
LEARNING OBJECT REENGINEERING BASED ON
PRINCIPLES FOR USABLE USER INTERFACE DESIGN
Robertas Damaševičius
Software Engineering Department, Kaunas University of Technology, Studentų 50, Kaunas, Lithuania
Lina Tankelevičienė
Department of Informatics, Šiauliai University, Visinskio st. 19, LT-77156 Šiauliai, Lithuania
Keywords: e-Learning, Learning Object, reengineering, web-based user interface design, usability.
Abstract: We analyze the problem of reengineering of Learning Objects (LO) for web-based education. Such reengi-
neering must be based on sound methodological background and design principles. We apply methods
adopted from software engineering domain for redesigning the structure and user interface of LOs and aim
both at usability and accessibility of learning material. We evaluate usability of a LO from the user interface
point of view, following the user interface development principles common both for Human-Computer In-
teraction (HCI) and e-Learning domains. We propose the LO reengineering framework based on the user in-
terface usability principles. In a case study, we demonstrate how these principles and recommendations can
be used to reengineer a LO to improve its learnability, understandability and usability in general.
1 INTRODUCTION
E-Learning is learning that uses computer networks
as the delivery or mediation mechanism (Piskurich,
2003). On the other hand, internet technologies are
only a prerequisite for e-Learning. In a holistic view,
e-Learning considers content, technologies, and ser-
vices for delivering well-designed, learner-centered,
interactive, and facilitated learning environment to
anyone, in anyplace, at anytime by utilizing the at-
tributes and resources of various digital technologies
along with other forms of learning materials tailored
for open, flexible, and distributed learning environ-
ment (Khan, 2005).
Main reusable resource in e-Learning is a Learn-
ing Object (LO). From the technological point of
view, the LO consists from (1) teaching material,
and (2) technologies that are used to provide a view
of a LO to the user, i.e. a user interface (UI). As a
part of a LO and entire e-Learning system, the UI is
a very important subsystem, because it is responsible
for the representation of the content and functional-
ity. Depending on the design of the UI, the users of a
computer system or device make their judgment on
the usability of the system as a whole. If the UI of
the system is easy to learn and to use, and it supports
the users in the tasks they wish to undertake, the
users consider the system to be usable (Shiratuddin
et al., 2005).
Different artifacts and instruments are employed
to solve the usability problem such as standards,
principles, guidelines and recommendations (Niel-
sen, 1993; Paramythis and Loidl-Reisinger, 2004;
Mariage et al., 2004). The design and development
of UIs for e-Learning solutions is time consuming,
cumbersome, and usually based on concrete models,
scenarios and recommendations, but not on general
framework or methodology. Furthermore, the reuse
of LOs and their integration into other e-Learning
environments and/or technological platforms also
requires extensive reengineering efforts, too. There-
fore, reengineering of LOs is necessary before im-
porting them into the e-learning system as well as
during LO maintenance. Unfortunately, this step is
often omitted, and the prepared material goes online,
but sound e-learning principles are not implemented.
Recent work in the area of LO reengineering in-
cludes the development of reengineering frame-
works for e-Learning systems (Choquet and Cor-
biere, 2006), and case studies in re-engineering of
LOs for e-Learning and m-Learning (Scalera et al.,
124
Damaševi
ˇ
cius R. and Tankelevi
ˇ
cien
˙
e L. (2008).
LEARNING OBJECT REENGINEERING BASED ON PRINCIPLES FOR USABLE USER INTERFACE DESIGN.
In Proceedings of the Tenth International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems - HCI, pages 124-129
DOI: 10.5220/0001673401240129
Copyright
c
SciTePress

2007). Reengineering of LOs is still an underdevel-
oped topic and Polsani et al. (2003) conclude that
the reengineering of the design and development
process of LOs itself must be improved. In general,
the aim of reengineering is to create knowledge that
is appropriate for the emergent network society
where Human-Computer Interaction (HCI) and web-
based education plays an important role.
The aim of our paper is to show how the concept
and methodology of reengineering adopted from
software engineering domain can be used in deploy-
ing the learning material for web-based education.
