
INTEGRATING LABOR SKILLS CERTIFICATION WITH
TRADITIONAL TRAINING FOR ELECTRIC POWER
OPERATORS
R. Molina
1
, I. Paredes
2
1
Gerencia de Sistemas Informáticos, Instituto de Investigaciones Eléctricas, México
2
Unidad de Servicios Técnicos, Comisión Federal de Electricidad, México
M. Domínguez, L. Argotte, N. Jácome
Gerencia de Sistemas Informáticos, Instituto de Investigaciones Eléctricas México
Keywords: Web Databases, Information Systems Integration, Competences, Skills, Training.
Abstract: In this paper the integration of a traditional training system with a competence management model is
conceptually described. The resulting e-system is accessed through powerful Web interfaces and contains a
comprehensive database that maintains information of the two models. The traditional model emphasizes
the contractual worker training rights and the skills model the alignment of the human talent with the
mission and objectives of the company. The paper describes the specific traditional training model of CFE
(Federal Electricity Commission), its competences model and the integration of the two models following a
thematic contents approach.
1 INTRODUCTION
Derived from governmental policies related to
training management and considering its strategic
planning objectives, CFE (Comisión Federal de
Electricidad – the National Electric Utility in
Mexico, a 70,000 employee power company) has
established a strategic program to improve its human
capital offering 10 training days per year for each
employee. This program is related to labor skills for
CFE that is responsible for generating, transmitting
and distributing electricity through out the Mexican
nation.
In the literature there are papers that describe
labor skills systems (Hatfield, 2007) (Glen, 2006)
(Riley, 1994) but none includes the integration with
training. In this paper first, a traditional training
model of CFE is presented, second, the model of
labor skills management and certification is
described, and third, the integration of the two
models is discussed.
2 THE TRADITIONAL TRAINING
MODEL
For more than 20 years, CFE has executed a training
program that includes a coherent and comprehensive
group of standards developed. The norms are
classified in four groups:
Planning: Position Profiles, Training Batteries,
Training profile per worker, Individual Knowledge
Matrix, Individualized Training Program, Specific
problem solution oriented program
Organization and Integration: Revision,
consolidation and authorization of the annual
training program, Instructors' development.
Execution: Execution, Budget, Reports, Statistical
Control: Diagnostic evaluations, Partial evaluations,
Course reports and credits, Worker's evaluation in
his position, aptitude record,
The objective of the traditional program is to
obtain an annual training program of individualized
courses with impact in the productivity indexes.
CFE classifies the hundreds of employee
positions of its organizational chart into organic
groups or levels (from I to XII) depending on the
429
Molina R., Paredes I., Domínguez M., Argotte L. and Jácome N. (2008).
INTEGRATING LABOR SKILLS CERTIFICATION WITH TRADITIONAL TRAINING FOR ELECTRIC POWER OPERATORS.
In Proceedings of the Tenth International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems - DISI, pages 429-432
DOI: 10.5220/0001682304290432
Copyright
c
SciTePress
position responsibility (director, manager,
department boss, operator, clerk, etc.), the position
participation in business processes (generation,
transmission, distribution) or support processes, if
the position is unionized, and the remuneration level.
For each employee a career plan defines the
positions that are allowed for the worker to pass
from his current position level to a position in an
organic level immediately superior and to other
positions up in the organizational hierarchy.
Each position in the organization has an assigned
profile that it includes one or more specialties, for
example:
Maintenance (mechanic, instrumentation,
electric);
Operation (analysis and results, engineering,
chemical);
Planning (supply, analysis, studies);
Services (billing);
etc.
The specialties are classified in levels that match
with the academic levels: secondary, high school,
primary technician, secondary technician, bachelor,
graduate, master, and doctorate. In this fashion, the
annual training needs are detected.
3 LABOR SKILLS
CERTIFICATION MODEL
A competency, job or labor skill is a specific
capacity to perform a productive function in
different labor contexts on the basis of obtaining
quality results in the corresponding productive
sector. A job skill standard indicates which
knowledge, abilities and attitudes define the
competence. A productive sector is a part of the
society that specializes in some type of activity, for
example, agriculture, health, or energy (Molina and
Rodriguez, 2005).
