
EMPIRICAL MULTI-ARTIFACT KNOWLEDGE MODELING
FOR DIALOGUE SYSTEMS
Porfírio Filipe
1, 2, 3
and Nuno Mamede
1, 4
1
L
2
F INESC-ID – Spoken Language Systems Laboratory, Lisbon, Portugal
2
GuIAA – Grupo de Investigação em Ambientes Autónomos, Lisbon, Portugal
3
ISEL – Instituto Superior de Engenharia de Lisboa, Lisbon, Portugal
4
IST – Instituto Superior Técnico, Lisbon, Portugal
Keywords: Human–Computer Interaction, Spoken Dialogue System, Dialogue Management, Domain Model.
Abstract: This paper presents a knowledge modeling approach to improve domain-independency in Spoken Dialogue
Systems (SDS) architectures. We aim to support task oriented dialogue management strategies via an easy
to use interface provided by an adaptive Domain Knowledge Manager (DKM). DKM is a broker that
centralizes the knowledge of the domain using a Knowledge Integration Process (KIP) that merges
on-the-fly local knowledge models. A local knowledge model defines a semantic interface and is associated
to an artifact that can be a household appliance in a home domain or a cinema in a ticket-selling domain. We
exemplify the reuse of a generic AmI domain model in a home domain and in a ticket-selling domain
redefining the abstractions of artifact, class, and task. Our experimental setup is a domain simulator
specially developed to reproduce an Ambient Intelligence (AmI) scenario.
1 INTRODUCTION
Speech-based human-computer interaction faces
several challenges in order to be more widely
accepted. One of this challenges is the domain
portability. In order to face this challenge we assume
that practical dialogue and domain-independent
hypothesis are true (Allen et al. 2000). The reason is
that all applications of human computer interaction
involve dialogue focused on accomplishing some
specific task. We consider the bulk of the
complexity in the language interpretation and
dialogue management is independent of the task
being performed. In this context, a clear separation
between linguistic dependent and domain dependent
knowledge allows reducing the complexity of
Spoken Dialogue System (SDS) typical components.
Summarizing, our contribution enables domain
portability issues. Section 2 gives an overview of the
proposed knowledge modeling approach. Section 3
gives an overview of the most relevant components
of the domain model. Section 4 describes the
Knowledge Integration Process (KIP). Section 5
describes the experimental scenario referring home
and ticket-selling domains. Finally, in Section 6, we
present concluding remarks and future work.
2 APPROACH
Within Ambient Intelligence (AmI) vision (Ducatel
et al., 2001), (Filipe and Mamede, 2006) a SDS
should be a computational entity that allows access
to any artifact by anyone, anywhere, at anytime,
through any media or language, allowing its users to
focus on the task, not on the tool.
Figure 1 shows a typical logical flow through
SDS components architecture to access a domain
database. The user’s request is captured by a
microphone, which provides the input for the Speech
Recognition component. Next, the Language
Understanding component receives the recognized
words and builds the related speech acts. The
Dialogue Manager (DM) processes the speech acts
and then calls the Response Generation component
to generate a message. Finally, the message is used
by the Speech Output component to produce speech.
The response of the SDS is final or is a request for
clarification. When everything is acceptable, a final
answer is produced based on an external data source,
traditionally a relational database (McTear, 2004).
286
Filipe P. and Mamede N. (2008).
EMPIRICAL MULTI-ARTIFACT KNOWLEDGE MODELING FOR DIALOGUE SYSTEMS.
