
THE DESIGN AND IMPLEMENTATION OF THE INTEGRATED
DECISION SUPPORT SYSTEM ON LABOR MARKET
Dongjin Yu
1,2
1
Hangzhou Dianzi University, Hangzhou, 310018, China
2
Zhejiang Gongshang University, Hangzhou, 310018, China
Shixin Feng
Information Center of Labor and Social Security, Hangzhou, 310003, China
Guangming Wang
Zhejiang Gongshang University, Hangzhou, 310018, China
Keywords: Decision Support System, Labor Market, Service Oriented Architecture, OLAP.
Abstract: Nowadays labor resources in China face the fierce situation in their employment. The decision support
system on labor market helps the government to have a sound grip of the composition, migration and trend
of regional labor resources’ supply and requirement . This paper proposes an integrated architecture of the
decision support system on regional labor markets, which leverages the Service Oriented Architecture. The
real system implemented on this architecture, called as LMDSS, is also presented to show the features of
the multi-dimension analysis of job introducing.
1 INTRODUCTION
Since 1990s, significant changes have taken place in
the labor market of China. According to Chinese
statistical yearbooks, the number of registered
unemployed persons in urban areas rises steadily
from 7.70 million in 2002, to 8.00 million in 2003,
8.27 million in 2004, 8.39 million in 2005 and 8.47
million in 2006 at the registered unemployment rate
no less than 4.0% approximately each year (National
Bureau of Statistics of China. (ed), 2002 to 2007).
With the implementation of so-called Golden
Security Project launched since 2001, many cities in
China have established the Labor Market
Information Systems (LMIS), which provide the
capabilities of employment related information
services. LMIS focuses on business functions such as
unemployment registering, job introducing,
professional training and unemployment fund
allocation. Although LMIS usually stores a large
amount of historical business data, it does not
support decision making. However, the decision
makers in government agencies usually want to
discover the composition and its migration for both
the regional unemployment and employment.
Questions frequently arise as: which group is most
vulnerable to unemployment? Which kind of
irregular employment is most popular? Only with
these information at hand, could they adopt the
effective and positive employment policies.
Decision Support System (DSS) represents the
promise of enhancing managerial effectiveness by
improving the quality of decision making, in terms of
depth of analysis, breadth of synthesis, timeliness,
and systemic perspective (Gonzhlez, 1993). Since the
concept of DSS was first launched by Gorry and
Scott Morton (Goory and Morton, 1971), substantial
research has been conducted, especially in its
different application fields. Study on DSS with the
area of labor market commonly focuses on the
selection of candidates for recruitment. For instances,
Nina gives a Decision Support System based on
fuzzy logic model for Human Resources Appraisal
and Selection (HRAS) (Ruskova, 2002), and
Liang-Chih Huang constructs a novel model for
evaluation of managerial talent in DSS through fuzzy
535
Yu D., Feng S. and Wang G. (2008).
THE DESIGN AND IMPLEMENTATION OF THE INTEGRATED DECISION SUPPORT SYSTEM ON LABOR MARKET.
In Proceedings of the Tenth International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems - AIDSS, pages 535-538
DOI: 10.5220/0001705805350538
Copyright
c
SciTePress
neural network (Huang and Huang, 2004). The
Recommender System for job seekers and employers
is another application field given much attention.
Tobias Keim presents a unified multilayer
framework supporting the matching of individuals
for recruitment in (Keim, 2007). However, the
analysis of composition, migration and trends for
regional labor market is less concerned.
This paper introduces the framework and its
implementation of decision support system for labor
market, called LMDSS. Based on Services Oriented
Architecture, LMDSS accomplishes the interaction
with other related information systems. It is
constructed on the data warehouse, and leverages the
technology of Online Analytic Processing (OLAP)
and data mining. OLAP helps ad-hoc query via data
slice, dice, drill up, drill down and swap, while data
mining helps discover the implicit and valuable
information such as patterns, trends and
characteristics.
The paper proceeds as follows. Section 2 shows
the overall architecture of LMDSS, as well as its
features. Section 3 discusses its characteristic on
services orientation. The implementation of LMDSS
is presented in Section 4, especially on it’s
multi-dimension analysis of job introducing. Finally,
in Section 5, some concluding remarks and
interesting open issues are sketched.
