
A BROADCASTING ALGORITHM USING ADJUSTABLE
TRANSMISSION RANGES IN MOBILE AD HOC NETWORKS
Toshihiko Sasama, Yasuhiro Abe
Department of Information and Knowledge Engineering, Tottori Univercity, Koyama town, Tottori prefecture, Japan
Hiroshi Masuyama
Department of Information and Knowledge Engineering, Tottori Univercity, Koyama town, Tottori prefecture, Japan
Keywords: Mobile ad hoc networks, virtual backbone, protocol, broadcast, 2-level clustering approach, 1-level flat
approach, 2-level clustering mesh approach, 1-level flat mesh approach, energy consumption.
Abstract: Reducing energy consumption is one of the major subjects in designing a good broadcasting algorithm for
mobile ad hoc networks. This paper discussed 2 approaches to communication algorithms; 2-level clustering
mesh approach and 1-level flat mesh approach, and proposes one of them which makes it appear that the
total amount of expended energy becomes lesser. (Wu and Dai, 2004) previously proposed 2 approaches; 2-
level clustering approach and 1-level flat approach. In mobile ad hoc networks mobile hosts move
frequently, and these moves may cause a change in communicating relationships. In designing a minimum
energy routing protocol for these mobile ad hoc networks with this inherent property, the use of a virtual
backbone has become popular. This study (Wu and Dai, 2004) is based on the virtual backbone conception.
Our 2 proposed approaches change the clustering performed in (Wu and Dai, 2004) into mesh so that energy
consumption becomes smaller. The efficiency of the 1 level flat mesh approach is confirmed through our
simulation study.
1 INTRODUCTION
Mobile ad hoc networks (simply MANET) consist of
wireless mobile hosts that communicate without the
need of any fixed infrastructure. Broadcasting is a
process in which the same massage is delivered to
every node. An overhead in MANET comes from
this broadcasting or blind flooding which is a
process to determine a necessary route in ordinary
one-to-one routing protocols in MANET.
Broadcasting or flooding may generate excessive
redundant message derivation. This redundant
message derivation causes not only a broadcast
storm problem (Tseng, Ni, Chen and Sheu, 2002)
but also serious redundant energy consumption. An
efficient broadcasting route is a conventional Steiner
tree which leads to NP-hard. Although MANET has
no physical backbone infrastructure, a virtual
backbone can be formed by nodes in a connected
dominating set (CDS) of unit-disk graph (Wu and
Dai, 2004) of a given MANET. More concisely, a
virtual backbone is an exclusive communication
path framed among imaginary partitioned groups.