Our prior work concerned reengineering of distance
study courses (Tankelevičienė and Demenis, 2007),
and the development of user interfaces for mobile
devices (Damaševičius and Tankelevičienė, 2008),
for eLearning-oriented web pages (Štuikys et al.,
2004) and LOs (Štuikys and Damaševičius, 2007).
The structure of the paper is as follows. Section 2
analyzes the concept of LO reengineering. Section 3
formulates the requirements for LO reengineering
based on Common HCI/e-Learning Principles
Model. Section 4 as a case study presents the reen-
gineering of a LO for teaching computer science
students about array sorting algorithms. Finally, Sec-
tion 5 presents conclusions.
2 CONCEPT OF LEARNING
OBJECT REENGINEERING
The concept of reengineering with its different inter-
pretations is used in software engineering and man-
agement sciences. Software reengineering is con-
cerned with re-implementing a system in order to
make it more maintainable (Sommerville, 2000). In
(Chikofsky and Cross, 1990), reengineering is de-
fined as „the examination and alteration of a subject
system to reconstitute it in a new form and the sub-
sequent implementation of the new form“.
The activities in the software reengineering proc-
ess are: a) Source code translation; b) Reverse engi-
neering; c) Program structure improvement; d) Pro-
gram modularisation; e) Data reengineering (Som-
merville, 2000). They are not all necessary, and are
applied depending on the level on which we want to
renew the system.
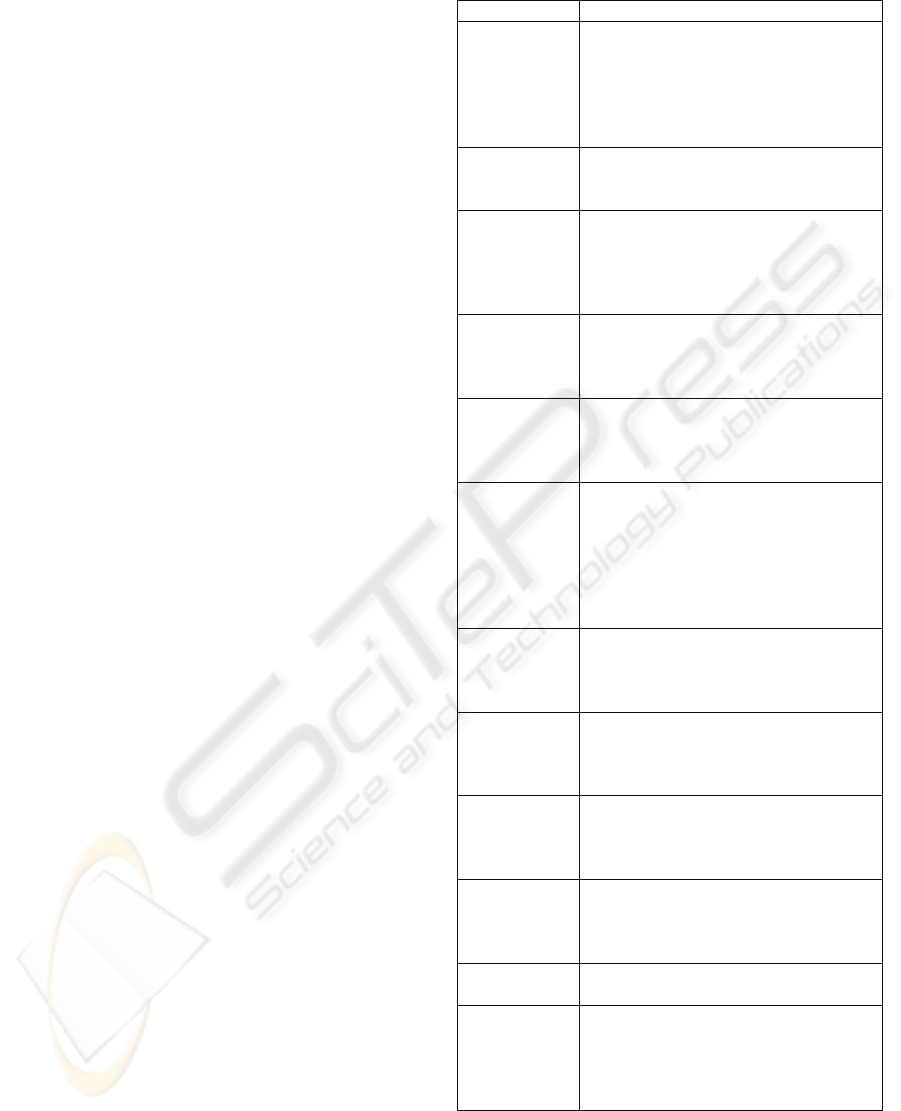
The difference between engineering and reengi-
neering is shown in Figure 1. In reengineering an old
system acts as a specification for a new system.