2 THE ARCHITECTURE OF
LMDSS
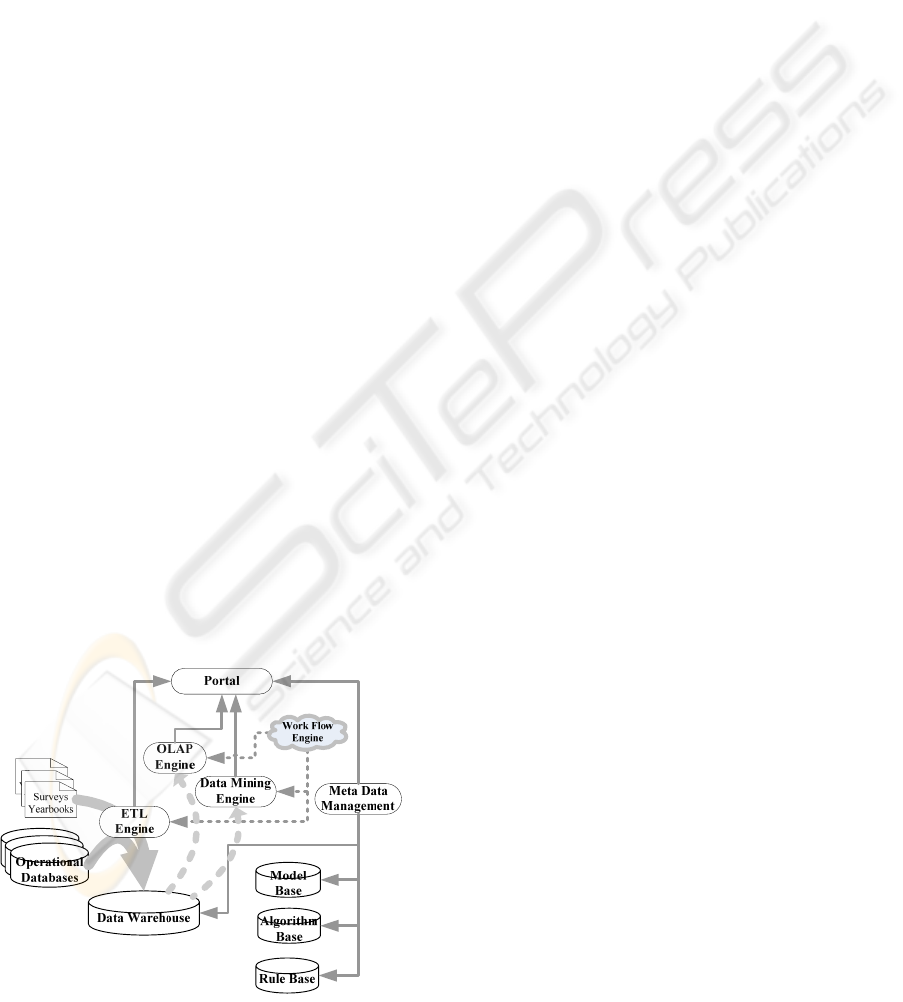
The overall architecture of LMDSS mainly consists
of the framework, meta-data management module,
data collection module, data online analysis module
and data mining module as showing in Fig 1.
Figure 1: The Architecture of LMDSS.
The framework provides the running-time
environment, supporting portal, workflow
management, security control and knowledge
sharing, while the meta-data management module
maintains the related models, algorithms and rules.
The core of system implements data collection,
analysis and mining. It integrates the records via the
ETL (Extract-Transform-Load) engine from the
related operational systems, the survey results and
the economic leading index published in yearbooks,
and then constructs the data warehouse. Currently,
LMDSS stores the following themes of data:
registering of unemployment, unemployment
funding, enterprise employment, individual
job-hunting records, and the urban and rural labor
resources.
The data analysis module focuses on the
multi-dimensional drilling of certain regional labor
market measures, like the number of posts wanted,
the amount of unemployment fund paid, etc. The data
mining module offers the medium-short-term
forecast of the overall labor resources’
supply-demand, the medium-long-term forecast of
it’s components, and also the profit-loss analysis of
unemployment fund. In addition, certain key features
could be discovered through the process of data
classification, clustering and association.
The resource layer in Fig. 1 is composed of the
data warehouse providing the standard JDBC
interfaces and other data sources located by JNDI,
including the model base for schemes of themes, the
algorithm base for data mining and the rule base for
constraint. For system administrating, the interface
layer provides the desktop application based on
Eclipse. Meanwhile, the browser based pages are
also given for data presentation.
3 DESIGN OF SERVICES
ORIENTED INTEGRATION
LMDSS is not independent and needs to interact with
other systems like the labor market operational
system, the social security operational system and so
on. For instances, LMDSS retrieves post-wanted
records from the labor market operational system and
unemployment payment records from the social
security operational system. Besides, operational
systems reuse the algorithms provided by LMDSS to
implement their own business analysis.
