
A CASE STUDY OF COMMUNITIES OF PRACTICE AND
ICT TOOLS IN KNOWLEDGE MANAGEMENT
ON INTERNATIONAL COOPERATION IN SCIENCE AND
TECHNOLOGY RESEARCH
Juan Miguel González-Aranda, Rafael Rodríguez-Clemente
Doñana Biological Station, Spanish Council for Scientific Research-CSIC
Avenida de Mª Luisa S/N Pabellón del Perú, 41013 Seville, Spain
Sebastián Lozano
Department of Industrial Management, University of Seville
ESI, Camino de los Descubrimeintos, s/n, 41092 Seville, Spain
Keywords: Knowledge Management, Communities of Interest, Communities of Practice, Tele-work and Collaboration,
Social Networks and Organizational Culture.
Abstract: This paper discusses how Formal Workgroups within the framework of Coordination Actions projects
funded by the EU Commission within the context of the MEDA and the different Framework Programmes
on Scientific and Technological Research (STR) initiatives, have assisted and nurtured the existing and
emerging Communities of Practice (CoP) in International Cooperation on STR, Development and
Innovation in the Euro-Mediterranean Area. It also illustrates how in some specific cases these CoP are
evolving towards Formal Electronic Networks of Practice (NoP) thanks to the application of specialized
thematic-oriented Knowledge Management (KM) methodologies, by means of the intensive use of new
Information and Communication Technologies (ICT) instruments, mainly based on the adaptation of open
source Content Management Systems (CMS) architectures. Hybrid platforms, specifically based on “mixed”
schemes between LAMP (Linux+Apache+MySQL+PHP) and Plone/Zope (Python programming language
scripting) architectures and technologies are proposed to achieve these ambitious objectives. A case study of
the Euro-Mediterranean Integrated Water Resources Management (EU-MED-IWRM) CoP is presented as
an example of an on-going development.
1 INTRODUCTION
The future creation of the Euro-Mediterranean Free
Trade Area (EU-MEFTA) (scheduled for 2010), the
development of the European Neighbourhood Policy
(ENP) and the activities of the MEDA Programme
that implements the Euro-Mediterranean Partnership
(launched as a consequence of the Barcelona
Declaration, November 28, 1995) have favoured
initiatives financed by the EU Commission which
have characterized the International Cooperation on
Science & Technology Research, Development and
Innovation in the Euro-Mediterranean Area (EU-
MED-STRDI).
This Cooperation has revolved around two main
axes:
• the bilateral cooperation initiatives between the
27 EU Member States (EU-MS) and the so-
called Mediterranean Partner Countries (MPC):
Algeria, Egypt, Israel, Jordan, Lebanon,
Morocco, Palestine, Syria, Tunisia and Turkey
• and the actions funded by the EU by means of
the use of several instruments, mainly the
MEDA Programme (e.g. the EUMEDIS Project
on IST) and the different EU Research
Framework Programmes (FP). The authors
have been actively engaged in applying KM
and ICT tools in several 6
th
and 7
th
FP funded
projects aimed at fostering the EU-MPC
cooperation, notably: MELIA, MED7,
ASBIMED and EUROMEDANET 1&2
(Rodríguez-Clemente and González-Aranda,
2007).
415
Miguel González-Aranda J., Rodríguez-Clemente R. and Lozano S. (2008).
A CASE STUDY OF COMMUNITIES OF PRACTICE AND ICT TOOLS IN KNOWLEDGE MANAGEMENT ON INTERNATIONAL COOPERATION IN
SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY RESEARCH.
In Proceedings of the Fourth International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies , pages 415-422
DOI: 10.5220/0001516904150422
Copyright
c
SciTePress

An in-depth analysis of the results of these
initiatives shows that the international cooperation
on EU-MED-STRDI is not a new phenomenon. It
has existed from around the middle of the 20
th
century or, even, earlier, i.e., when most of the MPC
get their independence from European powers.