The main advantages of reengineering are: a)
Reduced risk; b) Reduced cost.
Understanding and
transformation
System
specification
Existing software
system
Reengineered
system
Design and
implementation
New system
Figure 1: Forward engineering and reengineering (Som-
merville, 2000).
The objective of system re-engineering is to im-
prove the system structure and make it easier to un-
derstand. The cost of future system maintenance
should therefore be reduced (Sommerville, 2000).
Here we propose the following framework for
the reengineering of a LO:
1) Identification/evaluation of the existing
LO.
2) Formulation of requirements for reengi-
neering.
3) Development of a reengineering plan.
4) Re-evaluation and adaptation of teaching
objectives, methods and activities.
5) Rewriting of encapsulated teaching mate-
rials following newly formulated aims.
6) Redesign of the user interface of a LO.
7) Reimplementation of LO functionality.
8) Updating/rewriting of a LO documenta-
tion.
Formulation of requirements for reengineering is
the first and, perhaps, the most important step. The
requirements can be technological (e.g., motivated
by platform change), social (adaptation of a course
to a student group with different background), edu-
cational, etc. Technological requirements may in-
clude the following tasks: modularization of LO,
revision of the LO structure to eliminate its defects
according to the principles of structured program-
ming, identification and removal of unneces-
sary/duplicated material/functionality, migration of
LO to another learning environment, porting of LO
to another platform, rehosting (modification of the
LO architecture in order to exploit new technolo-
gies), conversion into another markup/scripting lan-
guage, validation of markup language code, bringing
up to a defined LO usability and web accessibility
standard, enhancement of user interface, optimiza-
tion of LO functionality, inclusion of additional
functionality, bug fixing, etc.
Once the reengineering requirements have been
identified, a reengineering plan needs to be written
on how these requirements are to be implemented.
To maintain control over this process it should be
broken down into distinct steps. The steps should
outline what must be done and what methods (tech-
nologies, standards) should be applied. At the end of
LEARNING OBJECT REENGINEERING BASED ON PRINCIPLES FOR USABLE USER INTERFACE DESIGN
125
each step, a copy of the LO must be saved for ver-
sioning. This means that any problems introduced
during the reengineering process can be quickly
identified and the cause eliminated or addressed.
Once the reengineering process has been com-
pleted and the LO has been tested, any existing LO
documentation should be updated or, if none exists,
written. Documentation is a very important part of
the re-engineering process as it is the primary source
of information that will assist in the future support
and maintenance of the LO. Alongside the descrip-
tion of the content and functionality of the LO and a
quick guide which describes how to use the applica-
tion, it should cover a description of any fundamen-
tal changes that were introduced during the reengi-
neering process.
3 FORMULATION OF
REQUIREMENTS FOR LO
REENGINEERING BASED ON
COMMON HCI/E-LEARNING
PRINCIPLES MODEL
3.1 Didactic e-Learning Principles
The E-Learning methodologies are based on com-
mon didactic principles. After analyzing the litera-
ture in the E-learning domain, the following E-
learning principles were identified (Clark, 2002;
Miles, 2003), which are summarized in Table 1.
3.2 Requirements for UI as a Part of
e-Learning System
The most important feature of e-Learning is interac-
tivity. Therefore, UI design is essential to e-
Learning. Common didactic e-Learning principles
dictate the requirements for designing UI. The main
goal of UI in this context is to support learning. In
order to reach this goal, UI must satisfy the set of
requirements. The basic requirements for UI design
from e-Learning domain are summarized in Table 2.
