
TOWARDS AN AGENT FRAMEWORK FOR A PASSENGER
TRANSPORTATION VIRTUAL ENTERPRISE
Claudio Cubillos and Daniel Cabrera
Escuela de Ingeniería Informática, Pontificia Universidad Católica de Valparaíso, Av. Brasil 2241, Valparaíso, Chile
Keywords: AOSE, Virtual Enterprise, Agent Framework, PASSI.
Abstract: This work presents the first approach for obtaining a framework based on the agent technology for the
passenger transportation problem, considering a virtual enterprise domain. The agent architecture obtained
provides a baseline for the integration between end-users of the transport service and multiple transport
operators affiliated to a virtual enterprise, which provides flexibility in the incorporation and leaving of
transport operators. The participation of governmental organizations and active destinations within the
system allows the virtual enterprise having additional information on potencial opportunities of business and
assures to the users of the transport system a wider and more complete service search. The PASSI
methodology has been used as base modelling methodology for leveraging the multiagent architecture.
1 INTRODUCTION
Passenger transportation in urban areas constitutes
an increasingly important problem in our society.
Geographical coverage problems among transport
operators services, difference in the volume and
quality of handled information, among other, gives
origin to problems that range from wrong
evaluations comming from state-regulatory entities,
up to direct problems with the system final users,
which definitively results in a poor quality of
service. Therefore, the existence of a group of
transport operators, partial or totally disconnected
among them, must move towards the conformation
of a unified transport service, sustained by a virtual
enterprise for passenger transportation.
The obtention of a software framework for the
passengers transportation problem will allow to
adapt this architecture according to concrete
required characteristics, reducing in a important way
the development cost, and not less important, while
using part of a solution that already has been used in
the past and therefore with the necessary maturity
and reliability.The framework development has been
realized based on the utilization of PASSI
(Burrafato, 2002), an agent-oriented methodology
for systems development. This work represents the
continuity of a past reseach in this transport domain
(Cubillos and Gaete, 2007), concerning the
development of an agent system for passenger
transportation for a single operator under a demand-
responsive scenario.
2 PASSENGER
TRANSPORTATION
The Intelligent Transport Systems (ITS) have been
attracting interest of the transport professionals, the
automotive industry and governments around the
world. The ITS aim at development of the road
infraestructure (for example, ways) and to integrate
them together with the persons and vehicles by
means of advanced technologies of integration, from
several research areas.
On the other hand, in the last years, the Demand
Responsive Transport Services (DRTS) have risen in
popularity for several reasons, among them, strong
incorporation of information and communications
technologies, increasing the efficiency and
diminishing the operations cost. A DRT is
understandable as a component of a long chain of
inter modal service, delivering local and
complementary mobility to other conventional
transportation alternatives, such as the bus or train.
292
Cubillos C. and Cabrera D. (2008).
TOWARDS AN AGENT FRAMEWORK FOR A PASSENGER TRANSPORTATION VIRTUAL ENTERPRISE.
In Proceedings of the Fourth International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies, pages 292-295
DOI: 10.5220/0001528602920295
Copyright
c
SciTePress

2.1 Virtual Enterprise
A virtual enterprise is a cooperation network of
legally independent companies, which quickly
constitute a whole and contribute mainly their core
competences in order to exploit a specific business
opportunity. In general terms, the life cycle of a
virtual enterprise is marked by four phases, that go
from the identification, evaluation and selection of
business opportunities, to the selection of partners
for conforming the virtual enterprise; later, a phase
of operation, where the business opportunity is
exploited and a phase associated to the end of the
virtual enterprise, with the corresponding separation
of assets.
2.2 Transport Requirements
In the DRTS, is identified a set of actors, who
interact in different ways. In general terms and by
considering any service, a normal way to understand
the term "users" is to only associate it to the "end
users", that is to say, to the people that actually use
the service. However, in a complex system like this
one of passengers transportation, there are many
other users or actors who have a direct interest in the
commercial, social and infraestructure impacts.
