
A MULTIAGENT SYSTEM FOR JOB-SHOP SCHEDULING
Claudio Cubillos, Leonardo Espinoza and Nibaldo Rodriguez
Escuela de Ingeniería Informática, Pontificia Universidad Católica de Valparaíso, Av. Brasil 2241, Valparaíso, Chile
Keywords: AOSE, PASSI, Planning & Scheduling, Agent System, JSSP.
Abstract: The present work details the design and implementation of a multiagent system devoted to the dynamic Job
Shop Scheduling problem. The agent system tackles the planning and scheduling of jobs and their
corresponding operations on a set of available machines. The system has been modeled with the PASSI
agent-based software development methodology and implemented over the JADE agent platform.
1 INTRODUCTION
In a multiagent system (MAS) diverse agents
communicate and coordinate generating synergy to
pursue a common goal. Hence as modeling artifact,
agent-based systems borrow their key characteristics
from us, humans, and our societies.
Therefore, multiagent systems can be seen as a
natural evolution from Distributed Artificial
Intelligence (DAI) and Distributed Computing (DC).
This higher level of abstraction has allowed agents
to tackle the increasing complexity of nowadays
open software systems where integration,
transparency and interoperation among
heterogeneous components are a must.
For this technology to get more mature and
widespread, the use of agent-oriented software
engineering (AOSE) methodologies and tools are a
key factor of success.
Hence, the present work describes the design of a
multiagent system using a particular AOSE
methodology called PASSI (Cossentino et al., 2003).
The chosen domain for the system corresponds
to the job-shop scheduling problem under a dynamic
scenario in which job requests coming from clients
must be processed on-the-fly and where changes can
occur due to changes in the environment.
2 THE JSSP PROBLEM
The traditional Job-Shop Scheduling Problem
(JSSP), can be described by a set of n jobs {J
j
}
1≤j≤n
which is to be processed on a set of m machines
{M
r
}
1≤r≤m
. Each job has a technological sequence of
machines to be processed.
The processing of job J
j
on machine M
r
is called
the operation O
jr
. Operation O
jr
requires the
exclusive use of M
r
for an uninterrupted duration p
jr
,
its deterministic processing time, and each operation
O
jr
has pre-assigned materials {W
i
}
1≤i≤k
. In addition,
each job has a due-date {D
j
}
1≤j≤n
.
A schedule is a set of completion times for each
operation {c
jr
}
1≤j≤n;1≤r≤m
that satisfies those
constraints. The considered JSSP involves the
scheduling of n jobs J on the m machines M and
consuming k materials W while minimizing the total
tardiness regarding the due-dates.
On the other hand, the dynamic variant of the
problem adds the fact that the jobs to be processed
are not known in advance and that they must be
scheduled as they arrive.
It is one of the most hard NP-complete
combinatorial optimization problems.
2.1 Related Work
Diverse proposals of agent-based systems can be
found in literature tackling the job-shop or
production scheduling problem.
In (Saad et al., 1995) a Production Reservation
approach was proposed by using a bidding
mechanism based on the Contract Net Protocol -
CNP (Smith, 1978) to generate the production plan.
In AARIA (Parunak et al, 1997), the
manufacturing capabilities (e.g. people, machines,
and parts) are encapsulated as autonomous agents
and use a mixture of heuristic scheduling techniques:
148
Cubillos C., Espinoza L. and Rodriguez N. (2008).
A MULTIAGENT SYSTEM FOR JOB-SHOP SCHEDULING.
In Proceedings of the Tenth International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems - SAIC, pages 148-153
DOI: 10.5220/0001705301480153
Copyright
c
SciTePress
forward/backward scheduling simulation scheduling,
and intelligent scheduling.
In (Maturana et al., 1999) the adaptive multi-
agent manufacturing system architecture called
MetaMorph combined the CNP with mediator-
centric federation architecture was presented.
Other recent CNP-based solutions can be found
in (Váncza, 2000) (Maturana et al., 1999) (Lim,
2002) and (Usher, 2002).