These collaborations started from the establishment
of spontaneous STR relationships between both
sides of the Mediterranean Area in the form of
small-sized Communities of Interest (CoI). These
relationships involved groups of individuals
(scientists, technicians, economists, industrialists,
Ph.D students,…) where knowledge sharing occurs
among them as they engage in debate and
discussion of each other’s ideas and results, and
through collaboration on joint research projects,
thus leading to the establishment of the first Formal
Workgroups, a process already studied in general by
Crane (1972). Thus, knowledge and innovations are
shared quickly across organizational, cultural and
national boundaries through these informal
relationships, which are usually reflected into the
form of many publications on specific common
interest topics. This reasoning is based on the
concepts of “reciprocity” in knowledge sharing,
respect for intellectual property rights and common
trust in research (Bouty, 2000; Liebeskind et al,
1996).
The analysis also shows how the role of KM in
these initially informal social networks has changed
due to the new paradigms associated to the
Information Society Technologies (IST) and how the
connection with the new Knowledge-Based
Economy also affects the EU-MED-STRDI
cooperation itself: Past are the times when all the
possible interactions were based on the exchange of
postal letters. Today, ICT tools and KM
methodologies creates a scenario where these social
networks are mainly structured around either CoI or
CoP. These social networks are themselves
reinforced and nurtured by ICT/KM through the
provision of coordination and management
mechanisms, implemented via existing or new
Formal Workgroups (FW), structured as Virtual
Teams by means of Tele-work and collaboration,
(a.k.a. groupware tools). Eventually, these networks
may increase in size and evolve towards the well-
known as Formal Electronic NoP (Brown and
Duguid, 2000; Teigland, 2003).
Recent advances in ICT have also enabled the
creation of computer-supported social networks akin
to CoP, where individuals are able to discuss and
debate issues electronically. The success of CoP for
facilitating knowledge exchange, both electronically
and in face-to-face meetings, has recently pushed
initiatives on how to take advantage of this type of
networks as well as gather their benefits in
workgroups and virtual teams. Note, however, that
CoP are broader than FW and their associated virtual
teams, as they tend to gather all interested parties in
a given domain that have interacted, in a way or
another. Yan and Assimakopoulos. (2003) discusses
this distinction in detail.
2 BACKGROUND AND
THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK
The literature offers several definitions for the
concept of CoP. Wenger et al (2002) define CoP as
follows: Communities of practice are groups of
people who share a concern, a set of problems, or a
passion about a topic, and who deepen their
knowledge and expertise in this area by interacting
in an ongoing basis.
According to the theoretical background
proposed by these authors, a CoP is combination of
three structural elements:
• the DOMAIN of knowledge, which defines the
area of shared inquiry and the set of issues
discussed in the community
• the COMMUNITY, its members, the social
fabric, their motivation, and interactions
• and the PRACTICE, the set of interacting
processes, frameworks, ideas, tools,
information, styles, language, stories and
documents that the community members share.
The DOMAIN is the space of questions that
could interest a number of parties, individuals,
organisations, etc. In this sense, it defines the
universe where different COMMUNITIES are
created, considering a COMMUNITY as the
network formed by the interested parties that have
entered into contact by any means (physical contact,
letters, news in journals, electronic communication,
etc.). The PRACTICE of the COMMUNITY is the
interaction among its members, in such a way that it
could be more or less guaranteed that a member of a
CoP can reach another member by a direct or an
indirect interaction. In a given DOMAIN there can
be several CoP that could expand or merge by
interacting with each other.
The COMMUNITY is subject to an evolution
process and changes itself as time goes by. It is
initiated and develops over time to the current shape
and it is also embedded in a political, environmental,
social and economical context that is always
evolving. There is a mutual interaction between the
WEBIST 2008 - International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies
416

COMMUNITY and its surrounding CONTEXT.
Every CoP has some kind of output, outcome and
impact. Outcomes are the results of a programme or
project relative to its objectives that are generated by
its respective partners’ outputs. Outputs are the
tangible products (goods, services) of a programme
or project. And impacts are the effects, positive and
negative, primary and secondary long-term changes
produced in a community by a programme or
project, directly or indirectly, intended or
unintended. In this sense, it is clear that depending
on this positive and/or negative impact the
sustainability will or will not be guaranteed.