In Proceedings of the Tenth International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems - HCI, pages 286-292
DOI: 10.5220/0001713902860292
Copyright
c
SciTePress
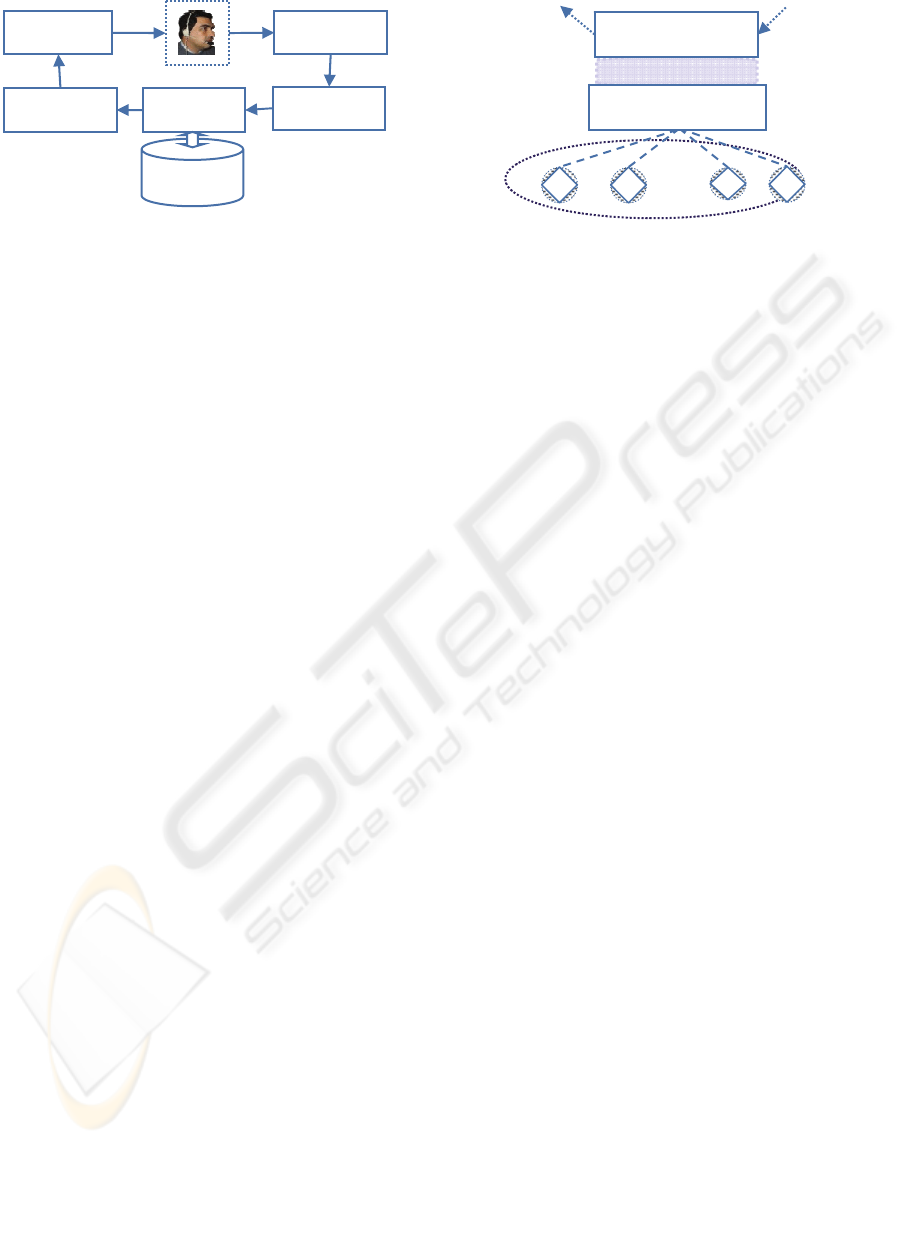
Figure 1: Logical flow through SDS components.
Nevertheless, a SDS cannot be directly used
within an Ambient Intelligent (AmI) scenario
because of is lack of portability, in view of the fact
that SDSs are not ubiquitous yet (Weiser, 1991).
