
INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY IN VIRTUAL ENTERPRISE
Stefan Trzcielinski and Aleksander Jurga
Institute of Management Engineering, Poznan University of Technology, Strzelecka 11, Poznan, Poland
Keywords: Information technology, communication technology, virtual enterprise.
Abstract: There is a common belief expressed in the subject literature that information technology (IT) is critical
contingency factor for virtual organization. Therefore our interest was to investigate the relation between the
intensity level of IT use and the level of the organization virtuality. In that purpose we elaborated a tree of
features describing virtuality and categorized IT tools into two groups taking into considerations the
functions which they play or can play in virtual organization and the range of their influence to cope with
cooperation of distributed partners. The research sample included 45 firms, mostly small and medium,
belonging to six branches. The firms had been chosen according to pre-selection criteria, confirming that
they construct a network to run their operations. Some indicators were elaborated to measure the level of
virtuality and intensity of use of IT. Next correlation was checked between these two levels. In this paper
we present what we have found about the relation.
1 INTRODUCTION
Virtual organization is being associated with the
information and telecommunication technologies (IT
technologies). The association appears in various
context. For instance, the following statements can
be found in the literature referring to the domain: IT
is a tool for coordination in the virtual organization
(Appel and Behr, 1998), IT technologies affected
directly the opportunity to develop the virtual teams
(Ishaya and Macaulay, 1999), IT connects the
partners into an virtual organization perceived as a
temporary partner’s network (Byrne, 1993, Jägers et
al., 1998), IT is the feature that constitutes the
virtual organization (Byrne, 1993, Gristock, 1997).
As the virtual organization is so widely perceived in
association with IT, and there is no systematic
research on such an association, the authors decided
to look at the problem more deeply.
2 THE RESEARCH PROBLEM
The problem that became the research subject can be
articulated in the following question:
Is there any correlation between the company’s
virtuality level (Trzcielinski, & Wojtkowski, 2007)
and the degree of the IT implementation by the
creator initiating the virtual organization?
To answer the question, we have
operationalized the notion of virtual organization
and we have prepared the IT’s typology.
2.1 Features of Virtual Organization
Referring to the studies on the domain’s literature,
fifteen features of the virtual organization have been
distinguished and then aggregated into four meta-
features defining the company’s virtuality
(Trzcielinski, 2007).
1. Openness. The feature associated mainly with a
special susceptibility of virtual organization to
construct the cooperative connections with other
entities. The proximate cause to arrange such
connections is a need for providing the adequate
competences necessary to make profit of the market
chance observed. This feature includes:
• Skill to choose and effectiveness to exploit the
key competences,
• Confidence and equal status of partners and
readiness to get the same/common goal,
• Tendency to give the firm’s resources to carry
out the tasks to be accomplished in the
network, to increase the resources and to widen
the access to the resources,
• Openness and honesty in sharing profits, costs
and risk by all partners,
• Skills to develop the one common customer
relationship management system, supervision
413
Trzcielinski S. and Jurga A. (2008).
INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY IN VIRTUAL ENTERPRISE.
In Proceedings of the Tenth International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems - HCI, pages 413-419
DOI: 10.5220/0001724904130419
Copyright
c
SciTePress

and fulfilling the customer needs, appropriate
customer segmentation.
2. Temporariness of Partnership. It is due to the
exploitation of the partners’ key competences for a
determined time period, i.e. the different time period
of participation in the virtual organization as well as
a different role in the organization (Christie, &
Levary, 1998). This feature includes:
• Temporariness of virtual organization related
to its short lifetime,
• Reconfigurability of the partners’ network
meant as a readiness to enter and to retire from
the virtual organization after having completed
the task,
• Institutional independence of the partners,
• Heterarchy expressed by the degree of
formalization, organizational structure’s
flattening, management decentralization and
variability of the decision center.
3. Orientation to Market Opportunities. The
success or failure of the venture depends, among
others, on the ability to identify and to immediately
reply to the market opportunities. The feature
includes:
• Organization’s flexibility to respond and adapt
its activities to the variable market conditions.
• Integrity of organization, i.e. the virtual
organization is perceived by outsiders as an
entity
4. Organizational Distance between Partners.
There are three basic component features of it:
territorial and time distance, social distance and
information distance among partners of virtual
organization. This feature includes:
• Territorial distance considered as a
geographical dispersion of partners; it could
refer to the dispersion within local, country,
European or worldwide market.