In contrast with a traditional training system, the
main objective of a job skills management system or
program is to certify individuals in knowledge,
skills, expertise, abilities, and attitudes appropriate
for specific enterprise productive functions
independent of how they acquired them.
3.1 Job Skills Technical Standards
Management
In this section, the JSTS management module of the
e-system is described. It includes the productive
functions map for the electric sector, the
collaboration mechanisms for the JSTS
development, printing and publishing, and the
content structures to manage their storage.
A Job Skill Technical Standard (JSTS) is defined
and developed by a Job Skill Standard Committee
(compose of methodologists, technicians and
specialists, among other) authorized by CFE, and
approved by the National Council for Job Skills
Standardization and Certification (CONOCER,
Spanish initials) and sanctioned by the Public
Education and the Work and Social Affairs
Secretaries of State. A JSTS establishes, for
repeated and common use in the whole Mexican
States territory, the characteristics and the guidelines
for the evaluation of capacity or labor competence.
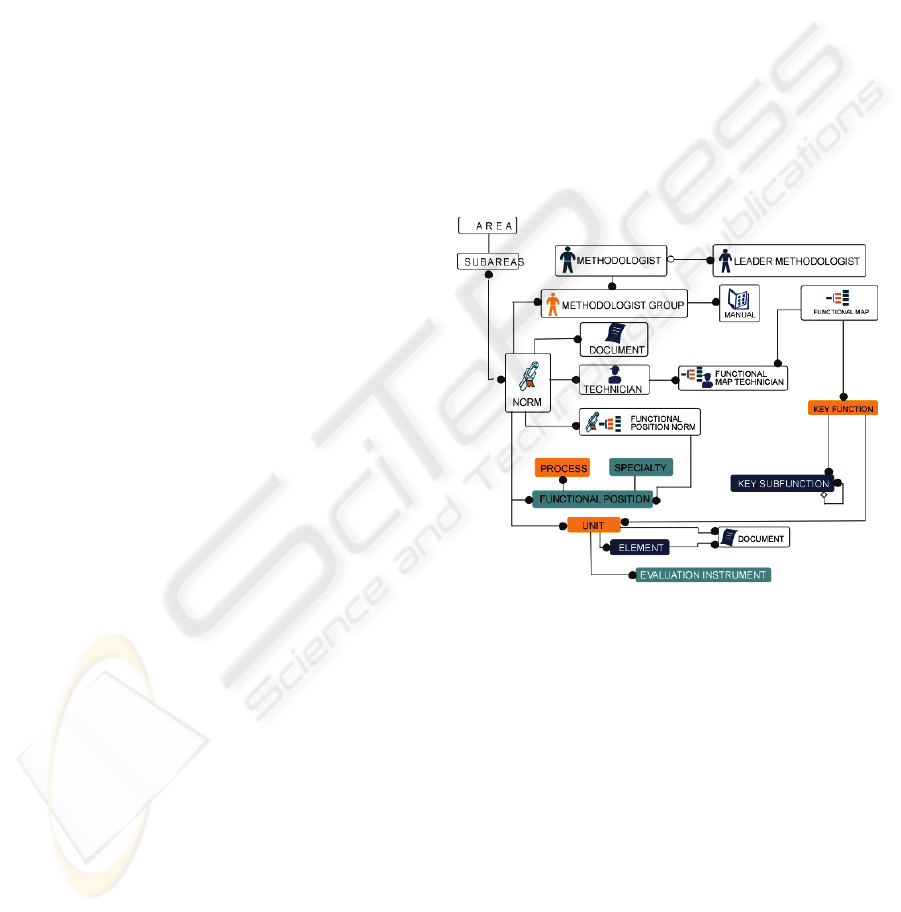
In Figure 1, a semantic model is shown for the
normalization management that has been
implemented with a relational database management
system.
Figure 1: Semantic Model for job skills normalization.