One of the contributions of the present work is to
provide a more formal design of multiagent system
devoted to Job-shop scheduling using the PASSI
methodology.
3 PASSI METHODOLOGY
PASSI is a step-by-step methodology for designing
and developing multi-agent societies. Its name
stands for a Process for Agent Societies
Specification and Implementation. PASSI integrates
design models and concepts from both OO software
engineering and artificial intelligence approaches
using the UML notation.
The models and phases of PASSI encompass
anthropomorphic representation of system
requirements, social viewpoint, solution architecture,
code production and reuse, and deployment
configuration supporting mobility of agents. The
design process with PASSI is supported by the
PASSI ToolKit (PTK, 2005) to be used as an add-in
for Rational Rose.
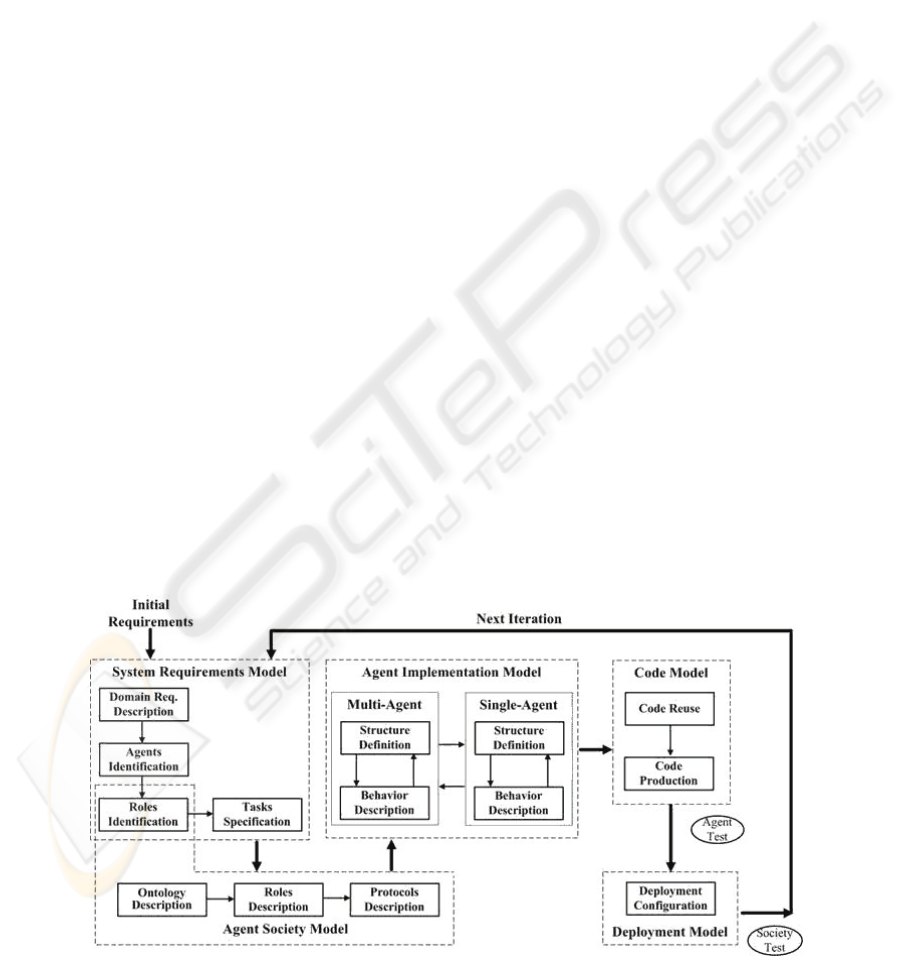
Figure 1 shows PASSI methodology consisting
of five models plus twelve steps in the process of
building multi-agent. These are briefly described in
the following. Please refer to (Burratato, 2002) for a
more detailed description.
System Requirements Model. Corresponds to an
anthropomorphic model of the system requirements
in terms of agency and purpose. It involves 4 steps:
a Domain Description (D.D.), an Agent
Identification (A.Id.), a Role Identification (R.Id.),
and a Task Specification (T.Sp.),
Agent Society Model. It considers the social
interactions and dependencies among the agents
involved. It considers 3 additional steps: an
Ontology Description (O.D.), a Role Description
(R.D.), and a Protocol Description (P.D.).