• Time distance related to the different time
zones the particular partners of virtual
organization are running their activities in. The
time distance can generate troubles due to
delayed flow of and access to information,
time-shifted response to the changing market
conditions, difficulties to create the virtual
organization and to coordinate its activities
• Social distance appearing mainly as a lack of
the face-to-face contact between partners and
informal horizontal communication.
• Information distance manifested by the
response time to the risks and disturbances
affecting the fulfilling of the company’s
functions.
The above four features has been decomposed into
detailed ones. The detailed features have been, in
turn, decomposed into the symptoms of the virtual
organization’s presence; referring to the last ones,
the questionnaire for interviewing the management
body of the companies under test has been
developed.
2.2 IT Tools
IT tools are meant here as a set of tele-computing
technologies, without splitting into software,
hardware or IT infrastructure. The IT tools are their
specific designation resulting from their special
properties. Therefore, different groups of the IT
tools can be defined referring to these features. In
this paper, the function-based and the range of
influence-based classifications have been assumed
(Trzcielinski, 2007). Referring to the functions, the
following types of IT tools are depicted.
1. Communication Supporting Tools. The notion
denotes the IT tools used to achieve the fast and
precise information exchange between partners,
customers and even competitors. The process of
planning and coordinating the tasks run by
distributed partners of virtual organization is more
difficult. The physical distance between partners
significantly increases the information distance
measured with the time of reaction to the noticed
market chances and to the risks and disturbances
arising when the virtual company is accomplishing
its tasks. The information flow is just necessary not
only to create the virtual organization but also to
complete successfully the tasks the virtual
organization has been brought into existence. The
classic communication - supporting tools are fixed
telephony and facsimile. A sharp technological
development caused the thorough integration of
solutions of information technology and
telecommunications. A new quality of the IT tools
has appeared enabling the efficient communication
between the business process players. At present, the
use of electronic mail, internet portals, mobile
telephony, internet communicators and VOIP as well
as transmission of information using mobile
telephony as well as opportunity to talk via internet
is often more convenient and efficient than
electronic mail. Thanks to variety of the IT-based
communication tools, the integration of partners
within a virtual organization becomes simple and
flexible.
2. Information-decision Process Supporting
Tools. This kind of tools supports the information-
decision making processes in virtual company.
Among others, the tools make use of the distributed
data bases located in both the data centers belonging
ICEIS 2008 - International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
414

to the virtual organization’s partners and the
common data bases accessible by internet.
Information in data bases can refer to material and
non-material resources, expertise of particular
partners, customer relation management, scenarios
of previous projects, competences of the virtual
company’s partners and the company environment
features. The IT tools of that kind are used to
perform among others the following:
• Financial, statistical, demographical analyses
etc.,
• Selection and sorting information,
• The physical and decision-making processes
coordination within the supply chain,
• Stock management,
• Scheduling the delivery,
• Cost calculation,
• Capacity planning and the use of resources,
• Process control,
• Demand forecasting,
• Document exchange (e.g. orders and invoices),
• Finance management.
3. Design Supporting Tools. In virtual organization,
the design functions (designing of product, for
example) can be accomplished by the physically
distributed designing team. Therefore, the
communication functions among partners and
function of the access to the shared resources in the
form of accessible files (data exchange), information
on the progress of the project have to be integrated
in these tools and to make possible the aligned
realization of anticipated tasks. The designing tools
used in the virtual organization depend on the
branch in which the perceived market opportunity is
located. For instance in case of production
companies, the IT tools and systems involve CAD,
CAM, CAPP, and others. However, the same group
encompass also the tools for WWW service design
(MS FrontPage), graphical project’s preparation
(Corel, Adobe), multimedia presentations (MS
PowerPoint), information flow modeling using the
UML standard (MS Visio).
The recent IT, regardless the classification
criterion, cannot be unambiguously assigned to their
function. Therefore, it should be assumed that the
types as mentioned above overlap each other.
Regarding the range of the influence, four
classes of the IT tools have been identified.
1. Desktop Tools. The group involves the tools
related directly to the workplace, and the usefulness
of these tools to develop the virtual organization is
very low. Such a limited usefulness results from the
fact the tools themselves do not form the IT network
connections to other players of the business
processes.