The methodologists (leader, group, and observer)
support the generation of the knowledge included in
a JSTS, and the experts (technicians) in a productive
function contained in the company’s functional map
provide the knowledge. Roughly, the functional map
of the CFE is a functions hierarchy or tree where the
functions corresponding to the highest level are four:
1. To operate the equipment for electric power
generation, transmission, transformation and
distribution.
2. To maintain the equipment for electric power
generation, transmission, transformation and
distribution under operating conditions.
3. To manage the operation and energy transactions
of the Power Electrical System.
4. To provide the electric power utility service.
ICEIS 2008 - International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
430
It is no the intention of this paper to show the
complete functional map for each one of the four
mentioned highest level functions, it would be very
extensive. All functions are composed of sub-
functions.
For example, for the function 2.2.1.4.2 several
standards are at hand, one of those is the norm:
CCFE0628.01 Mechanical maintenance of steam
turbines with high and low pressure cylinder.
In this way, CFE had to elaborate a JSTS for
each one of the lowest level productive functions of
the company (approximately two hundred norms).
A JSTS or norm contains units and a unit
contains elements. In turn, the elements include
evaluation instruments that are the performance
criteria related with categories, in such a way that
for an element different skills evidences can be
assessed, either for abilities, for knowledge or for
attitudes.
The functional map structure defines the
enterprise purpose; it defines the strategic key
functions, and recursively the more basic key sub-
functions. To the lowest level key functions of in
this hierarchy corresponds a certain number of
standard elements. Both the norms and the
functional map are documents that can be stored in
electronic format files.
Note that a JSTS applies to one or more
company processes (Generation, Transmission,
Transformation, Control or Distribution), and a
process is ruled by one or more norms.
In a similar way, a JSTS can be assigned to one
or more functional positions in the organization and
a position is ruled by one or more norms. One can
observe that to work in a company position, a
person will have to be certified in several labor
competences.
Each standardized competence or labor skill has
assigned a performance level according to the
English NVQ system (National Vocational
Qualification). This classification of the
competences is in five performance levels, based on
different variables: complexity of the behavior,
variety of acting in different contexts, autonomy
and responsibility, requirement level, and of the
collaboration management of other people and
resources.
3.2 Model for JSTS Certification
A Web system was developed for the planning,
evaluation and certification of CFE’s personnel in
labor competences. The model includes structures
to record and monitor the personnel's certification
process: from the candidate’s interview, his
evaluation, until his final registration at
CONOCER.
4 INTEGRATING THE LABOR
SKILLS MODEL AND THE
TRADITIONAL TRAINING
MODEL
The integration of the traditional model and the
labor skills model includes several aspects like the
personnel recruitment; the diverse levels the
specialties, and the course batteries of the
employees' career plans. The objective is that the
traditional training model supports to the
employees' labor competences certification without
affecting the training contractual rights.
The approach followed to integrate the labor
skills concept with traditional training is centered in
the concept of thematic content that the training
course programs will have to include to support the
employee in the labor skills certification. The idea
is to establish and achieve thematic consistency
between the elements of the labor skills norms of
the functional map key functions and the specialty
courses of the employee position profiles.
