c
1
t
is equal to the first component of c
2
t
. Figure 3 gives
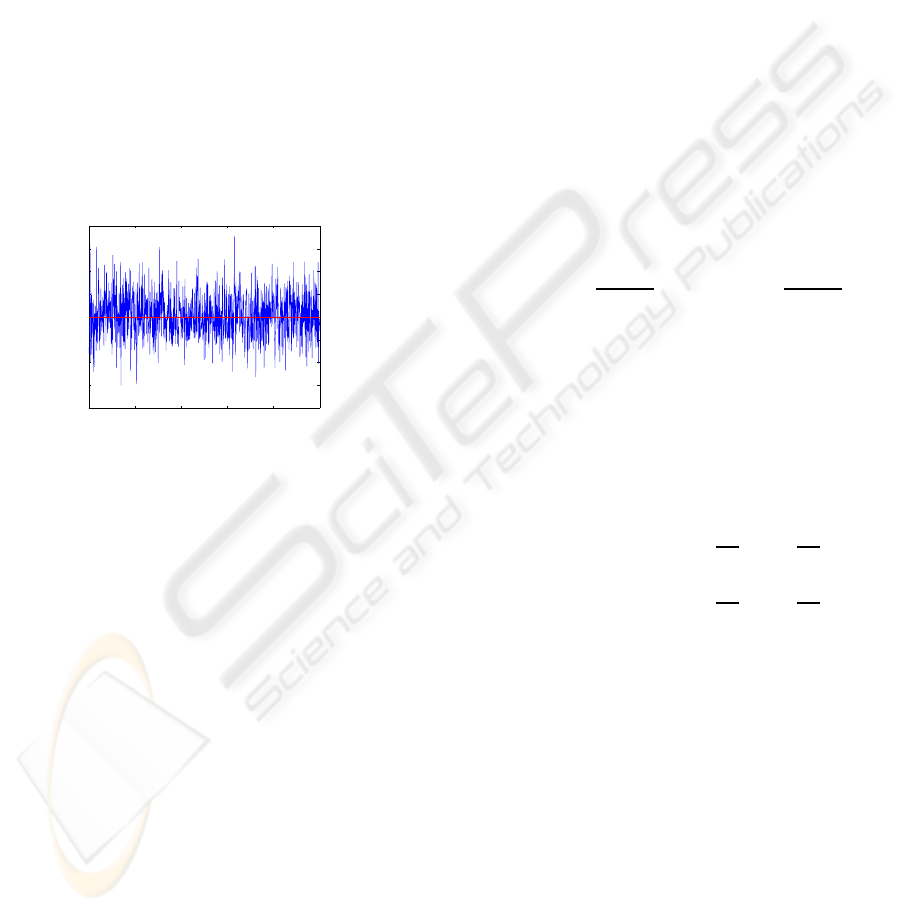
the variations of the predicted value of the first com-
ponent of one window when the first component of
the other window is fixed to be zero. The amplitude
variation of the predicted value of the first component
depends on the variance of the considered gaussian
noise.
0 200 400 600 800 1000
−4
−3
−2
−1
0
1
2
3
4
x 10
−3
Figure 3: Variation of the predicted value of the first compe-
nents of one window when the first component of the second
window is fixed at zero.
4.1.2 Method 2
Here, the vector state is defined by only one window
F
1
:
X
t
= (c
1
t
, v
t
, d
t
),
where d
t
is a vecor of R
2
. The prediction matrices are
defined by
A =
1 0 ∆t 0 0 0
0 1 0 ∆t 0 0
0 0 1 0 0 0
0 0 0 1 0 0
0 0 0 0 1 0
0 0 0 0 0 1
,
C =
1 0 0 0 0 0
0 1 0 0 0 0
0 0 1 0 0 0
0 0 0 1 0 0
1 0 0 0 1 0
0 1 0 0 0 1
We remark that if
d
t
= c
2
t
− c
1
t
, (11)
the observations Y
t
correspond to the barycenters of
the zones targeted. So the initial values of the vector
d
t
permit to introduce a constraint on the evolution of
the two windowsin the Kalman filter. The coordinates
of the barycenter of the window F
2
are deduced from
the estimation of d
t
and c
1
t
by the relation
c
2
t
= d
t
+ c
1
t
.
The initial value of the vector d
t
is computed from
the initial barycenters of the windows F
1
and F
2
.
