
TRANSFORMING A COMPETENCY MODEL TO
ASSESSMENT ITEMS
Onjira Sitthisak, Lester Gilbert and Hugh C. Davis
Learning Technologies Group, School of Electronics and Computing Science
University of Southampton, Highfield, Southampton, SO17 1BJ, U.K.
Keywords: Competency, adaptive assessment, knowledge level.
Abstract: The problem of comparing and matching different learners’ knowledge arises when assessment systems use
a one-dimensional numerical value to represent “knowledge level”. Such assessment systems may measure
inconsistently because they estimate this level differently and inadequately. The multi-dimensional
competency model called COMpetence-Based learner knowledge for personalized Assessment (COMBA) is
being developed to represent a learner’s knowledge in a multi-dimensional vector space. The heart of this
model is to treat knowledge, not as possession, but as a contextualized space of capability either actual or
potential. The paper discusses the automatic generation of an assessment from the COMBA competency
model as a “guide-on-the–side”.
1 INTRODUCTION
In recent years, a variety of tools and learning
environments have been created and installed in
schools, universities, and organisations to support
learning. Mostly these tools have been created to
support e-learning content and collaborative learning
activities like a virtual classroom (Koper and Specht,
2007). However, e-learning suggests not only new
technologies for instruction but also new
pedagogical approaches to enhance learning. One
new pedagogical approach is machine-processable
competency modelling. A competence model is
introduced for storing, organizing and sharing
learners’ performance data in order to seek and
interpret evidence for where the learners are in their
learning, where they want to go, and how they can
get there. Pedagogically effective and informed
competency data is vital in any assessment system.
One of the desired outcomes of an assessment
system is information about the learners’ knowledge,
identifying what learners can do by representing
their current state of knowledge (Shepard, 2000).
This information is collected and updated during the
assessment process. Most assessment systems
assume that knowledge is something that a learner
possesses or fails to possess, and seek to estimate a
learner’s “knowledge level”. As a result, such
assessment systems may measure “knowledge level”
inconsistently because they estimate this level
differently, and inadequately because they use one-
dimensional numerical values (Sitthisak et al.,
2007). The proposed solution is to consider the
learners’ “learned capability” instead of their
“knowledge level”, and to consider competencies
and learned capabilities as a multidimensional space.
In the context of an adaptive assessment system,
an assessment is part of the process of diagnosing
the learner’s competence. The key idea of an
adaptive assessment system is that questions are
selected by the computer to individually match the
learner’s competence (Way, 2005). The system’s
evaluation of the learner’s competence is then used
to guide the adaptation of the system (Aroyo et al.,
2006). The system may skip over what learners have
learned and find out what they should learn further.
While an adaptive system may be more efficient for
summative assessment, a system of adaptive
formative assessment is likely to be of greater
advantage to learners, since they would receive
relevant, personalized feedback. Establishing
adaptive formative assessment systems to support
lifelong learning is extremely challenging and relies
on introducing a competency model to the adaptive
assessment. Our intention is not to promote a
particular technological platform, but to demonstrate
333
Sitthisak O., Gilbert L. and C. Davis H. (2008).
TRANSFORMING A COMPETENCY MODEL TO ASSESSMENT ITEMS.
In Proceedings of the Fourth International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies, pages 333-338
DOI: 10.5220/0001524303330338
Copyright
c
SciTePress
how a competency model can be applied to adaptive
assessment.
In this paper, we introduce an advanced
competency model named COMpetence-Based
learner knowledge for personalized Assessment
(COMBA). The COMBA model is represented in a
multi-dimensional vector space, and we explore the
assembly of competencies into a tree structure. We
then consider the key task of adaptively generating
assessments from such a competencies structure.