Agent Implementation Model. Provides the
solution architecture in terms of classes and methods
and considers: an Agent Structure Definition
(A.S.D.) and an Agent Behavior Description
(A.B.D.)
Deployment Model. Describes a model of the
distribution of the parts of the system across
hardware processing units and the migration
between processing units.
4 THE AGENT SYSTEM
The multiagent job-shop scheduling system stands
over the Jade Agent Platform (Bellifemine et al.,
1999), which provides a full environment for agents
to work.
In the following subsections, the agent system is
described making reference to the most relevant
PASSI steps and artefacts, while considering space
restrictions.
Figure 1: PASSI diagram showing Models and steps required (Burrafato, 2002).
A MULTIAGENT SYSTEM FOR JOB-SHOP SCHEDULING
149
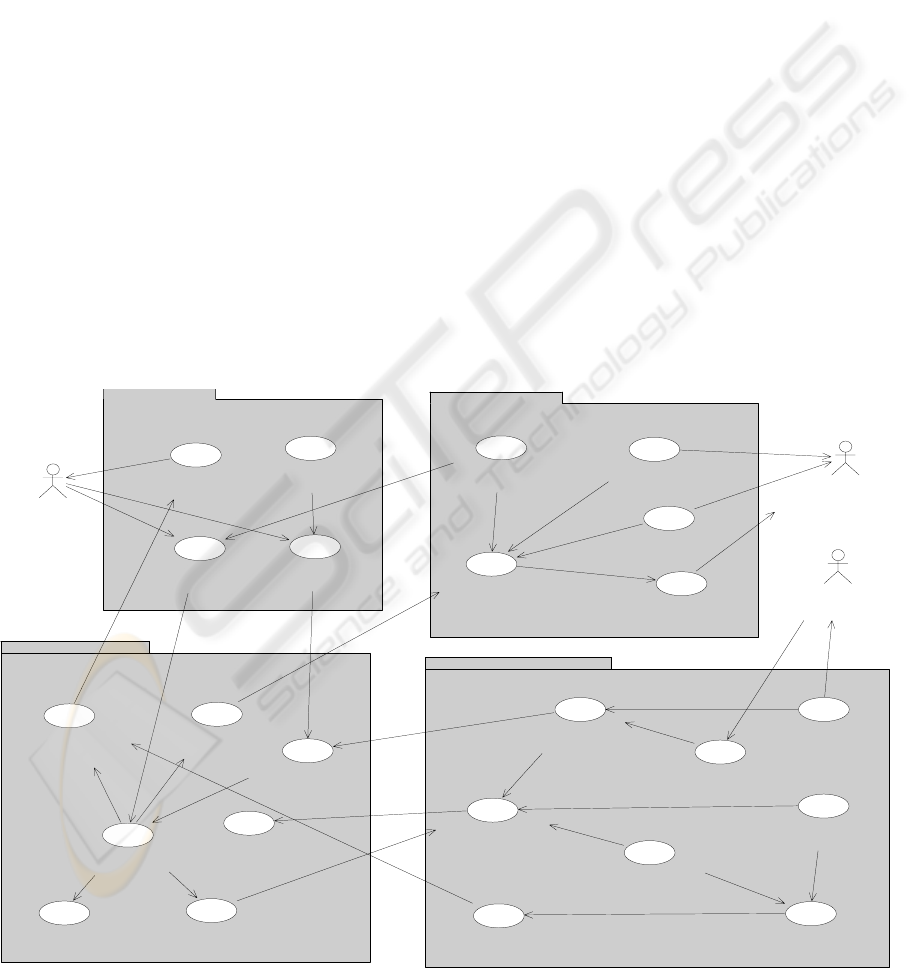
4.1 Agent Identification (A.Id.)
In this step the use cases capturing the system
requirements are grouped together to conform an
agent. The diagram in Figure 2 shows the identified
use cases for this job-shop system and the leveraged
agents.
