
NEURAL NETWORKS APPLICATION TO FAULT DETECTION
IN ELECTRICAL SUBSTATIONS
Luiz Biondi Neto, Pedro Henrique Gouvêa Coelho
Electronics and Telecommunications Department, State University of Rio de Janeiro - UERJ
Rua São Francisco Xavier, nº 524, Bl. A, Sala 5036, Maracanã, 20550-013, Rio de Janeiro, RJ, Brazil
Alexandre Mendonça Lopes, Marcelo Nestor da Silva
AMPLA Energia e Serviços S.A., Praça Leoni Ramos, nº 1, São Domingos, Niterói, RJ, Brazil
David Targueta
Pro-Energy Engenharia LTDA, Rua cinco de Julho nº322, sala 902, Icaraí, Niterói, RJ, Brazil
Keywords: Fault detection in substations, Alarm Processing, Neural Networks, Decision Making Support.
Abstract: This paper proposes an application of neural networks to fault detection in electrical substations, particularly
to the Parada Angélica Electrical Substation, part of the AMPLA Energy System provider in Rio de Janeiro,
Brazil. For research purposes, that substation was modeled in a bay oriented fashion instead of component
oriented. Moreover, the modeling process assumed a substation division in five sectors or set of bays
comprising components and protection equipments. These five sectors are: 11 feed bays, 2 capacitor bank
bays, 2 general/secundary bays, 2 line bays and 2 backward bays. Electrical power engineer experts mapped
291 faults into 134 alarms. The employed neural networks, also bay oriented, were trained using the
Levenberg-Marquardt method, and the AMPLA experts validated training patterns, for each bay. The test
patterns were directly obtained from the SCADA (Supervisory Control And Data Acquisition) digital
system signal, suitably decoded were supplied by AMPLA engineers. The resulting maximum percentage
error obtained by the fault detection neural networks was within 1.5 % which indicates the success of the
used neural networks to the fault detection problem. It should be stressed that the human experts should be
the only ones responsible for the decision task and for returning the substation safely into normal operation
after a fault occurrence. The role of the neural networks fault detectors are to support the decision making
task done by the experts.
1 INTRODUCTION
Electrical substations evolved rapidly in time not
only in their conception but also in their protection
equipment that are now fully electronic instead of
electromechanical, in the digital substation age. The
Standard IEC (International Electromechanical
Commission) 61850 and the possibility of using high
speed and reliable Ethernet LAN networks brought
new developments to the area. Such developments
include sharing information among several IEDs
(Intelligent Electronic Devices) as well as the
capability of providing these information to several
Electrical Energy Companies users or industrial
heavy consumers (Cascaes et alli., 2007) As a
natural consequence, the current supervision,
automation, and control systems are gradually being
adapted to that new reality that is present in the
Brazilian electrical sector. Nowadays, the main
facility to aid the operator in the supervision system
system comprised by multiple alarms having the
purpose of making the operator aware of the
problems that is afflicting the electrical sector
(Chan, 1990). The operator must detect the fault
based on the set of fired alarms and proceed to the
corrective action towards a quick recover of the
system and to normal operation conditions. So all
the responsibility to return the system to normal
operation lies on the shoulders of the operator which
can suffer a lot of stress and pressure. Due to
484
Biondi Neto L., Henrique Gouvêa Coelho P., Mendonça Lopes A., Nestor da Silva M. and Targueta D. (2008).
NEURAL NETWORKS APPLICATION TO FAULT DETECTION IN ELECTRICAL SUBSTATIONS.
In Proceedings of the Tenth International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems - AIDSS, pages 484-487
DOI: 10.5220/0001697204840487
Copyright
c
SciTePress
operator fatigue and inexperience, and an excessive
number of simultaneous fired alarms, usually a
significant number of wrong diagnostics occur
which seriously affects security and efficiency in
electrical systems (Kwang-Ho et alli., 1993).