The concept of this virtual backbone is powerful for
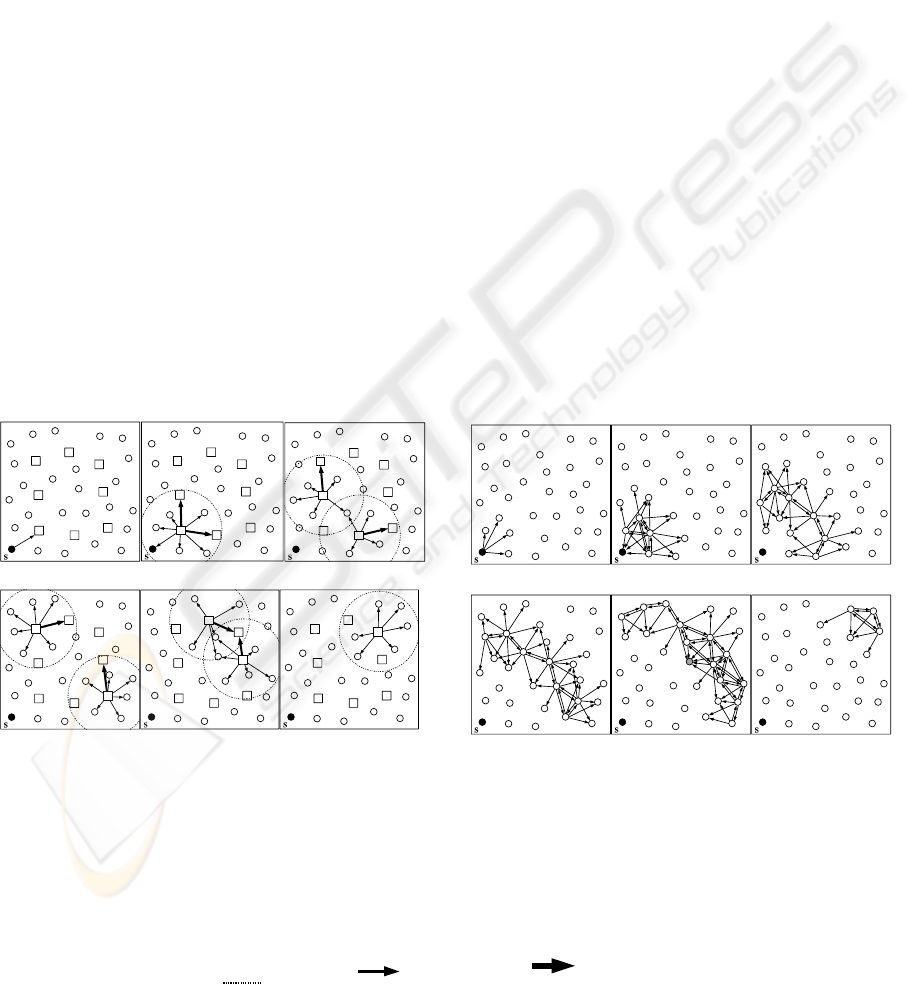
saving communication energy. Fig.1 (a) and (b)
shows the two broadcast processes; one using the
concept of a virtual backbone and the other without,
respectively. By way of the arrows depicted in the 6
frames of each graph, all necessary one-to-one
communications necessary to perform a broadcast
from source node s is described. Fig.1 shows that the
broadcasting process using the concept of a virtual
backbone requires fewer arrows, this means less
energy consumption.
Virtual Multicast Backbone (VMB) structures
are commonly used in current multicast protocols.
Instead of the conventional Steiner tree model, the
optimal shared VMB in ad hoc networks is modeled
as a Minimum Steiner Dominating Set in Unit-Disk
Graphs (Ya-feng, 2004) which leads also to NP-
hard.
Energy-efficient broadcasting has been widely
studied. Several protocols have been proposed to
123
Sasama T., Abe Y. and Masuyama H. (2008).
A BROADCASTING ALGORITHM USING ADJUSTABLE TRANSMISSION RANGES IN MOBILE AD HOC NETWORKS.
In Proceedings of the Fourth International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies, pages 123-128
DOI: 10.5220/0001521201230128
Copyright
c
SciTePress
manage energy consumption by adjusting
transmission ranges. For a comprehensive survey on
various aspects of broadcasting in MANET, refer to
(Stojmenovic and Wu, 2004). In this paper, we use
the static and source-independent approach for CDS
construction since it is more genetic. It is also
assumed that no location information is provided, as
was similarly mentioned in (Wu and Dai, 2004).
The remainder of this paper is organized as
follows: In Section 2, we introduce some
preliminary knowledge required to understand 2 new
protocols. The 2 level clustering mesh approach and
1 level flat mesh approach are introduced in Section
3. Section 4 shows our simulation experiences and
results. Finally, we will conclude in Section 5.
2 PRELIMINARIES
Instead of a physical backbone infrastructure,
MANET can form a CDS, as mentioned before. (Wu
and Li, 1999) proposed the “marking process” which
is a self-pruning process to construct a CDS: Each
node is marked if it has two unconnected neighbors,
otherwise it is unmarked. The marked nodes form a
CDS, which can be further reduced by applying
pruning rules (Dai and Wu, 2003).
Step.[1] Step.[2] Step.[3]
Step.[4] Step.[5] Step.[6]
Step[1] : A source node uploads.
Step[2] : The □ node transfers the data to every node and other
□ nodes in a range.
Step[3] – [6] : Similarly, the □ node transfers the data.