The use of a conventional monolithic model
makes difficult to acquire and to alter the knowledge
of the domain. Therefore, the use of a distributed
architecture enables system developers to design
each domain part independently. In this perspective,
the system is composed of two kinds of components:
a part that can be designed independently of all other
domains, and a part in which relations among
domains should be considered. Some existing
systems are based on this architecture (Lin et al.,
2001)(Pakucs, 2003)(O’Neill et al., 2004)(Nakano et
al., 2005)(Komatani et al., 2006).
However, AmI demands for spontaneous
configuration. In order to support domain
independent dialogue management strategies, we
propose a dynamic domain model that is
expanded/enriched, using the knowledge associated
with each one of the artifacts belonging to the AmI
environment.
Within a ubiquitous domain, we do not know, at
design time, all the devices that will be available and
which tasks they provide. In order to address this
problem we describe an approach for ubiquitous
knowledge modeling, which was introduced in
(Filipe and Mamede, 2004). The domain
customization of the SDS, is made by the Domain
Knowledge Manager (DKM), see Figure 2.
The main goal of the DKM is to support the
communication interoperability between the SDS
and a set of heterogeneous artifacts, performing the
domain knowledge management. For this, the DKM
includes a knowledge model that is updated at SDS
runtime, by a Knowledge Integration Process (KIP),
according to the domain’s artifacts. The DKM
adapts, via and adaptive interface (Filipe and
Mamede, 2007), the DM component, which should
only be concerned with phenomena related to the
dialogue.
Figure 2: SDS customization to a dynamic domain.
3 DOMAIN MODEL
This section gives an overview of the most relevant
components of the domain model that includes three
independent knowledge components: the discourse
model, the world model, and the task model. The
bridge component makes the connections between
these models. The domain model XML Schema is:
<xs:element name="DomainModel">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element
ref="DiscourseModel"/>
<xs:element ref="TaskModel"/>
<xs:element ref="WorldModel"/>
<xs:element ref="Bridge"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
3.1 Discourse Model
The discourse model defines a conceptual support,
grouping concept declarations, used to describe
artifact classes, artifacts, and the tasks they provide.
A concept declaration is an atomic knowledge
unit. Concept declarations are organized according
to types. “Action” and “Perception” types hold task
names. A perception task cannot modify the state of
the artifact, on the other hand an action task can.
“Active” and “Passive” types hold artifact classes
(artifact, equipment, application, furniture,
appliance, …) that can by referred in the type
hierarchy. “Quantity” type is about number (integer,
real, positive, integer, …). “Unit” type is for
measures (time, power, …). “Attribute” type are
generic attributes (color, shape, texture, …).
“Collection” holds groups of attributes (color: white,
black, red, …). “Name” holds generic names, such
as artifact names. The discourse model XML
Schema is:
<xs:element name="DiscourseModel">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
A
A
d
d
a
a
p
p
t
t
i
i
v
v
e
e
I
I
n
n
t
t
e
e
r
r
f
f
a
a
c
c
e
e
D
D
i
i
a
a
l
l
o
o
g
g
u
u
e
e
M
M
a
a
n
n
a
a
g
g
e
e
r
r
X
X
n
n
.
.
.
.
.
.
