
NEW DIRECTIONS FOR IT GOVERNANCE IN THE BRAZILIAN
GOVERNMENT
Fabio Perez Marzullo, Carlos H. A. Moreira, Jano Moreira de Souza
Federal University of Rio de Janeiro – UFRJ, COPPE Database Laboratory, Brazil
José Roberto Blaschek
State University of Rio de Janeiro – UERJ, Brazil
Keywords: IT Governance, Knowledge Management, Competency, Human Capital, Business Performance, Business
Strategy, Electronic Government.
Abstract: This paper presents an IT Governance Framework and a Competency Model that are being developed to
identify the intellectual capital and the strategic actions needed to implement an efficient IT Governance
program in the Brazilian Government. This work in progress is driven by the premise that the human assets
of an organization should adhere to a set of core competencies in order to correctly prioritize and achieve
business results that, regarding government issues, relates to public resources administration. It is now
widely accepted that IT Governance may help the organization to succeed in its business domain;
consequently, through effective investment policies and correct IT decisions the organization can align
business needs with IT resources, achieving highly integrated business services.
1 INTRODUCTION
Research conducted in recent years have shown that
to efficiently apply IT resources in a well designed
and responsible fashion it is necessary to implement
an IT Governance program that targets organization
strategic priorities. As for government organizations,
most of this paradigm applies; however we must
consider specific characteristics, such as rigid
functional structures, political interests and the
ethical use of public resources.
In many countries, the Government economy
share might get to 30% (Weill and Ross, 2004). The
Brazilian economy is not different and with massive
investments in all economic sectors, how does one
establish an efficient IT infra-structure that must be
pervasive to every Government sector in order to
avoid effort and public resources waste? And
mostly, how can IT become a strategic asset for the
Brazilian Government, helping with the investment
process, and consequently improving the quality of
its services? The pursuit of this new vision is
orchestrated in the following sections, in which we
present what has been done so far, and what is still
under research.
2 MOTIVATIONS
We have achieved a new era of competition.
Organizations can no longer afford to delegate IT
decisions to IT officers. What we see now is an
increasing need for business integration, and such
integration can only be achieved through strategic
business alignment with IT services.
Considering Government organizations, extreme
care should be exercised when using public
resources to sponsor public programs. Therefore,
how can governments invest public resources in
order to obtain the best results for the taxpayer? IT
assets not only contribute to Government actions,
but also help coordinate better ways of attending to
the needs of the country, whether by means of new
services or through the improvement of old ones.
Seeking that efficiency, the Brazilian Planning
Ministry (
MP, 2007), in conjunction with the Defence
Ministry (
MD, 2007) and the Federal University of
Rio de Janeiro, strived to create IT Governance
directives in order to standardize business and
customer needs. By business we mean every public
service (public value), from tax collection activities
to health care services.
179
Perez Marzullo F., H. A. Moreira C., Moreira de Souza J. and Roberto Blaschek J. (2008).
NEW DIRECTIONS FOR IT GOVERNANCE IN THE BRAZILIAN GOVERNMENT.
In Proceedings of the Tenth International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems - ISAS, pages 179-182
DOI: 10.5220/0001667901790182
Copyright
c
SciTePress

3 UNDERSTANDING
GOVERNMENT SCENARIO
The intensive and extensive use of Information
Technology in public administration is affecting, on
a daily basis, Government actions aimed at its
citizens. The successive growth in tax collection and
new economies brought up by electronic
Government programs, are examples of the
pervasive application of IT resources (
MP, 2007).
Despite the increasing rate in which, nowadays,
IT services contribute to governmental actions, IT
elements have not always been considered as an
essential and strategic asset. What we have seen was
dependence, in most of the public organizations, of
private organizations. And, as a sub-product of this
line of action, outsourcing has become a common
practice of corrupt politicians to defraud the
Brazilian Government.
By not understanding that IT services were no
longer fit for outsourcing (or at least the strategic
services), without risking missing Government goals
and incurring into quality depreciation, the impacts
were crippling the Government IT infrastructure.