According to the present development, the actors
considered in a DRTS correspond to:
User. Represents the end user of the passengers
transport system. The user has the faculty to make
transport requests (with their respective conditions),
as well as to indicate any problem that may affect
him and that can has incidence in the concretion of
the requested trip.
Transport Operator. Represents a transport
company within the system. A transport operator can
correspond to a single person (who is performing the
roles of operator and driver at the same time), or can
also correspond to a company composed by multiple
vehicles (fleet of vehicles). The virtual
transportation enterprise is conformed by
heterogeneous operators.
Government Entity. Represents a government party
with regulation or control faculties, which guard
current legislation and the correct service contracts
fulfillment.
Active Destination. Represents a frequent
destination within the total of existing destinations.
An active destination can make the virtual
transportation enterprise to realize a necessity or a
business opportunity available, as well as to indicate
problems associated to the transport services offered,
such as a loss in the quality of service, or restrictions
on the operation.
Traffic Information System. Represents an
external information system which gives information
on present traffic conditions, collisions, traffic jams,
alterations due to streets repair, among others.
Virtual Enterprise Information System. Contains
a transaction system and a management system of
affiliated enterprises. The first system controls all
satisfied transportation requests and those in course
of action, including all the information of the
transport request and of the transportation service
characteristics offered through the virtual
transportation enterprise. The second system
administers the virtual enterprise lifecycle, from the
affiliation of a transport operator, to the separation
among the operators and the virtual transportation
enterprise.
Transport Operator Information System. It is
made up of a Fleet Management System and a
Solver System. The first system manages at internal
level, within the transport operator, all its fleets
and/or vehicles affiliated to the virtual transportation
enterprise. The second system optimizes the
operations of transport by means of a solver of
heuristic nature.
3 AGENT TECHNOLOGY
In the last years an emergent paradigm has been
increasingly consolidating incide diverse study areas
related to the Artificial Intelligence filed. It
corresponds to the Agent paradigm, which
approaches the development of entities that could act
in an autonomous and reasoned way. Considering
that consensus does not exist on a single definition
for the term Agent, such term will be understood
according to what described in (Weiss, 1999): “An
agent is a computer system that is situated in some
environment, and that is capable of autonomous
