
PROACTIVE AUTONOMOUS RESOURCE ENRICHMENT FOR
E-LEARNING
Steffen Mencke, Dmytro Rud, Fritz Zbrog and Reiner Dumke
Faculty of Computer Science, Otto-von-Guericke University, Universitätsplatz 2, Magdeburg, Germany
Keywords:
E-learning, content, recommendation.
Abstract:
Information mastering is the major use case for learners in e-learning systems. Therefore they need appropriate
search and retrieval mechanisms. An approach to overcome potentially occuring problems, like e.g. high
recall and low precision or the high result sensibility to the used vocabulary, is the presentation of preselected
content. This paper presents an approach for the automatic ontology-based enrichment of e-learning content.
1 INTRODUCTION
E-learning is one of the most challenging “e-
domains”. In general it refers to a wide range
of applications and processes designed to deliver
instruction through computational means (Juneidi
and Vouros, 2005). Information mastering is the
major use case for learners. But the delivered content
is not always sufficient. There may be several reasons
for this lack, e.g.:
◦ Incomplete content because of weak course design
◦ Incomplete content due to author’s intention for
student motivation
◦ Too difficult content due to missing learner compe-
tencies
◦ Intended active learner involvement (e.g. for
assessments).
From these and other reasons an additional need
for information arises. In most cases standard search
and retrieval mechanisms are used to satisfy this need.
With the algorithm presented in this paper, the au-
thors propose a possible solution for the automated
enrichment of e-learning contents with ontologically
classified resources. The work is also valuably usable
for other users of e-learning systems, e.g. content cre-
ators, learning unit authors or didactical experts. Ad-
ditional application possibilities exist in every domain
where information needs to be presented to a user.
The presented approach differs from normal
e-learning recommendation systems as described in
(Adomavicius and Tuzhilin, 2005) or (Drachsler
et al., 2007). The goal is not to reason about the next
learning object, but to provide additional information
to the actual one. The underlying structure of the e-
learning course is not affected.
After this introductory notes, the process of
ontology-based content enrichment with a special fo-
cus on the developed enrichment algorithm is de-
scribed in section 2. In section 3 the paper fin-
ishes with conclusions and some remarks about future
work.
2 ONTOLOGY-BASED
RESOURCE ENRICHMENT
FOR E-LEARNING
We define an e-learning-related resource as any por-
tion of data that can be displayed to a user by the run-
time part of an e-learning system. According to this,
resource enrichment describes the process of search-
ing and displaying additional information, semanti-
cally related to the information to the e-learning re-
source.
In this chapter the authors describe their approach
for an adaptive, proactive and autonomous solution
for the addressed problem. The proposed enrichment
componentproactively scans e-learning resources and
provides additional semantic-based information, and
adapts in that way the delivered data.
2.1 Enrichment Algorithm
For the identification of enrichment points in an edu-
cational content an ’Enrichment Algorithm’ is devel-
464
Mencke S., Rud D., Zbrog F. and Dumke R. (2008).
PROACTIVE AUTONOMOUS RESOURCE ENRICHMENT FOR E-LEARNING.
In Proceedings of the Fourth International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies, pages 464-467
DOI: 10.5220/0001527104640467
Copyright
c
SciTePress

oped.
In the first step, an identification of appropri-
ate ontological elements within the ontology O(C, P)
with its concepts C and properties P is performed.
The function f
naming
(a) (Formula 1) delivers a
human readable name of an ontological element a.
The tuples, containing ontology elements a
i
and their
names determined using f
naming
(a
i
), constitute the set
T
O
as shown in Equation 2.
f
naming
: Ontological element 7→ String. (1)
T
O
= {ha
i
, f
naming
(a
i
)i|a
i
∈ (C ∪ (P\ P
tax
))}. (2)
At this point, taxonomic relations within the on-
tology (P
tax
) are neglected, because f
naming
(a) cannot
deliver any useful results for them.
A second step is the inflation of T
O
with ap-
propriate additional terms, for example taken from
the WordNet specifications for the English language
(Princeton University, 2006). The function f
syn
(a)
delivers additional terms (synonyms) (Formula 3).