Decisions were taken with little concern for proper
impact analysis and, most of the time, using criteria
that were aligned with political interest and as a
function of the cost and speed in which the actions
resulted for the group in charge. Governance
arrangements were typically feudalistic, and all IT
principles lacked proper definition and integration.
This old vision was critical to promote a shift on
the way in which IT assets were managed. The new
approach should be directed to Government areas
that were highly dependent on IT services and the
output of this new course of action should be a series
of official statements that should incorporate new
directions for sustaining the necessary organizational
changes (
MP, 2007). New perspectives meant that
new solutions, either by the adoption of new policies
or with the implementation of new management
models, should be defined to improve IT governance
inside Government organizations. Organizations that
managed to succeed, despite the chaotic scenario,
must be taken as examples of successful initiatives
(
Receita Federal, 2007), (SERPRO, 2007), and (TCU,
2007).
4 THE FRAMEWORK
Elaborating and implementing an appropriate IT
Governance program is not an easy task. It is
necessary to understand several organization aspects
such as Government vision; mission; business
strategies; goals; functional structure; human assets
and, along the process, to evaluate the level of
maturity attained by the organization. Having
identified the organization’s current status, it is
necessary to plan all the steps needed to improve the
IT Governance structure, its implementing and
managing (
Grembergen, 2004).
The framework defined below tries to align
aspects oriented by business goals and IT goals
without ignoring public administration aspects such
as political views, responsible investments, and the
population best interests and ethics.
Figure 1: The Government IT Governance Framework
was specifically designed, by this study, to accommodate
actual needs and constraints identified in the Brazilian IT
Organizations. Its elements, however, were extracted and
adapted from (Weill and Ross, 2004) and (Fernandes and
Abreu, 2006).
The IT Governance Framework initially states that,
all goals and policies should be carefully understood
in order to plan Government strategy; by doing this,
IT strategies may be defined in order to provide
ways to align, integrate and service Government
strategies; along this process, performance
measurement programs should be planed aiming
evaluating levels of alignment, integration and
service quality, so investments are not wasted in
futile efforts. Also, administration responsibility and
ethics should be employed to avoid waste of public
resources, and corruption, which is a serious
problem in the practice of many Brazilian
politicians.
Outputs from the framework are rules and
principle definitions to all IT aspects, from
infrastructure, architecture and services, to
outsourcing standards and performance indicators.
This approach allows a specific design for each
organization, meaning that each organization will
ICEIS 2008 - International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
180
have their organization culture preserved as long as
it does not influence the outputs. The final phase is
to put into practice the IT-Business alignment and
integration program designed for it.
Finally, an iterative process of performance
evaluation is conducted to guarantee that the
proposed framework and competency dimensions
will converge to an efficient IT Governance Model.
5 COMPETENCY DIMENSIONS
In general, individual and organizational knowledge
are the main aspects that should be considered when
analyzing intellectual capital, and it is important to
know that knowledge transfer activities should be
planned in order to create effective learning
processes. Through these learning processes,
organizations create background to develop new
leaders and, consequently, improve intellectual
capital (
Leibowitz, 2000).
In practice, accurately choosing and
implementing the best governance model, requires,
from the high administration and particularly top IT
managers (CIOs), a great diversity of knowledge
elements and skills. In the creation of a systematic
vision of such characteristics we proposed a general
competency domain that groups different
competency aspects needed to implement IT
Governance programs, as shown below.