2. Local Network Tools. The class encounters all IT
tools ensuring efficient communication, fast access
to data as well as the information exchange within
the local IT infrastructure of the company. It refers
mainly to the internal aspect of the virtual firm. The
examples are LAN, intranet, local post office and the
local database servers.
3. Distributed Network Tools. In the class, the
integrated local network tools and wide IT
infrastructure going beyond the physical framework
of the company (MAN and WAN, Internet,
Extranet) are placed. The integration of the IT tools
seems to be significant to the virtualization of
company and business. With this class of tools,
suppliers and customers can communicate and
cooperate with no limits resulting from their
territorial dispersion.
4. Mobile Tools. The tools of this class
present all
features of classes mentioned above and an
additional ability of remote connection to LAN,
WAN and to individual desktop tools. To establish
the communication, not but the mobile Access
Points are required and the physical IT infrastructure
is not needed.
3 RESEARCH SAMPLE AND
MEASUREMENT METHOD
The surveys has been carried out in 2003-2006 in
companies which were creating and are still
developing the virtual organization. The creator is
meant as a firm which notice a market opportunity in
its environment, enters into contract with customer
and realizes the contract in the networking.
3.1 Research Sample
The network partners ware chosen regarding their
key competencies required to accomplish the actual
contract. Thus, the choice of the sample has been
targeted, and the criterions were:
1. The creator develops a network with the virtual
organization features. The features being at least as
follows: temporary inter-partner relations, territorial
dispersion of partners, low degree of formalization
of the structures being developed to carry out the
business project.
2. Operational activity of particular companies is
placed in various branches.
3. In the company, at least one type and one class
INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY IN VIRTUAL ENTERPRISE
415

of the IT tools is used.
The test sample involved 45 firms from the
production and service sectors, located in the
Wielkopolska voivodeship in Poland. The branch
structure of the companies under consideration is as
follows: IT services – 10 firms, real estate related
services - 11 firms, turnkey fair stands services – 10
firms, constructions and building maintaining
services – 5 firms, printing services – 4 firms,
manufacturing – 5 firms.
3.2 Measurement Method and Results
To measure the level of the company’s virtual
organization and its IT tools implementation level,
an interview questionnaire has been elaborated to
enumerate the following: symptoms of presence of
the virtual organization assigned to particular meta-
features of the company’s virtuality, and use of the
IT tools.
Intensity of presence of the particular symptoms
and IT tools have been assessed according to the
Likert order scale ranging from 1 to 5. Referring to
the answers given by the companies, the company’s
virtuality level has been measured regarding the
actual meta-feature. Then, a synthetic virtuality level
has been found (Table 1).
5
5 *
∗
⎟
⎠
⎞
⎜
⎝
⎛
=
iTw
s
pkt
T
C
(1)
where:
C – virtuality level coefficient regarding actual
meta-feature,
spktT – sum of points obtained for total meta-
feature,
iTw – amount of virtual organization symptoms
assigned to an actual meta-feature.
(2)
where:
V – virtuality level coefficient for the company
under test,
spktTV – sum of points obtained for entire company,
iTwV – total number of the total organization
symptoms shown in the questionnaire.
The intensity level of IT use has been measured
using two below coefficients.
(3)
where:
V
IT
– IT application intensity coefficient,
SpktT
it
– a sum of points obtained by the firm which
creates the virtual organization, regarding the
intensity of use of IT,
ITw
it
– number of the questionnaire statements
referring to the IT technologies applications.
(4)
where:
V
ITK
– communication technologies application
intensity coefficient,
SpktT
itk
– a sum of points obtained by the firm
which creates the virtual organization, regarding the
intensity of use of communication technologies,
ITw
itk
– number of the questionnaire statements
referring to the communication technologies
applications.
The results of the measurements are presented in
Table 2.
Statistical analysis of the obtained data shown in
table 2 has been preceded by the test to answer the
question: if obtained results for variables: V
(synthetic virtuality level)), V
IT
(IT technologies
implementation level), V
ITK
(communication
technologies implementation level) agree with the
normal distribution.
Table 1: Average level of the firms’ virtuality regarding
actual meta-feature and the whole branch.