2 THE MULTI-DIMENSIONAL
COMBA MODEL
Competence-based approaches in the field of e-
learning, institutional admissions, learners seeking
courses, e-portfolios, job references, human resource
management, and job descriptions are becoming
more common. They appear to offer the opportunity
to develop tools and services for data exchange,
discovery, processing, analysis, and visualization to
meet needs of learners, tutors, program managers,
examination bodies, professional societies,
employers, legislators, and so on. We suggest that a
complete and coherent model of competencies
would support storing, organizing and sharing of
achieved, current, and intended performance data
relating to all aspects of education and training in a
persistent and standard way (Sitthisak et al., 2007).
We have been developing a competency model,
named COMBA, which is proposed for all domains
where learning and teaching take place.
In the first stage of developing the model
(Sitthisak et al., 2007), we conceptualised
“competency” as involving a capability associated
with a given subject matter content, requiring a
proficiency level, and associated with evidence, any
required tools, and a definition of the situation which
contextualizes the competency. In the second stage
of developing the model (Sitthisak et al., 2007), we
implemented an exemplar UK Royal College of
Nursing competency (UK Royal College of Nursing,
2005) reflecting relevant features of a learner’s
behaviour and knowledge that affected their learning
and performance. An outcome of this
implementation exposed a critical issue involving
the expression of ethical practice in the COMBA
model. One of the conceptions of competence for a
nursing graduate is competence in ethical practice
(Ramritu and Barnard, 2001) as well as the other
characteristics of professional service delivery
involving knowledge and psychomotor skill
(Defloor et al., 2006). Hence, attitude, the way in
which a learner exhibits their knowledge and skill, is
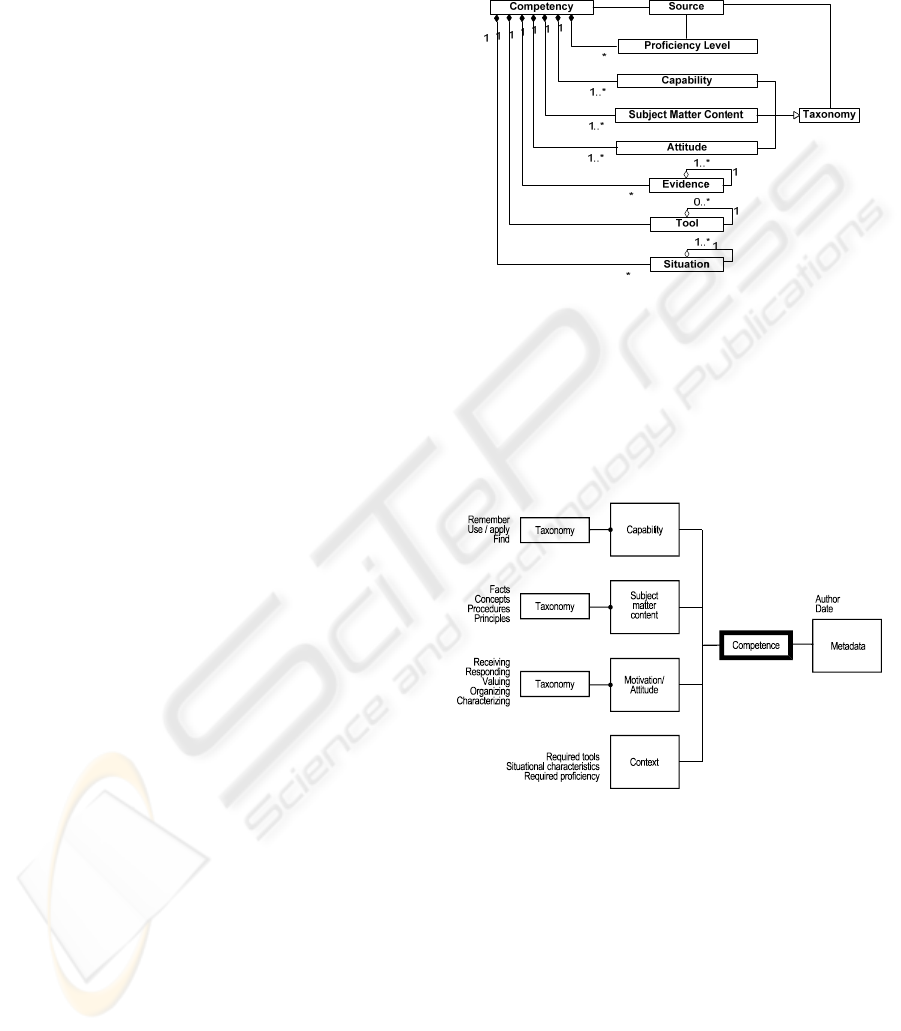
included in the COMBA model, as illustrated in
Figure 1.
