
MULTIPLICATIVE NEURAL NETWORK WITH SWARM
INTELLIGENCE FOR MULTICARRIER TRANSMITTER
Nibaldo Rodriguez, Claudio Cubillos
School Informatic, Pontifical Catholic University of Valparaiso, Av. Brasil 2241, Chile
Orlando Duran
School Mechanic, Pontifical Catholic University of Valparaiso, Av. Brasil 2241, Chile
Keywords:
Neural Networks, Swarm intelligence, Multicarrier Communications.
Abstract:
In this paper, we propose a novel effective distortion compensation scheme suitably developed to reduce
nonlinearities of the traveling wave tube amplifier (TWTA) in orthogonal frequency division multiplexing
(OFDM) systems at the multicarrier transmitter side. This compensator is developed in order to combine in
the most effective way the capability of the quantum particle swarm optimization technique and multiplicative
neural networks. The compensator effectiveness has been tested through computer simulations. The improve-
ments in the reduction of constellation warping and enhanced performance in terms of the bit error rate (BER)
are offered for the TWTA with an input back-off level of 0 dB.
1 INTRODUCTION
Multicarrier Transmitter based on orthogonal fre-
quency division multiplexing (OFDM) appears to be
an attractive transmission scheme in order to over-
come the impairments of wireless broadband chan-
nels. Due to this fact, various standards for wireless
communications using OFDM signals. However, the
main drawback of OFDM signal is the large enve-
lope fluctuations, making the system sensitive to the
nonlinearities introduced by the traveling wave tube
amplifier (TWTA) (A.M., 1981), which cause spec-
tral regrowth in adjacent channels and deformation
of the signal constellation. To reduce nonlinear dis-
tortions, it is necessary to operate the TWTA with a
large power back-off level. However, such amplifica-
tion schemes posses a low power efficiency since the
maximum power efficiency is only attained when the
TWTA is operated near its saturation point. Hence,
TWTA compensation techniques are often necessary
to achieve a trade-off between the linear amplifica-
tion and high power efficiency. Many compensation
schemes based on artificial neural network (Abdulka-
der F., 2002), (Rodriguez N. and R., 2003) to reduce
nonlinearities and their effects have been proposed in
the recent literature.
In most existing techniques, complex models’
input-output measured signals are initially converted
to either a polar or rectangular representation and
then two separate and uncouple real-valued mod-
els are used to estimate the amplitude and phase
output as a function of the input power amplitude.
The real parameters of the two models were ob-
tained during a training procedure based on back-
propagation algorithm and gradient descent method,
but the main disadvantage of these compensation
schemes is their slow convergence speed and ele-
vated requirements of computing resources. Parti-
cle Swarm Optimization (PSO) was originally pro-
posed by J. Kennedy as a simulation of social be-
havior of bird flock, and was initially introduced as
a heuristic optimization method in 1995 (Kennedy,
1995). Recently Sun et al. (Sun J. and W., 2004) pro-
posed a global convergence-guaranteed search tech-
nique called quantum-behaved particle swarm opti-
mization algorithm (QPSO), whose performance is
superior to the standard PSO. The proposed QPSO
algorithm, kept to the philosophy of PSO, is based
on Delta potential well and depicted only with the
position vector without velocity vector, which is a
simpler algorithm. The results show that QPSO per-
forms better than standard PSO on several benchmark
test functions and is a promising algorithm due to its
global convergence guaranteed characteristic. In this
575
Rodriguez N., Cubillos C. and Duran O. (2008).
MULTIPLICATIVE NEURAL NETWORK WITH SWARM INTELLIGENCE FOR MULTICARRIER TRANSMITTER.
In Proceedings of the Tenth International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems - AIDSS, pages 575-578
DOI: 10.5220/0001716305750578
Copyright
c
SciTePress
paper, we explore the effectiveness of the QPSO tech-
nique with a multiplicative neural networks (QPSO-
MNN) to maximize linearity and power efficient of an
OFDM multicarrier transmitter. The MNN has only
one hidden layer consists of product units, while the
output layer has additive units. Moreover, both layers
use linear activation function and QPSO is applied for
determining the MNN’s parameters.
The remainder of this paper is organized as fol-
lows: The compensation scheme of the TWTA and
an parameter identification algorithm are presented
in Section 2 and 3; respectively. The performance
curves of the constellation warping effect and bit er-
ror rate (BER) of 16QAM-OFDM signals with 256-
subcarrier are discussed in Section 4. Finally, the con-
clusions are drawn in the last section.