Virtuality degree with
regard to the meta-features
[V]
Branch
1 2 3 4 5 6
Constructions
and maintaining
3,89 4,29 4,22 3,40 3,95
IT services 3,74 4,37 3,77 3,46 3,84
Real estate
services
3,81 4,55 3,48 3,55 3,88
Printing 3,70 4,27 4,17 3,30 3,83
Turnkey fair
stands
3,96 4,39 4,19 3,62 4,04
Manufacturing 3,92 3,29 3,36 2,94 3,52
Average of all
groups
3,84 4,28 3,83 3,44 3,87
Columns: (2) Openness, (3) Relationship temporality
(4) Orientation for market opportunities
(5) Organizational distance
(6) Synthetic degree of virtuality [V]
5
5*
∗
⎟
⎠
⎞
⎜
⎝
⎛
=
iTwV
spktTV
V
5
5*
∗
⎟
⎟
⎠
⎞
⎜
⎜
⎝
⎛
=
iTw
it
spktT
it
V
IT
5
5*
∗
⎟
⎟
⎠
⎞
⎜
⎜
⎝
⎛
=
iTw
itk
spktT
itk
V
ITK
ICEIS 2008 - International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
416
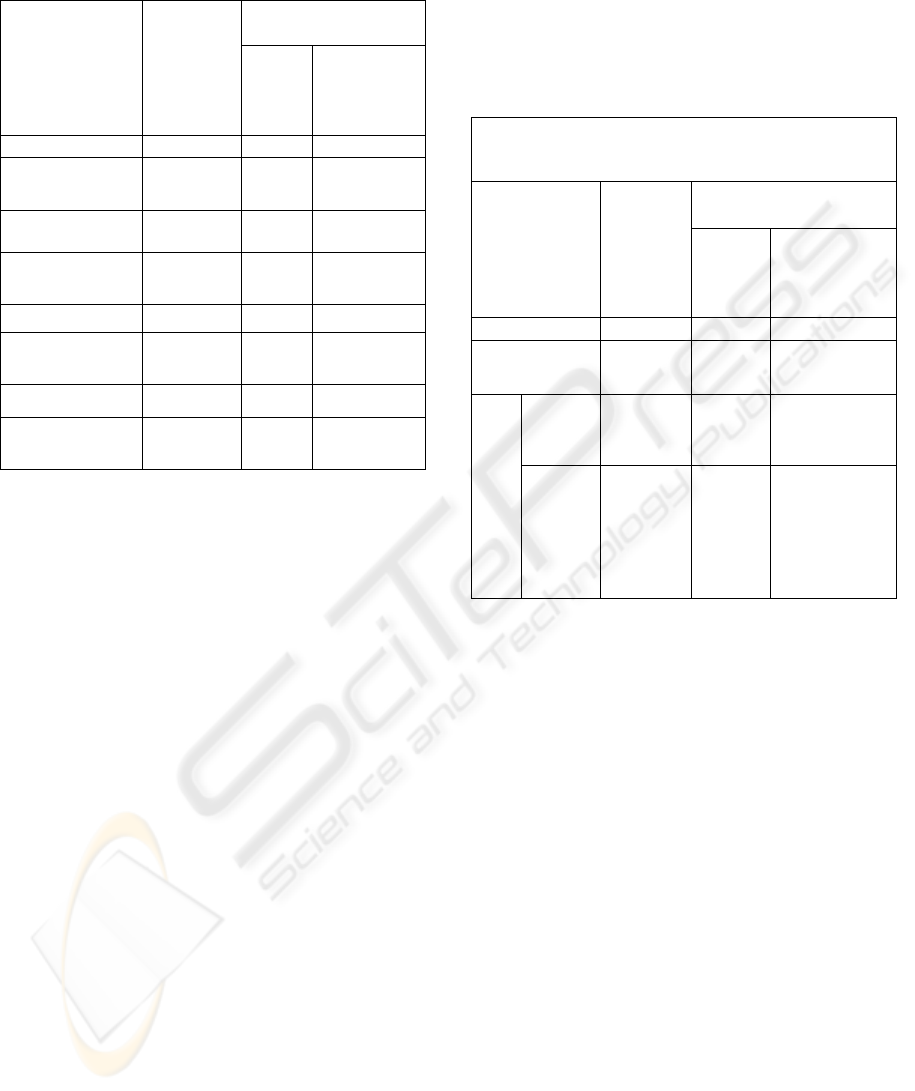
Table 2: Average level of the firms’ virtuality regarding
actual meta-feature and the whole branch.