Modern techniques (Biondi et alli., 2007) such as
Neural Networks can help in the solution of the
problem, leaving the operator focused on the
corrective action in which his or her participation is
very important. The investigated substation is part of
the AMPLA system and is called Parada Angélica
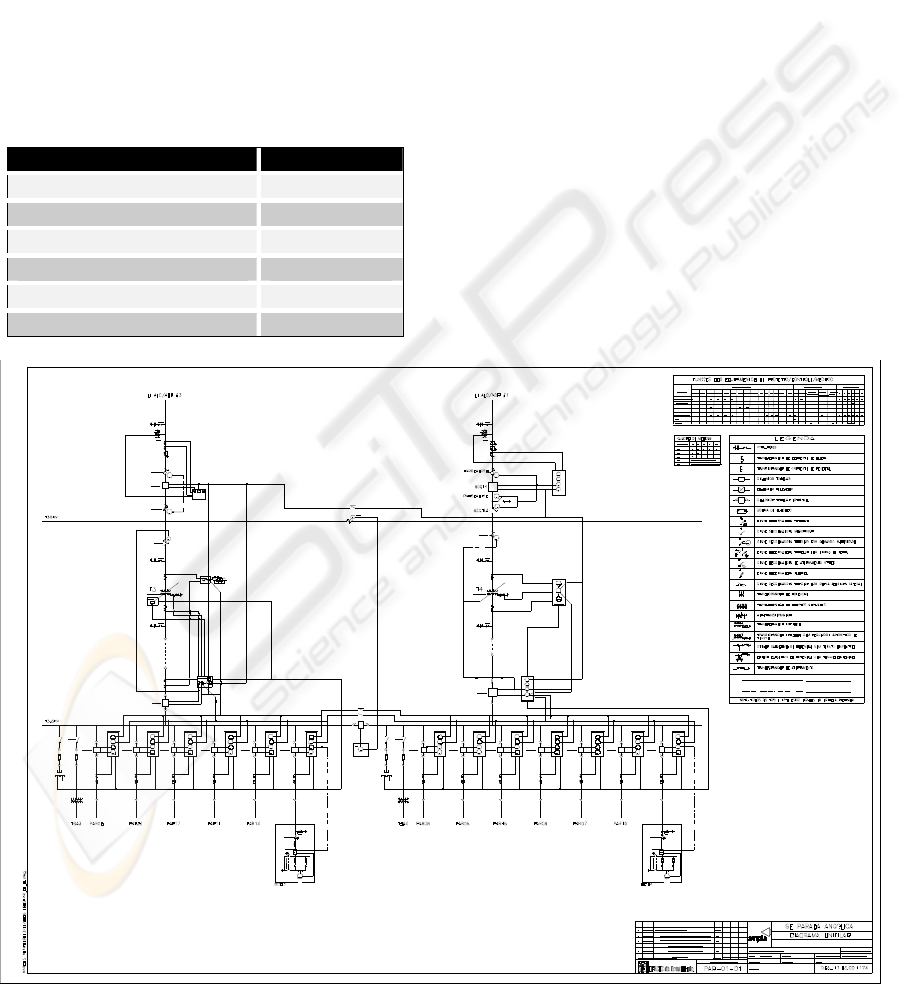
(PAR) which diagram is shown in Figure 1.
The susbstation comprises 19 BAY’s as indicated in
Table 1 and shown in Figure 1.
Table 1: BAY's Distribution in the substation.
Type of BAY Quantity
Feeder 11
Capacitor Bank 02
General/Secondary 02
Line 02
Backward 02
TOTAL 19
Feeder BAY’s are the following: PAR 5,
PAR 22, PAR 17, PAR 11, PAR 14, PAR
8, PAR 6, PAR 15, PAR 9, PAR 7, and
PAR 10.
Capacitor Bank BAY’s are: BCO 3 and
BCO 4.
General/Secundary BAY’s are: General
T3 and General T4.
Line BAY’s are: LI ALC/ADR # 3 and LI
ALC/ADR # 1.
Backward BAY’s are: all other BAY’s.
diferindo apenas, relativamente às linhas LI
#3 e LI #1.
The substation in study has two (138/13.8 KV)
three-phase transformers (TRAFO), and a high and a
low Bus (BUS), subdivided in two, connected by a
link disconnector.
Figure 1: Parada Angélica Substation Diagram.
NEURAL NETWORKS APPLICATION TO FAULT DETECTION IN ELECTRICAL SUBSTATIONS
485
2 DATA PREPROCESSING
The AMPLA data base concerning the mapping of
alarms into faults characterizes, in a reliable way,
the Parada Angélica substation operation in respect
of alarms processing. The dimension of the matrix
which maps alarms into faults, for each bay, is
shown in Table 2, for 291 faults.
Table 2: Mapping Dimension.