Figure 1(a): A broadcast process using the concept of
virtual backbone.
Pruning rule k: A marked node can unmark itself if
its neighbor set is covered by a set of connected
nodes with higher priorities.
The clustering approach is commonly used to
offer scalability and is efficient in a dense network.
Basically, the network is partitioned into a set of
clusters, with one cluster-head in each cluster.
Cluster-heads form a DS which is a subset of
nodes in the network where every node is either in
the subset or a neighbor of a node in the subset. No
two cluster-heads are connected. Each cluster-head
connects to all its members (non-cluster-heads) in
most k hops, which originates from the k-level
clustering approach. The classical clustering cluster
formation works are stated in (Wu and Dai, 2004):
(1) A node v is a cluster-head if it has the highest
priority in its 1-hop neighborhood including v. (2) A
cluster-head and its neighbors form a cluster and
these nodes are covered. (3) Repeat (1) and (2) on
all uncovered nodes.
Two new approaches to construct a backbone
will be proposed and discussed in this paper. These
approaches originate from two approaches; 2-level
clustering and 1-level flat approaches. In the lower
level of 2-level clustering, the network is covered by
the set of cluster-heads under a short transmission
Step.[1] Step.[2] Step.[3]
Step.[4] Step.[5] Step.[6]
Step[1] : A source node transfer the data to every node in a range.
Step[2] : Receiving nodes transfer the data to every node in a
range.
Step[3] – [6] : Similarly, receiving nodes transfer the data.
Figure 1(b): A broadcast process using none of the
concepts of a virtual backbone.
(● :Source node, ○:Node, □:The node which communicates between the groups,
Circle in broken line[
]:Group, :Data transfer, :Data transfer between groups)
WEBIST 2008 - International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies
124

range. In the upper level, all cluster-heads are
covered by the set of marked cluster-heads under a
long transmission range. Conversely, the 1-level flat
approach constructs a flat backbone, where the
network is directly covered by the set of marked
cluster-heads having a long transmission range.
2.1 2-level Clustering Approach
As mentioned above, this approach uses different
transmission ranges at different levels to connect not
only non-cluster-heads and cluster-heads but also to
connect cluster-heads where gateway nodes are
required to make selections.
Marking process on cluster-heads and marked
cluster-heads:
1. Select a node with the highest priority among
nodes which belong to none of the cluster
heads and let it be a cluster-head. Every
node in the cluster-head’s range of (1/3)r
belongs to the cluster-head.
2. Continue process 1 until every node is a
cluster-head or belongs to any one of the
existent cluster-heads.
3. Select a cluster-head which has the most
cluster-heads laid in its range of r and at
least one of them does not lay in every other
cluster-head. Let this be the first marked
cluster-head.
4. Select a cluster-head which has the most
cluster-heads laid in its range of r and lays
itself within the range of any other marked
cluster-heads of r.
5. Continue process 4 until all such cluster-
heads are gone.
Broadcast process:
1. A source node uploads its own data to the
cluster-head.
2. The cluster transfers the data to a marked
cluster-head located within the range of r.
3. The marked cluster-head transfers the data to
every cluster-head and marked cluster-head
within the range of r.
4. Receiving marked cluster-heads change into
transferors for the data if the data is new.
Conversely, receiving cluster-heads
automatically broadcast data within their
own range.
5. The process 4 terminates when every node
receives data sent by the source.
Figure 2 (a) shows a broadcasting process based on
this approach.
2.2 1-level Flat Approach
Though the two marking processes for cluster-heads
and marked cluster-heads are the same as in the
above approach, using a uniform transmission range
can prevent redundant energy consumption.
Marking process on cluster-heads and marked
cluster-heads:
1. Select a node with the highest priority among
nodes which belongs to no cluster head and
let it be a cluster-head. Every node in the
cluster-head’s range of (1/4)r belongs to the
cluster-head.
2. Continue process 1 until every node is a
cluster-head or belongs to any other cluster-
head.
3. Select a cluster-head which has the most
cluster-heads laid within its range of r and at
least one of them does not lay in every other
cluster-head. Let it be the first marked cluster-
head.