2 COMPENSATION SCHEME
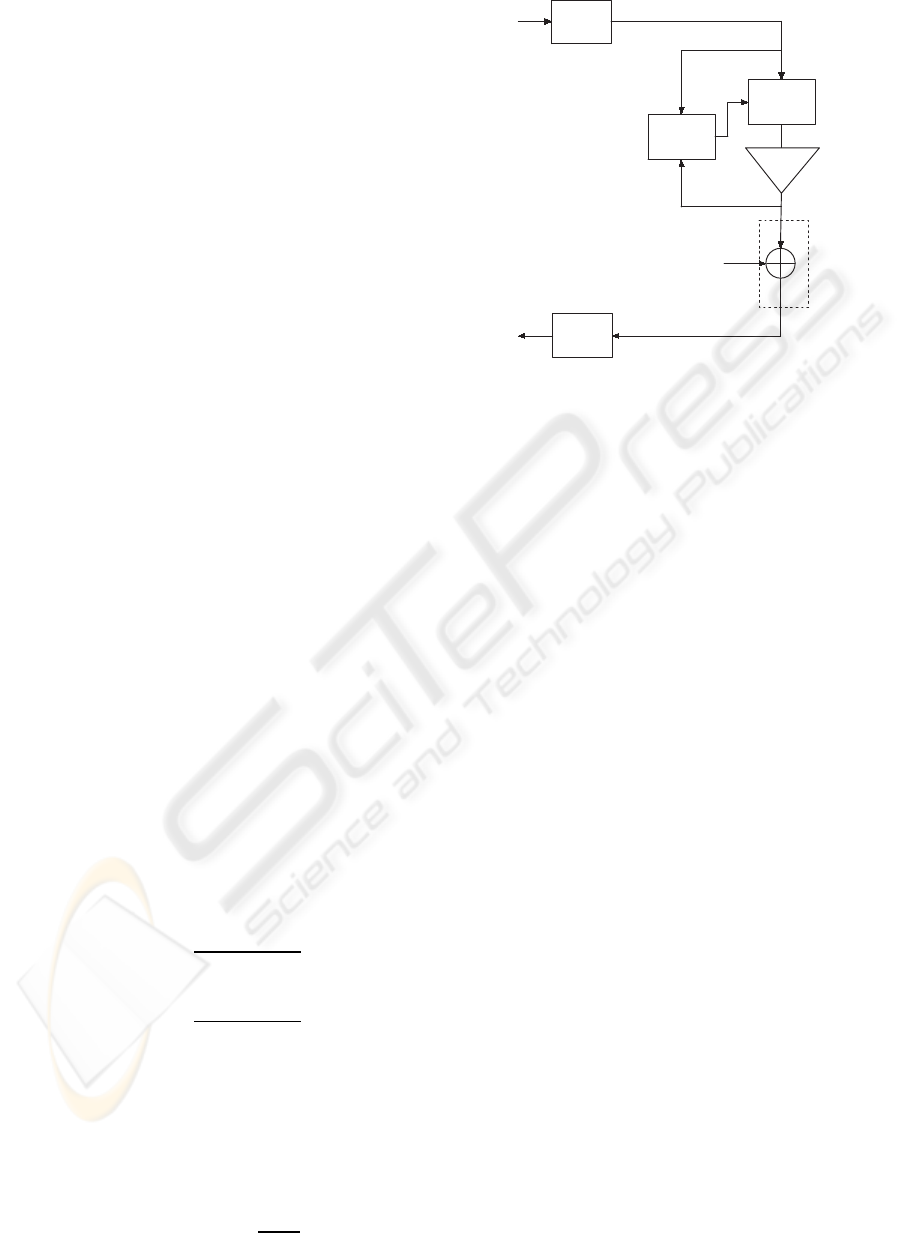
A baseband block model for a compensation scheme
with TWTA is shown in Fig. 1. The output of the
compensator is given as
y(n) = M(|x(n)|)exp{ j[θ
x
+ N(|x(n)|)]} (1)
where the functions M(·) and N(·) are used to invert
the nonlinearities introduced by the TWTA.
The combination of a TWTA and the correspond-
ing compensator will result in
z(n) = A[M(|x(n)|)]exp{j[θ
n
+ N(|x(n)|) + P[M(|x(n)|)]]}
(2)
where A(·) and P(·) are the nonlinear amplitude
(AM/AM) and nonlinear phase (AM/PM) conver-
sion of the TWTA; respectively. The AM/AM and
AM/PM conversion of a TWTA can be approximated
as (?)
A(|y(n)|) =
α
A
|y(n)|
1+ β
A
|y(n)|
2
(3)
P(|y(n)|) =
α
P
|y(n)|
2
1+ β
P
|y(n)|
2
(4)
with α
A
= 2,β
A
= 1,α
P
= π/3 and β
P
= 1
The nonlinear distortion of a high power amplifier
depends on the back-off. The input back-off (IBO)
is defined as the ratio of the input power saturation,
where the output power begins to saturate, to the av-
erage input power.