4.2 Initialization of the Optimization
Algorithm
The user chooses the initial size of the windows F
1
and F
2
manually The window size is updated with the
estimated values of d
t
with the relations:
L
l,x
t
= L
l,x
t−1
·
||d
t
||
||d
t−1
||
, L
l,y
t
= L
l,y
t−1
·
||d
t
||
||d
t−1
||
where L
l,x
t
is the length of the window l and L
l,y
t
is the
width of the window F
l
at the time t. The size of the
windows and their barycenters are used to initialize
the values of the transformations for the next step of
tracking. The initialization of the transformation for
the minimization routine ESM is achieved by using
the results of filtering to construct new homographic
transformations defined by
H
l,0
t
=
1 0 min
c
l,x
t
−
L
l,x
t
2
, c
l,x
t
+
L
l,x
t
2
0 1 min
c
l,y
t
+
L
l,y
t
2
, c
l,y
t
−
L
l,y
t
2
0 0 1
We note that, these homographies are computed from
the estimation at the previous iteration of the window
center. The update of the transformation by the trans-
formation H
l,0
t
gives more stable results than when
the initialization is performed with the transforma-
tions that we measured directely at the previous step.
The necessity to update the transformation is due to
the non-rigid motion of the target and changes of their
appearence.
4.3 Change of Appearance and
Resolution
Where the change of appearence and resolution be-
comes very large due to the deformation of the
VISAPP 2008 - International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
690

clothes, changes in the posture of the pedestrian and
the mobility of the camera, the update of the trans-
formations proposed in the previous section is insuffi-
cient. It is necessary to update the reference template
which is composed of the set of the targeted areas. In
this work, we have used the estimation of d
t
to update
the reference template. Indeed, when the condition
||d
t
|| − ||d
t−1
||
< Th
v
is not satisfyed, the set of areas is update from the
set of areas obtained at the previous iteration. This
criterion can be combined with another similarity
measurement that compars the reference and current
templates for example by using the sum-of-squared-
differences (SSD). In (Arnaud et al., 2004), the eigen-
values of the covariance error in tke Kalman filter is
used to define a threshold.
Intuitively, a more pertinent strategy to update the
reference template consists to accumulate the refer-
ence templates (Morency et al., 2003). The problem
with such an approach is to define a criterion of sim-
ilarity that can be applied to the reference data and
also the computing time can be expensive. In (Wu
and Huang, 2001), a particle filter is used to evolve
the reference template by a dynamical model. To deal
with the change of apparence, Headvig et al. (Siden-
bladh and Black, 2002) are use a learning approach
based on the cues edge, ridge and motion. The cues
are combined with a bayesian model.
4.4 Experiments
4.4.1 Data
We tested the proposed articulated models on data
from an urban traffic environment. The two video se-
quences used were recorded by Renault in the con-
text of the LOVe project
1
by a SMAL camera from
CYPRESS company. The following table gives the
main characteristics of the used camera. Since our
model is adapted to a monocular camera, only one of
the two sets of images obtained by the stereo camera
were used.
The first image sequence was aquired from an
immobile vehicle. The trajectory of the pedestrian
was perpendicular to the road. The second image se-
quence is acquired by a camera mounted on a moving
vehicle and shows pedestrians crossing the road.
1
http://www.love.univ-bpclermont.fr/
4.4.2 Results and Discussion
In the following section, some experimental results
obtained with the urban image sequences presented
in the last section are given to evaluate the articulated
model 4.1.1. We compare it to the results obtained
when only one area is trached with the ESM algo-
rithm. Figure 4 shows the result obtained by the ESM
algorithm: the tracker has lost the target at the sec-
ond image due to a non-rigid motion and due to the
background present in the initial area (pixels not be-
longing to the pedestrian). Figure 5 shows that the
articulated model has succeeded in tracking the tar-
get. These results were obtained without updating the
reference template.
Figure 6 shows the results of the tracking. The
pedestrian was correctly tracked until he made a 90
degree turn in relation to the camera in image t
8
=
2.0630s. The update of the reference template us-
ing the distance correlation between the barycenters
was insufficient to deal with the large change of ap-
pearance in frame t
8
= 2.0630s when the pedestrian
changed his posture completely. It will be interesting
to combine the proposed update method to another
update strategy based on the measurement of similar-
ity, see section 4.3.