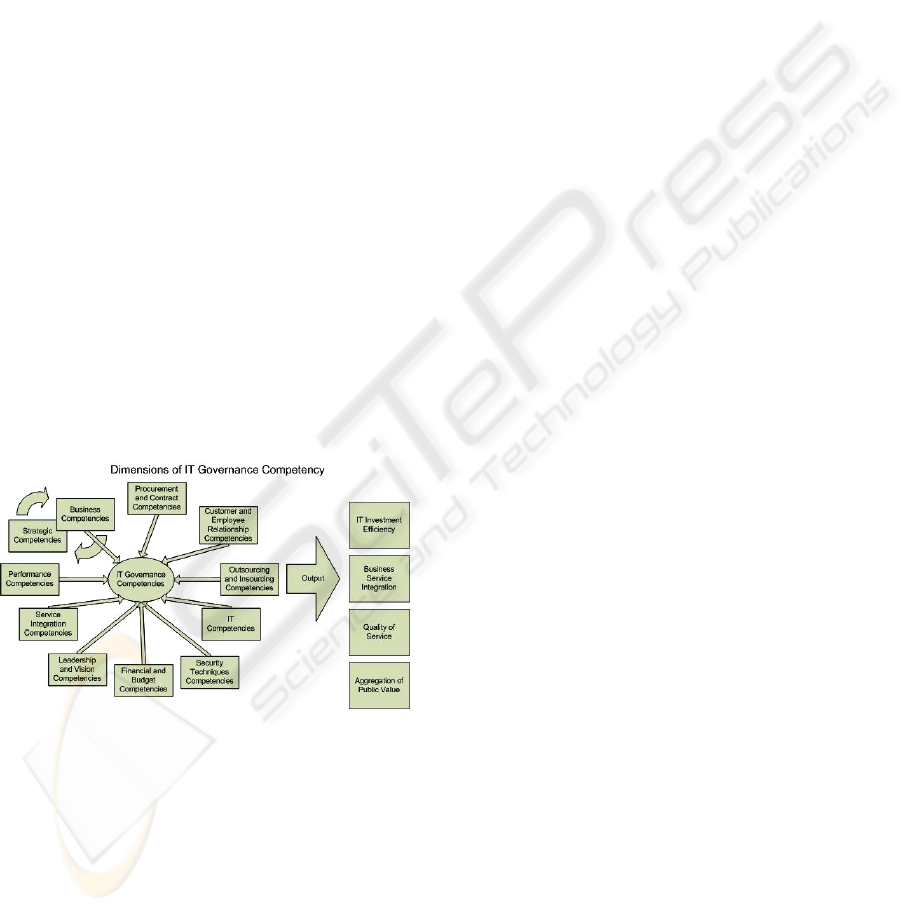
Figure 2: Dimensions of IT Governance Competency,
adapted from (Weill and Ross, 2004), (PMI, 2001),
(Schubert, 2004) and (ISO/IEC 17799, 2005).
We then describe each and every competency aspect
that was added to the competency domain model in
order to establish a general Government Knowledge
Base which all IT Governance programs might use
as base standard.
1. Business and Strategic Competencies.
Business and Strategic competencies are pivotal
elements for a successful IT Governance program.
This competency domain falls outside classic
technical skills and leverage the ability to acquire
and administer organizations needs through IT
services (
Schubert, 2004).
2. Customer and Employee Relationship
Competencies. Government must recruit and retain
employees who are capable of coping with their
daily job with responsibility and quality. It is
important to form a workforce of the right
competency and size, in order to achieve
Government goals and offer efficient services for its
population.
3. Outsourcing and In-sourcing
Competencies. Governments tend to contract
external services to comply with business demands,
but they should also know when to “bring it home”.
It is important to know that outsourcing is a strategic
decision that affects the organization budget, goals
and structure. Extreme caution should be applied not
only to know when to outsource but also to what
should be outsourced and why.
4. IT or Technical Competencies. This
competency domain involves IT aspects, such as
infrastructure, architectures, patterns, maturity
models, and programming standardizations
(
Schubert, 2004).
5. Service Integration Competencies. This
competency domain requires strategies to model
business and IT services together, so that they might
be able to assist business needs in an efficient
manner (
Peterson, 2004).
6. Performance Competencies. Requires
knowledge and skills to analyze and measure
whether the aspects presented in the Governance
Framework are complying with business needs and
public expectations.
7. Procurement and Contract Competencies.
Despite some people advocating that this
competency falls outside IT Governance aspects, we
decided to include it in our Competency Domain
because a Government environment will always
have needs related to technical aspects, such as
equipment, and, therefore IT officers should be
capable of managing service and supply contracts
(
Schubert, 2004).