4. Select a cluster-head which has the most
cluster-heads laid within its range of r and
one which lays itself within the range of r of
any other marked cluster-heads.
5. Continue process 4 until such a cluster-heads
are gone.
Broadcast process:
1. A source node uploads its own data directly
to the marked cluster-head.
2. The marked cluster-head broadcasts the data
to every node (other marked cluster-heads,
cluster-heads, and nodes) located within its
range of r.
3. The process 4 terminates when every node
receives data sent by the source.
Fig.2(b) shows a broadcasting process based on this
approach.
3 2-LEVEL CLUSTERING MESH
APPROACH AND 1-LEVEL
FLAT MESH APPROACH
A mesh-clustering protocol is introduced to the
above two approaches. A given domain is divided by
N×N lattices. In the following marking process, let
R=r1 in the 2-level mesh approach and let R=r2 in
the 1-level mesh approach where r1 and r2 are
shown in Fig.3.
A BROADCASTING ALGORITHM USING ADJUSTABLE TRANSMISSION RANGES IN MOBILE AD HOC
NETWORKS
125
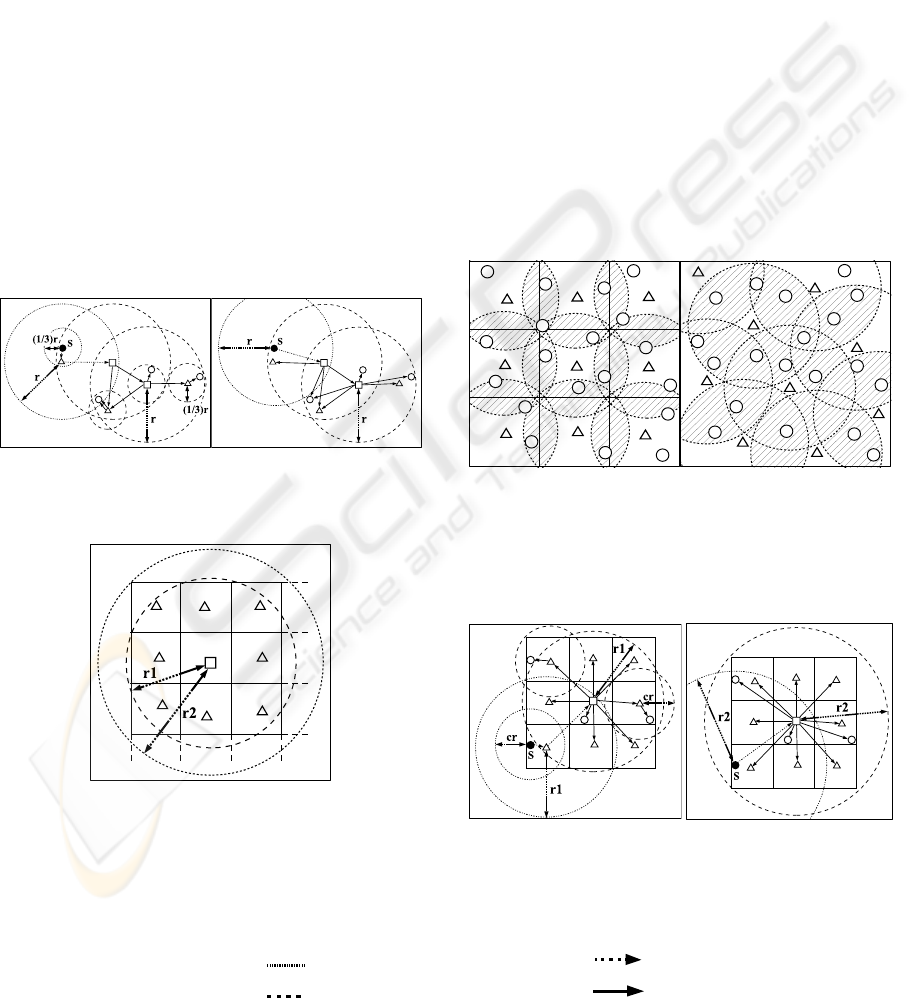
Marking process on cluster-heads and marked
cluster-heads:
1. Select the most central node in each lattice
and let it be the cluster-head in the lattice
and let randomly distributed nodes in the
lattice be subordinate nodes of the cluster-
head in the lattice.