The tuples of the extended set T
O+SY N
connect on-
tology elements a
i
with their synonyms (Equation 4).
f
syn
: String 7→ {String, . . . }. (3)
T
O+SYN
= T
O
∪ {ha
i
, b
i
i | a
i
∈ C ∪ P\ P
tax
,
b
i
∈ f
syn
( f
naming
(a
i
))}.
(4)
The function f
concept
(x) (Formula 5) applies to
both metadata LO
M
and the content LO
C
of learn-
ing objects LO (Formula 6) and extracts names of
concepts contained in them. A particular implemen-
tation of f
concept
can use classic mining algorithms.
For each learning object LO
i
, the initial set T
L+SYN
i
of
concept names and their synonyms, that can serve as
starting points of the enrichment, can be determined
as shown in the Equation 8.
f
concept
: Data object 7→ {String, . . . }. (5)
LO = {LO
i
} = {hLO
M
i
, LO
C
i
i}. (6)
CN
i
= f
concept
(LO
M
i
) ∪ f
concept
(LO
C
i
). (7)
T
L+SYN
i
= CN
i
∪
[
x∈CN
i
f
syn
(x). (8)
The next step is to match the identified concepts of
the learning objects with the human readable names
of ontological elements (Equation 9). T
S
i
maps onto-
logical elements to possible enrichment points within
the learning objects.
T
S
i
= {hc, di | d ∈ T
L+SY N
i
, hc, di ∈ T
O+SYN
}. (9)
T
S
i
is a set of tuples hc, di where d is a concept of
the educational content and c is the associated onto-
logical element. The set of all d is D (Equation 10).
D = {d | hc, di ∈ T
S
i
}. (10)
The algorithm’s next part is the selection of iden-
tified enrichment points D
′
⊆ D within the learning
object. Possible implementations can limit the set of
enrichment points, e.g. by selection of the first ap-
pearance of the enrichment points. The semantic rel-
evance is proposed as the key factor. For its deter-
mination several approaches can be (combined) im-
plemented: (a) choose those enrichment points that
are most relevant based on certain mining algorithms,
(b) choose those enrichments points that are most rel-
evant based on the semantic relevance according to
the metadata of the LO, (c) choose those enrichment
points that are most relevant based on the ontological
relevance of the associated ontological elements. For
the last option certain ontology metrics can be useful,
e.g. the Importance metric of (Tartir et al., 2005) and
the Class Density metric or the Centrality Measure of
(Alani and Brewster, 2005).
On the basis of the set RO (Equation 12) contain-
ing all ontological elements related to the selected en-
richment points, and the Semantic Window approach
described in subsection 2.2 of this paper,an additional
set of ontological elements can be computed. It will
be referred to as W.
f
onto
: String 7→ {Ontological element, . . . }. (11)
RO =
[
d∈D
′
f
onto
(d). (12)
The next step determines the amount of additional
information EC that is used to enrich the educational
content (Formula 13 and Equation 14).
f
enrich
: Ontol. element 7→ {Enrichment content, . . . }.
(13)
EC =
[
r∈RO∪W
f
enrich
(r). (14)
Other approaches as well as the ’Semantic Win-
dow’ described in the next subsection, relate to classic
adaptation algorithms for e-learning and may use ad-
ditional domain ontologies, specification ontologies
and of course user models.