3.3 User Interface Usability Principles
We formulate the requirements for reengineering
based on Common HCI/e-Learning Principles
Model, which we first proposed in (Damaševičius
and Tankelevičienė, 2008). Here we only summarize
it in Table 3.
Table 1: The e-Learning principles.
Principle Description
Accessibility/
openness
Learning material is accessible to all
potential students. Learners with differ-
ent input level, with specific educa-
tional needs, etc. can participate without
interruption of the work; Openness of
the communication forms and tools.
Adaptability/
Individualiza-
tion
The ability to adapt the e-learning sys-
tem and learning materials to the learner
and context.
Engagement The e-learning system should be pleas-
ant to use end ensure learners visual
satisfaction and active engagement,
supports learner’s motivation and desire
to pursue a goal or perform a task.
Flexibility/
Learner cen-
teredness
Freedom to chose time and place for
learning, content. Focus on the needs of
learner. Multiple instructional methods
are used in order to gain better results.
Interactivity/
Feedback
Support for indirect personal interac-
tions student-student, student-teacher,
etc. Provision of appropriate and infor-
mative feedback within reasonable time.
Modularity The curriculum consists of different
courses depending on the individual and
group educational necessities, learning
material and learning activities. The
content of the learning materials should
be built on the basis of the major learn-
ers’ activities.
Problem-
orientation
Learning content and activities must be
problem-oriented. The learning content
should reflect multiple viewpoints to the
problems and their possible solutions.
Relevancy,
reflexivity
Learners’ awareness of the content and
the ways to participate in the learning
activities, and especially – of their own
personal development and acquisitions.
Responsibility/
control
Strict regulation and management of the
activities using information technolo-
gies (IT). Control encourages responsi-
bility.
Self-direction/
autonomy
Instructions should be customized as
much as possible to the individual
learner. A trainer should act more as a
facilitator than a teacher.
Suitability Avoidance of unnecessary and peda-
gogically ungrounded use of IT.
Usability/
Support
Creation of a user-friendly environment
for learning process support. Support of
content, interface, methods, strategies,
etc. Efficient and convenient use of an
e-learning system.
ICEIS 2008 - International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
126
Table 2: E-learning domain requirements related to the UI
design.
Re-
quire-
ment
Description Strategies
(recommendations)
Multi-
modal-
ity
Modality is the communi-
cation path in which we
receive information from
surrounding environment.
There are four types of
modalities: verbal, visual,
aural, tactile-kinestetic.
Presenting content
and activities in more
than one modality to
increase choice and
control.
Mini-
mizing
cogni-
tive load
Cognitive load must be
oriented toward learning
task. The user doesn’t
need to think what to do in
the window (page, UI).
UI must be coherent,
consistent, transpar-
ent, polite, positive,
relevant and clear.
Reflec-
tion
Reflecting content struc-
ture, task, learning theory,
learning model (the
transmission model; the
learner centered model;
the participative model),
the learner (adaptivity,
personalisation).
Pay different atten-
tion to designing
appearance and func-
tionality. Realize
different levels of
adaptivity for presen-
tation, interaction,
course delivery,
content discovery
and assembly.
Building
mental
models
A mental model is a per-
son's internal (mental)
representation of some
area of the world. The
mental model is built or
reassembled as an out-
come of learning.
To show the various
states of and relation-
ships with the con-
cepts, for example,
including graphics
and animation.
Table 3: Principles of HCI for UI design.
Principle Description Example
recommendations
Accessibil-
ity
The degree to which a
system can be used com-
fortably by a wide variety
of people.
Allow adjustment
of font size.
Affor-
dance
Connection between a
user interface and its func-
tional and physical proper-
ties.
Use interface ele-
ments similar to
real world objects.
Consis-
tency/
organiza-
tion
A harmonious uniformity
or agreement among parts
of a system.
Use familiar pat-
terns of interac-
tion.
Error tol-
erance/
reliability
The ability of a system or
component to continue
normal operation despite
the presence of erroneous
inputs.
