
MODELING AND ESTIMATION OF POLLUTANT EMISSIONS
El Hassane Brahmi, Lilianne Denis-Vidal, Zohra Cherfi, Nassim Boudaoud
and Ghislaine Joly-Blanchard
University of Technology of Compi`egne, BP 20 529, 60205 Compi`egne, France
Keywords:
Modeling, Combustion, Diesel Engine, Kriging method, Pollutant.
Abstract:
The European laws lead to the increase of emission constraints. In order to take into account these constraints,
automotive constructors are obliged to create more and more complex systems. This paper presents two stage
approaches for the prediction of NOx (nitrogen oxide) emissions, which are based on an ordinary Kriging
method. In the first stage, a reduction of data will take place by selecting signals with correlations studies and
by using a fast Fourier transformation. In the second stage, the Kriging method is used to solve the problem
of the estimation of NOx emissions under given conditions. Numerical results are presented and compared to
highlight the effectiveness of the proposed methods.
1 INTRODUCTION
The diesel engine is an internal combustion engine.
At each cycle during the intake stroke, the combus-
tion chamber receives a mixture of air and vaporized
fuel via the injector (their flows are measured and
controlled). Afterwards fuel vapor and air are com-
pressed and ignited.
The mixture air-fuel is not stoechiometric during the
combustion process. The unfortunate consequence is
the creation of pollutants. In order to limit this prob-
lem, the European laws increase the constraints on
pollutant gas emissions.
The main aim is the minimization of the NOx emis-
sions under some constraints based on the Kriging
model, by making a compromise with engine perfor-
mance. In this case multi-objectives optimization will
be considered. Then, it is necessary to simulate the
pollutant behavior which is the subject of this paper.
A physical phenomenon model has been devel-
oped by S.Castric et al (S. Castric, 2007) in order to
simulate the engine behavior. It takes into account
the input parameters (fuel mass flow, air mass flow,
exhaust gas recirculation ratio,...) and gives the cor-
responding state variables, particularly pressure, tem-
peratures, fresh gas mass, mixed gas mass, and burned
gas mass. It leads to a good representation of the ex-
periment results. Strategies based on Lolimot (Local
Linear Model Tree) and Zeldovich mechanisms (Hey-
wood, 1988) have been developed in order to predict
emissions of NOx (Castric, 2007). In the first case,
the corresponding model can lead to singular points,
which reduces the precision of the results. In the sec-
ond case, the results are not satisfactory enough. On
the other hand, the trend surfaces can be used, but it
is difficult to go deeper with this approach because it
consists of a classical regression based on the assump-
tion of independence of observations, which is rarely
checked with spatial data (S. Baillargeon, 2004).
Our choice is the Kriging method which takes into
account the dependence of spatial data and has a vari-
ance that is minimal among estimators without bias.
Moreover it leads to efficient results.
This paper is organized as follows: In the first sec-
tion, the ordinary Kriging techniques are recalled. In
the second section, two different approaches for mod-
eling our problem are proposed. An efficient reduc-
tion model strategy is considered in order to apply the
kriging method. Finally the Kriging method is ap-
plied to the reduced model. In the last section, numer-
ical results are given followed by a short discussion.
2 ORDINARY KRIGING
TECHNIQUES
Kriging methods is used frequently for spatial inter-
polation of soil properties. Kriging is a linear least
squares estimation algorithm. It is a tool for interpo-
260
Hassane Brahmi E., Denis-Vidal L., Cherfi Z., Boudaoud N. and Joly-Blanchard G. (2008).
MODELING AND ESTIMATION OF POLLUTANT EMISSIONS.
In Proceedings of the Fifth International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics - SPSMC, pages 260-263
DOI: 10.5220/0001496102600263
Copyright
c
SciTePress

lation, which is to estimate the value of an unknown
real function F at a point x
∗
0
, given the values of a
function Z at some other points x
1
,....x
n
.