Firstly, the Client agent is a GUI agent in charge
of the communication between an actual client and
the rest of the system, providing the possibility of
generating a job order, and to communicate
inbound/outbound eventualities regarding such order
due to changes in the environment (e.g. order
modification/cancellation from client, order
delay/reject from the system).
Machine agents encapsulate each real machine,
being primarily in charge of its schedule
management. This involves processing requests
coming from Order agents and performing the
scheduling process.
For this, it carries out a search in the solutions
state space by implementing an optimization
heuristic. In the actual system, a search algorithm
presented by (Yoo et al., 2002), inspired in
simulated annealing was implemented.
On its turn, Order agents are devoted to the job
order management, its breakdown into operations,
the request of necessary materials for each operation
execution to Stock agents, and the request to
Machine agents for the scheduling of each operation.
For the interaction with the Stock agents the
FIPA Query Interaction Protocol (FIPA. 2002b)
standard is used. In the latter case, the FIPA Request
Interaction Protocol is used (FIPA, 2002a).
4.2 Task Specification (T. Sp.)
In this phase the scope is to focus on each agent’s
behavior, decomposing it into tasks, which usually
capture some functionality that forms a logical unit
of work and generating cohesion. Therefore for each
agent an activity diagram is developed containing
what that agent is capable of along the diverse roles
it performs. In general, an agent will be requiring
one task for handling each incoming and outgoing
message.
As example, a portion of the tasks of the Order
agent are depicted in Figure 3. The diagram shows
five tasks on the right that constitute the Order agent
capabilities. The ReceiveOrder task handles Client
Order Agent
<<Agent>>
Client Agent
<<GUI Agent>>
Stock Agent
<<Agent>>
Machine Agent
<<Agent>>
Stock Administrato
(from 01-Domain Des...
)
Material check-out
(from Stock Agent)
Stock Lev el Determining
(f rom St ock Agent )
Material Request
(from Stock Agent)
Stock Management
(f rom Stock Agent)
<<extend>>
<<include>>
<<extend>>
Inf orm Assignment
(from Client Agent)
Generate Material
(from Stock Agent)
<<ex tend>>
Orden Deletion
(from Client Agent)
Client
(from 01-Dom
a
...)
Div ide Job Order
(from Order Agent)
Request Materials
(from Order Agent)
<<communicate>>
Generate Order
(f rom Client Agent)
<<communicate>>
Inf orm Operations Plan
(from Machine Ag...
Machine's Operations Plan
Management
(from Machine Ag...
<<include>>
Order Modif ication
(from Client Agent)
<<extend>>
Send Processing Request
(f rom O r der Agent)
Perf orm Modif ication
(from Machine Ag...
<<include>>
Operation Assignment
(from Machine Ag...
<<include>>
Prov ide Order Inf ormation
(from Order Agent)
Manage Order Ev ents
(from Order Agent)
<<comm unicate>>
Request s Processing
(from Machine Ag...
<<comm unicate>>
<<extend>>
<<extend>>
<<comm unicate>>
Schedule Changes
Notification
(from Machine Ag...
Operator GUI
(from 01-Dom
a
...)
Machine Ev ents
Management
(from Machine Ag...
<<comm unicate>>
<<extend>>
<<extend>>
Schedule Changes
Communication
(from Machine Ag. ..
<<extend>>
Scheduled Operations'
Management
(from Order Agent)
<<comm unicate>>
Manage Job Order
(from Order Agent)
<<include>>
<<include>>
<<include>>
<<include>>
<<include>>
<<communicate>>
Figure 2: Agent Identification Diagram for the Job-shop scheduling system.