Error messages
should be in plain
language, indicate
a problem, and
suggest a solution.
Feedback The return of information
about the result of a proc-
ess or activity.
Keep the user
informed about the
state and actions
of a system.
Table 3: Principles of HCI for UI design (cont.).
Principle Description Example
recommendations
Flexibility The ease with which a LO
can be modified for use in
environments other than
those for which it was
originally designed.
Allow the users to
customize inter-
face according to
their preferences.
Learnabil-
ity/ memo-
rability
The ability of the user to
learn how to use a system
and to remember its opera-
tional principles.
Dialogues should
not contain irrele-
vant or unneeded
information.
Satisfac-
tion
The comfort of a system
to its users.
Avoid using very
bright colours.
Simplicity The degree to which a LO
has an interface that is
straightforward and easy
to understand.
Keep the number
of interface ele-
ments visible to
the user minimal.
Standardi-
zation
Adherence to standards/
recommenda-
tions/guidelines.
Follow standards
and/or guidelines
where possible.
4 REENGINEERING OF A LO
FOR TEACHING ARRAY
SORTING ALGORITHMS
4.1 Identification of the Existing LO
We consider LOs for teaching the array sorting algo-
rithms. Such LOs could be used in different pro-
gramming teaching courses to demonstrate the prin-
ciples and effectiveness of the array sorting algo-
rithms within the internet-based e-learning environ-
ment. The LO was assembled from the teacher’s
lecture materials and implemented in
HTML+Javascript, which can be distributed over
Internet. The HTML part of the LO is used for pres-
entation of the natural language description of a sort-
ing algorithm and presentation of its implementation
in a specific programming language, while
Javascript is used for demonstration of the principles
or effectiveness of a specific sorting algorithm.
The LO as seen via the internet browser is shown
in Figure 2. The LO introduces the student with the
description and implementation of the Bubble sort
algorithm, and demonstrates it in action. The array
for sorting is generated after pressing the button
“Generate”. And then the sorting process is demon-
strated after pressing the button “Bubble sort”.
LEARNING OBJECT REENGINEERING BASED ON PRINCIPLES FOR USABLE USER INTERFACE DESIGN
127
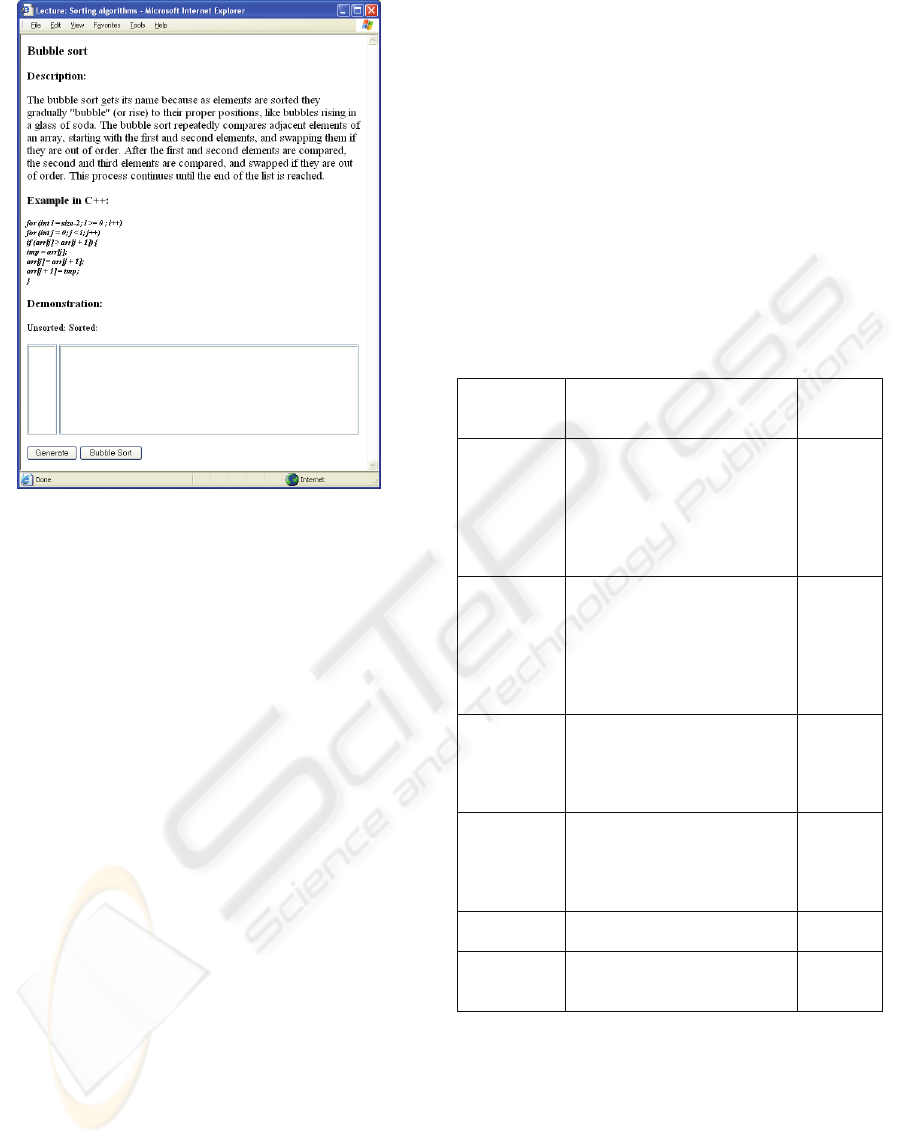
Figure 2: LO view before reengineering.
4.2 Formulation of Requirements
This LO was designed with no regards to the HCI
and e-Learning principles and therefore, it should be
reengineered to be usable for e-learning. The re-
quirements for reengineering are as follows: 1) in-
crease accessibility, 2) provide more visualization
capabilities, 3) provide modularity/structurization of
