
DESIGN AND IMPLEMENTATION OF GEOLOGICAL
THESAURUS IN KOREA
Jaehong Hwang and Kwanghoon Chi
KIGAM(Korea Instituted Geoscience And Mineral resources)
30 Gajeong-dong, Yuseong-gu, Daejeon 305-350, South Korea
Keywords: Thesaurus, Geologic term, spatiotemporal object.
Abstract: We divide into fifteen geological areas covered in this research contained ore deposit, geochemistry,
petrology, and so forth. We analyze each geological area and we standardize the fields of Korean, English,
abbreviation, and meaning about geological term. To construct the thesaurus for each thesaurus, we make
out: First, we limited the real world to the geologic world in Korea literatures. Second, we extract the 15
areas, about 3000 terms and 236 spatiotemporal objects of each geologic literature in Korea. Third, we
considered the standardization of geological term in Korean and English and make out each terms. Finally,
we classify the geologic terms and make a guideline each area
1 INTRODUCTION
Recently with the development of semantic Web
technologies in information search, the necessity for
thesaurus is increasing along with lexicons. A
thesaurus is the combination of classification and a
lexicon, and is a map of knowledge structure
expressing relations among concepts (terms) subject
to human knowledge activities such as learning and
research using formally organized and controlled
index terms for clarifying the context of
superordinate and subordinate concepts. However,
although thesauri are regarded as essential tools for
controlling and standardizing terms and searching
and processing information efficiently, we do not
have a Korean thesaurus for geology. To build a
thesaurus, we need standardized and well-defined
guidelines. The standardized guidelines enable
efficient information management and help
information users use correct information easily and
conveniently.
The present study purposed to build a thesaurus
system with basic terms used in geology. For this,
first, we surveyed related works for standardizing
geological terms in Korea and other countries.
Second, we defined geological topics in 14 areas and
prepared a classification system (proposal) for each
topic. Third, based on the geological thesaurus
classification system, we created the specification of
geological thesaurus. Lastly, we designed and
implemented an Internet-based geological thesaurus
system using the specification.
We divide into fifteen geological areas covered
in this research contained ore deposit, geochemistry,
petrology, and so forth. We analyze each geological
area and We standardize the fields of Korean,
English, abbreviation, and meaning about geological
term. To construct the thesaurus for each thesaurus,
we make out: first, we limited the real world to the
geologic world in Korea literatures. Second, we
extract the 15 areas, about 3000 terms and 236
spatiotemporal objects of each geologic literature in
Korea. Third, we considered the standardization of
geological term in Korean and English and make out
each terms. Finally, we classify the geologic terms
and make a guideline the specification of
spatiotemporal ontology model for geological maps
in Korea.
2 THE CLASSIFICATION
SPECIFICATION OF
GEOLOGIC TERMS (DRAFT)
In order to build a geological thesaurus DB, we first
developed the classification specification of
geological terms (draft). In order to systematize the
classification of geological terms, we made the
standardized classification of geological terms
253
Hwang J. and Chi K. (2008).
DESIGN AND IMPLEMENTATION OF GEOLOGICAL THESAURUS IN KOREA.
In Proceedings of the Fourth International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies, pages 253-259
DOI: 10.5220/0001530802530259
Copyright
c
SciTePress

referring to geological terminology standards in
Australia, digital geological map terminology
standards in the U.S., and Korean geological
dictionaries, and mapped Korean terms to the
corresponding English and Chinese terms for
Internet search. Besides, for geological terms, the
concepts and scopes of terms were defined by
specifying several data items. A total of 14
geological areas were defined including digital
geological informatics, ore deposits, geochemistry,
paleontology, geotechnology, geological process,
field mine terminology, geophysics, structural
geology, environmental geology, mineralogy,
lithology, historical geology, mathematical geology,
and geological GIS terminology. Particularly for the
area of digital geological map, this study analyzed
existing geological maps and then: first, extracted
objects by geological period necessary for digital
geological maps; second, extracted rock objects
distributed over digital geological maps; third, the
arranged rock unit adapted for Korean geological
maps into 6-stage classification items from the
broadest classification (sedimentary rocks, igneous
rocks and metamorphic rocks) to the most detailed
one referring to Australian thesaurus, lithological
classification (draft) in BGS(British Geological
Survey) and geological map unit classification in
USGS(United States Geological Survey); and fourth,
the assigned identification codes of geological age
and rock objects to the classification items. Through
this procedure, we made rock-time unit ontology
specification of digital geological maps. The digital
geological map classification system first divided
digital geological maps into spatial units and time
units. Spatial objects were extracted in rock units
composing geological maps for spatial units and in
geological time scale units for time units.