Additionally, there are two key factors:
• the Motivation of its members, visible in their
personal interest and in the priority they
attribute to CoP in their daily activities
• the Mandate of the concerned organisation(s)
defines, on the one side, the thematic focus with
the declared interest of the organisation in a
concrete outcome and, on the other side, the
mandate gives open space for self-commitment
to its members (working time and financial
resources).
Another concept to consider is Legitimate
Peripheral Participation (LPP), which refers to how
newcomers become members and eventually
experienced old timers of a CoP or collaborative
project. According to LPP, newcomers become
members of a community initially by manifesting
their interest and/or participating in minute and
superficial yet productive and necessary tasks that
contribute to the overall goal of the community.
These activities are typically simple and carry low
risk to the community as a whole, but are also
important. It crucially involves participation as a
way of learning —of both absorbing and being
absorbed in—the “culture of practice.” by means of
interacting and developing an “absorptive capacity”
of the new knowledge created and feedbacked again
by the CoP.
An extended period of LPP provides learners
with opportunities to make the culture of practice
theirs (Lave and Wenger, 1991).
CoP can be initially classified in 2 groups:
• Internal CoP: defined entirely within a single
organization
• and CoP in Network Organizations: A network
organization is a relationship among
independent organizations (Powell, 1990).
We will focus our analysis on the latter. Member
organizations in a network work in close and
continuous cooperation on projects or processes
involving partnerships, common products and/or
services, and possibly sharing a common strategy. In
solving problems in today’s environment, it is
becoming increasingly important to cross
boundaries, either within the organization or to
external organizations for fresh insights. Learning
and knowledge exchange through networks focuses
on the inter-organizational network as a resource
generator to enhance learning. Simultaneously, the
concept of NoP (Brown and Duguid, 2000;
Teigland, 2003) has emerged as a means to describe
informal, emergent social networks that facilitate
learning and knowledge sharing among individuals
conducting practice-related tasks. Brown & Duguid
(2000) argue that CoP are a localized and
specialized subset of NoP, typically consisting of
strong ties linking individuals engaged in a shared
practice, typically face-to-face and who usually
coordinate through third-party new ICT instruments
(e.g. internet-based groupware tools). In Electronic
NoP, the essential communication channel of
asynchronous computer-mediated communication
has a profound influence on how knowledge is
actually shared. In this respect, inter-organizational
CoP are close to NoP. A NoP is an open activity
system focused on work practice, and it may exist
primarily through electronic communication. It is a
type of CoP in which there is a social space where
individuals working on similar problems help each
other and share perspectives about their practice.
However, in a NoP, people working within
occupations or having similar interests engage in
knowledge exchange about the problems and issues
that are common to their occupational community
and shared practice.
In turn, NoP can be classified into:
• Self-organizing NoP: a loosely organized and
informal network that has no central
management authority or sponsor, whose
membership is voluntary, and where there is
little explicit commitment
• and “Formal” NoP: those which have a
membership that is controlled by fees and/or
acceptance through some central coordination
authority, usually based on a FW structure
(Programme, Project, etc) that also assists in
organizing, facilitating and supporting member
communications, events, and discussion topics.
However, a NoP has a focus on specific work
issues and strategies of immediate importance to the
membership, and it may in fact become an adjunct to
an affinity network. An example of an affinity
network is purchasing managers, members of an
association who may form NoP where they
communicate on a regular basis on strategies,
practices, opportunities, and innovations. Therefore,
the frame of a CoP or, even, a NoP can give rise to a
A CASE STUDY OF COMMUNITIES OF PRACTICE AND ICT TOOLS IN KNOWLEDGE MANAGEMENT ON
INTERNATIONAL COOPERATION IN SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY RESEARCH
417

FW when an structure, means, and deliverables are
foreseen. On the other hand, a FW can assist to
support the evolution of existing CoP, which, in
some specific cases, evolve towards Formal
Electronic NoP. A real-world example of how that
can be done is presented in the next section.