LO content, 4) increase consistency.
4.3 Development of a Reengineering
Plan
The developed reengineering plan: 1) change the
structure of the LO interface, add content and sepa-
rate pages for each LO part, 2) increase visualization
capabilities by providing animation using Java app-
let, 3) increase consistency by using CSS technol-
ogy, 4) increase accessibility by providing the user
with more flexibility for font size adaptation.
4.4 Re-evaluation of Teaching
Objectives, Methods and Activities
No modification of teaching objectives, methods and
activities was planned.
4.5 Rewriting of Teaching Materials
Modification of teaching material was not intended.
4.6 Redesign of the LO user Interface
Interface of the LO was redesigned following the
principles and recommendations of the Common
HCI/E-Learning Principles Model (Damaševičius
and Tankelevičienė, 2008). The modifications of the
LO during reengineering are summarized in Table 4.
The reengineered LO is shown in Figure 2.
The advantages of the reengineered LO are as
follows: better structure and organization of content,
support for learner engagement, better visualization
capabilities, higher interface flexibility, accessibility
and learnability.
Table 4: Changes/modifications of LO for adaptation to e-
Learning domain.
Change Motivation Sup-
ported
principles
Site structure
modified:
content sepa-
rated into
separate
views
To support simplicity, clarity, to
provide better structure, to in-
crease to modularity, to realize
individualization – the material
review sequence can be chosen
by the learner. Higher level of
interactivity implemented.
Simplic-
ity, Struc-
ture
Section
Vizualization
added
To support mental model build-
ing process, variety, multimo-
dality, to invoke attention, and
to support staying active
learner. Proportion of absorb
type (presentation) and do type
(discovery) activities increased.
Flexibil-
ity, En-
gagement,
Feedback/
Interaction
CSS file
added
To support consistency (layout
and position of navigation is
consistent across a site), easier
modification (content and its
layout are separated).
Accessi-
bility
Page design
modified
To show better structural parts
of information presented. Indi-
rect control implemented (parts
show learning objectives: to be
able to explain and to program).
Structure,
Learnabil-
ity
Page heading
incorporated
To show where the user is in the
space of information.
Structure
Font sizes
replaced with
ems (em).
To support accessibility func-
tions of web browsers.
Accessi-
bility
4.7 Reimplementation of Functionality
Visualization of Array sorting algorithms was im-
plemented in Java applet (see Figure 3), which al-
lows more capabilities for graphics and animation.