2.1 Extraction of Rock-Time Unit
Objects of Digital Geological Maps
The classification of minimum rock units of digital
geological maps aims at digitalization into
lithologically uniform minimum map units. The
minimum unit classification of digital geological
maps (proposal) targeted Korean geological maps,
and we selected a common 1:50,000 digital
geological maps as a material for analyzing rock
units. When the digital geological map was analyzed,
1961 rock facies objects were identified, and each
object was composed of rock, layer, stratum,
stratigraphy, age, geological structure, ore, the
chemical and physical properties of the rock,
geographical name, etc. These rock objects were
classified into rock units, and they were organized to
have atomicity from one another and to be in the
relation of spatial inclusion between superordinate
terms and subordinate stems. In this study,
‘minimum rock unit’ was used instead of ‘lithology’
for two reasons. One is that sediment, which is not a
rock but an unconsolidated layer, cannot be
classified lithologically in a strict sense, so we need
to classify rock units in a new way. The other is that
‘minimum unit’ means that objects on the same level
has indivisible atomicity.
2.2 Time Unit Classification of Digital
Geological Maps
Time unit classification of digital geological maps
used eon for broad classification, era for
intermediate classification, and period for narrow
classification. In the broad classification, time was
divided into the Precambrian Eon and the Cambrian
Eon, and the Cambrian Eon was again subdivided
into the Paleozoic Era, the Mesozoic Era and the
Cenozoic Era. Geological age identifiers used 4
upper-case alphabets for eons and eras and two
alphabets for periods. However, because the
Cambrian Period and the Carboniferous Period
overlapped with each other, they were given
identifiers CA and CB, respectively.
2.3 Rock Units Classification of Digital
Geological Maps
Rock units classification of digital geological maps
first made the broadest classification into
sedimentary rocks and unconsolidated sediments,
metamorphic rocks and igneous rocks, and then
broad, intermediate, narrow, detailed and most
detailed classification, so a total of 6 depths of
classification tree. Figure 1 shows a topic map of
major basic objects extracted from Korean digital
geological maps. Topic map is a methodology for
modeling a set of topics, organizing topics, relations
among topics, and resource information on topics
into ontology. A topic map is a technology standard
for defining knowledge structure in distributed
environment and mapping the defined structure to
knowledge resources. It is a new paradigm for
structuring, extracting and navigating information
resources. Terminology objects according to topic
marked as a box show Korean term, English term,
geological abbreviation and RGB color, and have a
classification identifier in subordinate classification
(Figure 1).
WEBIST 2008 - International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies
254

3 GEOLOGICAL THESAURUS
DB CONSTRUCTION AND
SYSTEM DESIGN
Thesaurus is a control lexicon that classifies
terminology systematically in order to distinguish
equivalent relations, hierarchical relations and
interconnected relations and to improve search
performance. The main purpose of a thesaurus is the
management of synonyms. Many synonyms or
similar forms of words are linked to one another
through the concept of a preferred term. This
prevents failure in information search caused by the
ambiguity of language. Major items used in building
a thesaurus are preferred terms, variant terms,
superordinate terms, subordinate terms, related
terms, USE, Used For, and domains of definition. In
this research, these terms were included in building
the geological thesaurus DB for 15 geological areas.
In particular, the area of digital geological maps was
divided into rock units and time units, and major
items such as Korean standard terms, English
standard terms, abbreviations, term descriptions and
colors were prepared, synonyms and variant terms
were interconnected with one another, the entire
classification system was defined as a specification,
and additionally the colors and definitions of rocks
and geological ages according to the classification
system and rock photographs were built up. The
geological information thesaurus DB was
implemented as a MSSQL DB for Web service. In
addition, for end users’ convenience, an Internet-
based geological information thesaurus system was
constructed through drafting the webpage of the
thesaurus system and designing the functions, the
database and the system structure .Figure 2 is the
system design showing the process of search service
on the Web using the thesaurus DB built with OTM.
3.1 Function Design
The system functions were designed separately for
graphic fonts, external image links, ontological
expression in DB, database term search, tree view,
etc. First, the system was designed to support colors
and fonts so that images for geological terms can be
inserted and colors can be applied to terms in the
Figure 1: The ontology map of rock-time unit for digital geological map(Main diagram).
DESIGN AND IMPLEMENTATION OF GEOLOGICAL THESAURUS IN KOREA
255
tree. Second, using links to external images,
geological terms were linked to external images.