IBO(dB) = 10log
10
P
i,sat
P
i,avg
(5)
OFDM
Modul .
MNC
)(nx
QPSO
Algorithm
)(nv
)(nu
)(nz
)(ny
OFDM
Demodul
)(nr
i
d
i
d
ˆ
AWGN
c
h
a
n
n
e
l
TWTA
Figure 1: Baseband OFDM transmission system.
where P
i,sat
is the input power saturation and P
i,avg
is the average power at the input of the TWTA.
In order to achieve the ideal linearizing function,
the signal z(n) will be equivalent to the input OFDM
signal x(n). That is:
A[M(|x(n)|)] = α|x(n)| (6a)
N(|x(n)|) = −P[M(|x(n)|)] (6b)
where α|x(n)| is the desired linear model. In this
paper, the desired linear gain was set to α = 1, so that
saturation power was reached at 0 dB. We therefore
write the ideal linearizing function as
where A
−1
[·] represents the inverse AM-AM func-
tion of the TWTA.
Finally, in order to achieve (6) , it is necessary
only to find the real-valued function A
−1
[·], which
can be approximated by using a multiplicative Neu-
ral Network and a finite number of samples of the
(AM/AM) function.
2.1 QPSO-MNN based Compensator
In quantum-behavedparticle swarm optimization, the
particles move according to the following iterative
equations (Sun J. and W., 2004):
p = ϕ· P
ij
+ (1− ϕ) · P
gj
ϕ ∼ U(0,1) (7)
X
ij
= p ± ·α· |mbest
j
− X
ij
|.ln(1/u) u ∼ U(0,1)
(8)
where X
ij
is an infinitesimal particle in the D-
dimensional space with i = 1, 2,... M and j =
ICEIS 2008 - International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
576

1,2,... D. The vector P
ij
is the best previous po-
sition of particle i, vector P
gj
is the position of the
best particle among all the particles and known as
the global best position. The parameter α is called
contraction-expansioncoefficient and the global point
mbest
d
is the mean best position among the particles.
The global point is defined as
mbest
j
=
s
M
∑
i=1
(P
ij
−
¯
P)
2
j = 1,2,...,D (9)
where
¯
P =
1
M
M
∑
i=1
P
ij
(10)
The compensator’s output signal y(t) is approxi-
mated using a multiplicative neural network, which is
given as:
ˆy(u) =
m
∑
j=1
a
j
· h
j
(u) (11a)
h
j
(u) =
D
∏
i=1
u
b
ji
(11b)
where a
j
are the linear parameters, b
ji
are nonlin-
ear weights, m is the number of hidden nodes, u is the
input value.
For a three-layered MNN, b
ji
and a
j
represent the
connection weight matrix between the input layer and
the hidden layer, and that between the hidden layer
and the output layer; respectively. During training of
the MNN, the k-particle is denoted by X
k
= (a
k
j
,b
k
ji
).
In order to determine the fitness of the k-particle is
used the mean square error of the MNN, which is de-
fined as
E(X
k
) =
1
N
s
N
s
∑
i=1
(u
i
− ˆy(u
i
))
2
(12)
where N
s
is the number of training set samples.
The desired output v
i
and input data u
i
are obtained as
v
i
=
|x(n)|
max{|x(n)|}
IBO (13a)
u
i
= |z(n)| (13b)
3 INTRODUCTION
The numerical results presented in this section are
based on the following setup: In the transmitter,
an OFDM signal with N = 256 subcarrier is gener-
ated and all subcarriers are 16-Quadrature Amplitude
0 500 1000 1500
−16
−14
−12
−10
−8
−6
−4
−2
0
2
4
Iterations
MSE (dB)
Figure 2: Best MSE history of neural network training.
modulated (16-QAM). The TWT amplifier is oper-
ated at IBO = 0 dB and the channel model under
consideration is an AWGN (Additive White Gaussian
Noise)channel. The parameters of the multiplicative
neural compensator(MNC) were estimated during the
training process using N
s
= 100 subcarrier 16-QAM-
OFDM and the TWTA was operated at IBO = 0 dB.
The MNC was configured with one input node, one
linear output node, three hidden nodes and one bias
units. In the training process the particles swarm
were initialized by a Gaussian random process with
a normal distribution U(0,1). The population size
was set to M = 20 and dimension space was set to
D = 3 + 3 + 1 = 7. The contraction-expansion co-
efficient varies linearly from 1.0 to 0.5 over the it-
erations. Training was only one run with 1500 it-
erations and the normalized mean square error after
convergence was approximately equal to −15 dB. In
decision-direct mode, the MNC is simply a copy of
the multiplicative neural network obtained during the
QPSO-training process.