3 THE EU-MED-IWRM COP
There exists a general perception that water
management models in the Mediterranean Countries
are still constructed from points of view that ignore
contributions from all the key stake-holders
(specially users and citizens), who are determinant
for the impact on the territory of water schemes and
the satisfaction of the water demand, specially from
the sustainability point of view and taking into
account the social, economic, environmental and
institutional dimensions. In this section, the process
and methodology that allow moving from FW
initiatives to Electronic NoP is illustrated with a
specific case study, namely the EU-MED-IWRM
CoP.
3.1 The MELIA Coordination Action
Project
Research in this topic (i.e. DOMAIN) is of common
interest of the EU and its MPC in view of the
economic integration of both sides of the
Mediterranean area, the risks associated to the
climatic change and the increase in frequency of
water risks events (such as droughts or floods).
Another general perception in the Mediterranean
area is the lack of visibility of the important role that
Science and Technology play in the sustainable
development of the region. Part of these problems
are due to communication gaps between political
and administrative institutions, scientists, cultural
workers, lawyers, economists, end-users and
citizens, who, following the theoretical framework
provided in the last section, make up the EU-MED-
IWRM COMMUNITY. Within this COMMUNITY,
there exist many individuals who have been actively
involved in past and ongoing initiatives, mainly in
form of Projects supported by the European
Commission through different Framework
Programmes or other Cooperation instruments:
WASAMED, FOGGARA, WADAMED, MED-
REUNET, SED-Net DESURVEY, WADI, MELIA,
SEMIDE-EMWIS, EU-MEDA-WATER, MED-
EUWI, EU-MEDSTAT-ENV, REMOC-INBO, etc,
and whose targeted objectives should be
disseminated by using appropriate instruments,
language and contents based on the DOMAIN
dealing with IWRM in the Mediterranean Area.
The MELIA (Mediterranean Dialogue on
Integrated Water Management) Coordination Action
(CA), was officially launched in September 2006 as
a strategic EU Commission funded FP6-INCO-MPC
project. Its aim is to establish an open dialogue
between experts from both sides of the
Mediterranean and among the key stakeholders
concerned and affected by water use and
management, that is, to strength the interactions,
PRACTICE, between the EU-MED-IWRM
COMMUNITY.
Some of the main goals of the MELIA
Coordination Action are:
• Building a knowledge base for IWRM planning,
based on integrating contributions from
different perspectives, involving the wide
spectrum of stakeholders and based on the EU
Water Framework Directive.
• Develop a Mediterranean-wide awareness of the
social (cultural and participatory), economic and
technological issues related to water
management.
• Propose participatory mechanisms and
prevention tools to avoid competition in
resources allocation between regions states and
different waters users.
• Provide legislative and administrative bodies
with criteria and arguments agreed in a
consensual way by a wide representation of
social, economic, scientific and political actors
from different countries, to support sustainable
water policies and economy.
• Provide the intellectual basis and the indicators
to perform a benchmarking exercise of
Integrated Water resources management in the
Mediterranean area.
• Contribute to the construction of a common
frame and knowledge, and to the development
of a common terminology and semantic and
help water negotiations.
On the other hand, the opening of MELIA to
interested people by the dissemination of the results
obtained, will be the most relevant and appreciable
output, namely: extending the CoP within the EU-
MED-IWRM COMMUNITY. This purpose needs a
wide communication strategy, addressed to all those
stakeholders involved in water use who set up the
EU-MED-IWRM CoP, in rising awareness at the
educational level, in research, administration and,
specially, policy making.
