
EVALUATION OF K-/LATTICE-CLUSTERING ALGORITHMS FOR
RANDOM WIRELESS MULTI-HOP NETWORKS
Toshihiko Sasama, Ryo Monde and Hiroshi Masuyama
Department of Information and Knowledge Engineering, Tottori University, Koyama town, Tottori prefecture, Japan
Keywords:
Ad hoc networks, Broadcast, Clustering, Energy consumption, Protocol, Simulation, Wireless.
Abstract:
A k-clustering protocol is an algorithm in which the wireless network is divided into non-overlapping sub
networks, referred to as clusters, and where every node of a sub network is at most k hops from a distinguished
station called the cluster-head. A lattice-clustering protocol is an algorithm in which a given area is divided by
lattices and randomly distributed hosts in a lattice are one hop from the cluster-head. In this paper, we evaluated
the energy eficiencies for the broadcasts designed in both k-clustering and lattice-clustering protocols. The
evaluation showed that the k-clustering protocol is characterized by the smallest broadcasting power of each
node, and a lattice-clustering protocol constitutes a characteristic feature of the most minimal total energy
consumption. The main source of greater energy consumption in k-clustering protocol is a large number of
transmissions between adjacent node pairs.
1 INTRODUCTION
Ad hoc networks consist of wireless hosts that com-
municate without the need of any fixed infrastructure.
These Ad hoc networks are well suited to specific
and often extreme situations, such as disaster-relief,
law-enforcement, and fire-detection where each host
works as a sensor node, or simply for collaborative
computation in some short-term public events. A k-
clustering protocol is an algorithm in which the wire-
less network is divided into non-overlapping sub net-
works, referred to as clusters, and where every node
of a sub network is at most k hops from a distin-
guished station called the cluster-head. A lattice-
clustering protocol is an algorithm in which a given
area is divided by lattices and randomly distributed
hosts in a lattice are one hop from the cluster-head.
Clustering is commonly used in ad hoc networks in
order to limit the amounts of both energy consumed
for communication and information stored for rout-
ing at individual nodes. The clustering approach is
used to offer scalability and is efficient in a dense net-
work. Several clustering algorithms have been pro-
posed for each different advantage. The basic idea of
(Wu and Dai, 2004) is to reduce the network density
through clustering using a short transmission range.
Then neighboring cluster heads which are 2 or 3 hops
away are connected using a long transmission range,
that is, without using any gateway selection process.
K-clustering, one of the main clustering protocol, re-
quires no special broadcasting power by heads, thus,
a surface can be clustered by nodes with a uniform
power. This advantage means that each node re-
quires and consumes a lesser amount of energy than
that of the 2-level clustering and the 1-level flat ap-
proach. Since, in broadcasting, all nodes are em-
ployed in receiving a message, it is important to dis-
cuss total energy consumption. We assume the sit-
uation that a node broadcasts to all other randomly
distributed (n-1) nodes which can use synchronous ra-
dio transmissions in each of their transmitting ranges.
In this situation, we evaluate the energy efficiencies
for the broadcasts designed in both k-clustering and
lattice-clustering. The remainder of this paper is or-
ganized as follows: In Section 2, we introduced the k-
clustering algorithm. The lattice-clustering algorithm
is introduced in Section 3. Section 4 shows our sim-
ulation experiences and results. Finally, our conclu-
sions are expressed in Section 5.
236
Sasama T., Monde R. and Masuyama H. (2008).
EVALUATION OF K-/LATTICE-CLUSTERING ALGORITHMS FOR RANDOM WIRELESS MULTI-HOP NETWORKS.
In Proceedings of the Fourth International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies, pages 236-239
DOI: 10.5220/0001521302360239
Copyright
c
SciTePress

2 K-CLUSTERING ALGORITM
2.1 Algorithm
A k-clustering protocol is an algorithm in which ev-
ery node locates at most k hops from its belonging
cluster-head. Each node knows its own position and
its ID (or IP address), but it is assumed that each node
has no topological information. The transmission ra-
dius of every node is set to the same. Then, for a given
number n of nodes deploying randomly and uniformly
on a surface of size s, there exist the optical values of
both this transmission radius r and the clustering value
k which lead to the condition where everynode knows
cluster in which its belongs and every gate way knows
the list of its adjacent clusters. Gate way is a node
whose communication range contains nodes belong-
ing to other clusters. This study has been performed
by (Ravelomanana, 2005), he gave the theorem that,
for any fixed constant l , there exists a constant C(l)
such that if r is set to
r =
p
(1+ l)|S|logn
πn
(1)
every node may have received all the identities of
each of its neighbors. In this paper, we use the above
r when l is 0, and the same k as in (Ravelomanana,
2005).k=an integer log(log n) discarded under the
decimal point.
[Algorithm]
1. Find a node with the smallest ID. Label a cluster
head to the node.