Traditional DSSs are somewhat difficult to
integrate new functions or connect to other systems
ICEIS 2008 - International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
536

due to the deficiency in openness (Chi et al., 2005).
The specific adapters are usually developed to
connect all these heterogeneous systems. Instead,
LMDSS leverages the Service Oriented Architecture
to achieve the application coupling. Service Oriented
Architecture (SOA) is a paradigm for organizing and
utilizing distributed capabilities that may be under
the control of different ownership domains. It
provides a uniform means to offer, discover, interact
with and use capabilities to produce desired effects
consistent with measurable preconditions and
expectations.
Using the standard SOA approach, LMDSS
provides open access to its OLAP engine with
multi-dimensional data through web services. In
LMDSS, the execution of MDX (Multidimensional
Expressions) statements is provided as web services
via XMLA (XML for Analysis) protocol, which
specifies a set of XML message interfaces that use
the industry standard Simple Object Access Protocol
(SOAP) to define data access interaction between a
client application and an analytical data provider
working over the Internet. Once receiving requests of
multi-dimensional queries, the OLAP engine in
LMDSS parses the MDX statement into SQL
statement and then access the data warehouse.
Finally, the OLAP engine reformats the result with
SOAP and returns the messages back to the client.
In addition, the core data mining algorithms are
encapsulated as SCA (Service Component
Architecture) components. Therefore, with the help
of WSDL defined interfaces, LMDSS provides the
capabilities of on-demand invoking of it’s inner
mining algorithms for outside systems.
4 THE IMPLEMENTATION OF
MULTI-DIMENSION ANALYSIS
The data online analysis module in LMDSS is
implemented through OLAP technology. The
multi-dimension data set is organized as cubes,
measures and dimensions, while the dimensions are
further expressed by hierarchies and levels. Once
fetched from the data warehouse, the result set is
temporarily kept in the server’s memory. If the new
query could be calculated directly from the data in
memory, no more reading of warehouse is needed.
Moreover, the frequently used joins of fact tables and
dimension tables are materialized in advance. If
possible, the SQL statements are rewritten to access
the materialized tables instead of the underlying fact
tables and dimension tables. Experiments have
shown the performance of data retrieving could be
significantly improved.
Fig. 2 gives the screen shot for the analysis of job
introducing in LMDSS, which presents 3 dimensions
as unit types, data issued and education levels, and
also 2 measures as the number of the wanted and the
number of the successfully introduced.
Figure 2: The screen shot for the multi-dimension analysis
of job introducing.
5 CONCLUSIONS
The decision support system for labor market need to
be architecturally flexible and extensible. LMDSS
leverages the SOA and aids the decision-makers by
presenting multi-dimension analysis. The data source
are mainly the records retrieved from the labor
market information systems, plus the statistical data
from surveys and yearbooks.
Because of the huge amount of related
operational records and their distribution, the model
of distributed data analysis need to be further studied.
For the next step, LMDSS is expected to be migrated
to the grid platform, and Globus is thought to be the
ideal candidate.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The work is supported by Zhejiang Provincial Key
Project with grant No. 2007C21044, of China.
THE DESIGN AND IMPLEMENTATION OF THE INTEGRATED DECISION SUPPORT SYSTEM ON LABOR
MARKET
537

REFERENCES
National Bureau of Statistics of China. (ed), 2002, 2003,
2004, 2005, 2006, 2007. China Statistical Yearbook:
2002, 2003, 2004, 2005, 2006, 2007. China Statistical
Press. Beijing.
Gasth T. Gonzhlez, 1993. Information architectures and the
successful implementation of decision support systems.
In Proceedings of IEEE Systems Man and Cybernetics
Conference.
G.A. Goory, and M.S. Scott Morton, 1971. A framework
for management information systems. In Sloon
Management Review, vol. 13, no. 1.
Nina At. Ruskova, 2002. Decision Support System for
Human Resources Appraisal and Selection. In First
International IEEE Symposium “Intelligent Systems”.
Liang-Chih Huang, Kuo-Shu Huang, 2004. Applying
Fuzzy Neural Network in Human Resource Selection
System. In NAFIPS '04.
Tobias Keim, 2007. Extending the Applicability of
Recommender Systems: A Multilayer Framework for
Matching Human Resources. In HICSS'07,
Proceedings of the 40th Annual Hawaii International
Conference on System Sciences.
Jia-Yu Chi, Ling Sun, Xue-Guang Chen, etc, 2005.
Architecture and Design of Distributed Decision
Support System Based on Agent Grid, In Proceedings
of the Fourth International Conference on Machine
Learning and Cybernetics.
ICEIS 2008 - International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
538