BAY Alarms X Faults
Feeder 16 x 20
Capacitor Bank 19 x 20
General/Secondary 19 x 62
Line 13 x 32
Backward 67 x 157
Table 3 shows the mapping of alarms into faults,
only for the line Bay. The mappings concerning the
other neural networks were not shown here due to
the oversize of such Tables. As seen in Table 3, each
fault is defined by the set of fired alarms and that
behavior is trained by 5 neural networks, one for
each substation Bay.
Table 3: Line BAY Mapping.
A 0
1
A
0
2
A
0
3
A
0
4
A
0
5
A
0
6
A
0
7
A
0
8
A
0
9
A
1
0
A
1
1
A
1
2
A
1
3
F1
0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
F2
1 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0
F3
1 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0
F4
1 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0
F5
1 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0
F6
1 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0
F7
0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
F8
1 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1
F9
0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
F10
1 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0
F11
1 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0
F12
1 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0
F13
1 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0
F14
1 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0
F15
0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
F16
1 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1
F17
0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
F18
1 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0
F19
1 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 0 0
F20
1 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 0
F21
1 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 0 0
F22
1 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 0
F23
0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
F24
1 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 1
F25
0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0
F26
1 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0
F27
1 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 0
F28
1 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 0 0 0
F29
1 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 0 0
F30
1 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 0
F31
0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1
F32
1 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 1
The Levenberg-Marquardt backpropagation
algorithm was used for the neural networks training.
3 MODELING, TRAINING AND
RESULTS
The neural network for the feeder BAY had two
hidden layers with 45 and 35 neurons and was
trained with the 16 input alarms and had 20 output
neurons. (16-45-35-20).
The training 16 x 20 matrix was validated by the
correlation statistics technique in order to avoid the
mapping of the same set of alarms into different
faults. The neural network general model that is the
basis for all neural networks used in this paper is
shown in Figure 2 for the feeder BAY. The best
neural network architecture was the (16-45-35-20)
one, that is the neural network with 16 input
neurons, 45 and 35 neurons in the hidden layers and
20 output neurons.
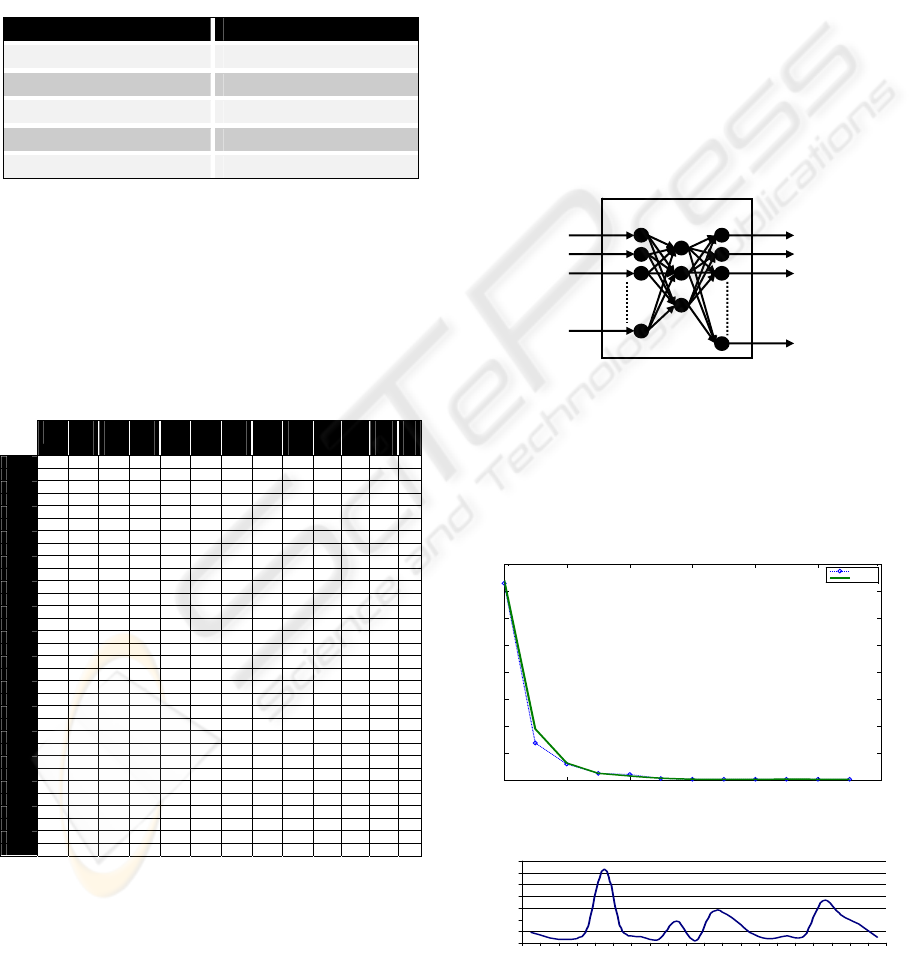
Figure 2: Neural Net Model - feeder BAY.