2. Let every node, located at most k hops from the
newest cluster head but not yet a member of other
clusters, be a member belonging to the newest
cluster head. Remove IDs from the cluster head
and the member nodes.
3. Repeat processes 1 and 2 until every node belongs
to a cluster.
4. Label a gateway to the node if a node belonging to
another cluster locates in the transmission radius
of the node.
An example of k=2: Fig. 1 shows an example of 2-
clustering where node ci (i=1-7) mean cluster heads.
2.2 Broadcasting in K-clustering
The procedure of broadcasting is as follows:
1. A source node broadcasts its information in its
transmitting range.
2. Each node which received the information broad-
casts it in the transmitting range.
Figure 1: A K=2 clustering where 2 dotted lines ... and
... mean 1 hop and 2 hops regions from each cluster head,
respectively.
Figure 2: An example of broadcasting in 2-clustering.
3. A cluster head which has received a source node’s
information broadcasts it to every one of its mem-
bers at most 2 steps.
4. A source node (gate way) which received the
information from a node (gate way) located in the
adjacent cluster broadcasts the information within
its transmitting range just like a source node in its
cluster.
Fig. 2 shows an example of broadcasting in 2-
clustering.
3 LATTICE-CLUSTERING
ALGORITHM
3.1 Algorithm
A lattice-clustering protocol is an algorithm in which
a given domain is divided by NN lattices as shown in
Fig.3 and randomly distributed hosts in a lattice are
one hop from the cluster-head. This lattice-clustering
protocol is divided into 2 kinds: one is where the
transmitting range of each cluster-head reaches all
8 adjacent cluster-heads and the other includes only
4 of the closest cluster-heads. They are labeled as
Lattice (8) and Lattice (4) in the following section.
[Algorithm]
1. Find the closest node to the center of each lattice-
cluster.
2. Label a cluster head to the node.
EVALUATION OF K-/LATTICE-CLUSTERING ALGORITHMS FOR RANDOM WIRELESS MULTI-HOP
NETWORKS
237
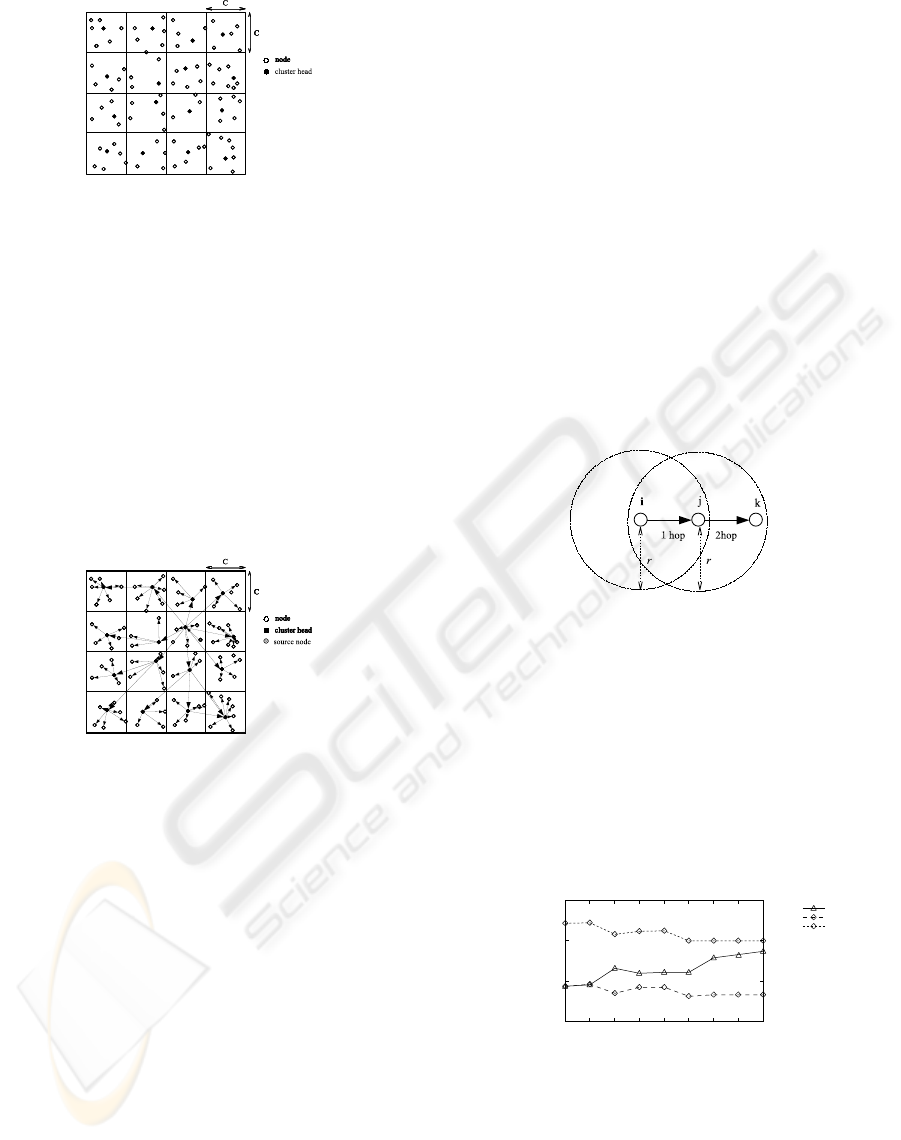
Figure 3: A lattice-clustering of 4 X 4.