D
D
o
o
m
m
a
a
i
i
n
n
K
K
n
n
o
o
w
w
l
l
e
e
d
d
g
g
e
e
M
M
a
a
n
n
a
a
g
g
e
e
r
r
X
X
2
2
X
X
1
1
L
L
a
a
n
n
g
g
u
u
a
a
g
g
e
e
U
U
n
n
d
d
e
e
r
r
s
s
t
t
a
a
n
n
d
d
i
i
n
n
g
g
D
D
i
i
a
a
l
l
o
o
g
g
u
u
e
e
M
M
a
a
n
n
a
a
g
g
e
e
r
r
R
R
e
e
s
s
p
p
o
o
n
n
s
s
e
e
G
G
e
e
n
n
e
e
r
r
a
a
t
t
i
i
o
o
n
n
S
S
p
p
e
e
e
e
c
c
h
h
O
O
u
u
t
t
p
p
u
u
t
t
S
S
p
p
e
e
e
e
c
c
h
h
R
R
e
e
c
c
o
o
g
g
n
n
i
i
t
t
i
i
o
o
n
n
D
D
o
o
m
m
a
a
i
i
n
n
D
D
a
a
t
t
a
a
b
b
a
a
s
s
e
e
EMPIRICAL MULTI-ARTIFACT KNOWLEDGE MODELING FOR DIALOGUE SYSTEMS
287

<xs:element name="Concept"
maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element
ref="LinguisticDescriptor" minOccurs="1"
maxOccurs="unbounded"/>
<xs:element
ref="SemanticDescriptor" minOccurs="0"
maxOccurs="unbounded"/>
<xs:element
ref="Collection" minOccurs="0"/>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute
name="Identifier" type="idConcept"
use="required"/>
<xs:attribute
name="Type" use="required">
<xs:simpleType>
<xs:restriction base="xs:string">
<xs:enumeration value="Action"/>
<xs:enumeration value="Perception"/>
<xs:enumeration value="Active"/>
<xs:enumeration value="Passive"/>
<xs:enumeration value="Quantity"/>
<xs:enumeration value="Unit"/>
<xs:enumeration value="Attribute"/>
<xs:enumeration value="Collection"/>
<xs:enumeration value="Name"/>
</xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType>
</xs:attribute>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
In order to guarantee the availability of
vocabulary to designate the domain’s concepts,
concept declarations include linguistic resources.
Each Word (or term), has a part of speech tag, such
as noun, adjective, verb, adverb or preposition; a
language tag, such as “pt-PT”, “pt-BR”, “en-UK” or
“en-US”; and some phonetic transcriptions. The
word descriptor XML Schema is:
<xs:element name="WordDescriptor">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:attribute name="Language"
use="required">
<xs:simpleType>
<xs:restriction
base="xs:string">
<xs:enumeration
value="pt-PT"/>
<xs:enumeration
value="pt-BR"/>
<xs:enumeration
value="en-UK"/>
<xs:enumeration
value="en-US"/>
</xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType>
</xs:attribute>
<xs:attribute name="Word"
type="xs:string" use="required"/>
<xs:attribute name="PartOfSpeech"
use="required">
<xs:simpleType>
<xs:restriction
base="xs:string">
<xs:enumeration
value="Noun"/>
<xs:enumeration
value="Adjective"/>
<xs:enumeration
value="Verb"/>
<xs:enumeration
value="Adverb"/>
<xs:enumeration
value="Preposition"/>
</xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType>
</xs:attribute>
<xs:attribute
name="PhoneticTranscription" type="xs:string"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
A linguistic descriptor holds a list of terms, or
more generically a list of Multi Word Unit (MWU),
referring linguistic variations associated with the
concept, such as synonymous or acronyms. The
linguistic descriptor XML Schema is:
<xs:element name="LinguisticDescriptor">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:choice maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:element
ref="MultiWordDescriptor"/>
<xs:element
ref="WordDescriptor"/>
</xs:choice>
<xs:attribute name="Type"
use="required">
<xs:simpleType>
<xs:restriction
base="xs:string">
<xs:enumeration
value="Synonym"/>
<xs:enumeration
value="Antonym"/>
<xs:enumeration
value="Acronym"/>
</xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType>
</xs:attribute>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
Optionally, each concept can also have semantic
resources references represented by a semantic
descriptor. The semantic descriptor has references to
other external knowledge sources, for instance, an
ontology (Gruber, 1992) or a lexical database, such
as WordNet. The attributes of the semantic
descriptor must be encoded using a data format
allowing a unique identification of the concept in the
knowledge source. The data format does not need to
be universal it is enough to keep the same syntax for
a particular knowledge source. The semantic
descriptor XML Schema is:
<xs:element name="SemanticDescriptor">
<xs:complexType>
ICEIS 2008 - International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
288

<xs:attribute name="Source"
type="xs:string" default="WordNet"/>
<xs:attribute name="Position"
type="xs:byte"/>
<xs:attribute name="Meaning"
type="xs:string"/>
<xs:attribute name="Label"
type="xs:string"/>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:unique name="keySemanticDescriptor">
<xs:selector xpath="."/>
<xs:field xpath="@Source"/>
<xs:field xpath="@Position"/>
<xs:field xpath="@Meaning"/>
<xs:field xpath="@Label"/>
</xs:unique>
</xs:element>
3.2 Task Model
The task model contains task descriptors that are
associated to artifact instances through domain
model bridges.