WEBIST 2008 - International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies
418
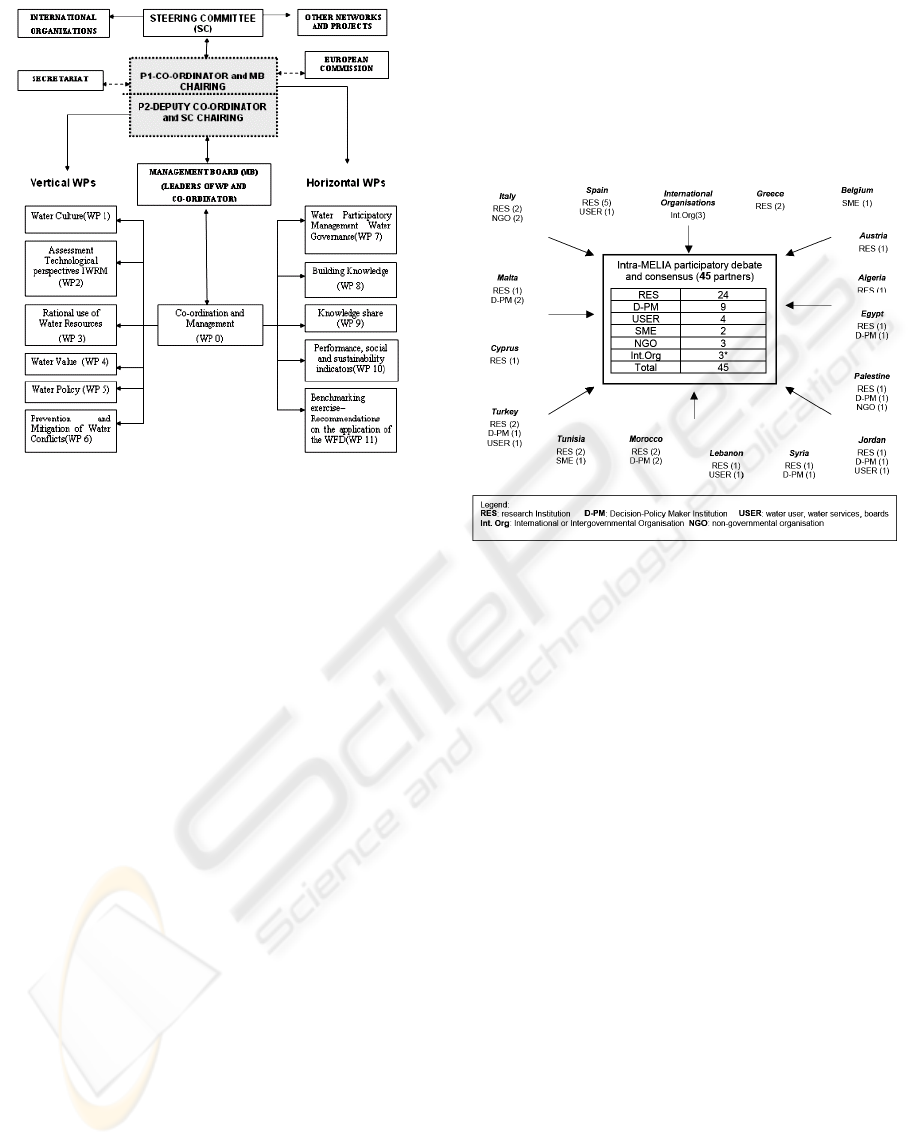
Figure 1: MELIA CA Governance structure and WP.
Initially, a scheme based on Vertical and
Horizontal Work Packages (WP) (see Figure 1) was
proposed to tackle the complex DOMAIN and its
relationship with the MELIA CA Governance. An
important question for internationally distributed
CoP is the degree of centralization or
decentralization. Who has responsibility, and how
much? Should there be a secretariat? Should there be
regional sub networks? There is no blueprint for the
ideal network structure and the governance
structures. Nevertheless, some core elements can be
found in every network. At the top of many CA are
some well-reputed chairpersons, who have a
strategic role. A steering committee and a
management board occupy a more active role, being
responsible for strategic questions and operational
planning. An initial MELIA Consortium (CORE
GROUP) (see Figure 2) was set up with 45 partners
representing 16 countries from both the EU (Italy,
Spain, Cyprus, Greece, Belgium, Malta, Austria) and
the MPC (Turkey, Morocco, Algeria, Tunisia,
Egypt, Syria, Lebanon, Jordan, Palestine) and
belonging to different categories.