Fig.2 demonstrate the training and the per-
formance of the MNC using conventional QPSO
scheme. From Fig.2, it is easy to see MNC trained
with QPSO algorithm converges quickly and can gen-
erate mean square error value about of -15dB.
To demonstrate the performance of the proposed
QPSO-MNC scheme, we evaluated the constellation
warping effect and the BER versus signal to noise rate
(Eb/No) using 50 Monte Carlo runs for an input data
stream of length equal to 10,000 bits and the input
back-off level was set at IBO = 0dB for TWTA com-
bined with MNC (MNC+TWTA). Moreover, we also
show the performance for the system without MNC
and the system with ideal (AWGN) channel. The BER
of the OFDM symbols without TWTA in the AWGN
channel is very similar to the corresponding 16-QAM
system and is used here for benchmarking the perfor-
mance of the 16QAM-OFDM system.
The effects of the TWTA on the 16QAM-OFDM
received constellations in the absence of the AWGN
MULTIPLICATIVE NEURAL NETWORK WITH SWARM INTELLIGENCE FOR MULTICARRIER TRANSMITTER
577

−4 −3 −2 −1 0 1 2 3 4
−4
−3
−2
−1
0
1
2
3
4
In−phase
Quadrature
(a) TWTA operated at IBO = -9 dB
without MNC
−4 −3 −2 −1 0 1 2 3 4
−4
−3
−2
−1
0
1
2
3
4
In−phase
Quadrature
(b) TWTA operated at IBO = 0 dB
with MNC
Figure 3: Received 16QAM-OFDM Constellation in ab-
sence AWGN channel.
2 4 6 8 10 12 14
−60
−50
−40
−30
−20
−10
0
Eb/No (dB)
B E R (dB)
16QAM−OFDM Theory
16QAM−OFDM MNC+TWTA IBO = 0dB
16QAM−OFDM TWTA IBO = −9dB
Figure 4: BER performance of 16QAM-OFDM over a non-
linear AWGN channel.
channel are shown in Fig. 3(a) and 3(b), which corre-
spond to the TWTA without and with MNC operated
at an input back-off level of −9 dB and 0 dB; respec-
tively. According to Fig. 3(a) and 3(b), it is observed
that square 16QAM constellation is severely distorted
by the nonlinear AM/AM and AM/PM characteristics
of the TWTA without MNC. This distortion is inter-
preted as in-band noise, and it is called constellation
warping effect. From Fig. 3(a) and 3(b) it can be seen
that the proposed multiplicative neural compensator
scheme significantly reduces the constellation warp-
ing effect on the received 16QAM-OFDM symbols.
Fig. 4 shows the BER performance for 16QAM-
OFDM with and without MNC in presence of a
TWTA. From Fig. 4 it can be seen that at Eb/No = 14
dB is achieved a BER = −10 dB when the TWTA
without MNC is operated at IBO = −9 dB. Thus, the
BER performance is very poor due to nonlinearities
of the TWTA. In addition, also the MNC achieves a
BER = −55.6 dB at Eb/No = 14dB, which is favor-
ably compared to the BER corresponding to the linear
amplification ideal case.
4 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper, we have presented the performance of a
TWTA without and with compensation scheme using
the QPSO technique with a multiplicative neural net-
work. We have also demonstrated the performance
enhancement achieved using QPSO-MNN compen-
sator with a simple and efficient algorithm for estimat-
ing the weights of the multiplicative neural network.
Simulation results have shown that the proposed
QPSO-MNN compensation offers a significant con-
stellation warping effect and BER reduction. More-
over, the QPSO-MNN compensator achieves a BER
very close to the one corresponding to the ideal case
of linear amplification.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work has been partially supported by the Vice-
rectoria of the Catholic University of Valparaiso.
REFERENCES
Abdulkader F., R. D. C. F. (2002). Natural gradient algo-
rithm for neural networks applied to non-linear high
power amplifiers. Int. Journal of Adaptive Control and
Signal Processing, vol. 16, pages 557-576.
A.M., S. (1981). Frecuency-Independent and Frecuency-
Dependent nolinear models TWT amplifiers. IEEE
Trans. Comm., vol. COM-29, pages. 1715-1719.
Kennedy, J., E. R. (1995). Particle Swarm Optimization.
Proc. of IEEE International Conference on Neural
Networks, NJ: Piscataway, pages 1942-1948.
Rodriguez N., S. and R., C. (2003). Adaptive predistortion
of COFDM signals for a mobile satellite channel. Int.
Journal of Comm. Systems, vol. 16, N 2, pages 137-
150.
Sun J., B. F. and W., X. (2004). Particle Swarm Optimiza-
tion with Particles Having Quantum Behavior. Proc.
Congress on Evolutionary Computation, pages 325-
331.
ICEIS 2008 - International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
578