ICEIS 2008 - International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
128
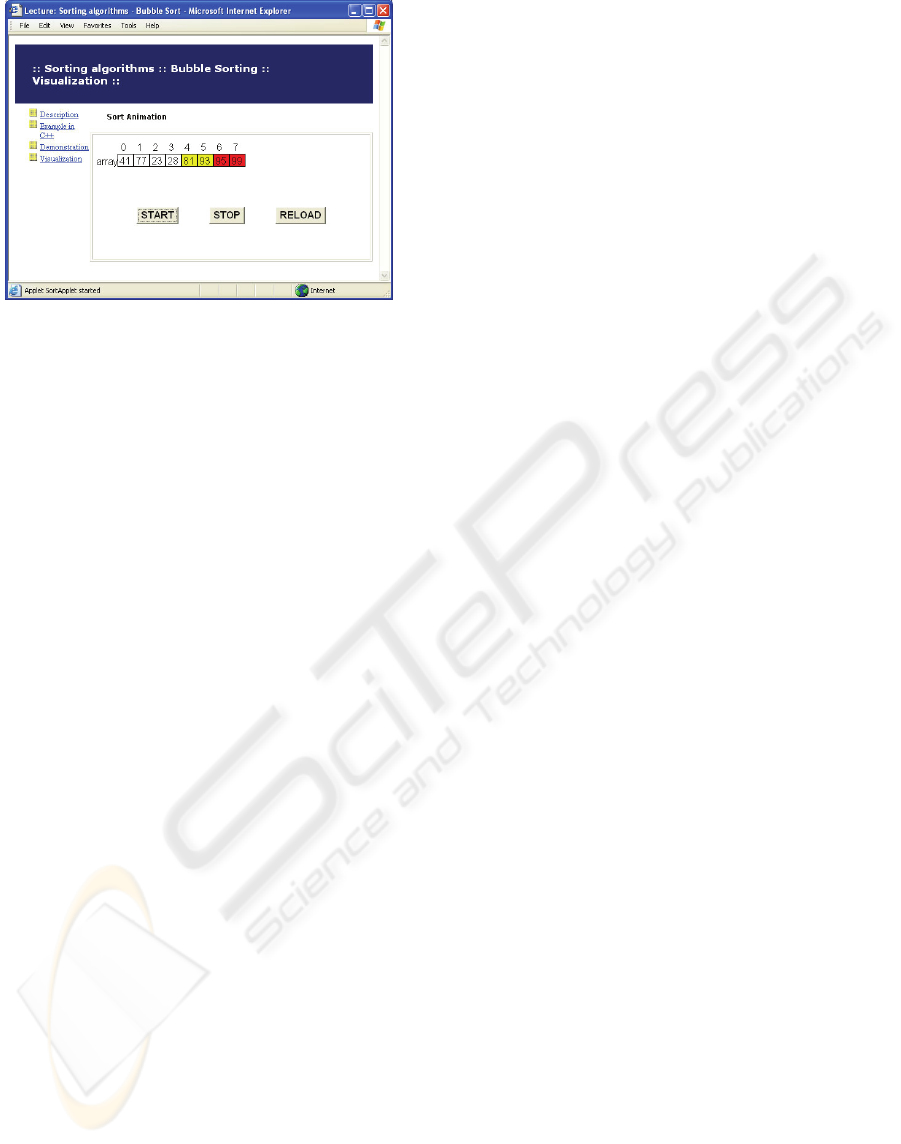
Figure 3: View of the LO after reengineering following
the HCI/e-Learning principles (a fragment).
4.8 Writing of LO Documentation
The original LO was undocumented. Therefore, its
documentation had to be written from scratch. It
contains creation/modification dates, author names,
title, learning objectives, short description of avail-
able learning materials, description of interaction
means (buttons, input/output forms, links), and re-
quirements for deployment.