action in this environment in order to meet its design
objetives”.
The need to develop complex applications
compound by multiple subsystems that interact with
each other does leverage the need to distribute the
responsabilities among different agents, moving us
to Multiagent Systems (in ahead MAS). Is generally
accepted that coordination is a key and
distinguishing characteristic in a MAS (Mas, 2005).
TOWARDS AN AGENT FRAMEWORK FOR A PASSENGER TRANSPORTATION VIRTUAL ENTERPRISE
293
4 TOWARDS A FRAMEWORK
USING AGENT TECHNOLOGY
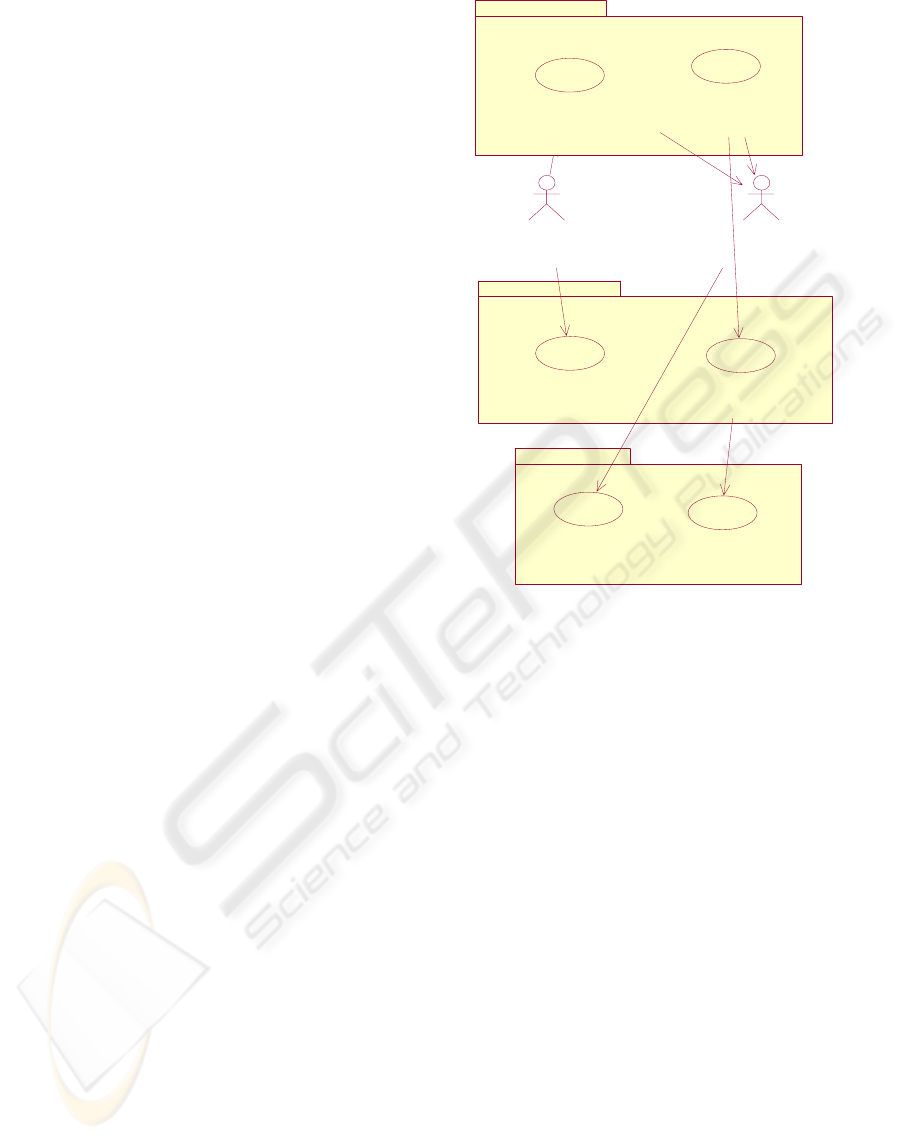
The Figure 1 shows a extract of the Agents
Identification Diagram, which takes as starting point
the description of UML use-cases, offering a general
view of all the functionality provided by the system
and in addition, it incorporates a grouping of use-
cases for each agent identified within the system in
order to visualize the responsability level that each
of the agents has regarding the system. It is possible
to indicate that the generation of diagrams is given
on the basis of the use of a graphical tool available
for PASSI, denominated PASSI Toolkit (PTK,
2007).
The VirtualEnterpriseAgent receives the transport
request and initiates a search of alternatives to
satisfy it, registering in the transaction system the
received transport request and the identifier of the
assigned vehicle. It handles information on all the
existing events. Considering the nature of the
triggered events, it can carry out changes and/or
apply countermeasures to the transport operators.
Furthermore, it can receive an affiliation request to
the virtual enterprise comming from a transport
operator and activates the mechanism to verify its
validity and feasibility. It can also drop from the
virtual transportation enterprise a specific operator.
The OperatorManagerAgent receives transport
requests from users and possible indications on
events caused by organizations external to the virtual
transport company. At any moment, it knows the
total number of vehicles available and the vehicles
that are in operation, and obtains the proposals to the
received requests of transport.
The ScheduleAgent verifies for a vehicle in
particular if it fulfills the conditions specified on a
requested trip (user conditions, conditions of the
virtual enterprise, or conditions caused by external
events), checking its itinerary obtained from the
information system of the transport operator.
Considering the feasibility verification, a proposal or
a declination takes place. For more details on the
underlying scheduling and optimization problem
please refer to (Cubillos et al. 2007)
A deployment/component hybrid diagram of the
general framework architecture is included (see
Figure 2). This initiative constitutes a first approach
in the conformation of a configurable and adaptable
architecture, based on object oriented and agent-
oriented technology together with considering the
virtual enterprise concept.