8. Security Techniques Competencies.
Defining, achieving, maintaining, and improving
information security may be essential to maintain
competitive advantage, cash flow, profitability, legal
compliance, and commercial image (
ISO/IEC 17799,
2005).
NEW DIRECTIONS FOR IT GOVERNANCE IN THE BRAZILIAN GOVERNMENT
181

9. Financial and Budget Competencies.
Government interests in financial and budget
management are vital for political base stability.
Managing budgetary processes, including preparing
and justifying a budget and operating a budget under
strict rules imposes a level of expertise that should
be more efficient than those applied in private
organizations.
10. Leadership and Vision Competencies. For
public organizations, besides having technical
competencies, a leader must show direction, must
understand and be capable of explaining the
organization’s vision, must have integrity, optimism,
ethics and responsibility towards the population
(
Warren, 2001).
This competency domain is a general overview of
the elements that compose the IT Governance
Program. According to our research, these levels of
competency are necessary to leverage IT
Governance in Brazilian Government organizations.
This approach will be used by the Planning Ministry
as baseline guidance to conduct future
implementations of IT Governance programs.
6 CONCLUSIONS
This paper presented the competency domain model
and the IT Governance framework created to align
all IT and Business goals of Brazilian Government
organizations. After studying the IT assets and
policies of current organizations we proposed a
governance standard that, according to the Brazilian
Planning Ministry, should be considered as a
baseline implementation.
Our contribution is only a small step towards a
much broader restructuring of IT services in
Brazilian public organizations.
Besides refinements of competency domain and
IT Governance framework, future work also
involves optimization of internal processes,
identification of new competency domains,
evaluation of change impacts in every targeted
organization, and development of supporting tools.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was supported by the Federal University
of Rio de Janeiro – UFRJ, COPPE Database
Laboratory.
New Directions for IT Governance in the
Brazilian Government.
Fabio Perez Marzullo, M. Sc. is with Federal
University of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. (e-mail:
fpm@cos.ufrj.br).
Carlos Henrique is with Federal University of
Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. (e-mail:
carlos.henrique@planejamento.gov.br).
José Roberto Blaschek , D. Sc. is with State
University of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, (e-mail:
blaschek@attglobal.net).
Jano Moreira de Souza, Ph.D. is with Federal
University of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, and is the head
of the Database and Knowledge Management
Department (e-mail: jano@cos.ufrj.br).
REFERENCES
Weill, P., Ross, J., 2004. IT Governance: How Top
Performers Manage IT Decision Rights for Superior
Results.
Fernandes, A. A., Abreu, V. F., 2006. Implantando a
Governança de TI – da Estratégia à Gestão dos
Processos e Serviços, Ed. Brasoft.
PMI, 2001. Project Management Competency
Development Framework. http://www.pmi.org/.
Leibowitz, J., 2000. Building Organizational Intelligence:
A Knowledge Management Primer - Transforming
Organizational Learning into Organizational
Learning.
Grembergen, W. V., 2004. Strategies for Information
Technology Governance, Idea Group Publishing.
SERPRO, 2007. http://www.serpro.gov.br/.
Receita Federal, 2007. Ministério da Fazenda, Governo
Federal. http://www.receita.fazenda.gov.br/.
TCU, 2007. Tribunal de Contas da União,
http://www.tcu.gov.br.
Schubert, K. D., 2004. CIO Survival Guide – The Roles
and Responsibilities of the Chief Information Officer,
Wiley.
ISO/IEC 17799, 2005. Information Technology – Security
Techniques – Code of Practice for Information
Security Management, International Standard
Organization.
Peterson, R. R., 2004. Chapter 2 - Integration strategies
and Tactics form Information Technology
Governance, Idea Group Inc..
Warren, B., 2001. Uma força Irresistível, HSM
Management.
MP, 2007. Ministério do Planejamento, Governo Federal,
www.planejamento.gov.br.
MD, 2007. Ministério da Defesa, Governo Federal,
www.defesa.gov.br.
ICEIS 2008 - International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
182