PROACTIVE AUTONOMOUS RESOURCE ENRICHMENT FOR E-LEARNING
465
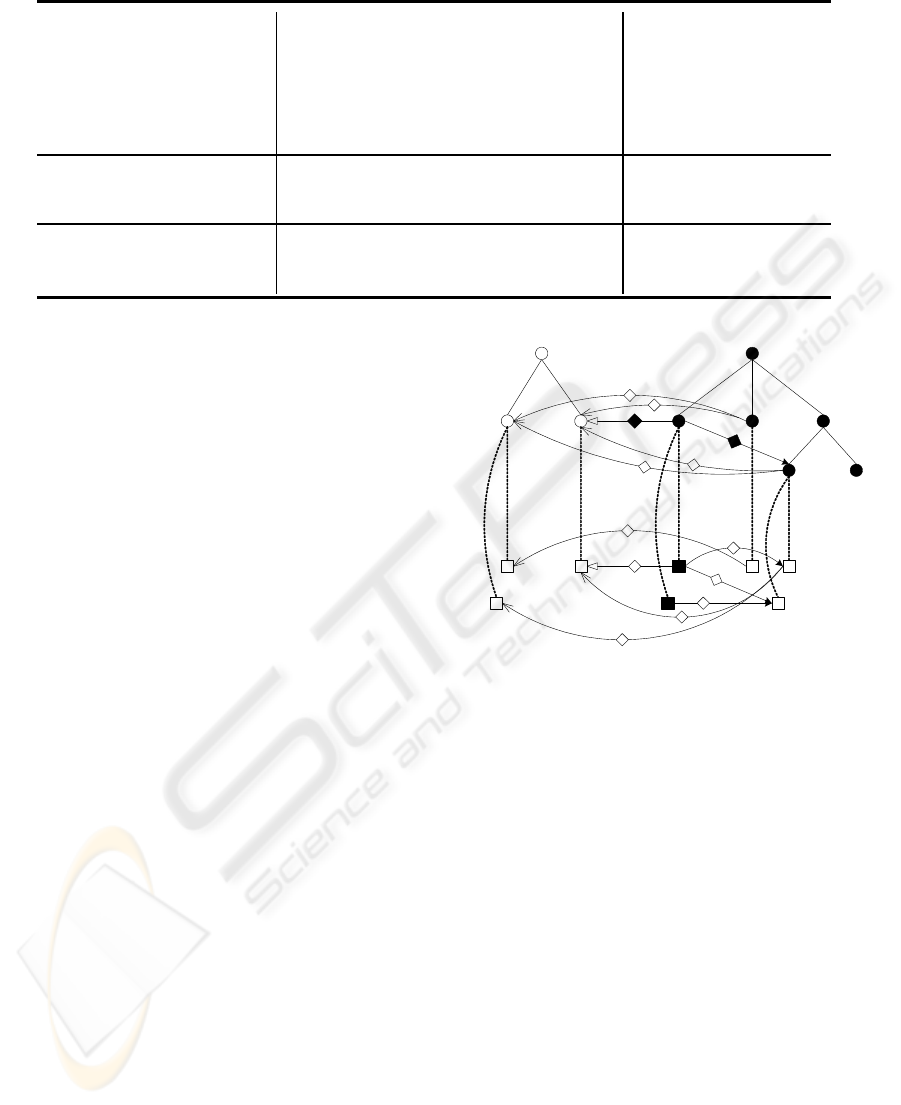
Table 1: Example of transition costs between ontological elements.
Parent concept /
object property
Child concept /
object property
Concept
Object property
Datatype
property
Concept
instance
Object property
instance
Datatype
property instance
Concept 1 1 ∞ 2 2 3 ∞ ∞
Object property 1 1 2 ∞ ∞ ∞ 3 ∞
Datatype property ∞ ∞ 2 ∞ ∞ ∞ ∞ 3
Concept instance ∞ ∞ 3 ∞ ∞ ∞ 2 2
Object property instance ∞ ∞ ∞ 3 ∞ 2 ∞ ∞
Datatype property instance ∞ ∞ ∞ ∞ 3 2 ∞ ∞
The presentation is not part of the algorithm
above, but results in the highlighting of all selected
d ∈ D
′
and the selective displaying the prepared en-
richment content EC
′
⊆ EC.
2.2 Semantic Window Algorithm
For the enrichment algorithm the authors defined the
concept of a ’Semantic Window’. This term describes
a set of elements of a given ontology within a certain
multi-dimensional distance. Dimensions for its def-
inition are related to the concepts of an ontology as
well as to the datatype properties. Furthermore in-
stances and taxonomic as well as non-taxonomic re-
lations are taken into consideration.
The function f
cost
returns the “cost” of the transi-
tion between two nodes, given their types as well as
the sequence of already accepted nodes (formula 15).