A task descriptor is a semantic representation of
an artifact competence and has a name and,
optionally, a role input and/or output list. The task
name is a concept previously declared in the
discourse model. A role describes an input and/or
output task parameter. The role name, range and
optional default value are also declared concepts in
discourse model. The restriction is a rule that is
materialized as regular expression and is optional.
An output role is similar to an input role without a
restriction rule and with no default value. The initial
and final rules perform state validation: the initial
rule (to check the initial state of the world before a
task execution) and the final rule (to check the final
state of the word after a task execution). These rules
can refer role names and values returned by
perception task calls. The task model XML Schema
is:
<xs:element name="TaskModel">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="Task"
maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element
name="Role" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:attribute name="Type" use="required">
<xs:simpleType>
<xs:restriction base="xs:string">
<xs:enumeration value="IN"/>
<xs:enumeration value="OUT"/>
<xs:enumeration value="IO"/>
</xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType>
</xs:attribute>
<xs:attribute name="Name" type="idConcept"
use="required"/>
<xs:attribute name="Range" type="idConcept"
use="required"/>
<xs:attribute name="Default"
type="idConcept"/>
<xs:attribute name="Optional"
type="xs:boolean"/>
<xs:attribute name="Restrition"
type="xs:string"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute
name="Identifier" type="idTask" use="required"/>
<xs:attribute
name="Name" type="idConcept" use="required"/>
<xs:attribute
name="InitialRule" type="xs:string"/>
<xs:attribute
name="FinalRule" type="xs:string"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
3.3 World Model
The world model has two components: a type
hierarchy and a mediator. The type hierarchy
organizes the artifact classes. The mediator manages
artifact instances linked to their classes. The world
model XML Schema is:
<xs:element name="WorldModel">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element
name="TypeHierarchy">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element
name="Class" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:attribute name="Identifier"
type="idClass" use="required"/>
<xs:attribute name="Name" type="idConcept"
use="required"/>
<xs:attribute name="Class" type="idConcept"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="Mediator">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element
name="Artifact" maxOccurs="unbounded">
EMPIRICAL MULTI-ARTIFACT KNOWLEDGE MODELING FOR DIALOGUE SYSTEMS
289

<xs:complexType>
<xs:attribute name="Identifier"
type="idArtifact" use="required"/>
<xs:attribute name="Name" type="idConcept"
use="required"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
4 KNOWLEDGE INTEGRATION
The goal of the Knowledge Integration Process
(KIP) is to update on-the-fly the global DKM
domain model, merging the knowledge provided by
the domain’s artifacts. We assume that each artifact
has its own identical local knowledge mode.
At its starting point, KIP puts side by side
concepts, tasks and classes descriptions using
similarity criteria:
a) Two concepts are similar when: its identifiers
are equal, one of its semantic descriptors is equal or
its linguistic descriptors are equal. If the concepts
type is collection, its members must be similar;
b) Two tasks are similar when: its names, roles
and rules are similar;
c) Two classes are similar when: its names are
similar.
For each new artifact, KIP follows the next six
steps:
i) Each concept descriptor without a similar (a)
concept is added to the DKM discourse model;
ii) Each task descriptor without a similar (b) task
is added to the DKM task model;
iii) Each class descriptor without a similar (c)
class is added to the DKM type hierarchy;
iv) The artifact descriptor is added to the DKM
mediator;
v) The artifact is associated with its class using a
bridge;
vi) The artifact is associated with its tasks using
a bridge.