Third, thesaurus expression functions were designed
to process graphic displays in various ways by a
building sophisticated database containing relations
such as superordinate and subordinate relations and
relations among related terms. Fourth, the search
function was designed to find geological terms
referring to Korean terms, English terms and
Chinese terms in the database.
3.2 DB and System Design
The geological term thesaurus built by Thesaurus
Manager (OTM; Object Thesaurus Manager) is
stored in DB and a manager and separate Java API
are supported for interlocking between Web search
service programs and the geological term DB so that
users can make visual queries conveniently on the
Web. Web search application programs
implemented using the API supports navigation
among terms through interlocking between the tree
structure and the graphic screen, so it can support
thesaurus-based intelligent search in connection to
other search engines available. The geological term
system first enters terminology data using OTM
after the verification of the terminology system by
specialists in geological resources, and then uploads
the DB on the Web through the interlocking
thesaurus API. Graphic user interface (GUI) is
implemented through programming of Java and Java
Server Page (JSP), and internet services are provided
to end users.
Figure 2: The thesaurus system Design of geological terms.
A
pplication Server
Web User
Inferred engine
…
Gra
p
hic web interface
Interface connected brainy natural lanaguage
A
PI connected
thesaurus
JDBC
Search engine
Window 2003 Server
ODBC
Geologic term thesaurus Manager
DBMS
Geologic term
thesaurus
D
B
User
q
uer
y
lo
g
Web User
Web User
Domain ex
p
ert
Domain ex
p
ert
Domain ex
p
ert
…
WEBIST 2008 - International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies
256

Figure 3: Retrieving terms with Korean, English and Chinese fields.
4 WEB SERVICE OF
GEOLOGICAL INFORMATION
THESAURUS
While existing information search services have
provided information limited to users’ knowledge,
the present geological term thesaurus provides broad
information in graphics including the location and
interrelation of information, upgrading information
to the level of knowledge. Figure 3 is retrieving
terms with Korean, English and Chinese fields each
map sheet. Fourth, database was built by inserting
the contents of the developed spatiotemporal
ontology model into the redefined digital geological
map table. Fifth, the patterns and colors of rocks
were refined using the symbology unit of the
spatiotemporal ontology model, and applied to the
geological map schema. While existing information
search services have provided information limited to
users’ knowledge, the present geological term
thesaurus provides broad information in graphics
including the location and interrelation of
information, upgrading information to the level of
knowledge. Figure 3 is retrieving terms with Korean,
English and Chinese fields Figure 4 make it possible
to web query using geologic thesaurus trees and
image service for Geologic terms
5 CONCLUSIONS
The results of this study are as follows. First,