ICEIS 2008 - International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
150
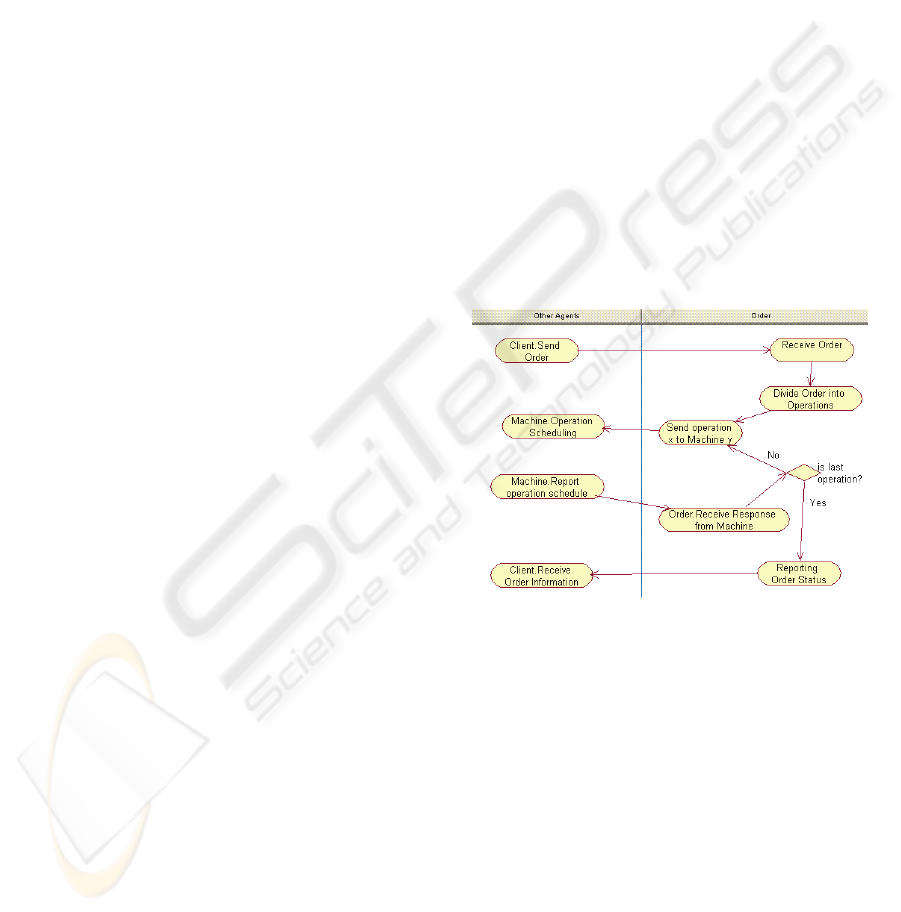
messages which request for an order to be processed.
This one calls the DivideOrderIntoOperations task
which splits the order into its corresponding set of
operations on different machines. Each operation is
forwarder to the SendOperation in charge of
constructing and sending the request message to the
Machine agent. The message is handled by the
OperationScheduling task of the Machine agent.
In the following, once the machine has found a
scheduling position of that operation, it answers
back the Order through a ReportOperationSchedule
task. Such a message is handled by the
ReceiveResponseFromMachine task in the Order
side. In this step an evaluation is performed in order
to check whether if the operation corresponds to the
last one within the order. In such a case, the order
has been scheduled completely; otherwise still
remain operations to be scheduled on machines.
After processing the last operation, the
ReportingOrderStatus task is called, being in charge
of collecting all the schedules of the order’s
operation set and informing the Client the actual
schedule of its order. Finally, the Client handles the
above message through its ReceiveOrderInformation
task.
4.3 Ontology Description (O.D.)
In this step the agent society is described from an
ontological perspective, providing them with a
common knowledge of the job shop domain, and
thus, enabling communication among involved
actors and agents.
The following Figure 4 shows a portion of the
Domain Ontology Description providing the
concepts necessary for mutual agent understanding
within the society.
On the center the JobOrder is depicted, which is
decomposed into Operations. Other related concepts
are MaterialList, Stock and StockLevel.
In the middle-upper part of the diagram we can
identify on the left the Machine concept and on the
right the Client concept. Both have Events and a
Utility Function associated.