5 EXPERIMENTAL SCENARIO
We have considered as reference a multi-propose
SDS architecture (Neto et al., 2003)(Neto et al.,
2006). The experimental setup is based on our AmI
simulator, originally developed for Portuguese users.
This domain simulator incorporates a basic dialogue
manager and several artifact simulators, such as a
microwave oven, a fryer, freezer, a lamp and a
window. The debug of an invoked task can be made
analyzing the interaction with the target artifact. We
can attach artifacts applying KIP, execute tasks,
obtain the answers and observe the subjacent artifact
behaviors. We can also consult and print several data
about the several knowledge representations.
Figure 3 contains a screenshot of the domain
simulator that is showing a kitchen lamp.
Figure 3: Screenshot of the kitchen lamp simulator.
AmI is a wide computational paradigm that
defines a generic domain. However, we consider that
a domain is different from another when it uses a
different type hierarchy. In order to illustrate the
proposed knowledge model approach, the next two
sections present distinct domains: the home domain
and the ticket-selling domain.
5.1 Home Domain
Figure 4 shows part of the type hierarchy of the
home domain.
Figure 4: Type hierarchy of the home domain.
The home domain is characterized by an
arbitrary set of common artifacts, such as appliances
or furniture. The type hierarchy does not need to be
complete because it can be improved, as new
artifacts are dynamically added to the domain.
The use of the propose knowledge model to
represent the available tasks provided by each one of
the home artifact is straightforward. Next XML
artifact
a
pp
liance
furn
i
ture
microwave
oven
freeze
r
fryer
dev
i
ce
alarm
li
g
ht
table
b
oo
k
shelf
window
ICEIS 2008 - International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
290

representation is a partial knowledge model of the
kitchen lamp where is represented a task that
modifies the lamp intensity.
5.2 Ticket-selling Domain
The ticket-selling domain is characterized by an
arbitrary set of entertainment places that allows
buying tickets to watch artistic or sportive events.
Each entertainment place or showground has its own
information about the timetable of it shows and
about the identification of the spectators seat.
The use of the propose approach for home
domain is possible but we must previously redefine
de mining of artifact, task, and class of artifact. An
entertainment place is modeled as an artifact. The
tasks for buying a ticket are modeled as artifact
tasks. The class of the entertainment place
(previously artifact) should be the kind of the
building (coliseum, stadium, amphitheatre, …)
where the event occurs or the show activity among
others. However, we choose to classify the
entertainment places by activity because is more
natural this reference in the user’s dialogue.
Figure 5 presents part of the type hierarchy of the
ticket-selling domain used to classify entertainment
places.
Figure 5: Type hierarchy of the ticket-selling domain.
Each one of the entertainment place has its own
knowledge model that is merged with the DKM
model by KIP. An entertainment place can have
specific and appropriate tasks to sell or to reserve
tickets.
6 CONCLUDING REMARKS AND
FUTURE WORK
We have devised an approach to deal with
communication interoperability between a SDS and
a multi-artifact domain, within an AmI vision. This
approach tries to reach the ubiquitous essence of
natural language. Although, the coverage of
handmade resources such as WordNet, in general is
impressive, coverage problems remain for
applications involving specific domains or multiple
languages.
For this, we have presented a DKM that supports
the SDS domain model that is updated by KIP
merging the artifacts knowledge. The knowledge
model together with KIP can be used to support a
SDS domain customization without restrictions
because AmI is a wide computational paradigm.
Nevertheless, some difficulties can occur in finding
the right abstractions.
Considering the amount of concepts related with
each one of the artifacts and the amount of concepts
related with the DKM the knowledge integration rate
achieved by KIP is typically about 50%. This value
is relevant because the artifacts within a domain are
quite similar when sharing the same type hierarchy.