Figure 1: Competency model including attitude
component.
The COMBA model considers knowledge in the
widest possible sense, and involves the following
four major components: subject matter, capability,
attitude, and context, along with metadata as
illustrated in Figure 2.
Figure 2: Individual competence model.
The challenge of capturing and using knowledge
starts with the problem of understanding its nature
and representation. The failure of previous efforts to
‘intelligently process knowledge’ (e.g. intelligent
tutoring systems) may be due to their pedagogically
and cognitively inadequate characterization of this
knowledge, and their simplistic assumptions that
knowledge is some thing a learner possesses or fails
to possess.
The heart of the COMBA model is to treat
knowledge, not as possession, but as a
contextualized multidimensional space of capability
either actual or potential. Accordingly, the three
WEBIST 2008 - International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies
334
important components of the COMBA model
(capability, subject matter content, and attitude),
which are referred from relevant taxonomies or
ontologies, may be represented in a vector space as
in Figure 3. The learned capability is the learner’s
required or observed behaviour, for example using
Bloom’s taxonomy (Bloom and Krathwohl, 1956).
The subject matter content in Figure 3 is based on
Merrill’s analysis (Merrill, 1983), and attitude is
based on a version of Krathwohl’s taxonomy
(Krathwohl and Anderson, 2002).
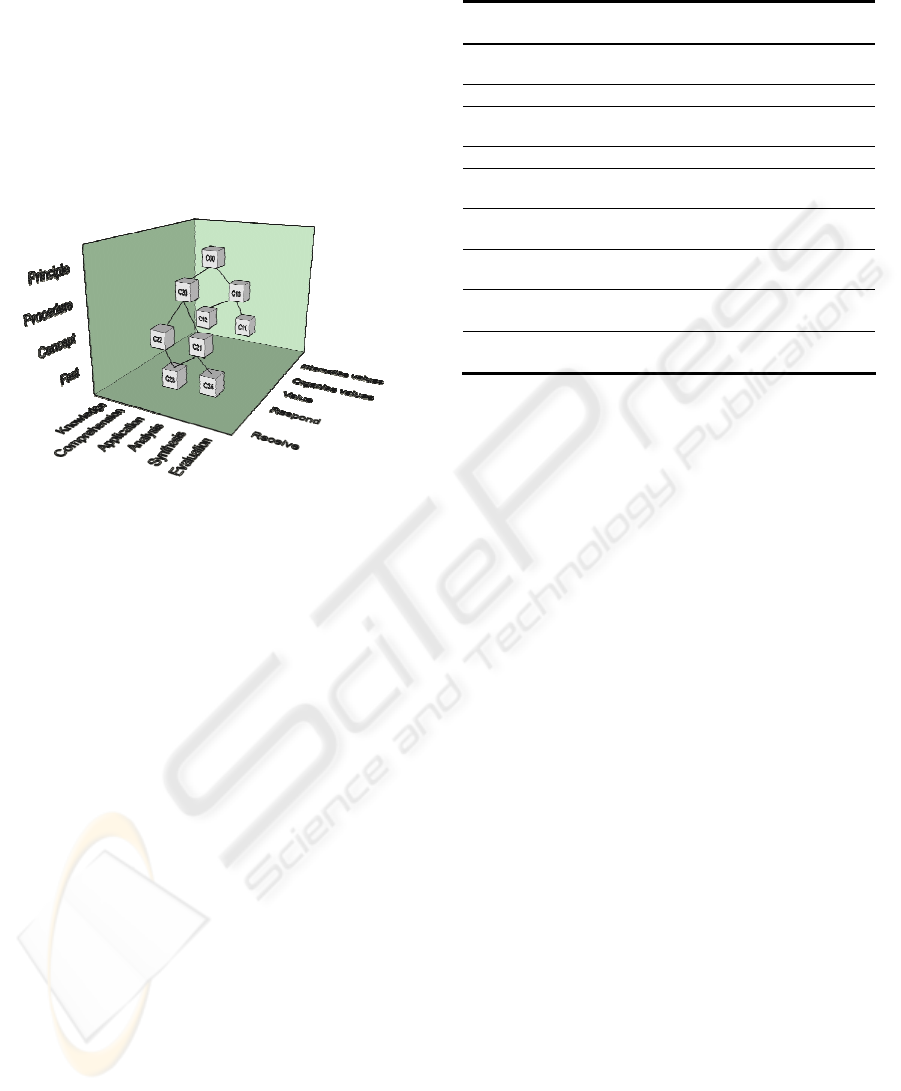
Figure 3: Multidimensional space of competency model.
In this paper, we choose competencies from health
care because they are amongst the most
sophisticated and challenging to implement
(Kunzmann, 2006). Table 1 represents some nursing
competencies based on the multidimensional space
of the COMBA model. For example, C00 (students
are able to use and value ethical principles)
comprises C10 (students are able to actively apply
ethical principles) and C20 (students are able to
actively use professional regulation). In order to
achieve C10, students should be able to demonstrate
client confidentiality respectfully (C11), and to
identify ethical issues sensitively (C12). In order to
achieve C20, students should be able to identify the
limitations in their own practice (C22), and to