2. Select a cluster-head which has the most
cluster-heads laid in its range of r and at
least one of them does not lay in every other
cluster-head. Let it be the first marked
cluster-head.
3. Select a cluster-head which has the most
cluster-heads laid within its range of r and
lays itself within the range r of any other
marked cluster-heads.
4. Continue process 3 until such cluster-heads
are gone.
Fig.4 (a) shows marked cluster-heads and cluster-
heads nominated based on this process and for
reference, and Fig.4 (b) shows them based on the
previous 2-level clustering approach.
(a)2-level clustering approach (b)1-level flat approach
Figure 2: Examples of broadcast processes based on two
approaches.
Figure 3: Two ranges in 2-level clustering and 1-level flat
mesh approaches.
Broadcast process: 2-level and 1-level mesh
approaches adopt the same broadcast
processes as those of the 2-level clustering
approach and the 1-level flat approach,
respectively.
Fig.5 (a) and (b) show a broadcasting process based
on these approaches.
4 SIMULATION EXPERIENCES
AND RESULTS
We adopt a commonly encountered model of a
network where n homogeneous nodes are randomly
thrown in a given region S, both uniformly and
independently. If more than two neighbors of a
node transmit simultaneously, the node is assumed
to receive no message. The neighbors of a node are
not permanent within a number of slots, because of
unstable network topology.
(a) 2-level clustering mesh (b) 2-level clustering
approach approach
Figure 4: Marked and non-marked cluster-heads
nominated based on two approaches.
(Shaded part is a duplication of clusters)
(a) 2-level clustering (b) 1-level flat
mesh approach mesh approach
Figure 5(a)(b): Examples of broadcast process based on
two new approaches.
( ●:Source node, ○:Node, △:cluster-head, □:marked cluster-head,
Circled by broken line[
]:Transmission range for upload, :Data upload,
Circled by dotted line [ ]:Transmission range for broadcast, :Data broadcast )
WEBIST 2008 - International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies
126
4.1 Simulation Experience
This section describes the input parameters and
output measures for the evaluation of the volume of
energy consumption in 4 kinds of clustering. For the
purpose of our simulation, we consider a 100×100
square domain where 1000 nodes are randomly
distributed. In mesh approaches, we set the square
domain divided by1×1(=N×N), 2×2, …, 9×9, and 10
×10. We evaluate the volume of energy consumption
for the broadcasting in transmitting range r as r
2
(Wieselthier and Nguyan and Ephremides, 2000).
We used the same value of r (=24m) as shown by
(Wu and Dai, 2004). We also performed
experimentation in the case where N is fixed as 3 but
the total number of nodes are 100,200, …,1000.