For the combinations of ontological elements’ types,
between which no transition is possible, the cost func-
tion is assumed to return the positive infinity.
f
cost
: Type, Type, hNode, . . . i 7→ Integer. (15)
Function f
type
returns the type of a given ontolog-
ical element (a member of the enumeration 17). New
types of ontological elements can be introduced by
splitting the sets of ontological elements of a partic-
ular type on the basis of some constraints (subclass-
ing). The domain of f
cost
for these new types obvi-
ously cannot be broader as for the original type.
f
type
: Ontological element 7→ Type. (16)
C
1
C
2
C
4
C
5
C
6
C
7
C
8
C
9
C
10
E
2
E
3
E
4
E
5
E
6
E
8
E
9
E
10
1
2 2
0
3
3
2
2
3
3
Figure 1: Example of a Semantic Window with enrichment
point C
6
, cost restrictor A = 3 and the transition costs given
in table 1.
Type ∈ {Parent concept, Parent object property,
Child concept, Child object property,
Concept, Object property,
Datatype property, Concept instance,
Object property instance,
Datatype property instance}.
(17)
Elements of a tuple hn
0
, . . . , n
m
i, n
i
∈ O, m ∈ N
are included to the Semantic Window, if n
0
is the en-
richment point of the enrichment and inequality 18
resolves to true, where A is the cost restrictor (“the
size of the Semantic Window”).
m−1
∑
i=0
f
cost
( f
type
(n
i
), f
type
(n
i+1
), hn
0
, . . . , n
i
i) ≤ A.
(18)
In figure 1 an example for the Semantic Window
is given. Concept C
6
is the enrichment point around
WEBIST 2008 - International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies
466
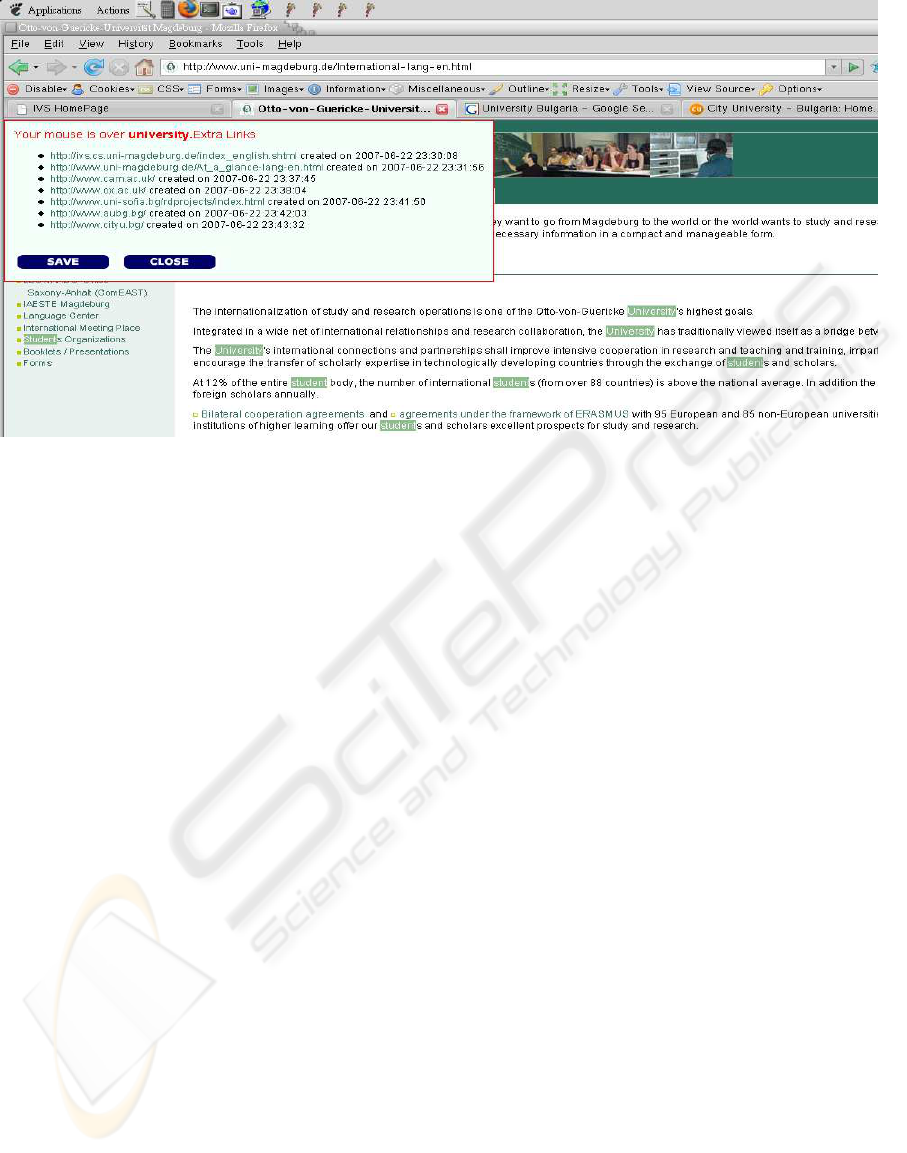
Figure 2: Screenshot of an enriched Web page.