As future work, we expect to explore, more
deeply, the knowledge integration perspective and to
improve the proposed approach to support the needs
of other SDS modules.
REFERENCES
Allen, J., Byron, D., Dzikovska, M., Ferguson, G.,
Galescu, L., Stent, A., 2000. An Architecture for a
generic dialogue shell. Natural Language
Engineering, 6(3–4):213–228.
Ducatel, K., Bogdanowicz, M., Scapolo, F., Leijten, J. and
Burgelman, J-C., 2001. Scenarios for Ambient
Intelligence in 2010. IST Advisory Group Report.
IPTSSeville.
Filipe, P. and Mamede, N., 2004. Towards Ubiquitous
Task Management. In 8
th
International Conference on
Spoken Language Processing, 3085-3088.
Filipe, P., Mamede, N., 2006. Hybrid Knowledge
Modeling for Ambient Intelligence. In 9
th
Workshop
User Interfaces for All (ERCIM-UI4ALL) Special
Theme: "Universal Access in Ambient Intelligence
Environments". Königswinter, Germany. Springer
Verlag.
Filipe, P., Mamede, N., 2007. An Adaptive Domain
Knowledge Manager for Dialogue Systems. In 9th
International Conference on Enterprise Information
Systems.
Gruber, T., 1992. Toward Principles for the Design of
Ontologies Used for Knowledge Sharing. In
International Workshop on Formal Ontology.
Komatani, K., Kanda, K., Nakano, M., Nakadai, K.,
Tsujino, H., Ogata, T., Okuno, H., 2006.
Multi-Domain Spoken Dialogue System with
Extensibility and Robustness against Speech
Recognition Errors. In 7
th
SIGdial Workshop on
Discourse and Dialogue, 9-17.
Lin, B., Wang, H. and Lee, L., 2001. A Distributed Agent
Architecture for Intelligent Multi-Domain Spoken
entertainment
s
p
ort
art
music
cinema
b
asketbal
theater
circus
b
ullfi
g
h
t
c
y
clin
g
motorin
g
tennis
soccer
EMPIRICAL MULTI-ARTIFACT KNOWLEDGE MODELING FOR DIALOGUE SYSTEMS
291

Dialogue Systems. In IEEE Trans. on Information and
Systems, E84-D(9):1217-1230.
McTear, M., 2004. Spoken Dialogue Technology,
Springer. ISBN 1-85233-672-2.
Nakano, M., Hasegawa, Y., Nakadai, K., Nakamura, T.,
Takeuchi, J., Torii, T., Tsujino, H., Kanda, N. and
Okuno, H., 2005. A Two-Layer Model for Behavior
and Dialogue Planning in Conversational Service
Robots. In IEEE/RSJ International Conference on
Intelligent Robots and Systems, pp. 1542–1548.
Neto, J., Cassaca, R., Viveiros, M., Mourão, M., 2006.
Design of a Multimodal Input Interface for a Dialogue
System. In 7
th
International Workshop PROPOR 2006,
LNAI 3960 Springer, 170-179.
Neto, J., Mamede, N., Cassaca, R. and Oliveira, L., 2003.
The Development of a Multi-purpose Spoken
Dialogue System. In Eurospeech 3003, 8
th
European
Conference on Speech Communication and
Technology.
O’Neill, I., Hanna, P., Liu, X. and McTear, M., 2004.
Cross Domain Dialogue Modelling: An Object-based
Approach. In 8
th
International Conference on Spoken
Language Processing, Korea, 205-208.
Pakucs, B., 2003. Towards Dynamic Multidomain
Dialogue Processing". In 8
th
European Conference on
Speech Communication and Technology, 741-744.
Weiser, M., 1991. The Computer of the 21
st
Century.
Scientific American, vol. 265, no. 3, 66 75, 1991.
ICEIS 2008 - International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
292