geological term standardization defined around 3500
terms commonly used in geology in English,
Chinese and Korean, and cataloged their concepts,
photographs, abbreviations, etc. Second, in the
classification of geological terms, geology was
divided largely into 14 areas, and for each area
intermediate, narrow and detailed classification were
made, a classification system of superordinate and
subordinate terms was established, and the
specification of geological term standard (proposal)
was drafted. Third, for the area of digital geological
maps, we extracted rock objects and geological age
objects existing in Korean geological maps and
expressed the unique color of each object using
RGB values. Lastly, while existing information
DESIGN AND IMPLEMENTATION OF GEOLOGICAL THESAURUS IN KOREA
257
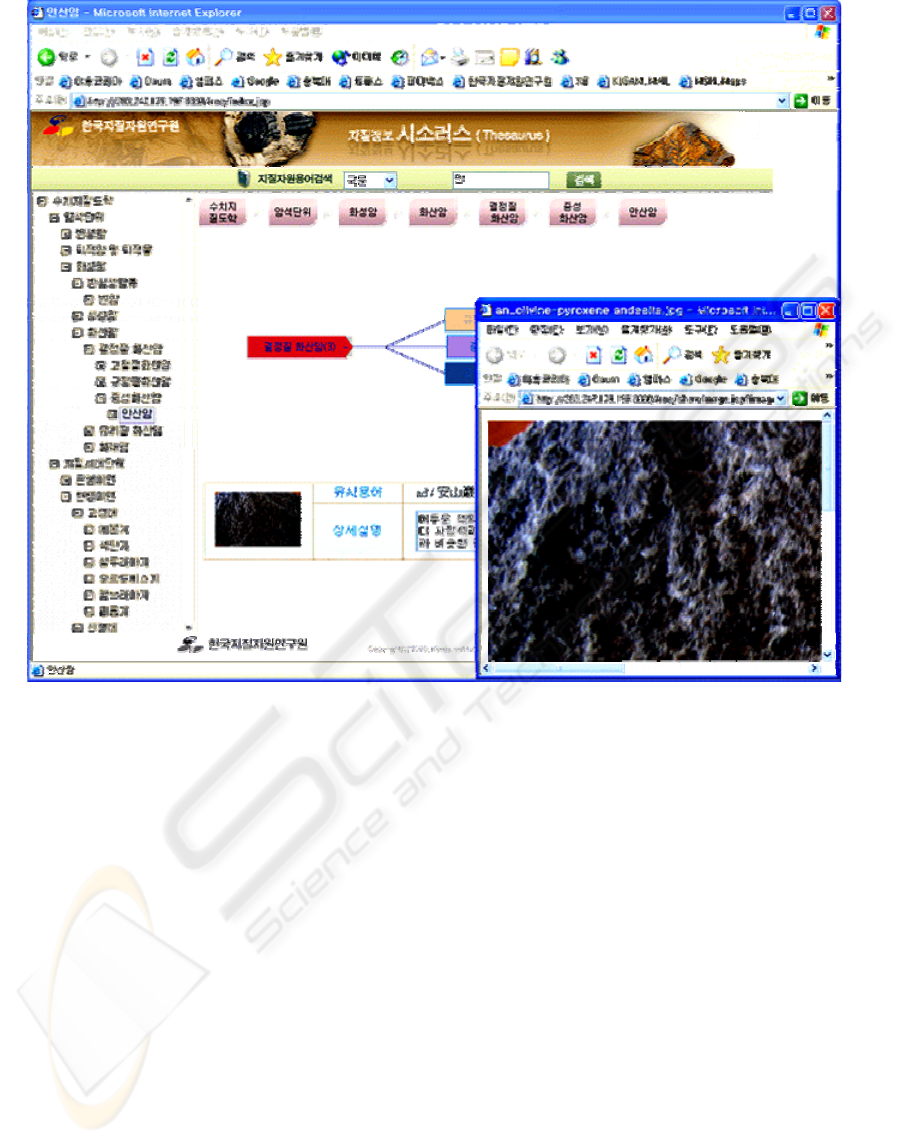
Figure 4: Image service for Geologic terms.
search services have provided information limited to
users’ knowledge, the present geological term
thesaurus provides broad information in graphics
including the location and interrelation of
information, upgrading information to the level of
knowledge. However, the geological term tree will
be designed through long-term deliberation of
opinions from many specialists in geology so that it
becomes most reasonable and highly accessible
through the Internet.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This research was supported by a grant(NEMA-07-
NH-Article) from the Natural Hazard Mitigation
Research Group, National Emergency Management
Agency.
REFERENCES
British Geological Survey(BGS), 2005. Proposals for the
British Geological Survey Core Strategic
Programme(2005-2010). pp.1-9
British Geological Survey(BGS), 2007. The British
Geological Survey Lexicon of Named Rock Units
(Unpublished Webpage:
http://www.bgs.ac.uk/scripts/lexicon/home.cfm). 2007
British Geological Survey(BGS). Geoscience Dictionaries
(Unpublished Webpage: http://www.bgs.ac.uk/data/
dictionaries.html). 2007
Europe Geological Surveys(Unpublished Webpage:
www.eurogeosurveys.org). 2007
Geological Survey of Japan(GSJ). 2007. (Unpublished
Webpage: www.gsj.jp).
Geoscience Australia(GA). 2007. (Unpublished Webpage:
www.ga.gov.au).
HARVEY BLATT, Robert J. Tracy, 1996. Petrology,
Freeman.
Jackson, J.A., 1997, Glossary of geology. American
Geological Institute, Washington, D.C.
WEBIST 2008 - International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies
258

Jane Edinger and Tracy Barker. 2003. GeMPeT: The
Geoscience, Minerals and Petroleum Thesaurus.
Loren A. Raymond, 1995, Petrology, Brown
Communication, Inc.
Milstead, J.L.(Editor), 1993, Ei Thesarus. Engineering
Information, Hoboken, N.J.
Walker, P. (Editor), 1991, Chambers Science and
Technology Dictionary. Chambers, Edinburgh
Telford, W. M., Geldart, L. P., sheriff, R. E., and Keys, D.
A., 1990, Applied Geophysics 2nd edition. Cambridge
University Press, 790p.
United States Geological Survey USGS, 2002. Geologic
Map Unit Classification, ver.6.1
U.S. Geological Survey(USGS). 2005. Geography for a
Changing World(USGS Strategic Plan 2005-2015).
1997. pp.1-8
DESIGN AND IMPLEMENTATION OF GEOLOGICAL THESAURUS IN KOREA
259