100 200 300 400 500 600
50
100
150
200
250
300
350
400
450
100 200 300 400 500 600
50
100
150
200
250
300
350
400
450
100 200 300 400 500 600
50
100
150
200
250
300
350
400
450
100 200 300 400 500 600
50
100
150
200
250
300
350
400
450
100 200 300 400 500 600
50
100
150
200
250
300
350
400
450
100 200 300 400 500 600
50
100
150
200
250
300
350
400
450
100 200 300 400 500 600
50
100
150
200
250
300
350
400
450
100 200 300 400 500 600
50
100
150
200
250
300
350
400
450
Figure 4: Results of the ESM tracking algorithm.
AN ARTICULATED MODEL WITH A KALMAN FILTER FOR REAL TIME VISUAL TRACKING - Application to the
Tracking of Pedestrians with a Monocular Camera
691

100 200 300 400 500 600
50
100
150
200
250
300
350
400
450
100 200 300 400 500 600
50
100
150
200
250
300
350
400
450
100 200 300 400 500 600
50
100
150
200
250
300
350
400
450
100 200 300 400 500 600
50
100
150
200
250
300
350
400
450
100 200 300 400 500 600
50
100
150
200
250
300
350
400
450
100 200 300 400 500 600
50
100
150
200
250
300
350
400
450
100 200 300 400 500 600
50
100
150
200
250
300
350
400
450
100 200 300 400 500 600
50
100
150
200
250
300
350
400
450
Figure 5: Results obtained with the first articulated model.
5 CONCLUSIONS
In this work, we propose a method for the tracking of
an articulated target with a monocular camera using
the Kalman filter. The advantages of this approach
are: the joints are introduced as a priori information
and not as constraints -e.g. the a priori informations
can be left unsatisfied if the measurements (extracted
from the images) are more pertinent-, a real time im-
plementation is possible, it is easy to implement, it is
stable and it smooths the trajectory of the target. For a
large number of areas the algorithm can be easily par-
allelized: the measurement is computed separately for
each area. However, this model is sensitive to large
changes in appearence. Further work is necessary to
tackle this problem, some directions are proposed in
section 4.3.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We thank A. Doucet, E. Malis, D. M. Pierre and P.
Rives for stimulating and useful discussions. We are
very grateful to F. Solanet for providing the image se-
quences, the two video sequences used were recorded
100 200 300 400 500 600
50
100
150
200
250
300
350
400
450
t
1
= 0.4601s
100 200 300 400 500 600
50
100
150
200
250
300
350
400
450
t
2
= 0.6348s
100 200 300 400 500 600
50
100
150
200
250
300
350
400
450
t
3
= 0.9395s
100 200 300 400 500 600
50
100
150
200
250
300
350
400
450
t
4
= 1.0747s
100 200 300 400 500 600
50
100
150
200
250
300
350
400
450
t
5
= 1.2444s
100 200 300 400 500 600
50
100
150
200
250
300
350
400
450
t
6
= 1.8285s
100 200 300 400 500 600
50
100
150
200
250
300
350
400
450
t
7
= 1.8540s
100 200 300 400 500 600
50
100
150
200
250
300
350
400
450
t
8
= 2.0630s
Figure 6: Tracking with the first articulated model ap-
plied to an an urban image sequence recorded with 30 im-
ages/seconde.
by Renault in the context of the LOVe project
2
REFERENCES
Arnaud, E., Memin, E., and Cernuschi-Frias, B. (2004).
Conditional filters for image sequence based tracking
- application to point tracker. In IEEE trans. On Im.
Proc.
Benhimane, S. and Malis, E. (2004). Real-time image-
based tracking of planes using efficient second-order
minimization. In In IEEE/RSJ International Confer-
ence on Intelligent Robots Systems, Sendai, Japan,
October 2004.
Bergen, J. R., Anandan, P., Hanna, K. J., and Hingorani,
R. (1992). Hierarchical model-based motion estima-
tion. In ECCV ’92: Proceedings of the Second Euro-
pean Conference on Computer Vision, pages 237–252,
London, UK. (Springer-Verlag).
Black, M. J. and Fleet, D. J. (1999). Probabilistic detection
and tracking of motion discontinuities. In ICCV (1),
pages 551–558.