3.2 Broadcasting in Lattice-clustering
The procedure of broadcasting is as follows:
1. A source node broadcasts its information in its
transmitting range.
2. A cluster head which received source node’s
information from the adjacent cluster head broad-
casts it to every one of its members in its own
lattice-cluster.
Fig. 4 shows an example of broadcasting in a 4 X 4
lattice-clustering.
Figure 4: Example of broadcasting in a 4 X 4 lattice-
clustering.
4 SIMULATION EXPERIENCES
AND RESULTS
We adopt a commonly encountered model of a net-
work where n homogeneous nodes are randomly
thrown in a given region S, uniformly and indepen-
dently, (Wieselthier, 2000). As is customary, the time
is assumed to be slotted and in each time slot every
node can act either as a transmitter or as a receiver,
but not both. In any given time slot, if and only if a
node acting as a receiver gets a message, exactly one
of its neighbors precisely transmits within the same
round. If more than two neighbors of a node trans-
mit simultaneously, the node is assumed to receive no
message. The neighbors of a node are not permanent
within a number of slots, because of unstable network
topology.
4.1 Simulation Experience
This section describes the input parameters and output
measures for the evaluation of the volume of energy
consumption in 2 kinds of clustering. For simula-
tion purposes, we consider a 100x100 square domain
where 100, 200,
...
, 800 and 900 nodes are randomly
distributed. In k-clustering, we set the values of clus-
tering k and the transmitting range as the values given
in (Ravelomanana, 2005) as mentioned in Section 1.
In lattice-clustering, we set a domain divided by 3x3,
4x4 ,
...
, 15x15, and 16x16. We evaluate the volume of
energy consumption for the broadcasting in transmit-
ting range r as r2 (Wieselthier, 2000). Therefore, the
broadcasting power Pik required from i to k as shown
in (2) and Fig. 5.
Pik = Pij + Pjk = r
2
+ r
2
= 2r
2
(2)
Figure 5: Broadcasting power required from i to k via j.
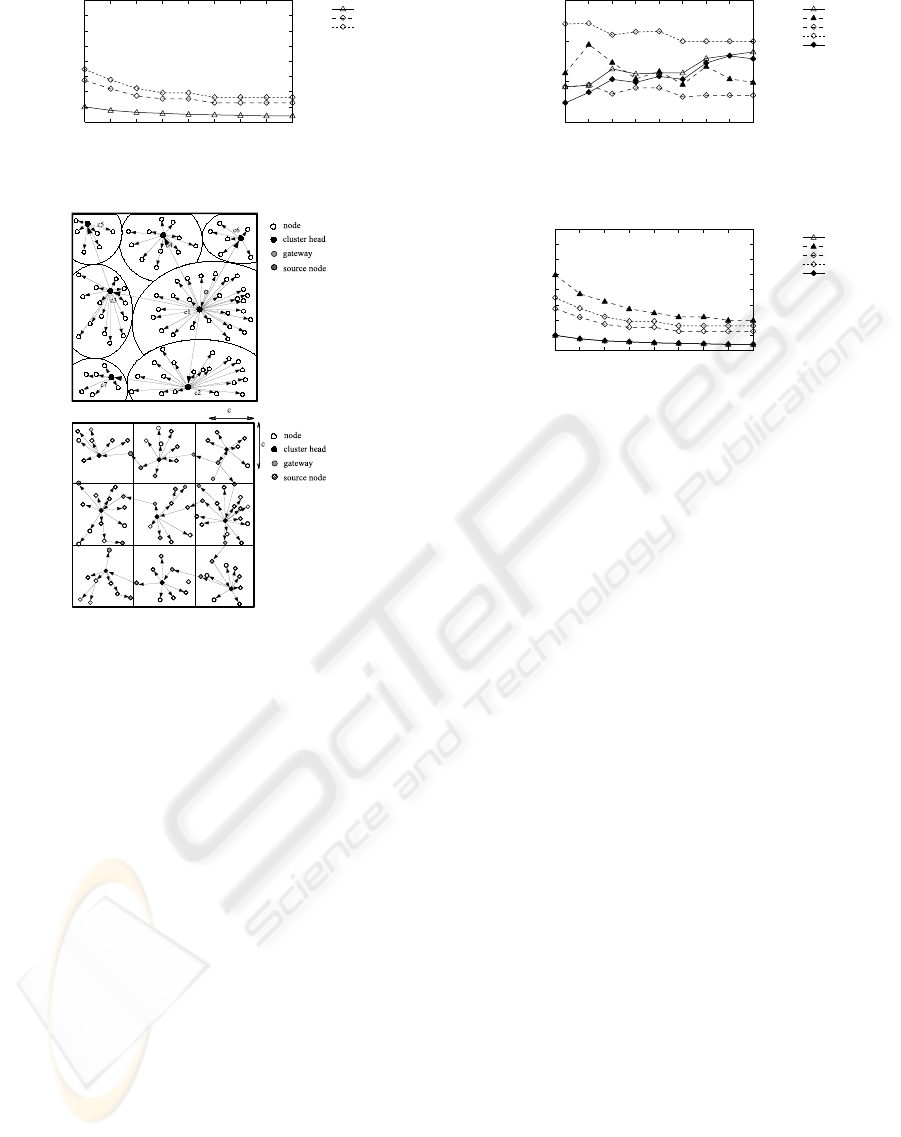
4.2 Results 1
Fig. 6 depicts the volumes of energy consumptions
required in a broadcast for the total number of nodes.