Intensity level of IT
use
Branch
Synthetic
degree of
virtuality
[V]
all IT
tools
[V
IT
]
only
communi-
cation tools
[V
IT
]
1 2 3 4
Constructions
and maintaining
3,95 2,16 3,96
IT services 3,84 2,29 3,80
Real estate
service
3,88 2,11 4,13
Printing 3,83 2,57 3,75
Turnkey fair
stands
4,04 2,52 4,28
Manufacturing 3,52 3,12 3,12
Average of all
groups
3,87 2,46 3,94
As the test sample size is lower than 2 thousand
cases, the Shapiro-Wilk test has been used to
estimate the normality of distribution of the
observations. For each of the variables mentioned
above, the test results permitted to state that the
distribution differs from the normal distribution.
Because the distribution of results obtained cannot
be considered as a normal distribution and the
correlation has been examined for two variables (V
and V
IT
, V and V
ITK,
respectively) measured on the
Likert scale, therefore, the Spearman-Rang
correlation coefficient has been applied to compute
their correlation. The found correlation results are
presented in Table 3.
In face of the low correlation coefficient V and
V
IT
a thesis can be advanced that the level of the
company’s virtual organization does not depend on
the IT tools implementation degree by the creator.
Moreover, the negative correlation coefficient
implies that an increase in the IT tools
implementation degree results in the decrease in the
company’s virtuality level. Such conclusions
undermine the opinion widely presented in the
literature which states that there exists a strong
relationship between the IT implementation and the
virtual organization.
The correlation between V and V
ITK
is different
than that mentioned above. The correlation
coefficient value allows to assess this correlation as
placed between the average and high one. Thus, the
conclusion can be drawn that the group of the IT
tools used especially for communication purposes
(communication tools) by the virtual organization’s
creator makes a crucial impact on the company’s
virtuality level.
Table 3: Matrix of correlation between the synthetic
virtuality level and the intensity level of IT tools use.
Spearman Rang-order correlation
Bold values of correlations are significant for p<0,05
Features (IT tools
application degree)
Features Synthetic
virtuality
level [V]
all IT
tools
[V
IT
]
only
communi-
cation tools
[V
IT
]
1 2 3 4
Synthetic
virtuality level
1,000
all IT
tools
[V
IT
]
-0,245 1,000
IT tools application
degree
only
commu
-
nicatio
n tools
[V
IT
]
0,474 -0,146 1,000
4 DISCUSSION OF THE RESULTS
In research work, a set of 45 firms showing
symptoms of creating the virtual organization have
been considered. The research has indicated that
different IT tools are used by the firms. Among
these tools are such once which are used to run the
firm’s operational regardless the firm’s participation
in the companies’ network organization. Analysis of
the correlation coefficients obtained has shown that
the commonly shared opinion presented in the
literature and indicating the strong relationship
between the IT [V
IT
] and the company’s virtuality
[V] is, in fact, a one going too far. In our opinion,
such a common statement comes from the
assumption that IT promote the creation of virtual
organization but it is not included into consideration,
that some tools can be applied by the company
regardless it creates or not the virtual organization.
Therefore, it cannot be stated that the virtual
organization’s creation and running is strongly
supported by the IT.
INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY IN VIRTUAL ENTERPRISE
417

The research work as well as the statistical analysis
of results have shown the reality in which the
processes related to the creation and running the
virtual form of a company z are mostly promoted by
the communication technologies. Communication
technology tools have been considered within a set
of the IT. However, due to its low percentage within
the set, such tools did not significantly affect the
correlation between the IT [V
IT
] and the company’s
virtuality level [V].
In our research, a relatively wide range of the IT
tools has been considered, including the tools
referred to, in both the literature and the subjective
assessment by the authors, as those supporting the
creation and running of the networking. Due to
research, it could be found that some IT tools have
been totally dismissed in the firms creating the
virtual company. Thus, the assumed set of IT tools
has shown an ‘excess’. Evidently, it reduced the
correlation factor’s value. In addition, the reduction
in the correlation coefficient resulted from the fact,
that the firms are using the application-oriented
specialized IT tools. Therefore, the variety of
applied IT increases while the share of the
‘commonly used’ IT tools relatively decreases; the
‘commonly used’ IT tools being meant the tools
applied regardless the firm’s/branch’s specialization.