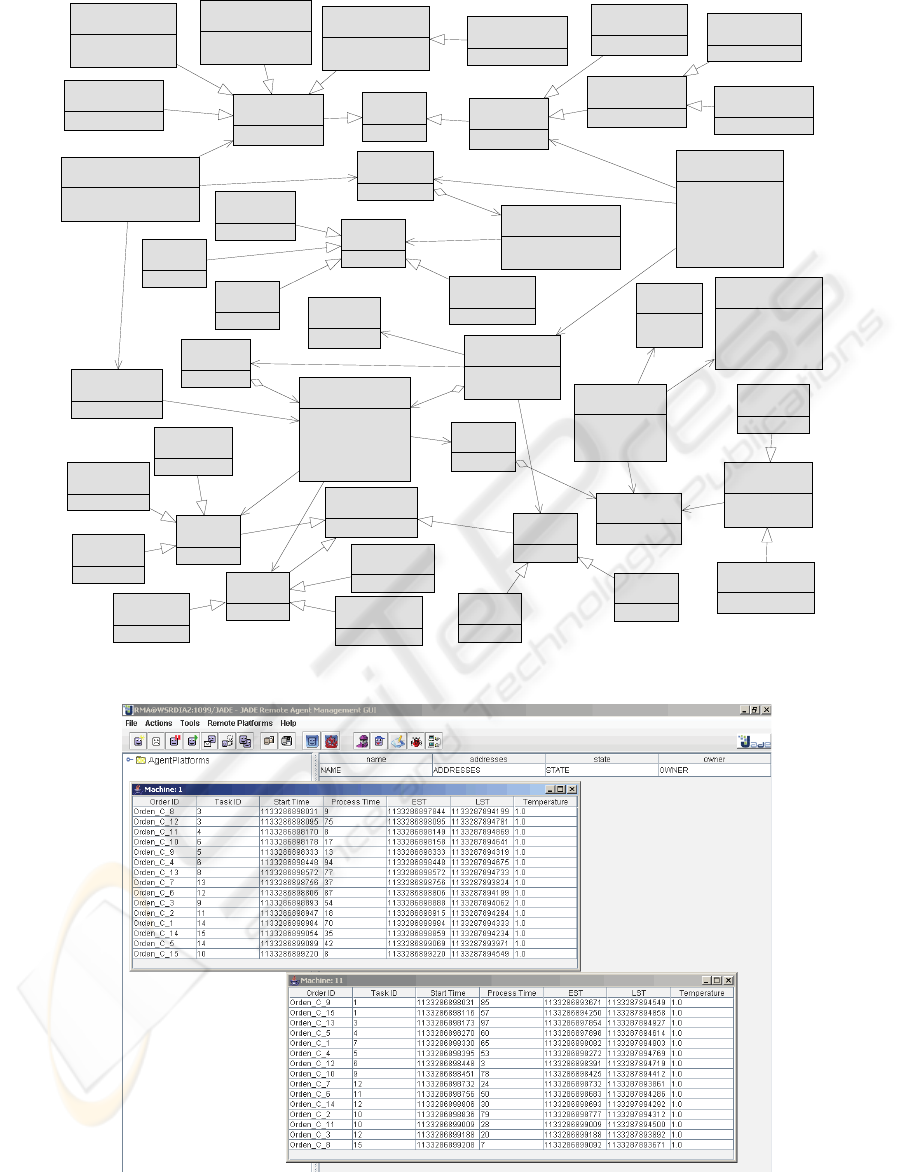
5 IMPLEMENTATION
As stated before, a system was implemented over the
Jade Framework. In addition to the described agents,
other simulation agents were created in order to
coordinate the correct creation, execution and
destroy of the agents along the diverse experiments
and runs.
Other implementation issue regards the
development of GUIs for Machine and Order agents.
The above Figure 5 shows a screenshot of two
Machine agent GUI’s. The machines 1 and 11 are
depicted in the foreground while having the Jade
platform GUI at the background.
The GUI of each Machine agent shows a grid
indicating the Job Order ID (e.g. Orden_C_8) and
the task ID, that is, the relative order of the operation
within the set of operations of the job order.
The grid also details the starting and processing
times together with the Early and Latest Start Times
(EST & LST respectively).