Inside each package a set of software components
are identified, those of which can correspond to
agents (as is the case of the package with the
<<Virtual Enterprise Terminal>> stereotype) or to
independent systems (as in the "Virtual Enterprise
Information System" package) or to a mixture of
both, agents with applications and managements
systems, as it happens in the case of the remaining
packages.
This architecture allows each transport operator
affiliated to the virtual transportation enterprise to
control at any moment the status of its operative
fleets, as well as to administer, if they wish, all the
information of their own information systems, in
such a way that independence between the different
operators of transport stays in the operative scope.
Each transport operator has his own mechanism
for allocation and control of the itineraries for the
different vehicles that conform his fleets, having the
virtual transportation enterprise the responsibility of
only receiving trip requests and the assignment of
these requests to the vehicle that constituted the
most attractive provider for the service user.
Anyway, the virtual transportation enterprise
maintains an own transaction system, in order to
register its daily tasks, satisfied requests, aborted trip
requests, information and/or alerts from government
organizations or active destinations, among other
things.
Transport Operator
(from 01-Domain Descri
p
...)
Virtual Enterprise Information System
(from 01-Domain Description phase)
VirtualEnterpriseAgent
<<Agent>>
OperationManagerAgent
<<Agent>>
ScheduleAgent
<<Agent>>
Generate Proposals
(f rom ScheduleAgent)
Vehicle Itinerary
Management
(f rom ScheduleAgent)
<<communicate>>
<<communicate>>
Proposals Management
(f rom OperationManagerAgent)
Operative Fleet Visualising
(f rom OperationManagerAgent)
<<communicate>>
Virtual Enterprise Affiliation
Management
(f rom VirtualEnterpriseAgent)
Virtual Enterprise
Management
(f rom VirtualEnterpriseAgent)
Figure 1: Agent Identification Diagram for the Job-shop
scheduling system.
WEBIST 2008 - International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies
294

5 CONCLUSIONS
The first version of a framework architecture for a
virtual enterprise devoted to passengers
transportation has been reached. The domain context
and their involved actors have been defined, which
can correspond to information systems or people.
The architecture includes a set of identified
agents which conform a society of agents and that
interact with both, the final user of the transport
system, and information systems and applications
external to it.
The future work will led to the refinement of the
software framework, verifying the points of
variability and the mechanisms of reusability.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Partially funded by Project No. 209.746/2007 of the
Pontifical Catholic University of Valparaíso
(www.pucv.cl).
REFERENCES
Burrafato, P., and Cossentino, M. 2002. Designing a
multiagent solution for a bookstore with the passi
methodology. In Fourth International Bi-Conference
Workshop on AgentOriented Information Systems
(AOIS-2002).
Cubillos, C., Gaete, S. 2007. Design of an Agent-Based
System for Passenger Transportation using PASSI. In:
Mira, J., Alvarez, J.R. (eds.) IWINAC 2007, Part II.
Springer Heidelberg LNCS, vol. 4528, pp. 531–540.
Cubillos, C., Crawford, B., Rodríguez, N. 2007.
MADARP: A Distributed Agent-based System for On-
Line DARP. In: I. Stojmenovic et al. (Eds.): ISPA
2007, Springer Heidelberg LNCS, Vol. 4742, pp. 160–
169.
Mas, A. 2005. Agentes Software y Sistemas Multi-Agente:
Conceptos, Arquitecturas y Aplicaciones. Pearson
Educación, Madrid, España.
PTK. 2007. The PASSI Toolkit (PTK) Available at
http://sourceforge.net/projects/ptk. Weiss, G. 1999.
Multiagent Systems: A Modern Approach to
Distributed Artificial Intelligence. MIT Press,
Massachusetts, USA.
Figure 2: Deployment/Component hybrid diagram of the virtual enterprise framework.
TOWARDS AN AGENT FRAMEWORK FOR A PASSENGER TRANSPORTATION VIRTUAL ENTERPRISE
295