which the Semantic window is created. For the sake
of simplicity datatype properties are not taken into
consideration. The cost function f
cost
is given in ta-
ble 1 and the maximum cost is A = 3. Filled circles
represent concepts, filled squares represent instances
and filled diamonds on arrows represent object prop-
erties, all being located within the range of the Se-
mantic Window around C
6
.
Based on the developed architecture, a prototype
was implemented. To proof the applicability of the
proposed approach a web-based example was chosen
for the enrichment of web pages using semantic infor-
mation from an ontology (cp. figure 2).
3 CONCLUSIONS AND FURTHER
WORK
In this paper the authors presented an algorithm for
the ontology-based content enrichment for the do-
main of e-learning. Other areas of application are the
enrichment of courses, assessments, interaction tools
as well as tools for the creation and management of
content and more complex learning units.
Another key aspect of this paper is the presenta-
tion of the Semantic Window idea. It support the se-
lection of semantically-related enrichment resources.
Based on a given cost function and a maximum cost,
the size of the Semantic Window can be determined.
The integration of ontology adaptation mecha-
nisms as well as a central ontology repository for
a community-based usage are possible future exten-
sions. Another focus will be the refinement and im-
provement of the enrichment algorithm.
REFERENCES
Adomavicius, G. and Tuzhilin, A. (2005). Toward the Next
Generation of Recommender Systems: A Survey of
the State-of-the-Art and Possible Extensions. IEEE
Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering,
17(6):734–749.
Alani, H. and Brewster, C. (2005). Ontology Ranking Based
on the Analysis of Concept Structures. In K-CAP
’05: Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference
on Knowledge Capture, pages 51–58, New York, NY,
USA. ACM Press.
Drachsler, H., Hummel, H., van den Berg, B., Eshuis,
J., Berlanga, A., Nadolski, R., Waterink, W., Boers,
N., and Koper, R. (2007). Recommendation Strate-
gies for e-Learning: Preliminary Effects of a Personal
Recommender System for Lifelong Learners. URL:
http://hdl.handle.net/1820/1010.
Juneidi, S. J. and Vouros, G. A. (2005). Engineering an E-
learning Application using the ARL Theory for Agent
Oriented Software Engineering. In 2005 AAAI Fall
Symposium, Arlington, Virginia, USA. MIT press.
Princeton University (2006). WORDNET - A Lexi-
cal Database for the English Language. URL:
http://wordnet.princeton.edu/.
Tartir, S., Arpinar, I. B., Moore, M., Sheth, A. P., and
Aleman-Meza, B. (2005). OntoQA: Metric-Based
Ontology Quality Analysis. In Proceedings of IEEE
ICDM 2005 Workshop on Knowledge Acquisition
from Distributed, Autonomous, Semantically Hetero-
geneous Data and Knowledge Sources.
PROACTIVE AUTONOMOUS RESOURCE ENRICHMENT FOR E-LEARNING
467