In the case of the Order GUI a similar approach
was taken. In this case the grid shows the list of all
the tasks (or operations) for the given Job order
indicating times and the corresponding machines on
each case.
Regarding the benchmark data for the
experimentations, Figure 6 shows the format of the
plain .txt file used to feed the Order and Machine
agents. The example shows the 15x15 example (15
machines, 15 orders) from (Taillard, 1994).
Figure 3: Part of the Task Specification Diagram for the
Order Agent.
6 CONCLUSIONS
The design of an agent-based software system for
dynamic job shop scheduling was described.
The agent formalization with PASSI promotes
the architecture maintainability, its ability to cope
with newer requirements and the possibility to scale
and integrate other actors and systems.
Next steps consider the testing with benchmark
data tackling diverse scenarios and topologies of
distribution and the implementation of diverse
scheduling algorithms (e.g. Genetic algorithm, tabú
search, sa).
A MULTIAGENT SYSTEM FOR JOB-SHOP SCHEDULING
151
ActualStartTime
<<c oncept>>
MachineSchedule
<<concept>>
OrderStatus
Status : String
<<concept>>
DateTime
Actual Time : Date
<<concept>>
Early StartTime
<<concept>>
Lat eSt artTime
<<concept>>
Early FinishTime
<<concept>>
LateFinis hTime
<<concept>>
ActualFinishTime
<<c oncept>>
JobDate
<<concept>>
StartTime
<<concept>>
FinishTime
<<concept>>
DueDate
<<concept>>
FinishDate
<<concept>>
Mac hineBrea k D own
<<concept>>
OperationCancelled
OperationID : string
<<concept>>
MachineDelay
Mac hineI D : String
Delay Estimate : Date
<<concept>>
OperationDelay
OperationID : String
Delay Estimate : Date
<<concept>>
OperationScheduled
OperationID : String
ActualStartTime : Date
<<concept>>
Ev ent
<<concept>>
Machine Ev ent
MachineID : string
<<concept>>
Client Ev ent
ClientID : String
<<concept>>
Operation
OperationID : String
Step : int
MachineID : St rin g
ProcessingTime : Date
Priority : f loat
<<concept>>
0..*
0..1
0..*
0..1
0..3
1
0..3
1
0..3
1
0..3
1
Mat erialLis t
<<c oncept>>
1
1
1
1
CancelOrder
JobOrderID : String
<<concept>>
ChangeDueDate
NewDueDate : Date
<<concept>>
AnticipateDueDate
<<concept>>
Post icipateDueDate
<<c oncep t>>
StockLev el
Quantity : int
Unit : String
<<c oncept>>
JobOrder
JobOrderID : String
Priority : f loat
<<concept>>
1..*
1
1..*
1
1
1
1
1
1..2
1
1..2
1
OperationList
<<c oncep t>>
0..*
0..*
0..*
0..*
1
0..1
1
0..1
Tardi ne s s
<<concept>>
MeanTardines s
<<concept>>
Non-placed Jobs
<<c onc ept>>
Throughput
<<concept>>
Stock
StockID : String
Mat e rialD : St ring
ProviderID : String
<<c oncep t>>
1
1
1
1
Prov ider
ProviderID : String
Address : String
PhoneNumber : String
Email : String
<<concept>>
1..*
1..*
Client
ClientID : String
Surname : String
Names : String
Address : String
PhoneNumber : String
Email : String
<<concept>>
1..*
1
1..*
1
0..*
1
0..*
1
Machine
MachineID : string
Schedule : MachineSchedule
<<concept>>
1
1
1
1
0..*
1
0..*
1
Utility Function
<<concept>>
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
UtilityProperty
Property Ty pe : Propert y
Weight.float
<<c oncept>>
1..*
1
1..*
1
Property
<<concept>>
Material Entry
<<c onc ept>>
Mat erial Ex it
OperationID : String
<<c oncept>>
Stock Movement
Mat e rial D : St ring
Quantity : int
<<c oncept>>
Mat eri al
MaterialD : String
<<concept>>
1..*
1..*
1..*
1..*
1
1
1
1
1..*
1..*
Figure 4: Part of the Domain Ontology Diagram for the Job-shop system.