4.2 Results
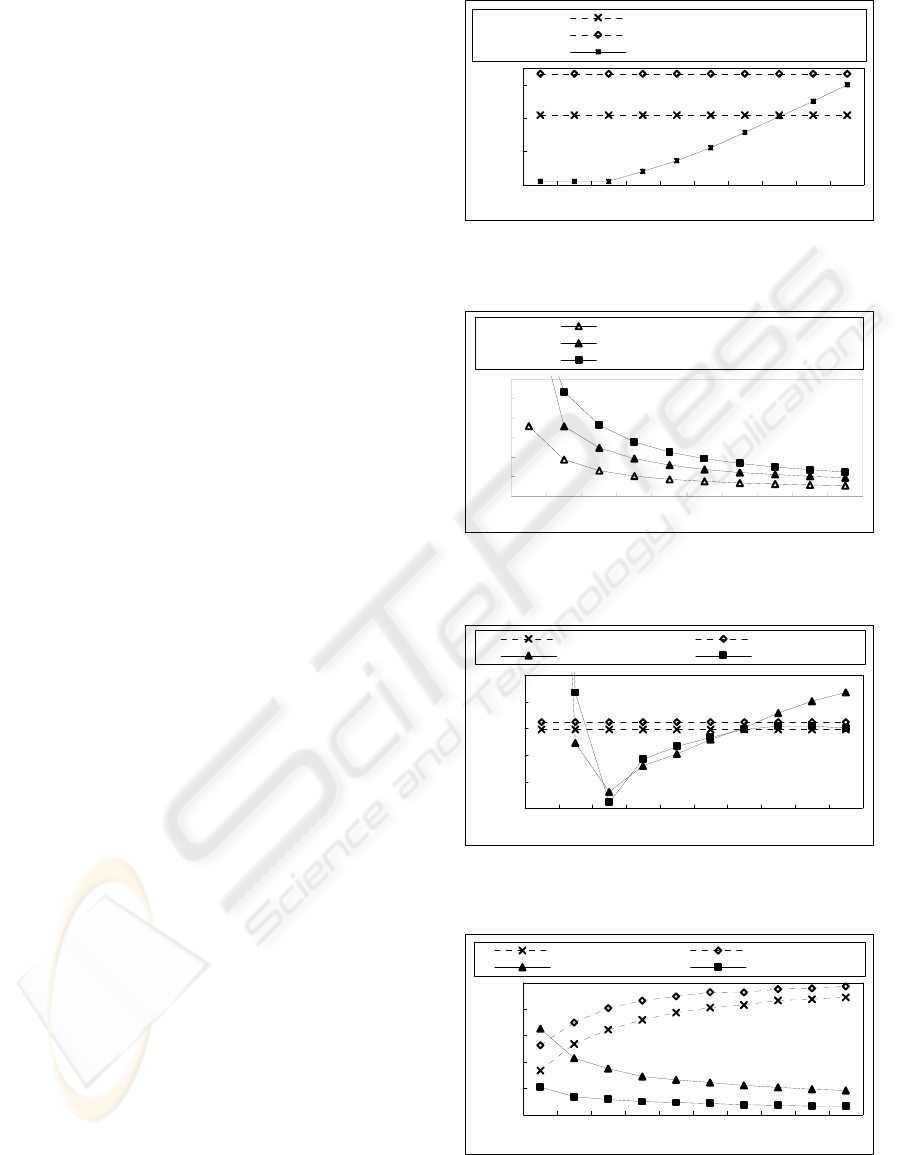
Fig.6 shows the number of marked cluster-heads for
different numbers of divisions. Fig.7 shows the
ranges of each cluster-head and marked cluster head
for different numbers of divisions. Figs.8 and 9
show the energy consumption for different numbers
of divisions and for different numbers of distributed
nodes, respectively. These results mean that 1-level
mesh approach provides excellent results, especially
when 3×3.
4.3 Improved Methods and the
Simulation Results
The above results show that the efficiency of 1-level
flat mesh approach can be confirmed. However, both
this approach and the 2-level clustering mesh
approach require an extremely large amount of
energy in special nodes (marked cluster-heads),
making this a problem. This problem is more
evident when the divided square domains become
smaller. We further evaluated the volume of energy
consumptions required in the case where two ranges
in 2-level clustering and 1-level flat mesh
approaches are restricted in the smaller sizes as
shown in Fig.10. These restrictions make the number
of marked cluster-heads larger but the load of each
marked cluster-head smaller. Figs.11 (a), (b) and (c)
show the energy consumption for different numbers
of divisions in the cases of 100, 500, and 1000
nodes, respectively. These results show that the
improved 1-level flat mesh approach proves to be
superior when the number of divisions becomes
larger.
0
10
20
30
12345678910
Number of divisions
Number of
marked clust er- heads
2- level clust ering
1- level flat
2- level mesh, 1-level mesh
Figure 6: Number of marked cluster-heads for different
number of divisions.
0
20
40
60
80
100
120
12345678910
Number of divisions
Transmission ranges
clust er- head (2- level mesh)
marked clust er- head (2- level mesh)
marked clust er- head
(
1- level mesh
)
Figure 7: Ranges of each cluster-head and marked cluster
head for different numbers of divisions.