The computed correlation degree between [V
IT
]
and [V] (Table 3, column 2) determines only the
force of the relationship. The correlation does not
explain the quantitative relationship between [V
IT
]
and [V].Therefore, to explain the latter, the
regression anlysis has been performed. The
regression analysis has been carried out for both the
relationship between [V
IT
] and [V] (Fig. 1) and
between [V
ITK
] and [V] (Fig.2).
After having tested different regression models
with the Statistica 6.0 package, the exponential
regression model has been chosen. The choice was
based on the variance analysis with which the degree
of matching the model to the empirical data can be
determined.
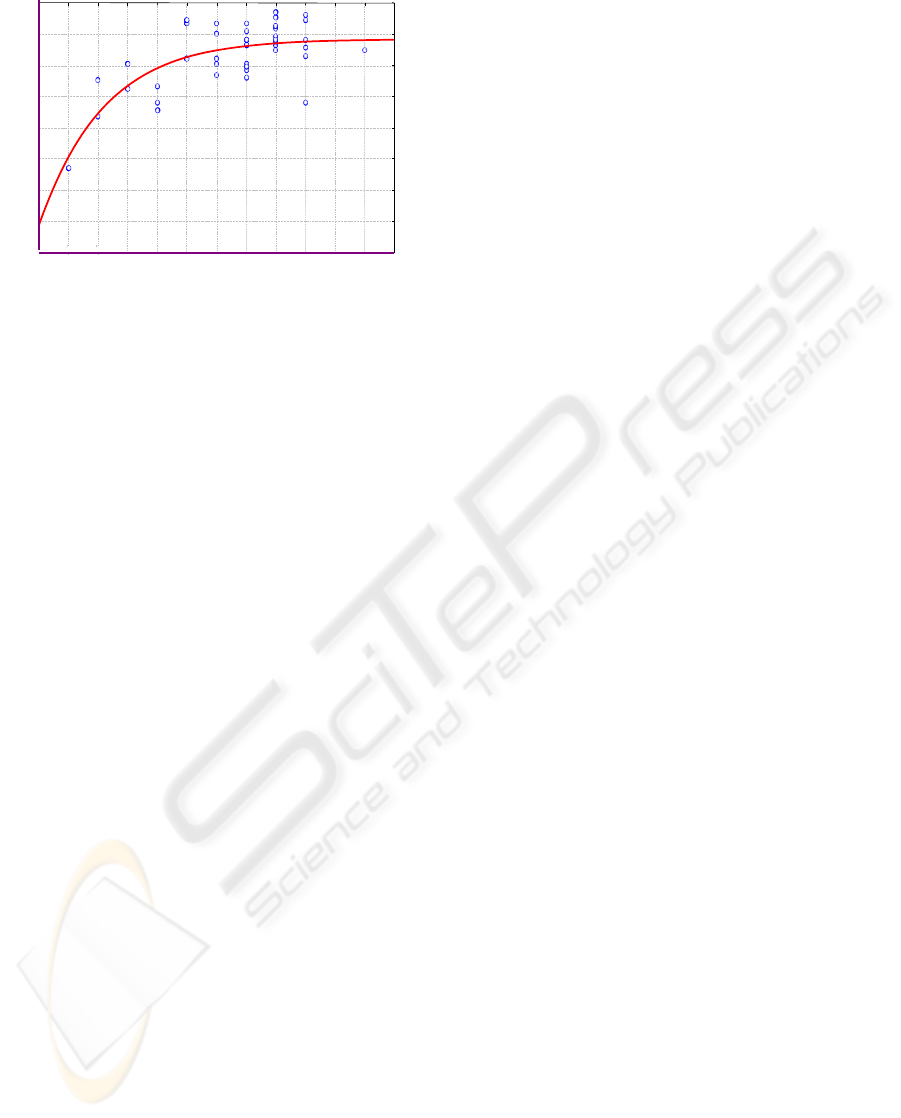
In Fig.1 one can notice that the company’s
virtuality level increases slightly when the IT
implementation level ( in the range 1,8; 2,3)
increases. The continued increase in the IT
implementation level results in an decrease in the
company’s virtual organization level [V]. The
explanation of the latter is that only some kinds of
the IT tools promote the virtual organization. The
company’s virtuality level does not increase because
some technologies do not serve the virtual
organization but are used just to run normal
operations of the firm.