Figure 5: Screenshot of Order Agents GUI under a JADE Platform.
ICEIS 2008 - International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
152

Figure 6: Part of the Task Specification Diagram for the
Order Agent.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work is part of Project No. 209.746/2007
entitled “Coordinación en una sociedad
multiagentededicada a la programación y control
bajo ambiente dinámico”, funded by the Pontifical
Catholic University of Valparaíso (www.pucv.cl).
REFERENCES
Bellifemine, F. et al. 1999. JADE - A FIPA Compliant
Agent Framework. C-SELT Internal Technical Report.
Burrafato, P., and Cossentino, M. 2002. Designing a
multiagent solution for a bookstore with the PASSI
methodology. In 4th International Bi-Conference
Workshop on Agent-Oriented Information Systems
(AOIS-2002).
Cossentino, M., P. Burrafato, S. Lombardo, and L.
Sabatucci. 2003. Introducing pattern reuse in the
design of multi-agent systems. In Agent Technologies,
Infrastructures, Tools, and Applications for E-
Services, eds. R. Kowalszyk, J. P. Mu ller, H.
Tianfield, and R. Unland, LNAI 2592, pages 107--
120, Berlin: Springer-Verlag.
FIPA. 2002a. FIPA Request Interaction Protocol
Specification, Standard, version H, 2002-12-06
Available at http://www.fipa.org/specs/fipa00026/
FIPA. 2002b. FIPA Query Interaction Protocol
Specification, Standard, version H, 2002-12-06
Available at http://www.fipa.org/specs/fipa00027/
Fischer, K. 1994. The design of an intelligent
manufacturing system. Proc. of CKBS’94, University
of Keele, England, pp. 83–99.
Lim, M. K. and Zhang, Z. 2002. Iterative multi-agent
bidding and co-ordination based on genetic algorithm.
Proceeding of 3 Complex Systems, and E-Businesses,
Erfurt, pp. 682--689.
Maturana F, Shen Weiming, Norrie D. 1999. MetaMorph:
an adaptive agent-based architecture for intelligent
manufacturing. International Journal of Production
Research, 37: 2159-2173,.
Parunak, H.V.D., Baker, A.D. And Clark, S.J. 1997. The
AARIA agent architecture: an example of
requirements-driven agent-based system design. Procs.
1st Int. Conf. on Autonomous Agents, Marina del Rey,
CA.
PTK. 2007. The PASSI Toolkit (PTK) Available at
http://sourceforge.net/projects/ptk. Accessed on
09/10/2005
Saad, A., Biswas, G., Kawamura, K., Johnson, M. E.
Salama, A. 1995. Evaluation of contract net-based
heterarchical scheduling for flexible manufacturing
systems. Procs. Int. Joint Conf. on Artificial
Intelligence, Workshop on Intelligent Manufacturing,
Montreal, Canada, pp. 310-321.
Smith, R. G. and R. Davis. 1978. Distributed Problem
Solving: The Contract Net Approach. Proceedings of
the 2nd National Conference of the Canadian Society
for Computational Studies of Intelligence.
Taillard. E. D. 1994. Benchmark problems. available at:
http://ina2.eivd.ch/Collaborateurs/etd/problemes.dir/or
donnancement.dir/ordonnancement.html
Usher, J.M. 2002. Negotiation-based Routing in Job Shops
via Collaborative Agents. World Manufacturing
Congress, Distributed Intelligence in Technology,
Economic and Social Applications: An International
Symposium, Workshop on Agent-Based Process
Planning and Scheduling, Rochester, New York.
Váncza, J. and Márkus, A. 2000. An agent model for
incentive-based production scheduling. Computers in.
Industry, Vol. 43, Issue 2,pp. 173-187.
Yoo, M. J., Müller, J. P. “Using Multi-agent System for
Dynamic Job Shop Scheduling”. 4th Int. Conf. on
Enterprise Information System (ICEIS 2002), Ciudad
Real, Spain, April 2002.
A MULTIAGENT SYSTEM FOR JOB-SHOP SCHEDULING
153