2
http://www.love.univ-bpclermont.fr/
VISAPP 2008 - International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
692

Blake, A. and Isard, M. (1998). Active Contours. Springer,
Berlin Heidelberg New York.
Blake, A., North, B., and Isard, M. (1999). Learning multi-
class dynamics. Advances in Neural Information Pro-
cessing Systems, 11:389–395.
Bregler, C., Malik, J., and Pullen, K. (2004). Twist based
acquisition and tracking of animal and human kine-
matics. Int. J. Comput. Vision, 56(3):179–194.
Cuzol, A., Hellier, P., and Mmin, E. (2007). A low dimen-
sional fluid motion estimator. Int. Journ. on Computer
Vision.
Del Moral, P. (1997). Nonlinear filtering: interacting par-
ticle resolution. C. R. Acad. Sci. Paris S´er. I Math.,
325(6):653–658.
Doucet, A., de Freitas, N., and Gordon, N., editors
(2002). Sequential Monte Carlo Methods in Prac-
tice. Statistics for Engineering and Information Sci-
ence. Springer-Verlag, New York Berlin Heidelberg.
Faugeras, O., Luong, Q.-T., and Papadopoulou, T. (2001).
The Geometry of Multiple Images: The Laws That
Govern The Formation of Images of A Scene and Some
of Their Applications. MIT Press, Cambridge, MA,
USA.
Gavrila, D. M. (1999). The visual analysis of human move-
ment: A survey. Computer Vision and Image Under-
standing: CVIU, 73(1):82–98.
Gavrila, D. M. and Davis, L. S. (1995). Towards 3d model-
based tracking and recognition of human movement.
In Proc. of the IEEE International Workshop on Face
and Gesture Recognition, pages 272–277, Zurich,
Switzerland.
Gordon, N. (1993). Bayesian methods for tracking. PhD
thesis, University of London.
Kakadiaris, I. A. and Metaxas, D. (1996). Model-based es-
timation of 3D human motion with occlusion based
on active multi-viewpoint selection. In Proceedings
of the 1996 Conference on Computer Vision and Pat-
tern Recognition (CVPR ’96), page 81, Washington,
DC, USA.
Kalman, R. E. and Bucy, R. S. (1961). New results in linear
filtering and prediction theory. Trans. ASME Ser. D. J.
Basic Engrg., 83:95–108.
Malis, E. (April 2004). Improving vision-based control us-
ing efficient secondorder minimization techniques. In
ICRA’04, New Orleans.
Morency, L., Rahimi, A., and Darrell, T. (2003). Adaptive
view-based appearance models. In Proc. IEEE Conf.
on Comp. Vision and Pattern Recogn., pages 803–810.
Murray, R. M., Sastry, S. S., and Zexiang, L. (1994). A
Mathematical Introduction to Robotic Manipulation.
CRC Press, Inc., Boca Raton, FL, USA.
Perez, P., Hue, C., Vermaak, J., and Gangnet, M. (2002).
Color-based probabilistic tracking. In ECCV, number
2350 in LNCS, pages 661–675.
Rouchdy, Y., Pousin, J., Schaerer, J., and Clarysse, P.
(2007). A nonlinear elastic deformable template for
soft structure segmentation. Application to the heart
segmentation in MRI. Inverse Problems, 23:1017–
1035.
Sidenbladh, H. and Black, M. (2003). Learning the statistics
of people in images and video. Int. Journ. on Com-
puter Vision, 54(1-3):183–209.
Sidenbladh, H. and Black, M. J. (2002). Learning the statis-
tics of people in images and video. Int. Journal of
Computer Vision, 54.
Weiss, Y. and Adelson, E. H. (1996). A unified mixture
framework for motion segmentation: Incorporating
spatial coherence and estimating the number of mod-
els. In Proceedings of the 1996 Conference on Com-
puter Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR ’96),
page 321, Washington, DC, USA.
Wu, Y. and Huang, T. (2001). A co-inference approach to
robust visual tracking. In Proc. IEEE Conf. on Comp.
Vision, pages 26–33.
Zhang, X., Liu, Y., and Huang, T. S. (2006). Motion anal-
ysis of articulated objects from monocular images.
IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine
Intelligence, 28(4):625–636.
AN ARTICULATED MODEL WITH A KALMAN FILTER FOR REAL TIME VISUAL TRACKING - Application to the
Tracking of Pedestrians with a Monocular Camera
693