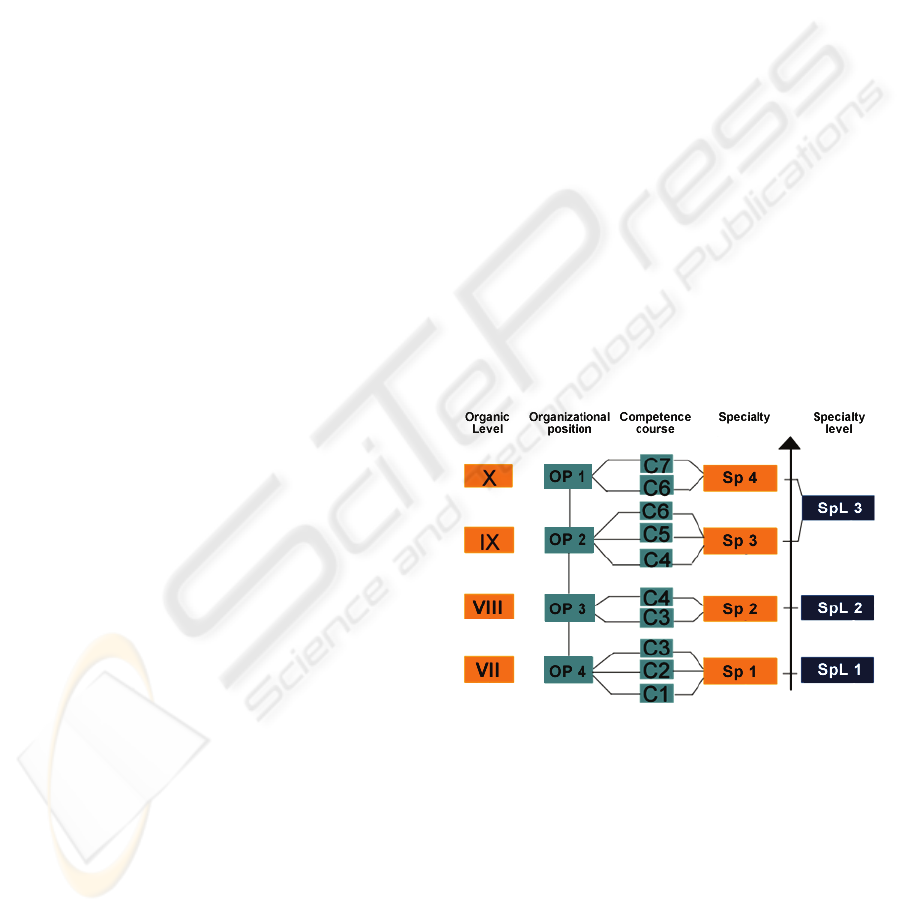
Figure 2: Competence oriented specialty courses.
The convergence process includes the following
steps:
1. Find the business and productive functions from
the organizational positions.
2. Correlate the elements of the functional map key
functions with the productive functions of the
organizational positions.
3. The set of specialties (SP1, SP2,... SPn) is
obtained from the position profiles of the productive
organizational functions.
4. The configuration of specialties based on skills or
competences (c1, c2, … cn) is achieved by
INTEGRATING LABOR SKILLS CERTIFICATION WITH TRADITIONAL TRAINING FOR ELECTRIC POWER
OPERATORS
431
correlating the thematic content of the skills norm
with the content of the specialties courses and
adapting them or creating new contents to impact
the competence certification.
In this fashion, a specialty is a group of
competences, Sp1 = C1 + C2 +. + Cn, (see Figure
2).
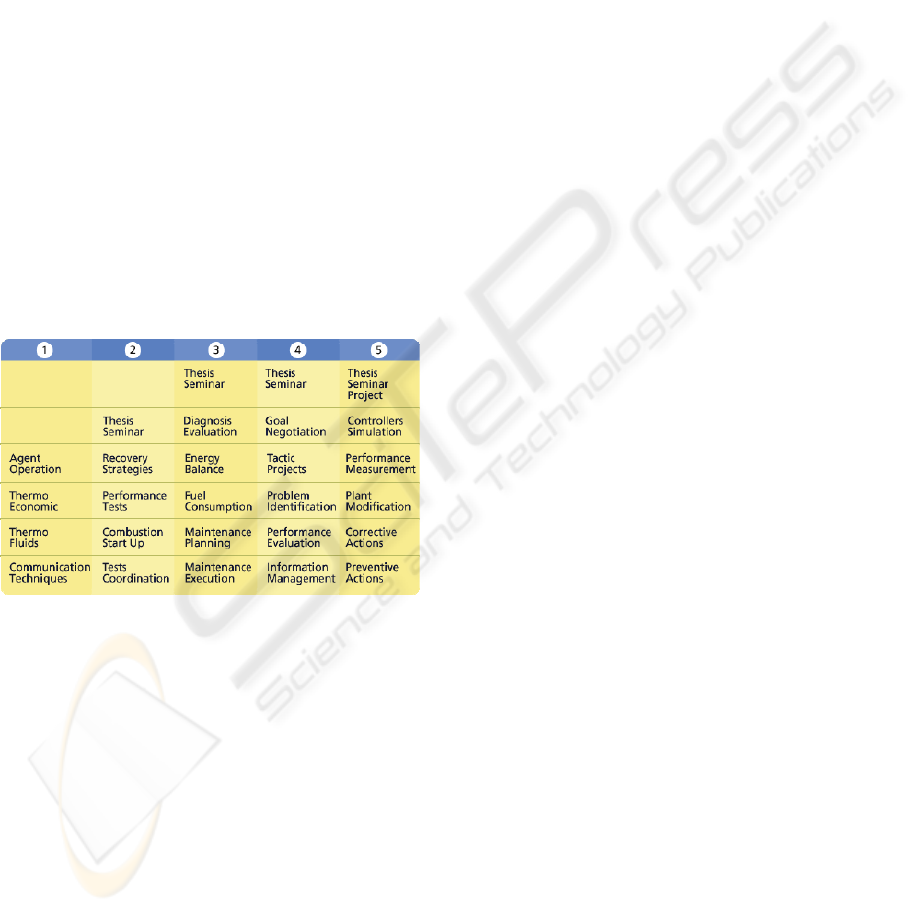
As an example of a competence oriented
analysis for the courses thematic contents of master
level specialty, the design of a master degree
curriculum in power plant operation is briefly
described.
The analysis was carried out in a joint project
with the National Polytechnic Institute, one of the
most prestigious academic institutions en Mexico,
and the result is a 5 semester master in engineering
curriculum shown in the Table 1 where the courses
in shady background represent competence oriented
courses with thematic contents matched to the
thematic contents of labor skills. The first generation
of 15 employees will graduate by the end of the
spring of 2008.
Table 1: Competence oriented master in power plant
operation specialty courses.
The dimensions used in CFE to classify the
training levels are the organic position levels of the
employees, the competence or skill levels and the
specialty levels.
With these levels CFE knows if its personnel
have the appropriate qualification to his position
profile, competences and specialties, and to make
decisions with regard to the alignment of the labor
activities of his workers with the processes and
functions of the company.
5 THE e-SYSTEM