considerately evaluate professional regulation (C21).
There is a common competency for C21 and C22
which is C23 (students are able to recognize the
need for referral willingly). In order to achieve C21,
students should be able to recall relevant
professional regulations willingly (C24). This shows
that we can map effectively these more complicated
competencies into the COMBA model. The subject
matter, capability taxonomy, attitude taxonomy, and
competence were ontologically represented based on
the Simple Knowledge Organisation System
(SKOS).
Table 1: Some example nursing competencies represented
in the competency model.
Competency
No.
Capability Subject Matter Attitude
C00 Use Ethical
principles
Values
C10 Apply Ethical issues Actively
C11 Demonstrate Client
confidentiality
Respectfully
C12 Identify Ethical Issues Sensitively
C20 Use Professional
regulation
Actively
C21 Evaluate Professional
regulation
Considerately
C22 Identify Limitation in
own practice
Values
C23 Recognize Need for
referral
Willingly
C24 Recall Professional
regulations
Willingly
3 THE COMPETENCY TREE
Competencies are assembled into trees. A tree
structure is a particular way of representing a
structure in a graphical form (Johnson and
Shneiderman, 1991). While the relationship between
nodes is modelled as a family relation such as parent
and child, there is no ordering of nodes on the same
level, and this yields a tree structure rather than a
hierarchy. It is assumed that all children of a defined
competency are required in order to achieve
proficiency for the parent. While the tree structure
defines a top-down or bottom-up structure, it does
not imply sequencing as might be implied in a
hierarchy. For example, a competency tree may
specify how to roll up the assessment for each
competency throughout a competency tree without
implying sequencing of assessments of same level
competencies. So the issue of pedagogical
sequencings are not considered at this stage by
representing competencies as a tree structure instead
of a hierarchy.
One of the advantages of a competence tree
structure is that a tree structure separates the
composition rule in the domain from other structural
components. Hence, an application of the
competency model, such as in adaptive assessment,
may add other rules, perhaps based on pedagogical
sequencing, in order to control the adaptation within
the competency tree.