2.1 Ordinary Kriging
The ordinary Kriging estimator
ˆ
Z(x
∗
0
) is defined by:
ˆ
Z(x
∗
0
) =
n
∑
i=1
λ
i
Z(x
i
). (1)
where m is the number of surrounding observations
Z(x
i
) and λ
i
is the weight of Z(x
i
). The weights
should sum to unity in order to make the estimator
unbiased. The weights are also determined such that
the Kriging variance is minimal.
This leads to a classical optimization problem with
equality constraint. The Lagrange multiplier theory
is used in order to work out this problem. It gives a
linear system to be solved (Davis.J.C, 1986)
2.2 Semivariogram
The semi-variogram is a function representing the
spatial dependency, and has been obtained from the
stationarity definition. It is based on the assumption
of intrinsic stationarity for spatial data, the variation
of a data set that is only dependent on distance r be-
tween two locations where the variables values are
Z(x
i
+ h) and Z(x
i
) with r = |h|, can be given by the
following semi variogram:
ˆ
γ(r) =
1
N(r)
∑
N(r)
[Z(x
i
) − Z(x
j
)]
2
(2)
where
N(r) =
(i, j) tel que
x
i
− x
j
= r
(3)
where N(r) is the pair number of Z(x
i
+ h) and
Z(x
i
) and
ˆ
γ(r) is the experimental semivariogram.
A variogram model should be fitted to such semi-
variogram. Different form of variogram model are
available. In this study a power model was used:
γ(r) = C
0
+ m.r
d
as h ≥ 0, 0 < d < 2 (4)
where C
o
is called the nugget effect, The least
square method was used to estimate the parameters
of experimental variogram and variogram models.
2.3 Cross-Validation
To evaluate the reliability of kriging estimation, cross-
validation was used,and the mean square error (MSE)
of the kriging-estimated values had been calculated.
The mean error ME is a measure of the estima-
tion bias, and it should be close to zero for unbiased
methods.
3 DESCRIPTION OF TWO
MODELS
S. Castric et all (Castric, 2007), have developed a
physical model for modeling the engine behavior, in
order to minimizing the NOx emessions. To do this,
he has divided into two sub-model: The first is a phys-
ical model, making the link between the input param-
eters and state variables. The second study the impact
of the latter on NOx, the second part was not com-
pletely done. In this work, we are inspired of this
original idea to give the two modelings below.
3.1 First Modeling
The first one consist of studying the impact of input
parameters on the NOx without taking into account
the state variables. In this case, a model will be built
by taking into consideration 8 input parameters like:
pressure in the rail injection,the exhaust gas recircula-
tion ratio..., with the corresponding value of the NOx
flow.
The choice of these parameters was recommended by
experts, and multiple regression to study the impact
of these parameters on the NOx, was confirmed it.
3.2 Second Modeling
The second one consist of studying the impact of state
variables on the NOx, which is tantamount to build a
model that uses ten state variables like: cylinder low
pressure, temperature in the cylinder...
which are each one represented by a vector of 1334
components and the corresponding value of NOx
flow.
3.3 Model Reduction
The data of the first model can be directly used for
applying the Kriging method. It is not the case for
the second one. In the latter case, the data have to be
reduced.
The reduction process begins by studying the dif-
ferent correlations between the state variables and
their corresponding p-value. The criterion which has
been chosen consists in testing the p-value: if it is in-
ferior to 0.05 the correlation is considered significant.
This analysis allows us to retain two state vari-
ables only: the cylinder low pressure P and the mixed
gas temperature in the cylinder T
e
.
In the second step, the number of components of
the two remaining signals is reduced. It has been ac-
complished by using the discrete Fourier transform.
The function fft of Matlab returns the discrete Fourier
MODELING AND ESTIMATION OF POLLUTANT EMISSIONS
261

transform (DFT) of a vector, computed with a fast
Fourier transform (FFT) algorithm. After calculating
the coefficients, a minimum number of these are re-
tained. This number allows to reproduce the initial
signal with a relative error of order 10
−2
, which is
reached with only 40 Fourier coefficients. The reduc-
tion of the number of points of each signal is tanta-
mount to minimizing the number of Fourier coeffi-
cients representing that signal.