An e-system was developed that implements the
Web interfaces and the semantic nets that contain
the information of the training traditional system,
the competence management model and the
integration of the two models with competence
oriented courses.
The system has software for the production of
more than 130 interactive reports including the
following executive ones: Functional maps
displays; Listings of norms, granted certificates and
evaluation centers; The worker's record in terms of
positions, taken courses, competences and
specialties; Number of employees by organic level
that comply or not with the position profile of the
level of specialty and skills; Etc.
6 CONCLUSIONS
An e-system that integrates the competence
certification management and the traditional training
in a company that generates, transmits and
distributes electric power was conceptually
described. In the system CFE registers, among other
information, functional maps, competence and
training standards, planned and taken courses, and
the training record of each one of the 70,000
employees, and obtains executive reports that allow
to know if the employees comply or not with the
their organization position profile in terms of
specialty and competence levels.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We thank to Guillermo Rodriguez for his
collaboration in writing and reviewing this paper.
REFERENCES
Hatfield, D., 2007. Using a skills bank for work-based
learning. Education + Training. Emerald Group
Publishing Limited.
Glen, C., 2006. Key skills retention and motivation: the
war for talent still rages and retention is the high
ground. Industrial and Commercial Training. Emerald
Group Publishing Limited, ISSN 0019-7858.
Riley, M., 1994. Tracing Skills Accumulated through
Experience. A Method of Skill Auditing. Education +
Training, MCB University Press.
Molina, R., Rodríguez-Ortiz, G., Paredes-Rivera, I.,
Argotte, L., Domínguez, M., Jácome, N., 2005. A
Knowledge Management Model for Job Skills in a
Power Company. 9th World Multi-Conference on
Systemics, Cybernetics and Informatics. ISBN 980-
6560-29-9, pp. 1-6
ICEIS 2008 - International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
432