5 CONCLUSIONS
We have analyzed the problem of reengineering of
Learning Objects. and formulated 8 basic steps for
the reengineering process: 1) Identification/ evalua-
tion of the existing LO. 2) Formulation of re-
quirements for reengineering. 3) Development of a
reengineering plan. 4) Re-evaluation and adaptation
of teaching objectives, methods and activities. 5)
Rewriting of encapsulated teaching materials
following newly formulated aims. 6) Redesign of
the user interface of a LO. 7) Reimplementation of
LO functionality. 8) Updating/writing of LO docu-
mentation.
The requirements for reengineering are formu-
lated based on common user interface design princi-
ples formulated for the HCI and E-Learning do-
mains: Accessibility, Affordance, Consis-
tency/Organization, Error tolerance/Reliability,
Feedback, Flexibility, Learnability/Memorability,
Satisfaction, Simplicity, Standardization.
The LO reengineering framework proposed in
this paper allows to increase quality and usability of
LOs for web-based distance education systemati-
cally.
REFERENCES
Chikofsky, E.J., and Cross, J.H., II. (1990). Reverse engi-
neering and design recovery: a taxonomy. IEEE Soft-
ware 7(1):13 – 17.
Choquet, C., and Corbière, A. (2006). Reengineering
Framework for Systems in Education. Educational
Technology & Society, 9 (4), 228-241.
Clark, R. (2002). Six Principles of Effective e-Learning:
What Works and Why. Learning Solutions e-
Magazine, September, 2002.
Damaševičius, R., and Tankelevičienė, L. (2008). Merging
HCI and e-Learning Domain Oriented Design Princi-
ples for Developing User Interfaces for Mobile De-
vices. Int. Conf. on Innovations in Learning for Future
E-Learning, March 27-29, 2008, Istambul, Turkey.
Khan, B. H. (2005). Managing E-Learning: Design, De-
livery, Implementation and Evaluation. Information
Science Publishing.
Mariage, C., Vanderdonckt, J. and Pribeanu, C. (2004).
State of the Art of Web Usability Guidelines. In Proc-
tor, R.W. and Vu, K., The Handbook of Human Fac-
tors in Web Design, Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Miles, D.H. (2003). The 30-Second Encyclopedia of
Learning and Performance: A Trainer's Guide to The-
ory, Terminology, and Practice. AMACOM.
Nielsen, J. (1993). Usability Engineering. Academic
Press, San Francisco.
Paramythis, A. and Loidl-Reisinger, S. (2004). Adaptive
Learning Environments and e-Learning Standards.
Electronic Journal of e-Learning 2(2).
Piskurich, G. M. (Ed.) (2003). The AMA Handbook of E-
Learning: Effective Design, Implementation, and
Technology Solutions, AMACOM, USA.
Polsani, R. P. (2003). Use and Abuse of Reusable Learn-
ing Objects. Journal of Digital Information, 3(4), 164.
Scalera, M., V.N. Convertini, A. Marengo, V. Marengo,
and A. Serra (2007). Re-Engineering of a Flash Based
Application for Mobile Learning. Proc. of the 2007
Computer Science and IT Education Conference.
Shiratuddin, N., Hassan, S., Landoni, M. (2003). A usabil-
ity study for promoting e-content in higher education.
Educational Technology & Society 6(4):112-124.
Sommerville, I. (2000). Software Engineering (6th Ed.).
Addison-Wesley, Reading Massachusetts.
Štuikys, V. and Damaševičius, R. (2007). Towards
Knowledge-Based Generative Learning Objects. In-
formation Technology and Control 36(2), pp. 202-212.
Štuikys, V., Damaševičius, R. and Montvilas, M. (2004).
A Metaprogramming-Based model for Generation of
the eLearning-Oriented WEB Pages. Proc. of the 2nd
Int. Conf. on Information Technology: Research and
Education (ITRE 2004), June 28-July 1, London, Eng-
land, 64-68.
Tankelevič
ienė, L., and Demenis, T. (2007). Distance
study course reengineering based on triple consistency
principle and requirements for computer science stu-
dents. Proc. of Conf. on Innovative Information Tech-
nologies IIT-2007, November 8-9, Vilnius, Lithuania.
LEARNING OBJECT REENGINEERING BASED ON PRINCIPLES FOR USABLE USER INTERFACE DESIGN
129