The two retained signals, representing respec-
tively the cylinder low pressure and the temperature
of the mixed gas in the cylinder, have been reduced to
a number of 40 Fourier coefficients. Each signal has
been reconstructed from these 40 coefficients with an
acceptable error.
The following table presents the relative error
committed, for the reconstruction of the two signals
from the 40 selected coefficients.
Type of signal relative error
Cylinder low pressure 0.01
Temperature of the mixed gas 0.02
4 NOX ESTIMATION
4.1 Numerical Results using the First
Model
This subsection will be devoted to the presentation of
the numerical results obtained in the case of the first
modelisation, more precisely we give the mathemati-
cal model used to adjust the experimental variogram
and the corresponding graph.
The model used in this part is given by equation 5.
where:
C
0
= 9.909432.10
−1
, m = 5.281263.10
−8
, and d =
1.798734
Figure 1 shows the experimental semi-variogram
and the mathematical model which adjusts it. This
model has the power form, without bearing and with
a nugget effect C
0
. Several models were adjusted
and then compared, it was difficult to select the better
model by eye.The cross validation has facilitated the
work. She allows us to select the one, that minimizes
the mean square error, which is presented in this Fig-
ure.
Type of Indice Value
Mean Error 0.1082633
Mean square error 11.23740
Finally the kriging model is obtained and Figure 3
illustrate the comparison between measured and sim-
ulated emissions of NOx by using this first model.
Figure 1: Experimental semivariogram and semivariogram
model obtained using the input parameters.
Figure 2: Experimental semivariogram and semivariogram
model obtained using low pressure and temperature.
4.2 Numerical Results using the Second
Model
This subsection is devoted to the presentation of the
numerical results obtained in the case of the secon
modelisation more precisely we give the mathemat-
ical model used to adjust the experimental variogram
and the corresponding graph
The model used in this part is given by equation 5.
where:
C
0
= 9.917759.10
−1
, m = 1.277732.10
−
7, and d =
1.648926.
Figure 2 shows the experimental semi-variogram
and the mathematical model which adjusts it. This
model has the power form, without bearing and with
a nugget effect C
0
. Several models were adjusted
and then compared, it was difficult to select the better
model by eye. The cross validation has facilitated the
choice.
Type of Indice Value
Mean Error 0.205614
Mean square error 10.45415
The green straight lines in the Figure 3 and 4 is
the regression straight lines of NOx values estimated