Regression: y=a+b*x*exp(c*x)
1,8 2,0 2,2 2,4 2,6 2,8 3,0 3,2 3,4
3,0
3,2
3,4
3,6
3,8
4,0
4,2
Synthetic level of virtuality [V]
Intensity level of IT use
Figure 1: [V] and [V
IT
] regression analysis.
Referring to the results presented in Table 3
(column 2), the high correlation between the
communication tools and the company’s virtual
organization level can be noticed (correlation
coefficient is near to 0.5). From this observation, the
thesis can be advanced: Among the IT tools used by
the creator to develop the company’s virtual
organization, the communication technologies are
the dominating ones.
High degree of relationship between the
communication technologies [V
ITK
] and the
company’s virtual organization [V] can be explained
in the following way: the fast flow of information is
the most important factor for virtual organizations
enabling to achieve the competitive advantage in its
business environment. As the virtual organization
encounters the partners in territorial dispersion, the
communication technologies are crucial when
developing and running the companies in
networking. These technologies are crucial in any
network as they ensure the contact between partners,
coordination of activities (by the creator),
supervision or just accomplishment of tasks by the
distributed partners. Therefore, the communication
technologies such as fixed and mobile telephony,
internet services including electronic mail,
communicators and fax are highly exploited by the
virtual organizations to realize the emerging market
opportunities.
Fig. 2 shows that the company’s virtuality level
increases sharply for a given range of the
communication tools implementation level. The
higher limit of the range can be assumed to be of
3.6. The continued increase in the implementation
level value does influence the company’s virtual
organization level very slightly. The explanation is
that such tools are substitutes to each other (mobile
telephony versus fixed telephony, e-mail versus
communicators).
ICEIS 2008 - International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
418
2,6 2,8 3,0 3,2 3,4 3,6 3,8 4,0 4,2 4,4 4,6 4,8 5,0
2,6
2,8
3,0
3,2
3,4
3,6
3,8
4,0
4,2
Synthetic level of virtuality [V]
Regression: y=a+b*x*exp(c*x)
Intensity level of use of communication technologies
Figure 2: Regression analysis between [V] and [V
ITK
].
5 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper we have focused on the research results
that significantly undermine the wide spread
opinion, referred in the literature, about the strong
relationship between the IT and virtual organization.
The studies carried out in this work have shown that
the virtual organization level of the company
depends on its specialization. Moreover, there is
higher level in the small business. The notice seems
to be logical as such companies has limited
capacities in their disposal. Therefore, especially
when facing the complex projects, to have access to
necessary capacities, the networking, including
virtual organization, is arranged. Thus, the
conclusion can be drawn that the a concept of agile
enterprise is an appropriate solution mainly for small
businesses. Meanwhile, the bigger companies
(represented by production entities in our survey)
arrange the more stable networks; therefore, a
concept of lean management is more suitable for
them.
REFERENCES
Appel, W., Behr, R., 1998. Towards the theory of Virtual
Organisations: A description of their formation and
figure, Newsletter, Vol. 2, No. 2, Institute of
Information Systems, Department of Information
Management, University of Berne.
Byrne, J. A., 1993. The virtual corporation. Business
Week, 8.2.
Christie, P.M.J., & Levary, R.R., 1998. Virtual
Corporations: Recipe for Success. Industrial
Management, 40, 61-71.
Ishaya, T., Macaulay, L., 1999. The Role of Trust in
Virtual Teams, P. Sieber and J. Griese (Eds.)
Organizational Virtualness and Electronic Commerce,
Smowa Verlag. Bern.
Jägers, H., Wendy, J.W., Steenbakkers, W., 1998.
Characteristics of Virtual Organizations. P. Sieber and
J. Griese (Eds.). Organizational Virtualness. Simowa
Verlag. Bern.
Gristock, J., 1997. Communications and Organisational
Virtuality Newsletter Vol. 1, No. 5. Institute of
Information Systems, Department of Information
Management, University of Berne.
Trzcielinski, S. (Ed.), 2007. Agile Enterprise. Concepts
and Some Results of Research. IEA Press, Madison.
Trzcieliński S., Wojtkowski W., 2007. Toword the
Measure of Organizational Virtuality. Human Factors
and Ergonomics in Manufacturing, Vol.17, (6), 575-
586.
INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY IN VIRTUAL ENTERPRISE
419