The wide range of categories involved in
MELIA and the governmental and
intergovernmental status of some partners will help
to obtain concrete results and will be effective
advising those responsible about problems related to
water management in the territory. The
interdisciplinary of the MELIA CoP COMMUNITY
also led to many critical reflections and kept the
discussions lively. Moreover, the general Public
should participate in these debates in order to avoid
lack of concern or, worse, the loss of opportunities
to reach a sustainable management of water with the
complicity and participation of ALL users, including
the common citizens. Raising awareness of the
competing demands of water, and the conflicts
related to this issue is one of the targets of MELIA.
Figure 2: MELIA CA CORE GROUP.
This reasoning fits the LPP model described
above, where MELIA CA assists newcomers to join
and learn into the Mediterranean IWRM CoP. In any
case, a basic prerequisite for a successful CoP is
common interest among its Members. People will
only share knowledge if they think that all parties
will obtain benefits. Trust in the partners is a basic
value, and has to be maintained again and again
through intensive communication and shared
experiences (Ahuja et al, 2003; Ardichvili et al,
2003;Govindarajan and Gupta, 2001).
3.2 The MELIA Knowledge
Management Strategy
Based on the existing feedback between the defined
Work Packages, it is necessary to define a KM
Methodology. Managing information within
networks, produces a continuous organizational
process in which knowledge is generated, adapted
and shared, and transferred to water sector target
groups and partners. Information management
allows MELIA CA to explicitly enable and enhance
the productivity of these activities and to leverage
their value for the group as well as for individual
members. This KM Methodology foreseen into the
MELIA CA will assist specific knowledge functions
and link them with institutions or individuals outside
the network, thus expanding the CoP. The cycle of
A CASE STUDY OF COMMUNITIES OF PRACTICE AND ICT TOOLS IN KNOWLEDGE MANAGEMENT ON
INTERNATIONAL COOPERATION IN SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY RESEARCH
419

information management and knowledge creation
will be organized in a way that the following cycle
of functions is ensured: (1) Establishment of the
information base; (2) Adaptation of information and
sharing within the network; (3) Transfer of the
information to target groups (water users, managers,
IWRM implementers); (4) Generation – or better –
consolidation of common knowledge (local and
global levels).
The essential outcomes of information
management, knowledge generation and transfer,
will be to provide innovative strategies for relevant
stakeholders, such as the Directors of Water and the
Ministries of EU and
MED Countries, and, on the other hand, to raise
public participation and awareness. Their level of
impact is in direct relation with their level of activity
and operation.
4 MELIA CA ICT PLATFORM
Figure 3 shows the visible face of the MELIA CA
Platform, which consists of a Groupware web-based
portal (http://www.meliaproject.eu). This type of
user interface can be considered as a common, well-
understood and friendly paradigm. Its Extranet
platform is based on “hybrid-mixed” schemes
between LAMP (Linux+Apache+MySQL+PHP) and
Plone/Zope architectures, where specific PHP and
Python programming language scripts were designed
and implemented, providing a series of tools:
• synchronous tools (web conferencing, chats,…)
• asynchronous tools (fora, external editors, both
very useful in the scientific context for the
exchange of common ideas and publications
collaborations, etc.)
Given the large amount of actors involved (45
partners in the MELIA CA case), using just the
traditional mechanisms of interaction, mainly based
on the exchange of emails, would be inefficient and
practically unmanageable. One of the main
distinctive features is the Virtual Teams design,
which aims at a symbiosis of physical and virtual
work environments. There exists a simple premise:
one Work Group per WP and one Virtual Team per
Work Group. In order to get a feeling of the working
of the Platform, Figure 4 shows the internal folders
structure of one of the WP, namely WP0:
Coordination and Management.
4.1 Platform Members’ Role scheme
Each WP follows the following Role-oriented
scheme.