ICINCO 2008 - International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
262
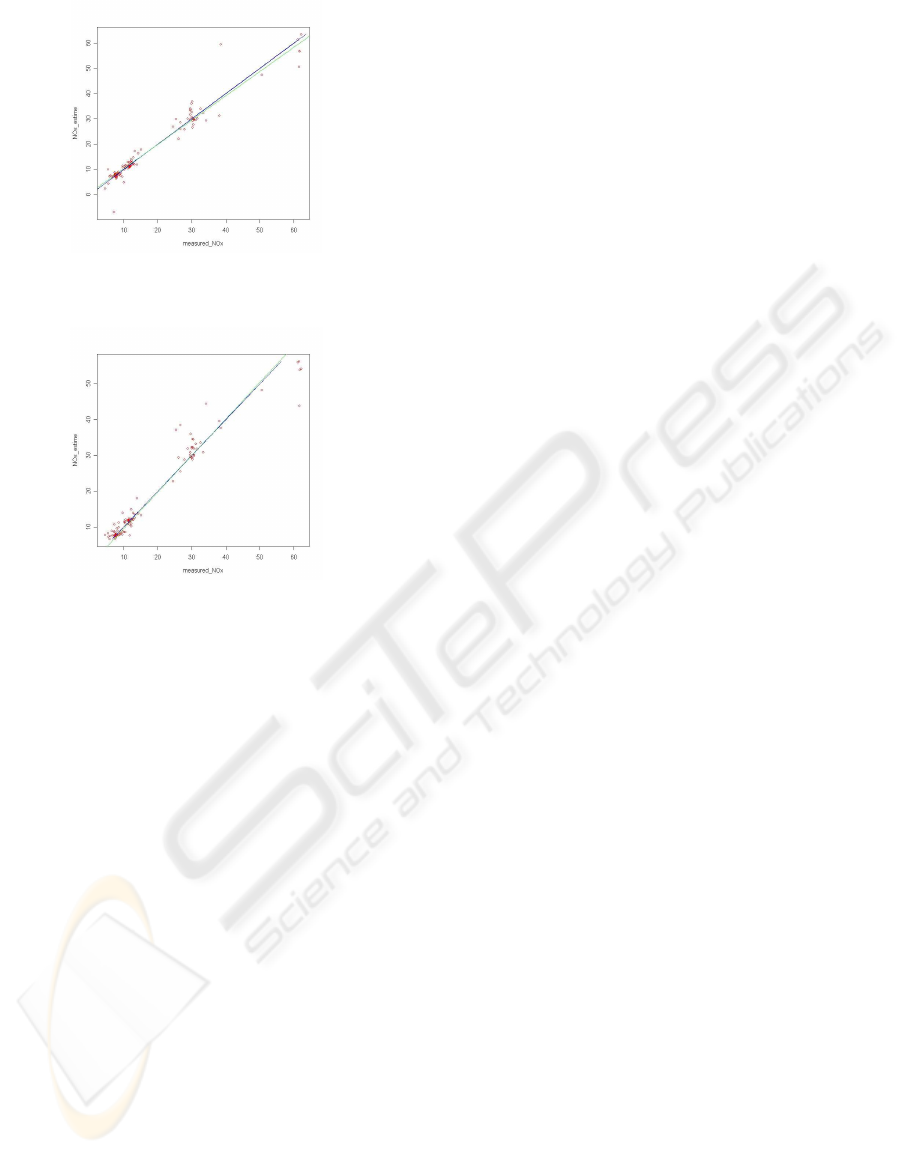
Figure 3: The scatter plot of the observed and predicted
values of NOx, using the Kriging method (first model).
Figure 4: The scatter plot of the observed and predicted
values of NOx, using the Kriging method (second model).
by the model, on the values of NOx observed. We
notice that this straight lines coincide with the Black
straight lines given by equation y = x, which is why
the estimate obtained is effective
Both experimental variogram calculated in the
framework of these two approaches are almost sim-
ilar. We notice that the two sructures spatial show a
strong dependence.
In both cases the estimations and the results given
by cross-validation are good. On the other hand, it is
clear that, for some experiments, the first one is the
best, and, for other experiments, it is the second one
which gives the best results.
These results impel us to adopt, in future work, a
combination of these models in order to optimize the
estimation of NOx emissions.
5 CONCLUSIONS
This paper describes a pollutant emissions simula-
tor of compression ignition engine. The effort has
been put into building a model based on the kriging
method. The resulting model can predict engine pol-
lutant emissions and can be used to predict the en-
gine performance and noise, it is easy to generalize
for various diesel engine configurations. This model
is also suitable for real time simulations. The predic-
tions obtained by this simulator are satisfactory com-
pared to the results obtained by using of a physical
model given by S.castric et al (Castric, 2007). Our
future aim is to estimate the engine performance by
using the proposed model. This latter will be adopted
in order to make the multi-objective optimization, us-
ing the stochastic methods.
REFERENCES
Castric, S. (2007). Readjusting methods for models and ap-
plication for diesel emissions. In PhD thesis, Universit
Technologique de Compi`egne.
Davis.J.C (1986). Statistics and Data Analysis in Geology.
John Wiley and Sons, New York, 2nd edition.
Heywood, J. (1988). Internal combustion engine fundamen-
tals. Mac Graw-Hill, London.
S. Baillargeon, J. P. (2004). interpolation statistique mul-
tivariable de donn´ees de prcipitations dans un cadre
de modlisation hydrologique. In Colloque Gomatique
2004: un choix strat`egique, Montr`eal.
S. Castric, V. T. (2007). A diesel engine combustion
model for tuning process and a calibration method.
In IMSM07 The Third Int. Con. on AVCS’07, Buenos
Aires, Argentine.
MODELING AND ESTIMATION OF POLLUTANT EMISSIONS
263