More technically, the COMBA model specifies the
network of assembled competencies as a directed
acyclic graph. In competency terms, Figure 4
Subject Matter
Attitude
Capability
TRANSFORMING A COMPETENCY MODEL TO ASSESSMENT ITEMS
335

implies that competency C00 is decomposed into
sub-competencies C10 and C20, such that C10 and
C20 contribute to C00. A node may have more than
one parent, provided the parent is not a child of the
node. Figure 4 shows a “forest” of two competency
trees, where arrows represent parent-child
relationships. A competency tree may specify
common children for more than one node, or more
than one origin node. For example, C00 and A
represent different competencies that have certain
competencies in common such as C22.
It is expected that competency trees will be
different for different communities and users. For
example, a tree of nursing competencies from the
UK Royal College of Nursing would have many
points of difference from a similar tree from the
Canadian Nursing Association. At a personal level, a
student nurse may develop his or her own tree to
reflect their own competencies, both achieved and to
be attained.
Figure 4: Competency tree.
4 GENERATING ASSESSMENT
ITEMS FROM A COMPETENCY
TREE
Assessments may be categorized as formative,
summative, or diagnostic (McMillan, 2006).
Formative assessment provides prescriptive
feedback to assist learners in achieving their
competences (Rolfe and MaPherson, 1995). It is
intended to help the learner deal with deficiencies in
their understanding, knowledge, or competence. In
contrast, summative assessment is generally given at
the end of a period of learning to establish what
knowledge, skills, and/or attitudes the learner has
acquired over a period of time. It helps to establish
whether learners have attained the competences
required, and is not focussed on supporting learning.
Diagnostic assessment is an in-depth assessment
related to strengths and weaknesses in each skill
area, which identifies priorities and needs (Sewell,
2004). It helps to determine what learners can
already do within the goals of the curriculum. This
paper focuses on formative and diagnostic
assessment.
There are two problems of traditional formative
assessment. First, learners are likely to need
different kinds of formative assessment at different
stages in their ‘learning journeys’ (Brown, 2006).
Second, formative assessment usually only provides
a list of the learner’s deficiencies (Rolfe and
MaPherson, 1995) without clearly specifying their
boundaries. These problems are relieved by using an
assessment tree suggested in this paper.
4.1 Constructing an Assessment Item
We assume an assessment which takes place in the
context of the COMBA model. The competency tree
might be used to drill down into component
competencies for the tested competency, helping to
define what to test and how to test it. An assessment
for a competency often actually tests component
competencies. For example, a paediatric nurse
course (Nursing and Midwifery Council) may test
knowledge of professional regulation by testing the
learners’ ability to demonstrate and evaluate
understanding of professional regulation including
the demonstration of a variety of specific skills and
attitudes, as illustrated in Table 1.
A generic assessment item can be directly
formulated from a competence specification by
using the parameters of that competence: capability,
subject matter content, attitude and other contexts
such as tool and situation as the authoring question
templates in Table 2. For example, the assessment
corresponding to C11 might be something like
“What information must be kept confidential in
situation A?”, or “Identify the information which
doesn’t need to be kept confidential in situation B”,
as illustrated in Table 3.
A formative assessment may contain items to
test finer grained competencies. A competency tree
can be used as a guide to assemble the necessary set
of test items for assessing each competency. In this
process, the competency tree is transformed to an
assessment tree. An assessment tree consists of
question nodes from Table 3, where each question
node corresponds to a competency node, as
illustrated in Figure 5.
WEBIST 2008 - International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies
336

Table 2: Question templates.
No. Question Templates
a [Capability] + [Subject]
b [Capability] + [Subject] + [Situation]
c [Capability] + [Subject] + [Attitude]
d [Subject] + [Situation]
Table 3: Some example questions represented from the
competencies.