The cross-validation technique entitled to train,
validate, and test all the neural networks during
training. The training results for training and tests
and, the percentage error curve are shown in Figure
3 and, Figure 4 respectively.
0 2 4 6 8 10 12
0
0.05
0.1
0.15
0.2
0.25
0.3
0.35
0.4
Epoch
Squared Error
Training
Tes t
Figure 3: Test and Training - feeder BAY.
0
0,2
0,4
0,6
0,8
1
1,2
1,4
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1011121314151617181920
TESTES
ERRO
%
Figure 4: Error Percentage - feeder BAY.
f
eede
r
-BAY
A-1
A-16
F-1
F-20
ICEIS 2008 - International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
486
The neural network for the Capacitor bank BAY was
trained for 19 input alarms and had two hidden
layers with 46 and 33 neurons, and an output layer
with 20 neurons resulting in a (19-46-33-20)
architecture. The neural network for the
General/Secundary BAY was trained for 19 input
alarms and had two hidden layers with 78 and 44
neurons, and an output layer with 62 neurons
resulting in a (19-78-44-62) architecture. The neural
network for the line BAY was trained for 13 input
alarms and had two hidden layers with 65 and 46
neurons, and an output layer with 32 neurons
resulting in a (13-65-46-32) architecture.
Finally, the neural network for the backward BAY
was trained for 67 input alarms and had two hidden
layers with 410 and 220 neurons, and an output layer
with 157 neurons resulting in a (67-410-220-157)
architecture. For all neural networks used, the
activation functions were of the sigmoid type and
the training algorithm was the Levenberg-Marquardt
method. Over 5000 tests proposed by the AMPLA
experts were carried out and validated the mapped
faults in Parada Angélica substation and the results
were within the quality standards required by the
AMPLA energy provider group. Table 4 shows the
maximum percentage error found for each BAY.
Table 4: Maximum Percentage Error.
BAY Maximum
Percentage Error
Feeder 1.2610 %
Capacitor Bank 0.6450 %
General/Secondary 0.4679 %
Line 0.8385 %
Backward 1.4493 %
4 CONCLUSIONS
The results indicate the success of BAY oriented
application of fault detection in electrical
substations. Table 4 shows that the highest
percentage error found in all BAYs is less than
1.5%. According to AMPLA experts, the application
produces faster and more reliable responses
compared to traditional procedures of fault detection
which are completely dependent on human beings
empirical analysis. Due to the good results so far, the
authors of this paper are pursuing an ongoing action
for a man-machine interface to be imbedded in an
expert system in order to explain each occurred fault
and also in the concept modeling of a knowledge
base for that project.
REFERENCES
Kwang-Ho Kim and Jong-Keun Park, 1993. Application
of hierarchical neural networks to faults diagnosis of
power systems, Electrical Power & Energy Systems,
Vol 15 No. 2 , pp 65-70.
Biondi Neto, L. ; Ferreira, R. A. B., Targueta, David ;
Mello, João Carlos Correia Baptista Soares, 2007.
Intelligent System for Detection Fault in Electrical
Systems, III European-Latin-American Workshop on
Engineering Systems, 2007, Curicó, 2007.
Cascaes Pereira, A.; Cáceres, David; Biondi Neto, L.;
Ordacgi Filho, J. M.; Correia, J. R.; Pellizzoni, R.,
2007. Rede de IEDs de Proteção como obter o máximo
benefício para proteção e automação de Subestações,
XII Encontro Regional Ibero-americano do CIGRÉ -
ERIAC, 2007, Foz do Iguaçu. XII ERIAC.
NEURAL NETWORKS APPLICATION TO FAULT DETECTION IN ELECTRICAL SUBSTATIONS
487