Fig. 7 depicts the broadcasting power required in each
cluster head for the number of nodes. As shown in
Fig. 6, Lattice (4) is best among three clustering algo-
rithms. Fig. 7 shows that k(=2)-clustering saves the
broadcasting power to cluster heads the most.
30000
50000
70000
90000
100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900
Energy counsumption
Number of node
k
mesh(4)
mesh(8)
Figure 6: Volumes of energy consumption required in a
broadcast.
4.3 Results 2
Further investigation in the following cases can be
considered: The k-clustering protocol adopts the di-
rect communication between adjacent cluster heads
WEBIST 2008 - International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies
238
0
20
40
60
80
100
120
140
160
100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900
Power of clusterhead
Number of node
k
mesh(4)
mesh(8)
Figure 7: Broadcasting power required in each cluster head.
Figure 8: Examples of broadcasting in new K-and lattice-
clustering.
(New k-clustering protocol). The lattice-clustering
protocol adopts mediate communications between ad-
jacent cluster heads (New lattice-clustering protocol).
We briefly summarize the results in the case of these
new protocols. In the new lattice-clustering, a given
domain is divided by N X N lattices as is in the old
lattice-clustering protocol. In order to avoid an in-
crease in the number of gateways, the new proto-
col must take a certain measure, the details of which
are omitted in this paper due to space. The new k-
clustering protocol takes the same measure as in the
old k-clustering protocol. Fig. 8. shows examples of
broadcasting in new k- and lattice- clustering.
We evaluated the total energy consumption, the
average broadcasting powers of each head in Fig. 9
and 10, in 5 clustering protocols.
5 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper, we evaluated the energy efficiencies
for the broadcasts designed in both k-clustering and
lattice-clustering protocols. The evaluation showed
that the k-clustering protocol is characterized by the
30000
50000
70000
90000
100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900
Energy counsumption
Number of node
k
k(new)
mesh(4)
mesh(8)
mesh(new)
Figure 9: Comparison of the total energy consumption re-
quired in 5 clustering protocols.
0
20
40
60
80
100
120
140
160
100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900
Power of clusterhead
Number of node
k
k(new)
mesh(4)
mesh(8)
mesh(new)
Figure 10: Comparison of broadcasting power required in
each cluster head.
smallest broadcasting power of each node, and the
Lattice (4)-clustering protocol constitutes a charac-
teristic feature of the smallest total energy consump-
tion. The main source of the energy consumption in
k-clustering protocol is a large number of transmis-
sions between adjacent node pairs. Therefore, the ob-
tained results mean that, in the kind of communica-
tions such as those in broadcasting, direct communi-
cation between cluster heads should be also be taken
into the consideration. Further investigationshas been
performed for the new protocols: The k-clustering
protocol adopts direct communication between adja-
cent cluster heads, and the lattice-clustering proto-
col adopts mediate communications between adjacent
cluster heads.
REFERENCES
J. E. Wieselthier (2000). On the construction of energy-
eficient broadcast and multicast tree in wireless net-
works.. IEEE INFOCOM.
V. Ravelomanana (2005). Distributed k-clustering algo-
rithms for random wireless multihop networks. IEEE
ICN.
Wu, J. and Dai, F. (2004). A distributed formation of a vir-
tual backbone in manets using adjustable transmission
ranges. IEEE ICDS.
EVALUATION OF K-/LATTICE-CLUSTERING ALGORITHMS FOR RANDOM WIRELESS MULTI-HOP
NETWORKS
239