10000
13000
16000
19000
22000
25000
12345678910
Number of divisions
Energy consumption
2- level clust ering 1- level flat
2- level mesh 1- level mesh
Figure 8: Energy consumption for different numbers of
divisions.
10000
12000
14000
16000
18000
20000
100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900 1000
Number of nodes
Energy consumption
2- level clust ering 1- level flat
2- level mesh
[
3× 3
]
1- level mesh
[
3× 3
]
Figure 9: Energy consumption for different numbers of
distributed nodes.
A BROADCASTING ALGORITHM USING ADJUSTABLE TRANSMISSION RANGES IN MOBILE AD HOC
NETWORKS
127
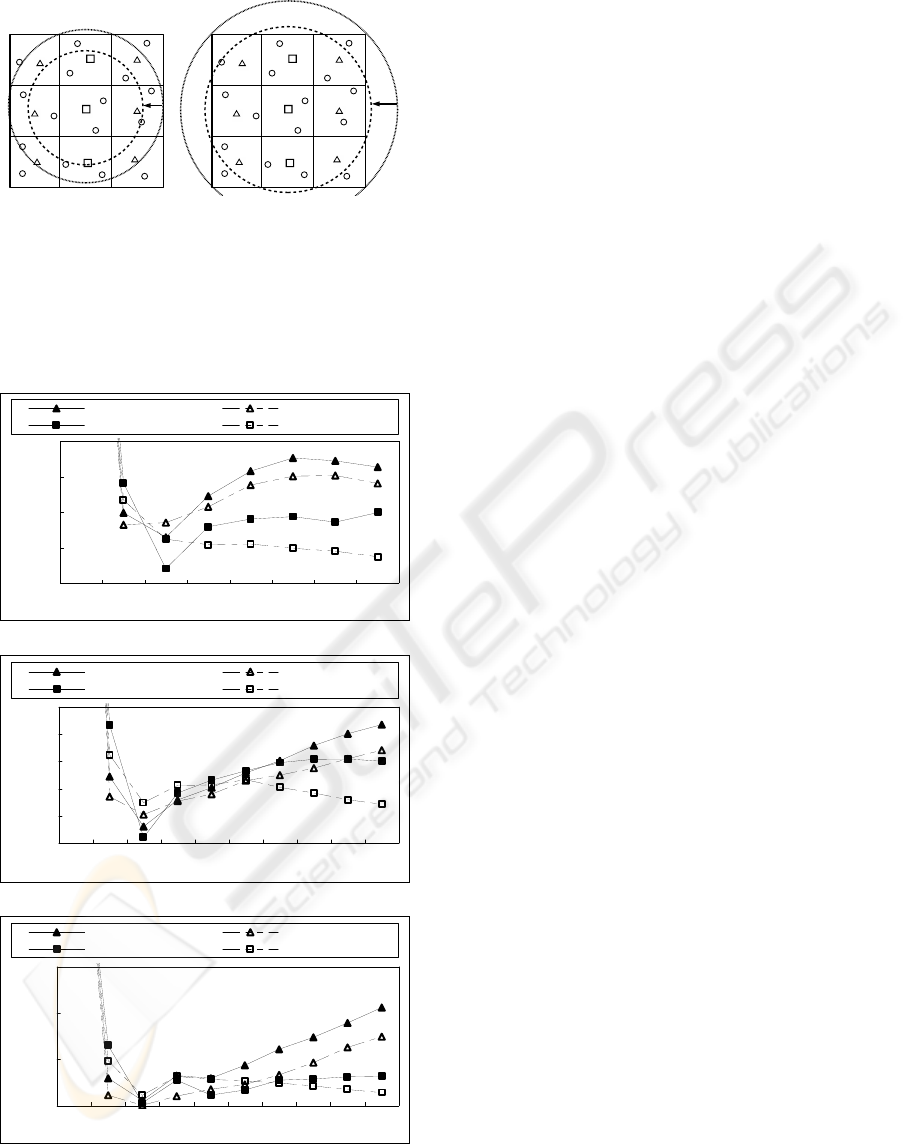
(a)2-level clustering (b)1-level flat mesh
mesh approach approach
Figure 10: Restricted range in (a) 2-level clustering mesh
and (b) 1-level flat mesh approaches.