Compet-
ency
No.
Ques-
tion
No.
Question Temp-
late
No
C00 Q1 Identify the outcomes if
ethical principles were
not valued.
c
Q2 List ethical principles. a
Q3 What ethical principles
are involved [in situation
X]?
d
C10 Q4 Identify the possible
outcomes if ethical issues
were not actively applied.
c
Q5 How would you apply
ethical issues [in situation
Y]?
b
Q6 Define the specific
ethical issues [in situation
Z].
b
Figure 5: The group of questions based on a competency
tree.
Different organizations or communities of practice
may have different processes and policies for
assessment. By specifying a particular competency
tree or sub-tree to be assessed, it is possible to align
the assessment needed based on the needs of the
organization or community of practice. Hence, the
competency tree defines a standard way to specify
explicitly the component competencies to be
assessed, and provides a “guide on the side”,
automatically generating a set of general assessment
items.
4.2 Navigating Assessment Items on the
Competency Tree
There are a number of adaptive assessment methods
and technologies that can be used to assess learners’
strengths and weaknesses based on item-by-item
and learner responses (Brusilovsky, 2001). These
allow learners to be tested on materials at a level
appropriate to their current understanding. Adaptive
assessments change their behaviour and structure
depending on the learners’ responses and inferred
abilities.
There are two major adaptation techniques;
presentational adaptation and navigational
adaptation (Brusilovsky, 2001). An adaptive system
may apply these two techniques with questions.
Traversing the competency tree may start at the leaf
node or the root node depend on the objective of
each application. As a result, a competency tree may
be traversed, mapped, extended, visualized, and
searched by a variety of applications and tools. For
example, a competency tree may be used to specify
how to roll up the assessments for each competency
in order to personalize the assessment and match
assessment items to the individual competences of
each learner.
There is a set of possible assessment items
associated with each competence node, as illustrated
in Figure 5. Given a pruned competency tree (a tree
whose remaining branches and leaves represent
competencies not yet attained by a learner), an
adaptive assessment system now needs to sequence
the assessment items. Sequencing could be based
upon pedagogical considerations, and arranged
according to the taxonomies of subject matter
content (Merrill, 1983), of capability (Bloom and
Krathwohl, 1956), and so on. For example, an
adaptive assessment system may start with
assessment items at the lower level of the capability
taxonomy and progress to the higher levels, in order
to reach the boundary of the learner’s understanding.
On the other hand, sequencing could be based on the
learner’s preferences. Depending on the learner’s
answers, the next assessment item will be presented.
This involves regenerating the sequence based on
the learner’s unfolding competences. The result of
an adaptive assessment partitions the competency
tree into “what the student can do” and “what the
student is ready to learn” (Falmagne et al., 2003)
and finding the boundaries of competence for the
learner.
TRANSFORMING A COMPETENCY MODEL TO ASSESSMENT ITEMS
337

5 CONCLUSIONS
We have proposed the next generation of a
competency model named COMBA to support
adaptive assessment. The COMBA model includes
“attitude”, identified as a critical issue exposed by
working with nursing competencies, as well as
including subject matter domain knowledge, and
learned capabilities. The multi-dimensional
COMBA model represents competency in terms of a
tree structure. Generating assessment items from the
competency tree is illustrated. Then, an adaptive
assessment involves constructing an item sequence
which dynamically reconfigures as the learner’s
competency develops.
The benefits of a COMBA-enabled adaptive
system are to help learners identify and diagnose
their boundaries of their own competencies,
understand them, and find out how to progress by
comparing them with a given or ideal competency
tree. Adaptive assessment involves the dynamic
sequencing of assessment items derived from the
COMBA competency tree depending on the learner's
responses.
Learning is improved by allowing the learner to
become familiar with the variety of assessment items
that correspond to the variety of situations, tools,
capabilities and subject matter content, expressed in
a COMBA competence tree, of the domain of
interest. We believe that a COMBA competency
model is critical to successfully ensuring a
pedagogic focus on learner and learning activities.