• General Public: They are not registered into the
system and they have only Read permission to the
contents that have been published (“Public
content state”).
Figure 3: MELIA CA web Platform.
WEBIST 2008 - International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies
420

Figure 4: Folder structure of WP0: Coordination and Management.
• Intranet Members: Members who are registered
into the system. They have a login and password
to access into the Intranet. There are two types:
• WP members: At least, an Intranet
member belongs to one WP. WP
members have at their disposal interactive
tools to add new contents: files, folders,
links, HTML web-pages; etc. they can
work collaboratively on these contents
(using external editors,…) and interact
among them (Fora and P2P tools).
• WP Leaders and Deputy Leaders: They are WP
members who assume the role of activity
coordinators within the WP. They are
“Reviewers” of the KM products generated into
their WP, and they decide if they can be
published or not. They have the responsibility of
giving visibility of the contents to the General
Public, allowing them to be indexed by the
search engines in Internet, etc…
• Manager: This is a role only reserved to the
MELIA Coordinator and the Webmaster.
4.2 Contents Workflow and Members’
Role Scheme
The Role-oriented scheme used is complemented
with a Contents Workflow, with its corresponding
states and transitions. This Workflow assists the
users to upload, submit for reviewing and, if
approved by the WP Leaders/Deputy Leaders
(acting as KM WP Managers), publish new contents.
In a first phase, an initial Knowledge Base
Taxonomy was implemented, structured through:
• One Thematic Area Library corresponding to each
Thematic WP
• One Library for each MPC.
• One Library for each EU-MS
In order to compile a single final EU-MED
Knowledge Base on IWRM, semantic-oriented
mechanisms are necessary for using the Platform. In
this sense, some OWL Web Ontology Language
instances have been designed. They are mainly
based on the key terms of reference suggested by the
IWRM experts within each WP. Presently they are
running as Beta prototypes.
All these features are complemented by the
users’ personal areas, where users can configure
their profiles, shared activities, consult their tasks
and deliverables “smart” calendar, etc.
5 CONCLUSIONS
This paper presents MELIA CA as a FW initiative
created within and aiming to assist the Euro-
Mediterranean IWRM CoP, to uncouple its work
environment from physical locations. MELIA Work
groups offer team members intuitive and ubiquitous
access to each other, and to information and
resources of their Virtual Work Teams and their own
tools. It is observed in some cases an evolution
towards a Virtual Electronic NoP model.
A CASE STUDY OF COMMUNITIES OF PRACTICE AND ICT TOOLS IN KNOWLEDGE MANAGEMENT ON
INTERNATIONAL COOPERATION IN SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY RESEARCH
421

Despite these technological developments,
‘human factors’ should not be neglected in an
increasing virtual environment. Useful as they are,
ICTs cannot fully replace face-to-face contacts and
more conventional means of communication
(telephone). Many people are yet unfamiliar with
these new developments. In fact, it has taken around
one year to expand the use of the MELIA CA
Platform to acceptable levels. Additionally, the costs
associated to the displacements (travels and
accommodations) justify the creation of this type of
supporting Coordination Action structures which,
assisted by Tele-work and Collaboration tools based
on these Virtual Teams schemes, provide essential
instruments to the sustainability of these Euro-
Mediterranean RDI social networks.
The ongoing success and the experience
acquired during the course of the MELIA CA
Project has led to the application of the same
adapted ICT tools in the MIRA “Mediterranean
Innovation and Research” CA Project
(http://www.miraproject.eu). Necessary research and
continuous innovation on the new technological
trends (i.e., research on the Web 2.0 requirements,
essentially focused on the semantic web
mechanisms, (OWL)) as well as their development
is guaranteed during the next years in order to
nurture these types of social networks.
REFERENCES
Ahuja, M.K., Galetta, D.F., Carley, K.M. (2003).
Individual centrality and performance in virtual R&D
groups: An empirical study. Management Science, 49(1)
21-38.
Ardichvili, A., Page, V., Wentling, T. (2003). Motivation
and barriers to participation in virtual knowledge-
sharing communities of practice. Journal of
Knowledge Management, 7 (1) 64-77.