(● :Source node, ○:Node, △:cluster-head,
□:marked cluster-head)
10000
15000
20000
25000
30000
12345678
Number of divisions
Energy consumption
2- level mesh(8近傍) 2- level mesh(4近傍)
1- level mesh
(
8近傍
)
1- level mesh
(
4近傍
)
(a)The case of 100 nodes.
10000
13000
16000
19000
22000
25000
12345678910
Number of divisions
Energy consumption
2- level mesh(8近傍) 2- level mesh(4近傍)
1- level mesh(8近傍) 1- level mesh(4近傍)
(b)The case of 500 nodes.
10000
20000
30000
40000
12345678910
Number of divisions
Energy consumption
2- level mesh(8近傍) 2- level mesh(4近傍)
1- level mesh
(
8近傍
)
1- level mesh
(
4近傍
)
(c)The case of 1000 nodes.
Figure 11: Energy consumption for different numbers of
divisions in the cases of (a)100, (b) 500 and (c) 1000
distributed nodes.
5 CONCLUSIONS
Reducing energy consumption is one of the major
objectives in designing a good broadcasting
algorithm for mobile ad hoc networks. This paper
discussed 2 approaches to communication
algorithms; 2-level clustering mesh approach and 1-
level flat mesh approach, and proposes one of them
which makes it appear as though the total amount of
expended energy becomes lesser. Our 2 proposed
approaches not only use the concept of a virtual
backbone but also adopt mesh in clustering so that
energy consumption becomes less. The efficiency of
1-level flat mesh approach is confirmed through our
simulation study.
REFERENCES
Jie Wu and Fei Dai, “A Distributed Formation of a Virtual
Backbone in MANETs using Adjustable Transmission
Ranges,” Proceedings of ICDS’04, pp.372-379, 2004.
Y.C.Tseng, S.Y.Ni,Y.S.Chen, and J.P.Sheu, “The broad-
cast storm problem in a mobile as hoc network,”
Wireless Networks, Vol.8, No.2-3, pp.153-167, Mar.-
May 2002.
WU Ya-feng et al., “On the Construction of Virtual
Multicast Backbone for Wireless Ad Hoc Networks,”
Proceedings of pp.294-303,
I. Stojmenovic and J. Wu, "Broadcasting and Activity -
Scheduling in Ad Hoc Networks," to be published in
Ad Hoc Networking, S. Basagni et al., eds., IEEE
Press, 2004.
J.Wu and H.Li, “On calculating connected dominating set
for efficient routing in ad hoc wireless networks,”
Proceeding of DialM, pp.7-14, 1999.
F.Dai and J.Wu, “Distributed dominant pruning in ad hoc
wireless networks,” Proceeding of IEEE ICC, vol.1,
pp.353-357, May 2003.
J.E.Wieselthier and G.D.Nguyan and A.Ephremides, ”On
the Construction of Energy-Efficient Broadcast and
Multicast Tree in Wireless Networks,” Proc. of IEEE
INFOCOM 2000, pp.585-594.
W.Ya-feng, X. Yin-long, C.Guo-liang, and W.Kun, “On
the Construction of Virtual of Virtual Multicast
Backbone for Wireless Ad Hoc Networks,”
Black, U., Mobile and Wireless Network, Prentice-Hall,
1996.
Perkins, C. E. Ad Hoc Networking. Addison-Wesley,
2001.
Basagni, S. Distributed Clustering for Ad Hoc Networks.
In Proc. Inter. Symp. Par. Architectures, Algorithms
and Networks (ISPAN), 1999.
Santi, P. and Blough D.M., “The Critical Transmitting
Range for Connectivity in Sparse Wireless Ad Hoc
Networks,” IEEE Trans. on Mobile Computing, No.2,
pp.1-15, 2003.
WEBIST 2008 - International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies
128