REFERENCES
Aroyo, L., Dolog, P., Houben, G. J., Kravcik, M., Nilsson,
A. N. a. M. and Wild, F., 2006. Interoperability in
Personalized Adaptive Learning. Education
Technology and Society 9(2): 8-14.
Bloom, B. S. and Krathwohl, D. R., 1956. Taxonomy of
educational objectives: The classification of
educational goals by a committee of college and
university examiners. New York, Longman.
Brown, S., 2006. Using Formative Assessment to promote
student learning. from
http://www.ldu.leeds.ac.uk/news/events/documents/Br
ownPowerPoint.pdf.
Brusilovsky, P., 2001. Adaptive Educational hypermedia.
Defloor, T., Hecke, A. V., Verhaeghe, S., Gobert, M.,
Darras, E. and Grypdonck, M., 2006. The clinical
nursing competences and their complexity in Belgian
general hospitals. Journal of Advanced Nursing 56(6):
669-678.
Falmagne, J.-C., Cosyn, E., Doignon, J.-P. and Thiery, N.,
2003. The Assessment of Knowledge, in Theory and
in Practice. Integration of Knowledge Intensive Multi-
Agent Systems.
Johnson, B. and Shneiderman, B., 1991. Tree-Maps: a
space-filling approach to the visualization of
hierarchical information structures. Proceedings of the
2nd conference on Visualization '91, San Diego,
California, IEEE Computer Society Press.
Koper, R. and Specht, M. (2007). TenCompetence:
Lifelong Competence Development and Learning.
Competencies in Organizational E-Learning:
Concepts and Tools. M.-A. Sicilia, Idea Group.
Krathwohl, D. R. and Anderson, L., 2002. A revision of
bloom's taxonomy: An overview. Theory into Practice
41(4): 212-218.
Kunzmann, C., 2006. Ontology-based Competence
Management for Healthcare Training Planning: A
Case Study. Proceeding of the International
Conference on Knowledge Management, Austria.
McMillan, J. H., 2006. Classroom Assessment: Principles
and Practice for Effective Instruction, Pearson
Technology Group.
Merrill, M. D., 1983. Component Display Theory.
Encyclopeadia of Educational Technology, from
http://coe.sdsu.edu/eet/articles/cdt/index.htm.
Nursing and Midwifery Council. from http://www.nmc-
uk.org/aFrameDisplay.aspx?DocumentID=171.
Ramritu, P. L. and Barnard, A., 2001. New nurse
graduates' understanding of competence. International
nursing review.
Rolfe, I. and MaPherson, J., 1995. Formative assessment:
how am I doing? Lacent 345(8953): 837-839.
Sewell, J., 2004. Diagnostic assessment within the Skills
for Life strategy. 30th IAEA Conference, Philadelphia.
Shepard, L. A., 2000. The Role of Assessment in a
Learning Culture. Journal Information for
Educational Researcher 29(7): 4-14.
Sitthisak, O., Gilbert, L. and Davis, H. C., 2007. Towards
a competency model for adaptive assessment to
support lifelong learning. TENCompetence Workshop
on Service Oriented Approaches and Lifelong
Competence Development Infrastructures,
Manchester, UK.
Sitthisak, O., Gilbert, L., Davis, H. C. and Gobbi, M.,
2007. Adapting health care competencies to a formal
competency model. The 7th IEEE International
Conference on Advanced Learning Technologies,
Niigata, Japan, IEEE Computer Society Press.
UK Royal College of Nursing. 2005. from
http://www2.rcn.org.uk/cyp/resources/a-
z_of_resources/competencies.
Way, W. D., 2005. Practical Questions in Introducing
Computerized Adaptive Testing for K-12 Assessments.
Research Report 05-03.
WEBIST 2008 - International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies
338