Bouty, I. (2000). Interpersonal and interaction influences
on informal resource exchanges between R&D
researchers across organizational boundaries.
Academy of Management Journal, 43 (1) 50-66.
Brown, J.S., Duguid, P. 2000 Organizational learning and
community-of-practice: toward a unified view of
working, learning and innovation. In: Cross, R.;
Israelit, S. Strategic learning in a knowledge economy.
Woburn: Butterworth-Heinemann.
Crane, D. (1972). Invisible colleges. Diffusion of
knowledge in scientific communities. Chicago;
London: The University of Chicago Press.
Govindarajan, V., Gupta, A.K. (2001). Building an
effective global business team. MIT Sloan
Management Review, (Summer), 63-71.
Lave, J., Wenger, E., 1991. Situated learning Legitimate
peripheral participation Cambridge University Press
Liebeskind, J.P., Oliver, A.L., Zucker, L., Brewer, M.
(1996). Social networks, learning and flexibility:
Sourcing scientific knowledge in new biotechnology
firms. Organization Science, 7 (4), 429-443.
Powell, W.W. (1990). Neither market nor hierarchy:
Network forms of organization. In B.M. Staw &L.L.
Cummings (Eds.), Research in organizational
behaviour (vol.12, pp.295-336). Greenwich, CT: JAI Press.
Rodríguez-Clemente R., González-Aranda J.M. (2007),
Euro-Mediterranean Scientific Cooperation: Facts,
Obstacles and Solutions Using ICTs. Practical Cases.
MED 2007. IEMed, Barcelona, Spain.
Teigland, R. (2003). Knowledge networking: Structure
and performance in networks of practice. Published
Doctoral Dissertation, Stockholm School of
Economics, Sweden.
Wenger, E., McDermott, R., Snyder, W., 2002.
Cultivating Communities of Practice: A Guide to
Managing Knowledge, Harvard Business School
Press, 2002.
Yan, J., Assimakopoulos, D. (2003). Knowledgesharing
and advice seeking in a software engineering
community. In L. M. Camarinha-Matos & H. A.
Afsarmanesh (Eds.), Processes and foundations for
virtual organizations (pp. 341-350). Dordrecht:
Kluwer Academic.
Links to Other cited Resources (last access October 2007):
ASBIMED Project “Assessment of the bilateral scientific
co-operation between the EU-MS, Accession
Countries, Candidate Countries and the MPC”.
Funded by the European Union 6th Framework
Programme FP6-INCO-CT-2004-510659. http://
www.asbimed.net
Barcelona Declaration and Euro-Mediterranean Partnership
(1995)
http://europa.eu/scadplus/leg/en/lvb/r15001.htm
EUMEDIS Project (http://www.eumedis.net)
European Research Area (ERA) http://
ec.europa.eu/research/era/index_en.html
EU Directorate General on RTD [DG-RTD],
http://ec.europa.eu/dgs/research/index_en.html
EU International Policy on Science and Technology (RTD-
INCO), http://ec.europa.eu/research/iscp/index_en.cfm
EU Water Initiative. International Cooperation (INCO):
From Knowledge to Action “Water for Life”
http://ec.europa.eu/research/water-initiative/index_en.html
MED 7 Project “Thematic Workshops for the definition of
the Science and Technology Euro-Mediterranean
Policy within FP7”. Funded by the European Union
6th Framework Programme FP6-2002-INCO-
COMultilatRTD/SSA-5 http://www.asbimed.net/MED7/
home.htm
MELIA Coordination Action Project official website
http://www.meliaproject.eu
MIRA Coordination Action Project official website
http://www.miraproject.eu
OWL Web Ontology Language W3C Recommendation
(Overview)
http://www.w3.org/tr/owl-features/
Php programming language (http://www.php.net/)
Plone CMS (http://plone.org/)
Python programming language (http://python.org)
Zope CMS (http://www.zope.org)
WEBIST 2008 - International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies
422
